

基于信息扩散技术的华南极端台风灾害风险评估
|
刘合香(1962—), 女, 山东省聊城市人, 教授,硕士研究生导师, 研究方向为概率统计、数学模型、自然灾害风险分析. E-mail:hx_post@163.com |
收稿日期: 2019-08-13
要求修回日期: 2019-10-24
网络出版日期: 2020-05-19
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(41665006)
国家自然科学基金(11561009)
广西重点研发计划.(AB19110020)
版权
Risk assessment of extreme typhoon disasters based on information diffusion technology
Received date: 2019-08-13
Request revised date: 2019-10-24
Online published: 2020-05-19
Supported by
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(41665006)
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(11561009)
Guangxi Key Research and Development Program(AB19110020)
Copyright
利用2005—2016年登陆华南地区的12个极端台风灾害样本, 综合考虑了承灾体脆弱性和防灾减灾能力, 对华南地区进行极端台风灾害风险评估, 步骤如下: 1) 以各指标的灰色关联度为基础, 构造华南极端台风的危险性指数、脆弱性指数和防灾减灾能力指数; 2) 根据灾害风险数学表达式, 以层次分析法确定的系统权重为基础, 构造华南地区极端台风灾害风险指数; 3) 通过二维正态扩散技术构造原始信息矩阵和模糊关系矩阵, 利用因素空间理论进行模糊近似推理, 计算得到由风险指数近似估计直接经济损失指数的风险估计值; 4) 利用超概率评估模型, 对极端台风的直接经济损失率进行超概率评估。结果表明, 构造的风险指数与实际情况较为吻合, 计算得到的风险估计值与直接经济损失指数变化趋势较为一致, 均方误差为0.20, 相关系数为0.78。结果还表明, 由极端台风造成的直接经济损失率为0.1%, 已成为常态风险, 华南地区极端台风灾害的超越概率与直接经济损失率呈现出良好的线性关系。
刘合香 , 卢耀健 , 王萌 , 李广桃 . 基于信息扩散技术的华南极端台风灾害风险评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020 , 39(3) : 31 -41 . DOI: 10.11978/2019071
Based on 12 cases of extreme landfalling typhoon disasters in South China from 2005 to 2016, extreme landfalling typhoon disaster risk assessment in South China was carried out by considering the vulnerability of disaster bearers and the ability of disaster prevention and mitigation. First, based on the grey relational degree of each index, the risk index, vulnerability index and disaster prevention and mitigation ability index of extreme typhoons in South China are constructed. Then, according to the mathematical expression of disaster risk, based on the system weight determined by analytic hierarchy process, an extreme typhoon disaster risk index in South China is constructed. Next, the original information matrix, fuzzy relation matrix and factor space theory are constructed by using two-dimensional normal diffusion technology. In this paper, the fuzzy approximate reasoning is carried out to obtain the risk estimate value of the direct economic loss index estimated by the risk index approximately. Finally, the super probability evaluation model is used to evaluate direct economic loss rate of each extreme typhoon. The results show that the constructed risk index is in good agreement with the actual situation, and the calculated risk estimate is consistent with the change trend of direct economic loss index, the mean square error is 0.20, and the correlation coefficient is 0.78 The results also show that the direct economic loss rate caused by extreme typhoons is 0.1%, which means it has become the normal risk, the transcendence probability and direct economy loss rate of extreme typhoon disaster in South China shows a good linear relationship.
