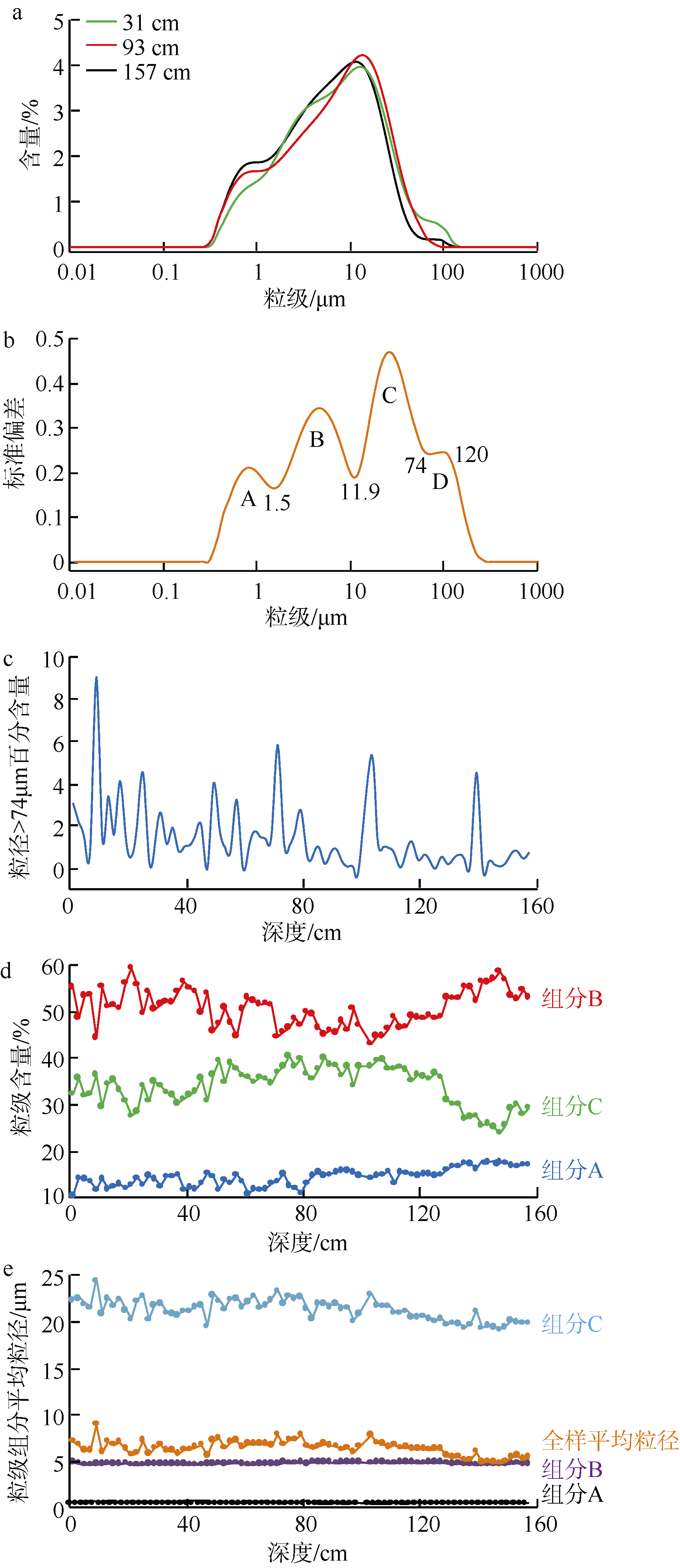
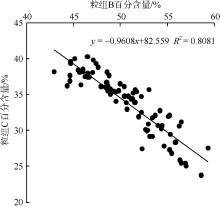
