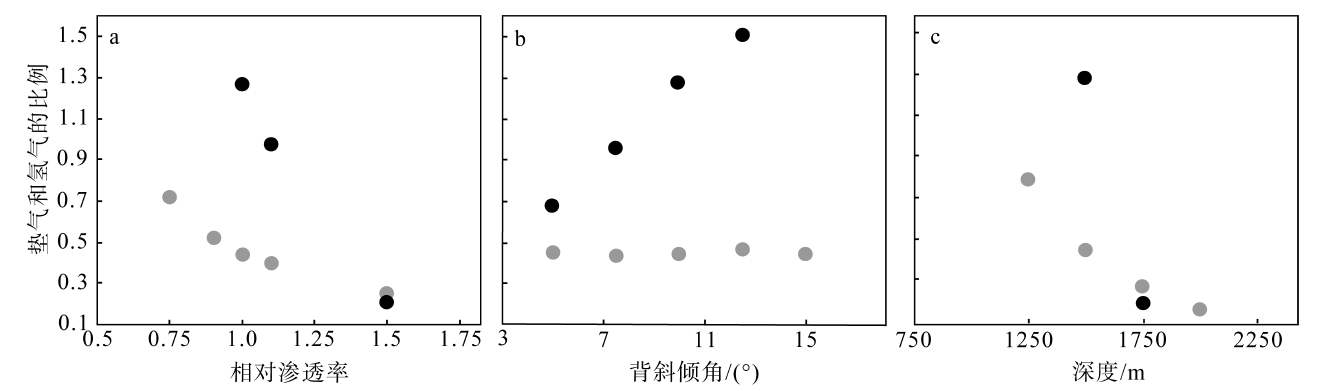
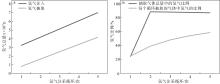
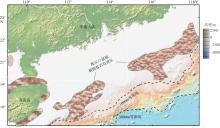
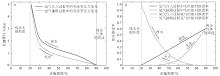
热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 1-17.doi: 10.11978/2024115CSTR: 32234.14.2024115
• 综述 • 下一篇
海下地质储氢技术研究进展及挑战*
- 1.中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 511458
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2024-05-31修回日期:2024-08-01出版日期:2025-03-10发布日期:2025-04-11 -
通讯作者:赵明辉 -
作者简介:关慧心(1990—), 女, 辽宁省沈阳市人, 副研究员, 博士, 主要研究方向为海洋地质学。email: huixinguan@scsio.ac.cn.
*本文中部分图件的制作使用了制图软件CorelDRAW (
https://www.coreldraw.com/ ), 感谢相关软件的创作者。 -
基金资助:广州市基础与应用基础研究项目(2023A04J0182)
Research progress and challenges of offshore geological hydrogen storage technology*
GUAN Huixin1( ), ZHAO Minghui1,2(
), ZHAO Minghui1,2( ), HUANG Ruifang1, XU Hehua1
), HUANG Ruifang1, XU Hehua1
- 1. Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 511458, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2024-05-31Revised:2024-08-01Online:2025-03-10Published:2025-04-11 -
Contact:ZHAO Minghui -
Supported by:Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic Research Project(2023A04J0182)
摘要:
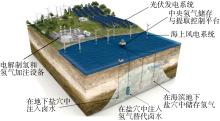
随着全球对清洁能源需求的增长, 氢能作为重要的可再生能源储备, 其储存技术受到广泛关注。陆上储氢系统存在氢气泄漏、污染饮用水和灾变伤人等风险。而海下岩层地质环境相对稳定, 密闭性好, 海下离岸储氢技术受到广泛关注与快速发展。目前主要的地下储气技术包括盐穴、含水层和枯竭油气藏储气库3种, 其中盐穴储气库在欧美多国已经运行多年, 技术基础较为成熟, 然而我国滨海并无适合建设盐穴的地层, 盐穴储氢库只能在内陆建设。我国滨海地下含水层和油气藏较为丰富, 亟须及时开展海下储氢的相关地质研究, 推动不同海域相关技术的发展和应用, 以及氢能产业的全面发展。发展海下储氢技术不仅在选址过程中需要运用最新的地球物理方法, 结合氢气特殊的物理化学特性, 详细评估海下特殊的地质条件, 同时要综合考虑地质、水文、生物化学和矿物学等因素, 以确保合理规划和安全运行。
中图分类号:
- P744.41
引用本文
关慧心, 赵明辉, 黄瑞芳, 许鹤华. 海下地质储氢技术研究进展及挑战*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(2): 1-17.
GUAN Huixin, ZHAO Minghui, HUANG Ruifang, XU Hehua. Research progress and challenges of offshore geological hydrogen storage technology*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 1-17.
表 1
3种主要地下储氢技术对比"
| 储氢方式 | 技术手段 | 储氢类型 | 优势 | 缺陷 | 储氢价格/(USD·kg-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
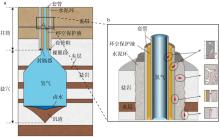
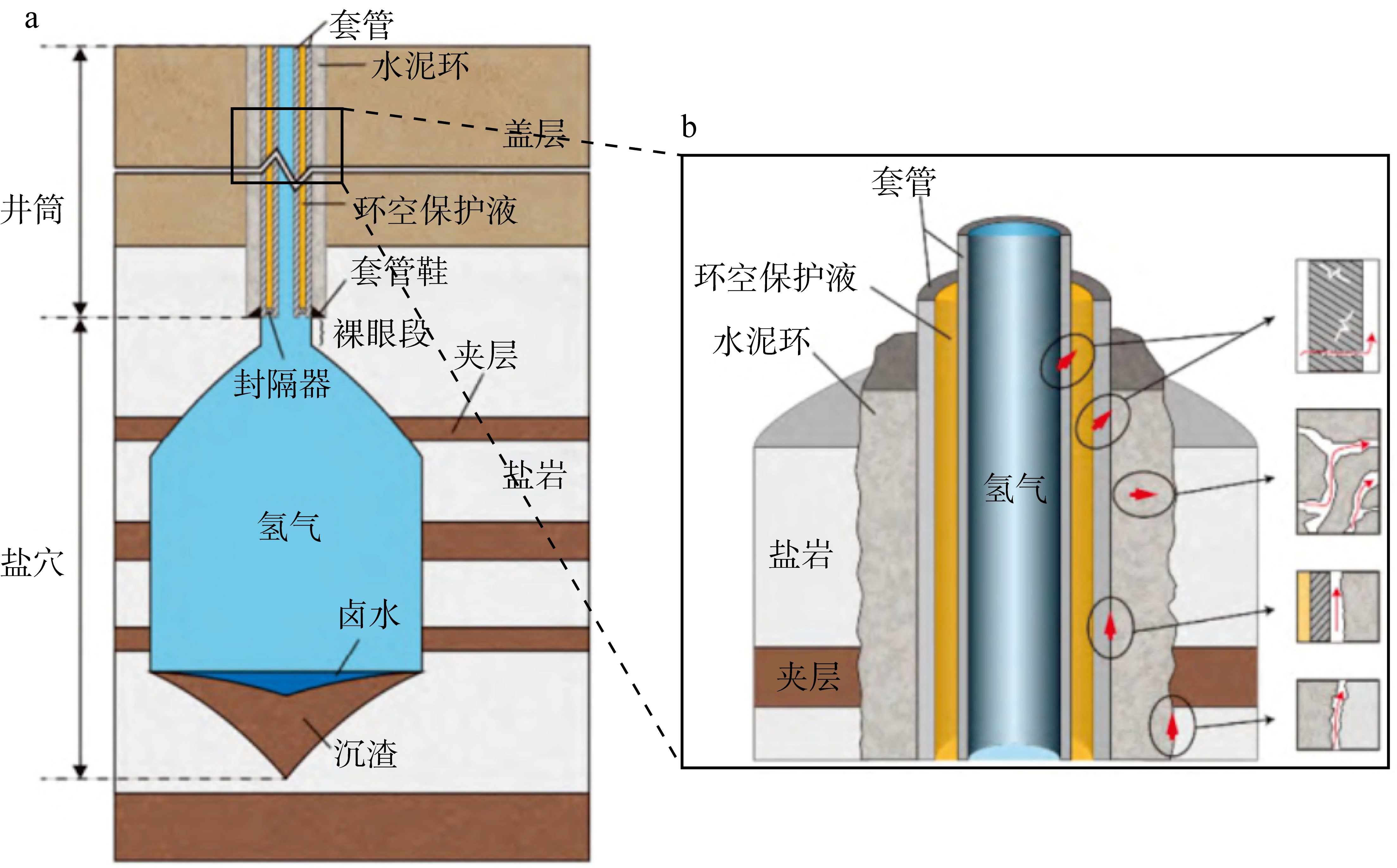
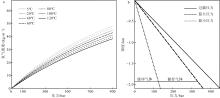
| 盐穴 储氢库 | 通过水溶开采方式, 在地下较厚盐岩层或盐丘层制造洞穴, 形成空间以储存气体。 | 纯氢 | 1. 技术较成熟; 2. 盐岩自我封闭性好, 能够有效防止氢气泄漏; 3. 储库压力上下限较宽, 储氢效率高。 | 1. 选址受限(必须挑选盐层较厚地层); 2. 前期建造成本较高, 容积相对较小。 | 1.61 | |
| 含水层储氢库 | 通过向盖层下注气驱替岩层中的水来储存氢气。 | 与CH4、CO2、CO等其他气体以一定比例混合 | 1. 潜在库址资源广; 2. 地层条件合适可大规模储氢。 | 1. 可能对周围地下水资源和生态系统产生不良影响; 2. 储库内氢气与原位细菌发生反应可能产生甲烷、硫化氢等气体, 损耗和污染氢气, 降低储氢效率。 | 1.29 | |
| 枯竭油气藏储氢库 | 通过已采尽原有油气资源的地下储层来储存氢气。 | 与CH4、CO2、CO等其他气体以一定比例混合 | 1. 容积大、密封性好、分布广; 2. 可大量利用现有地面地下设施, 前期建设成本低, 储氢综合成本最低。 | 1. 缺乏相关地质力学现象的研究; 2. 缺乏对单个岩性岩石类型的地质力学相互作用的综合研究。 | 1.23 | |
表2
全球部分国家地下储氢项目"
| 项目名称 | 所属 国家 | 牵头组织机构 | 研究目的 | 研究周期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plan-DelyKaD | 德国 | 德国航空航天中心 | 深入比较相关的电解技术, 确定和选择德国最相关的盐穴地点的标准, 研究将存储的氢应用于不同终端用户的商业案例潜力, 并致力于确定大规模存储的氢在德国能源系统中的未来作用。 | 2012—2014年 |
| InSpEE | 德国 | KBB地下技术有限公司 | 盐穴设计原则与基础地质/岩土数据、盐穴的选址标准的开发和部署, 以及德国北部盆地盐构造的可再生能源储存潜力的评估。 | 2015年结束 |
| H2 research cavern | 德国 | HYPOS联盟(hydrogen power storage & solutions east Germany) | 开发并正式批准一个盐穴储氢研究平台。 | 2019年5月— 2021年6月 |
| HyCAVmobil | 德国 | 德国氢和燃料电池技术组织 | 测试氢是否可以储存在盐穴中, 然后用于燃料电池车。 | 2019年6月— 2022年5月 |
| STOPIL H2 | 法国 | Storengy | 在法国真正的盐洞中进行氢储存的工业试验。 | 2019—2020年 |
| HyPSTER | 法国 | Storengy | 利用盐穴储存电解氢并与工业和出行用途相连接。测试该技术在欧洲其他地区的技术和经济可复制性。 | 2021—2023年 |
| HyStock | 荷兰 | Gasunie | 研究和测试荷兰北部盐穴大规模储存绿氢。 | 2020至今 |
| RP1.10-08 | 澳大 利亚 | Future fuels cooperative research centre | 研究和测试澳大利亚大规模地下储存氢气的可行性, 评估预期需求。 | 2021—2024年 |
| HyStorPor | 英国 | Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council | 评估氢气储存在英国地下储层(包括滨海地下盐穴)岩石中的可行性。 | 2023年结束 |
| HyUsPRe | 英国 | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme | 评估欧洲的多孔储层中实施大规模储存氢气的可行性和潜力。 | 2021—2023年 |