表1 华南地区极端台风灾害风险评价指标体系Tab. 1 Evaluation index system of extreme typhoon disaster risk in South China |
| 系统层 | 准则层 | 指标层 |
|---|---|---|
| 极端台风灾害风险评价系统 | 致灾源危险性 | 中心气压极值A1 |
| 登陆时最大风速A2 | ||
| 降雨极值A3 | ||
| 承灾体脆弱性 | 人口密度B1 | |
| 人均GDP B2 | ||
| 农业占GDP比重B3 | ||
| 防灾减灾能力 | 卫生机构床位数C1 | |
| 电力消费量C2 | ||
| 移动电话交换机容量C3 | ||
| 医疗卫生机构数C4 | ||
| 执业(助理)医师数C5 | ||
| 铁路营业里程C6 | ||
| 公路里程C7 | ||
| 普通高等学校在校学生数C8 |
表2 各极端台风危险性指数、脆弱性指数、防灾减灾能力指数和风险指数Tab. 2 Extreme typhoon risk index, vulnerability index, disaster prevention and mitigation capacity index, and risk index |
| 台风名称 | 发生年份 | 危险性 指数 | 脆弱性 指数 | 防灾减灾能力指数 | 风险指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 达维 | 2005 | 0.47 | 1.88 | 0.39 | 1.38 |
| 珍珠 | 2006 | 0.22 | 2.43 | 0.08 | 0.90 |
| 黑格比 | 2008 | 0.29 | 2.13 | 0.15 | 1.01 |
| 纳沙 | 2011 | 0.19 | 2.18 | 1.00 | 0.59 |
| 韦森特 | 2012 | 0.26 | 2.15 | 0.29 | 0.90 |
| 尤特 | 2013 | 0.54 | 2.18 | 0.24 | 1.92 |
| 天兔 | 2013 | 0.32 | 2.18 | 0.24 | 1.13 |
| 威马逊 | 2014 | 0.94 | 2.24 | 0.14 | 3.44 |
| 海鸥 | 2014 | 0.09 | 2.24 | 0.14 | 0.32 |
| 彩虹 | 2015 | 0.48 | 2.29 | 0.04 | 1.84 |
| 莎莉嘉 | 2016 | 0.26 | 2.35 | 0 | 1.01 |
| 海马 | 2016 | 0.09 | 2.35 | 0 | 0.34 |
表3 防灾减灾指标与直接经济损失的灰关联度及权重Tab. 3 Grey relational degree and weight between disaster prevention and mitigation indexes and direct economic losses |
| 防灾减灾指标 | 灰色关联度 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.58 | 0.10 |
| C2 | 0.73 | 0.13 |
| C3 | 0.67 | 0.12 |
| C4 | 0.66 | 0.11 |
| C5 | 0.77 | 0.13 |
| C6 | 0.64 | 0.11 |
| C7 | 0.87 | 0.15 |
| C8 | 0.90 | 0.15 |
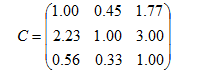
表4 信息矩阵方法估计的风险值Tab. 4 Risk value estimated by Information Matrix method |
| 台风编号 | 台风名称 | 直接经济损失/亿元 | 直接经济损失指数 | 风险估 计值 | 风险 指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0518 | 达维 | 121.57 | 0.25 | 0.53 | 1.38 |
| 0601 | 珍珠 | 37.00 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 0.90 |
| 0814 | 黑格比 | 195.74 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 1.01 |
| 1117 | 纳沙 | 138.28 | 0.30 | 0.46 | 0.59 |
| 1208 | 韦森特 | 20.60 | 0.00 | 0.49 | 0.90 |
| 1311 | 尤特 | 190.70 | 0.43 | 0.62 | 1.92 |
| 1319 | 天兔 | 236.40 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 1.13 |
| 1409 | 威马逊 | 416.70 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 3.44 |
| 1415 | 海鸥 | 176.40 | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.32 |
| 1522 | 彩虹 | 288.09 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 1.84 |
| 1621 | 莎莉嘉 | 52.94 | 0.08 | 0.50 | 1.01 |
| 1622 | 海马 | 46.00 | 0.06 | 0.45 | 0.34 |
表5 2005—2016年华南极端台风灾害直接经济损失率Tab. 5 Direct economic loss rate of extreme typhoon disasters in South China from 2005 to 2016 |
| 台风编号 | 台风名称 | 直接经济损失率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0518 | 达维 | 0.46 |
| 0601 | 珍珠 | 0.12 |
| 0814 | 黑格比 | 0.44 |
| 1117 | 纳沙 | 0.21 |
| 1208 | 韦森特 | 0.03 |
| 1311 | 尤特 | 0.24 |
| 1319 | 天兔 | 0.30 |
| 1409 | 威马逊 | 0.48 |
| 1415 | 海鸥 | 0.20 |
| 1522 | 彩虹 | 0.31 |
| 1621 | 莎莉嘉 | 0.05 |
| 1622 | 海马 | 0.05 |
表6 华南极端台风灾害的超越概率值Tab. 6 Transcendence probability of extreme typhoon disasters in South China |
| 直接经济损失率/% | 超越概率 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 0.1 | 0.81 |
| 0.2 | 0.60 |
| 0.3 | 0.39 |
| 0.4 | 0.20 |
| 0.5 | 0.03 |
| 1 |
白海玲, 黄崇福 , 2000. 自然灾害的模糊风险[J]. 自然灾害学报, 9(1):47-53.