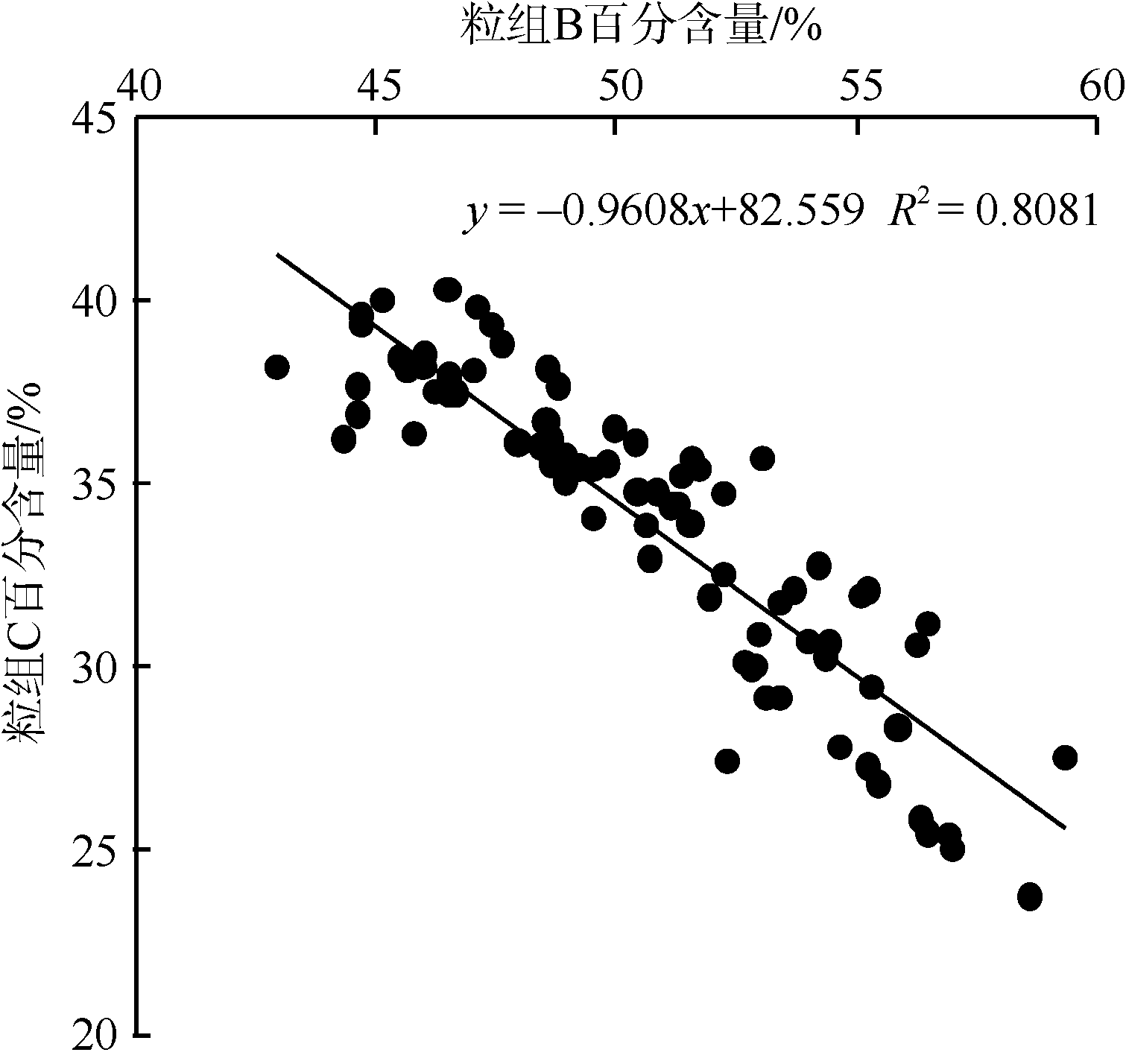