| Underground Sun Storage | 奥地利 | Rohöl-Aufsuchungs Aktiengesellschaft Austria AG Company | 将可再生能源以氢气形式安全、季节性、大规模储存在地下枯竭油气田中的技术。 | 2017—2030年 |
| Hychico | 阿根廷 | Capex Company | 是一个结合了风电场、氢气生产和地下储存的项目。在地下油气藏中储存90%的甲烷和10%的氢气。 | 2010—2018年 |
| RWE-Lobodice/Haje | 捷克 | Gas Storage Českárepublika | 在地下含水层中储存一种含50%氢气和25%甲烷的混合气体, 供应所在城市的煤气需求。 | 1962年至今 |
| Beynes | 法国 | Gaz de France | 通过地下盐水层储存含有50%~60%的氢气。经过一年储存后提取的气体中含有微量的镍和铁羰基化合物, 1973年被改为天然气储存场所。 | 1956—1972年 |
| Ketzin | 德国 | GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences and Ketzin partners | 通过地下含水层储存氢气、甲烷和二氧化碳。其中氢气含量为62%。 | 2008—2013年 |
| FRS(170)/2022-2023/PE | 印度 | 印度理工学院 | 评估印度滨海地层中实施大规模储存氢气的可行性。 | 2022—2023年 |
| [1] |
崔传智, 任侃, 吴忠维, 等, 2022. 地下含水层储存氢气的可行性分析[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 51(5): 41-50.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
付盼, 罗淼, 夏焱, 等, 2020. 氢气地下存储技术现状及难点研究[J]. 中国井矿盐, 51(6): 19-23.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
韩欢欢, 王梦哲, 王雪泽, 等, 2023. 新型储氢技术研究进展[J]. 化纤与纺织技术, 52(3): 53-55 (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
何奇, 冯永存, 邓金根, 等, 2022. 国内盐穴储气库空间利用技术及展望[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 44(6): 711-718.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
胡超, 付星辉, 何卉, 等, 2023. 浅谈我国地下盐腔储氢发展可能[J]. 中国井矿盐, 54(2): 20-23.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
刘继宝,2023-06-19(08). 地质储氢推动氢能产业高质量发展[N]. 中国石化报 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
李小春, 张九天, 李琦, 等, 2018. 中国碳捕集、利用与封存技术路线图(2011版)实施情况评估分析[J]. 科技导报, 36(4): 85-95.
doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.04.013 |
|
|
|
| [8] |
刘冰冰, 冯进千, 武志德, 等, 2023. 盐穴地下储氢库稳定性研究[J]. 盐科学与化工, 52(7): 8-12, 17.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
刘翠伟, 洪伟民, 王多才, 等, 2023. 地下储氢技术研究进展[J]. 油气储运, 42(8): 841-855.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
罗小明, 贾子寒, 张宏阳, 2023. 枯竭油气藏地下储氢技术挑战及展望[J]. 油气储运, 42(9): 1009-1023.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
马玉波, 吴时国, 张功成, 等, 2009. 南海北部陆缘深水区礁相碳酸盐岩的地球物理特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 33(4): 33-39.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
完颜祺琪, 2015. 中国盐穴地下储气库建库地质条件评价及其对策研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学:173.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王浩, 徐俊辉, 陆佳敏, 等, 2024. 大规模地质储氢工程现状及应用展望[J]. 中国地质, 52(1): 1-25.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
王建强, 梁杰, 陈建文, 等, 2021. 中国海域基岩油气藏特征及未来勘探方向[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 41(6): 151-162.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
王玉芳, 2023. 中国含水层储气库建设的发展前景[J]. 石油知识, (3): 38-39 (in Chinese).
|
| [16] |
王元刚, 薛雨, 李心凯, 2019. 盐穴储气库表征渗透率研究[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版), 21(6): 78-81.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
卫平生, 刘全新, 张景廉, 等, 2006. 再论生物礁与大油气田的关系[J]. 石油学报, 27(2): 38-42.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200602008 |
|
doi: 10.7623/syxb200602008 |
|
| [18] |
杨春和, 王贵宾, 施锡林, 等, 2024. 中国大规模盐穴储氢需求与挑战[J]. 岩土力学, 45(1): 1-19.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
张苏宁,2023-01-29. 国内首座盐穴储气库采气量突破50亿立方米[EB/OL]. 中国常州网, https://www.changzhou.gov.cn/ns_news/616167495295537 (in Chinese).
|
| [20] |
张益炬, 2014. 枯竭油气藏型地下储气库方案优选及安全性评价方法研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学:115.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
周庆凡, 张俊法, 2022. 地下储氢技术研究综述[J]. 油气与新能源, 34(4): 1-6.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
周守为, 李清平, 2022. 构建自立自强的海洋能源资源绿色开发技术体系[J]. 人民论坛·学术前沿, (17): 12-28.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
IEA, 2019. The future of hydrogen-seizing today’s opportunities[R]. Karuizawa:Report prepared by the IEA for the G20.
|
| [43] |
IEA, 2021. Global hydrogen review 2023[EB/OL]. [2023-09-22]. https://www.iea.org/reports/global-hydrogen-review-2023.
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: S0168-1656(17)31777-7 pmid: 29273562 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| No related articles found! |
|
||