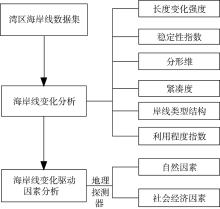
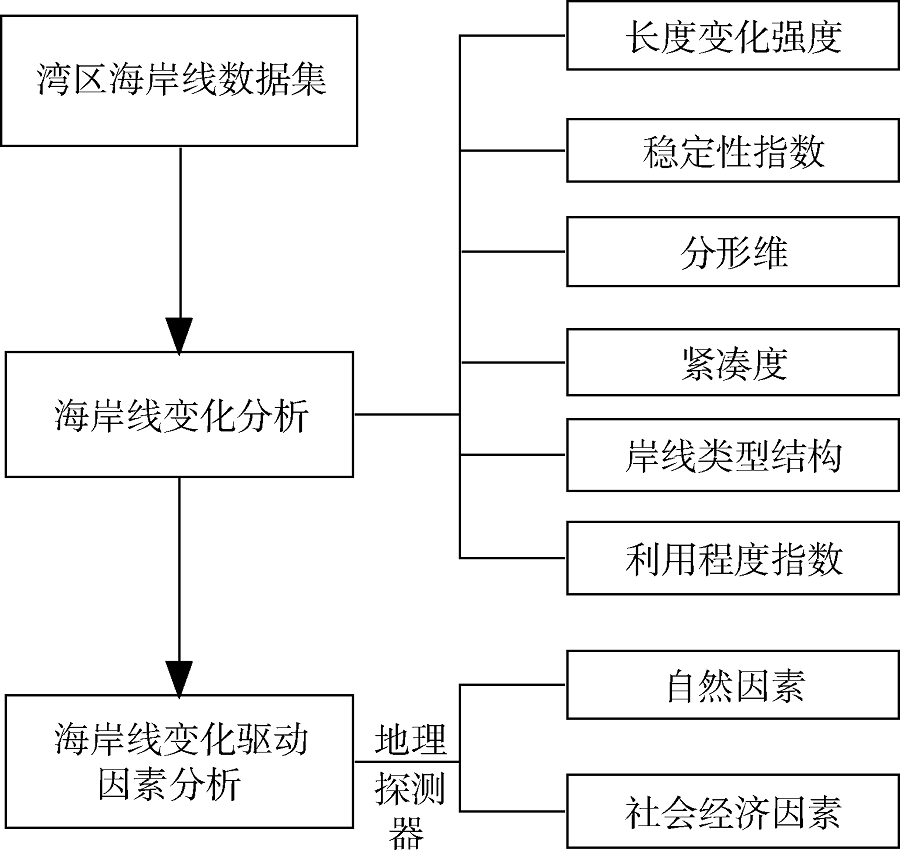
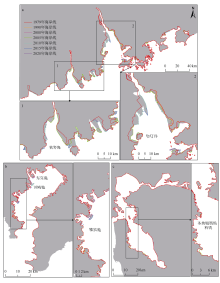
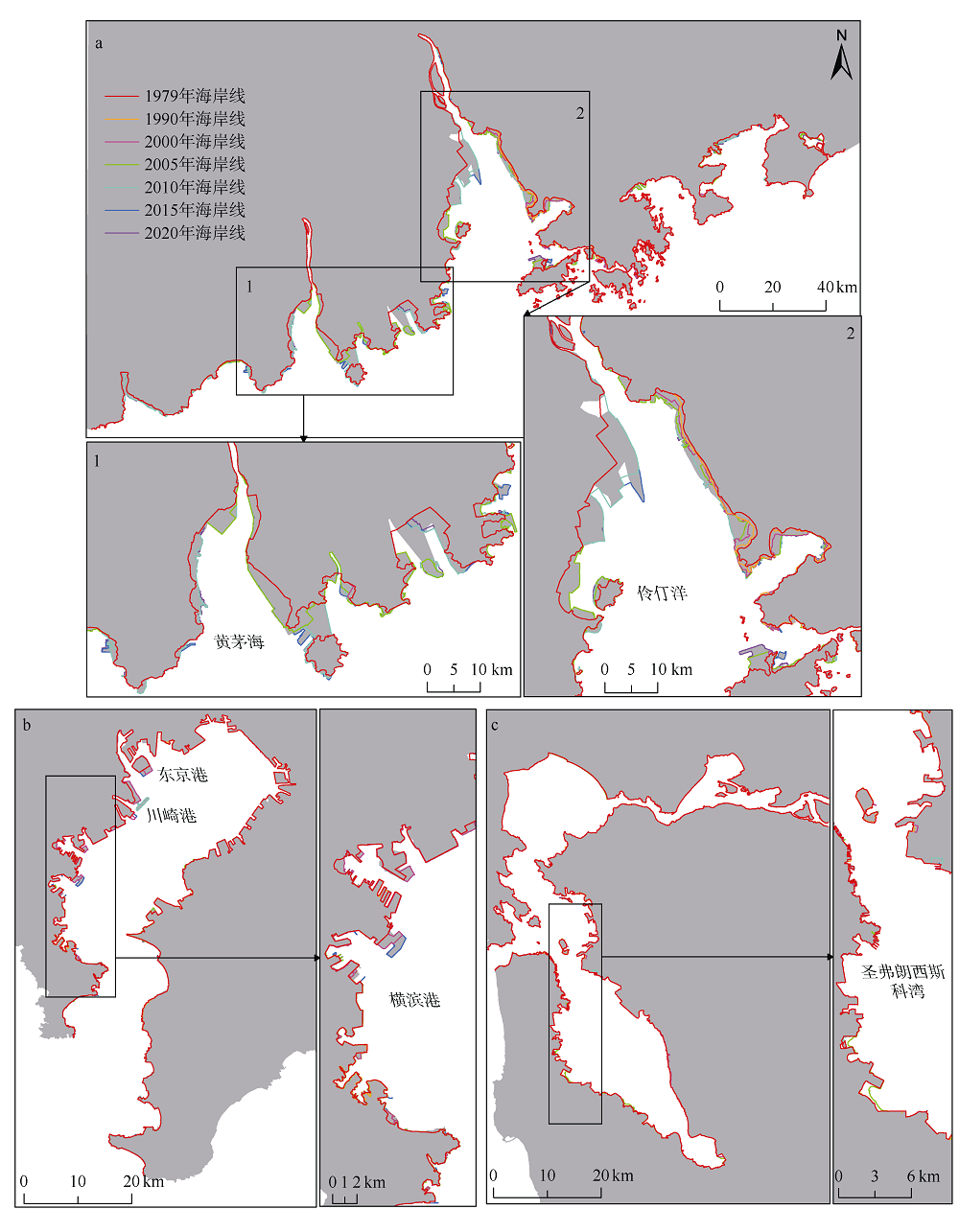
| [1] |
陈金月, 2017. 基于GIS和RS的近40年珠江三角洲海岸线变迁及驱动因素研究[D]. 成都: 四川师范大学: 64-67.
|
|
CHEN JINYUE, 2017. Changes and driving factors of coastline in the Pearl River Delta in recent 40 years based on GIS and RS[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Normal University: 64-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
刘旭拢, 邓孺孺, 许剑辉, 等, 2017. 近40年来珠江河口区海岸线时空变化特征及驱动力分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 19(10): 1336-1345.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2017.01336
|
|
LIU XULONG, DENG RURU, XU JIANHUI, et al, 2017. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of coastlines and driving force analysis of the Pearl River Estuary in the past 40 years[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 19(10): 1336-1345. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1047.2017.01336
|
| [3] |
王劲峰, 徐成东, 2017. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 72(1): 116-134.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701010
|
|
WANG JINFENG, XU CHENGDONG, 2017. Geodetector: principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(1): 116-134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201701010
|
| [4] |
肖锐, 2017. 近三十五年中国海岸线变化及其驱动力因素分析[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 22
|
|
XIAO RUI, 2017. Analysis of change and driving force of the coastline of mainland in the nearly 35 years[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 22 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
邢婧, 孟丹, 白沁灵, 等, 2021. 近30年来我国河口海岸线变迁及驱动因素分析[J]. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5): 58-65.
|
|
XING JING, MENG DAN, BAI QINLING, et al, 2021. Analysis of coastline changes of Chinese estuaries and its driving factors in the past 30 years[J]. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 42(5): 58-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
赵玉灵, 2018. 粤港澳大湾区自然资源遥感调查与保护建议[J]. 国土资源遥感, 30(4): 139-147.
|
|
ZHAO YULING, 2018. Remote sensing survey and proposal for protection of the natural resources in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 30(4): 139-147. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
赵永玉, 阿里木江·卡斯木, 高鹏文, 等, 2021. 基于地理探测器的乌鲁木齐市城区扩展及影响因素分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 44(6): 1729-1739.
|
|
ZHAO YONGYU, ALIMUJIA NG·KASIMU, GAO PENGWEN, et al, 2021. Quantitative analysis of urban expansion and response factors in Urumqi city based on random forest algorithm and geographical detector[J]. Arid Land Geography, 44(6): 1729-1739. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2004. GB/T 18190-2000海洋学术语海洋地质学[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2004. GB/T 18190-2000 Oceanological terminology-Marine geology[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [9] |
ALESHEIKH A A, GHORBANALI A, NOURI N, 2007. Coastline change detection using remote sensing[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 4(1): 61-66.
|
| [10] |
BIDORN B, SOK K, BIDORN K, et al, 2021. An analysis of the factors responsible for the shoreline retreat of the Chao Phraya Delta (Thailand)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 769: 145253.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145253
|
| [11] |
BOAK E H, TURNER I L, 2005. Shoreline definition and detection: a review[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 21(4): 688-703.
|
| [12] |
CAI FENG, SU XIANZE, LIU JIANHUI, et al, 2009. Coastal erosion in China under the condition of global climate change and measures for its prevention[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 19(4): 415-426.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.05.034
|
| [13] |
CONOMOS T J, SMITH R E, GARTNER J W, 1985. Environmental setting of San Francisco Bay[J]. Hydrobiologia, 129(1): 1-12.
doi: 10.1007/BF00048684
|
| [14] |
DALLAS K L, BARNARD P L, 2011. Anthropogenic influences on shoreline and nearshore evolution in the San Francisco Bay coastal system[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 92(1): 195-204.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.12.031
|
| [15] |
DING XIAOSONG, SHAN XIUJUAN, CHEN YUNLONG, et al, 2019. Dynamics of shoreline and land reclamation from 1985 to 2015 in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 29(12): 2031-2046.
doi: 10.1007/s11442-019-1703-1
|
| [16] |
SU QIANXIN, LI ZHIQIANG, 2021a. Coastline types and their spatiotemporal variations in Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao Bay Area (1979-2020)[J/DB/OL]. Digital Journal of Global Change Data Repository, https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.04.07.V1.
|
| [17] |
SU QIANXIN, LI ZHIQIANG, 2021b. Coastline types and their spatiotemporal variations in Tokyo Bay (1980-2020)[J/DB/OL]. Digital Journal of Global Change Data Repository, https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.04.08.V1.
|
| [18] |
SU QIANXIN, LI ZHIQIANG, 2021c. Coastline types and their spatiotemporal variations in San Francisco Bay (1980-2020)[J/DB/OL]. Digital Journal of Global Change Data Repository, https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.04.09.V1.
|
| [19] |
SU QIANXIN, LI ZHIQIANG, 2021d. Coastline datasets of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area, Tokyo Bay, and San Francisco Bay (1980-2020)[J]. Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery, 5(2): 148-155.
|
| [20] |
WU XUELING, LIU CHAOXIAN, WU GUOFENG, 2018. Spatial-temporal analysis and stability investigation of coastline changes: A case study in Shenzhen, China[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11(1): 45-56.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755444
|
| [21] |
ZHANG YUXIN, HOU XIYONG, 2020. Characteristics of coastline changes on Southeast Asia Islands from 2000 to 2015[J]. Remote Sensing, 12(3): 519.
doi: 10.3390/rs12030519
|
 ), 李婧2, 李志强1(
), 李婧2, 李志强1( ), 王爱军3,4, 李高聪1
), 王爱军3,4, 李高聪1
 ), LI Jing2, LI Zhiqiang1(
), LI Jing2, LI Zhiqiang1( ), WANG Aijun3,4, LI Gaocong1
), WANG Aijun3,4, LI Gaocong1