|
| 2 |
陈佩燕, 杨玉华, 雷小途 , 等, 2009. 我国台风灾害成因分析及灾情预估[J]. 自然灾害学报, 18(1):64-73.
|
| 3 |
陈香 , 2007. 福建省台风灾害风险评估与区划[J]. 生态学杂志, 26(6):961-966.
|
| 4 |
丁燕, 史培军 , 2002. 台风灾害的模糊风险评估模型[J]. 自然灾害学报, 11(1):34-43.
|
| 5 |
黄崇福, 刘新立, 周国贤 , 等, 1998. 以历史灾情资料为依据的农业自然灾害风险评估方法[J]. 自然灾害学报, 7(2):1-9.
|
| 6 |
黄崇福 , 2005. 自然灾害风险评价: 理论与实践[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
| 7 |
黄崇福 , 2006. 自然灾害风险分析的信息矩阵方法[J]. 自然灾害学报, 15(1):1-10.
|
| 8 |
黄崇福 , 2009. 自然灾害基本定义的探讨[J]. 自然灾害学报, 18(5):41-50.
|
| 9 |
黄崇福 , 2018. 用信息扩散模型改进台风风险估计[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 38(9):2315-2325.
|
| 10 |
刘合香, 徐庆娟 , 2011. 基于r维正态扩散的区域热带气旋灾害模糊风险分析[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 41(3):150-159.
|
| 11 |
毛熙彦, 蒙吉军, 康玉芳 , 2012. 信息扩散模型在自然灾害综合风险评估中的应用与扩展[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 48(3):513-518.
|
| 12 |
史培军 , 1996. 再论灾害研究的理论与实践[J]. 自然灾害学报, 5(4):6-17.
|
| 13 |
史培军 , 2002. 三论灾害研究的理论与实践[J]. 自然灾害学报, 11(3):1-9.
|
| 14 |
史培军 , 2005. 四论灾害系统研究的理论与实践[J]. 自然灾害学报, 14(6):1-7.
|
| 15 |
史培军 , 2009. 五论灾害系统研究的理论与实践[J]. 自然灾害学报, 18(5):1-9.
|
| 16 |
吴联要, 雷小途 , 2012. 内核及外围尺度与热带气旋强度关系的初步研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 28(5):719-725.
|
| 17 |
于小兵, 俞显瑞, 吉中会 , 等, 2019. 基于信息扩散的东南沿海台风灾害风险评估[J]. 灾害学, 34(1):73-77.
|
| 18 |
张俊香, 李平日, 黄光庆 , 等, 2007. 基于信息扩散理论的中国沿海特大台风暴潮灾害风险分析[J]. 热带地理, 27(1):11-14.
|
| 19 |
张韧, 徐志升, 申双和 , 等, 2013. 基于小样本案例的自然灾害风险评估——信息扩散概率模型[J]. 系统科学与数学, 33(4):445-456.
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |