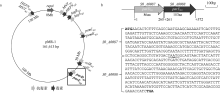
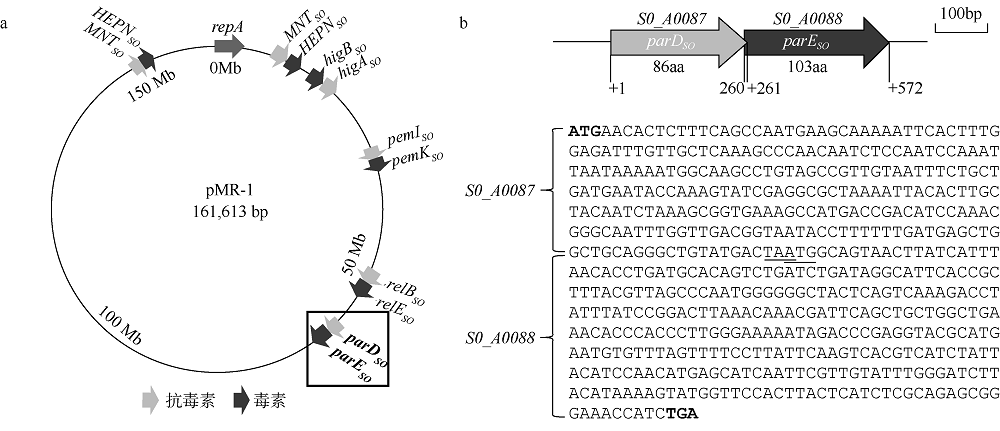
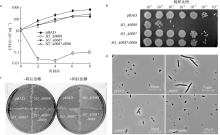
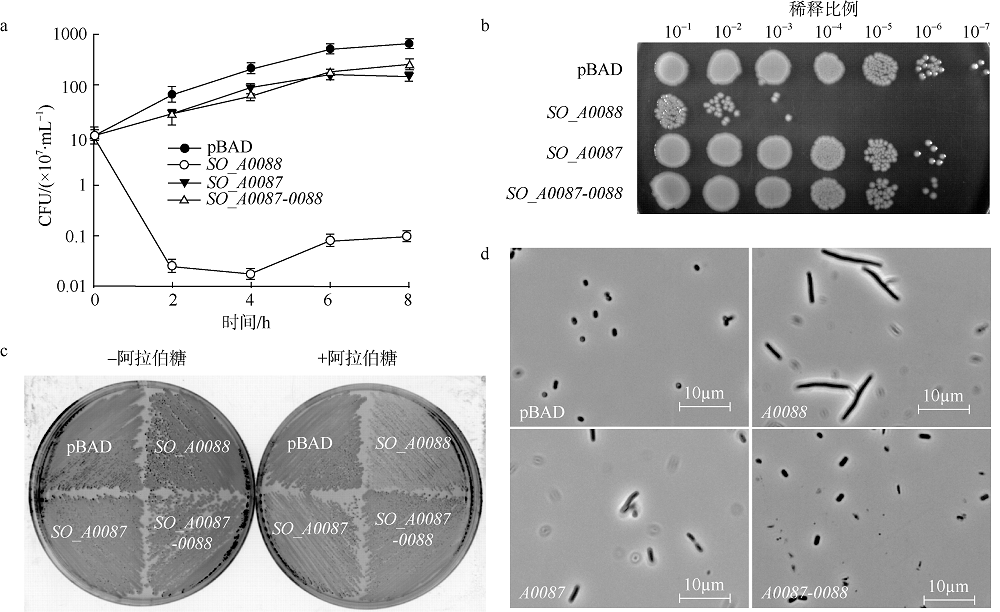
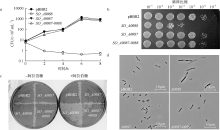
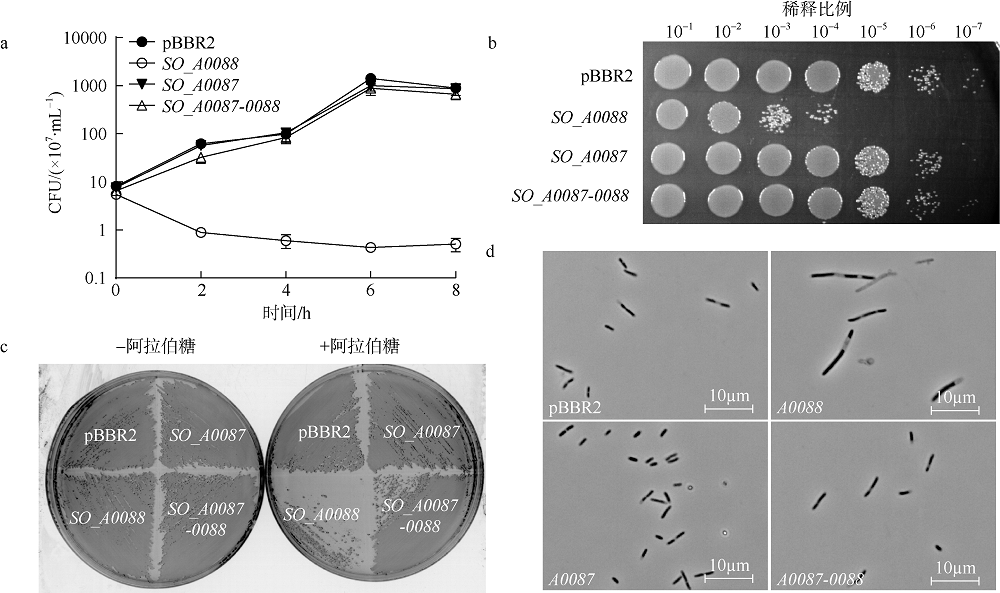
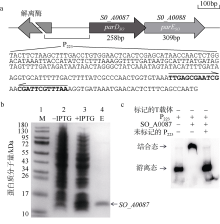
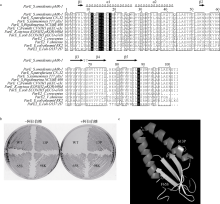
| [1] |
BARBOSA L C B, GARRIDO S S, GARCIA A, et al, 2010. Function inferences from a molecular structural model of bacterial ParE toxin[J]. Bioinformation, 4(10): 438-440.
|
| [2] |
CHAN W T, ESPINOSA M, YEO C C, 2016. Keeping the wolves at bay: Antitoxins of prokaryotic type II toxin-antitoxin systems[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 3: 9.
|
| [3] |
DALTON K M, CROSSON S, 2010. A conserved mode of protein recognition and binding in a ParD-ParE toxin-antitoxin complex[J]. Biochemistry, 49(10): 2205-2215.
|
| [4] |
DUPRILOT M, DECRE D, GENEL N, et al, 2017. Diversity and functionality of plasmid-borne VagCD toxin-antitoxin systems of Klebsiella pneumoniae[J]. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 72(5): 1320-1326.
|
| [5] |
FIEBIG A, CASTRO ROJAS C M, SIEGAL-GASKINS D, et al, 2010. Interaction specificity, toxicity and regulation of a paralogous set of ParE/RelE-family toxin-antitoxin systems[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 77(1): 236-251.
|
| [6] |
FISHMAN A, TAO YING, BENTLEY W E, et al, 2004. Protein engineering of toluene 4-monooxygenase of Pseudomonas mendocina KR1 for synthesizing 4-nitrocatechol from nitrobenzene[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 87(6): 779-790.
|
| [7] |
HALLEZ R, GEERAERTS D, STERCKX Y, et al, 2010. New toxins homologous to ParE belonging to three-component toxin-antitoxin systems in Escherichia coli O157:H7[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 76(3): 719-732.
|
| [8] |
HARMS A, LIESCH M, KÖRNER J, et al, 2017. A bacterial toxin-antitoxin module is the origin of inter-bacterial and inter-kingdom effectors of Bartonella[J]. PLoS Genetics, 13(10): e1007077.
|
| [9] |
HAU H H, GRALNICK J A, 2007. Ecology and biotechnology of the genus Shewanella[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 61(1): 237-258.
|
| [10] |
HEIDELBERG J F, PAULSEN I T, NELSON K E, et al, 2002. Genome sequence of the dissimilatory metal ion-reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 20(11): 1118-1123.
|
| [11] |
JIANG YONG, POGLIANO J, HELINSKI D R, et al, 2002. ParE toxin encoded by the broad-host-range plasmid RK2 is an inhibitor of Escherichia coli gyrase[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 44(4): 971-979.
|
| [12] |
KONSTANTINIDIS K T, SERRES M H, ROMINE M F, et al, 2009. Comparative systems biology across an evolutionary gradient within the Shewanella genus[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(37): 15909-15914.
|
| [13] |
LEPLAE R, GEERAERTS D, HALLEZ R, et al, 2011. Diversity of bacterial type II toxin-antitoxin systems: a comprehensive search and functional analysis of novel families[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(13): 5513-5525.
|
| [14] |
LOVLEY D R, 2012. Electromicrobiology[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 66(1): 391-409.
|
| [15] |
MAGNUSON R D, 2007. Hypothetical functions of toxin-antitoxin systems[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 189(17): 6089-6092.
|
| [16] |
MCKENZIE J L, ROBSON J, BERNEY M, et al, 2012. A VapBC toxin-antitoxin module is a posttranscriptional regulator of metabolic flux in mycobacteria[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 194(9): 2189-2204.
|
| [17] |
NG C K, SIVAKUMAR K, LIU X, et al, 2013. Influence of outer membrane c-type cytochromes on particle size and activity of extracellular nanoparticles produced by Shewanella oneidensis[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 110(7): 1831-1837.
|
| [18] |
OGURA T, HIRAGA S, 1983. Mini-F plasmid genes that couple host cell division to plasmid proliferation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 80(15): 4784-4788.
|
| [19] |
PANDEY D P, GERDES K, 2005. Toxin-antitoxin loci are highly abundant in free-living but lost from host-associated prokaryotes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 33(3): 966-976.
|
| [20] |
ROBERTS R C, HELINSKI D R, 1992. Definition of a minimal plasmid stabilization system from the broad-host-range plasmid RK2[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 174(24): 8119-8132.
|
| [21] |
SCHÄGGER H, 2006. Tricine-SDS-PAGE[J]. Nature Protocols, 1(1): 16-22.
|
| [22] |
SYED M A, LÉVESQUE C M, 2012. Chromosomal bacterial type II toxin-antitoxin systems[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 58(5): 553-562.
|
| [23] |
TSILIBARIS V, MAENHAUT-MICHEL G, MINE N, et al, 2007. What is the benefit to Escherichia coli of having multiple toxin-antitoxin systems in its genome?[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 189(17): 6101-6108.
|
| [24] |
WANG XIAOXUE, KIM Y, HONG S H, et al, 2011. Antitoxin MqsA helps mediate the bacterial general stress response[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 7(6): 359-366.
|
| [25] |
WEN YURONG, BEHIELS E, FELIX J, et al, 2014. The bacterial antitoxin HipB establishes a ternary complex with operator DNA and phosphorylated toxin HipA to regulate bacterial persistence[J]. Nucl Acids Research, 42(15): 10134-10147.
|
| [26] |
WIATROWSKI H A, WARD P M, BARKAY T, 2006. Novel reduction of mercury (II) by mercury-sensitive dissimilatory metal reducing bacteria[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(21): 6690-6696.
|
| [27] |
WINTHER K S, GERDES K, 2011. Enteric virulence associated protein VapC inhibits translation by cleavage of initiator tRNA[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(18): 7403-7407.
|
| [28] |
YAO JIANYUN, GUO YUNXUE, WANG PENGXIA, et al, 2018. Type II toxin/antitoxin system ParESO/CopASO stabilizes prophage CP4So in Shewanella oneidensis[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 20(3): 1224-1239.
|
| [29] |
YAO JIANYUN, GUO YUNXUE, ZENG ZHENSHUN, et al, 2015. Identification and characterization of a HEPN-MNT family type II toxin-antitoxin in Shewanella oneidensis[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 8(6): 961-973.
|
| [30] |
YUAN JIE, STERCKX Y, MITCHENALL L A, et al, 2010. Vibrio cholerae ParE2 poisons DNA gyrase via a mechanism distinct from other gyrase inhibitors[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(51): 40397-40408.
|
 ), Fei SHI1, Xiaoxue WANG1,2(
), Fei SHI1, Xiaoxue WANG1,2( )
)