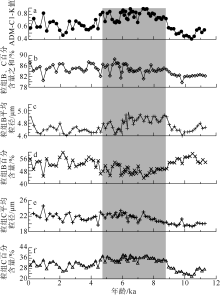
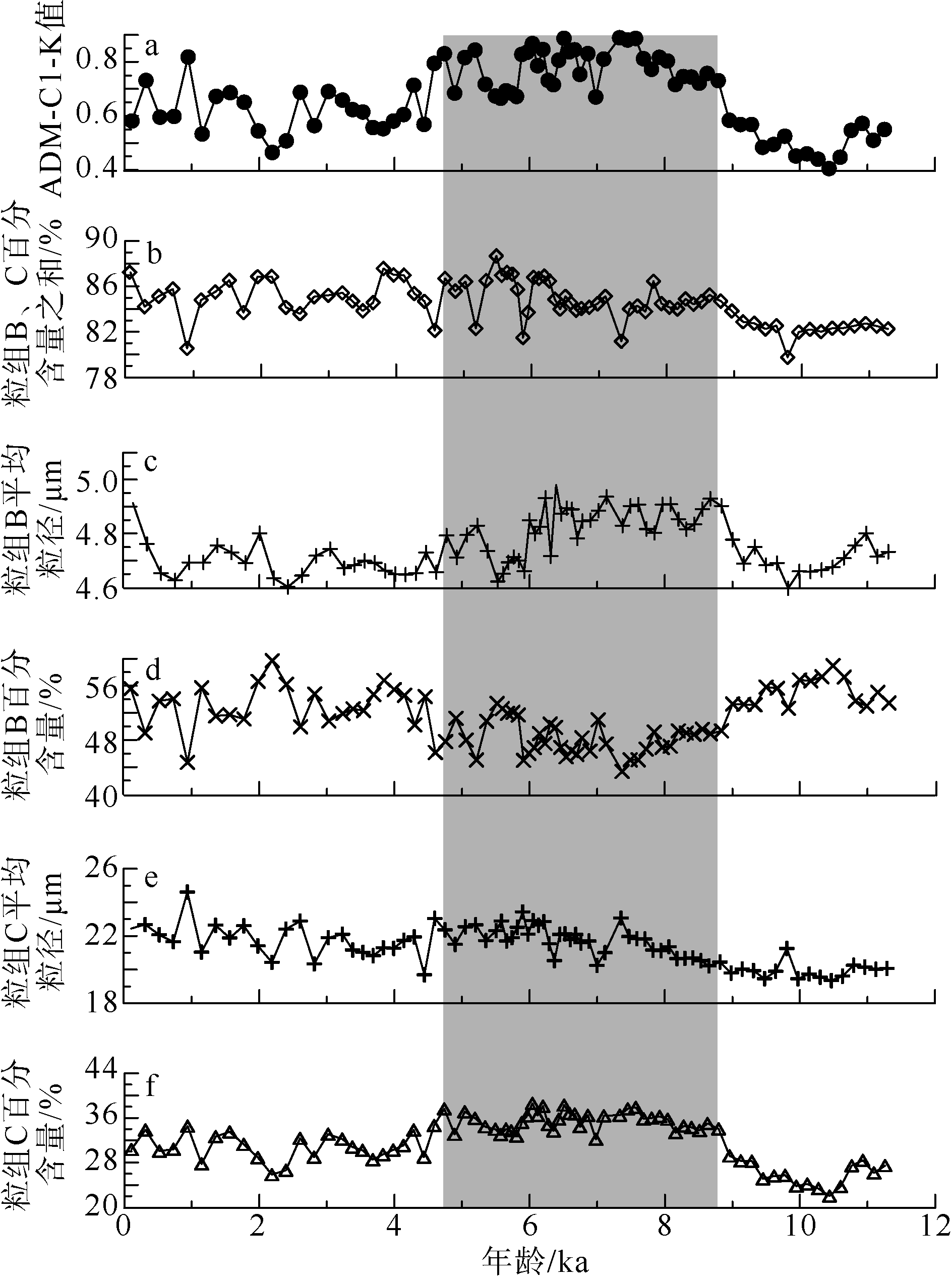
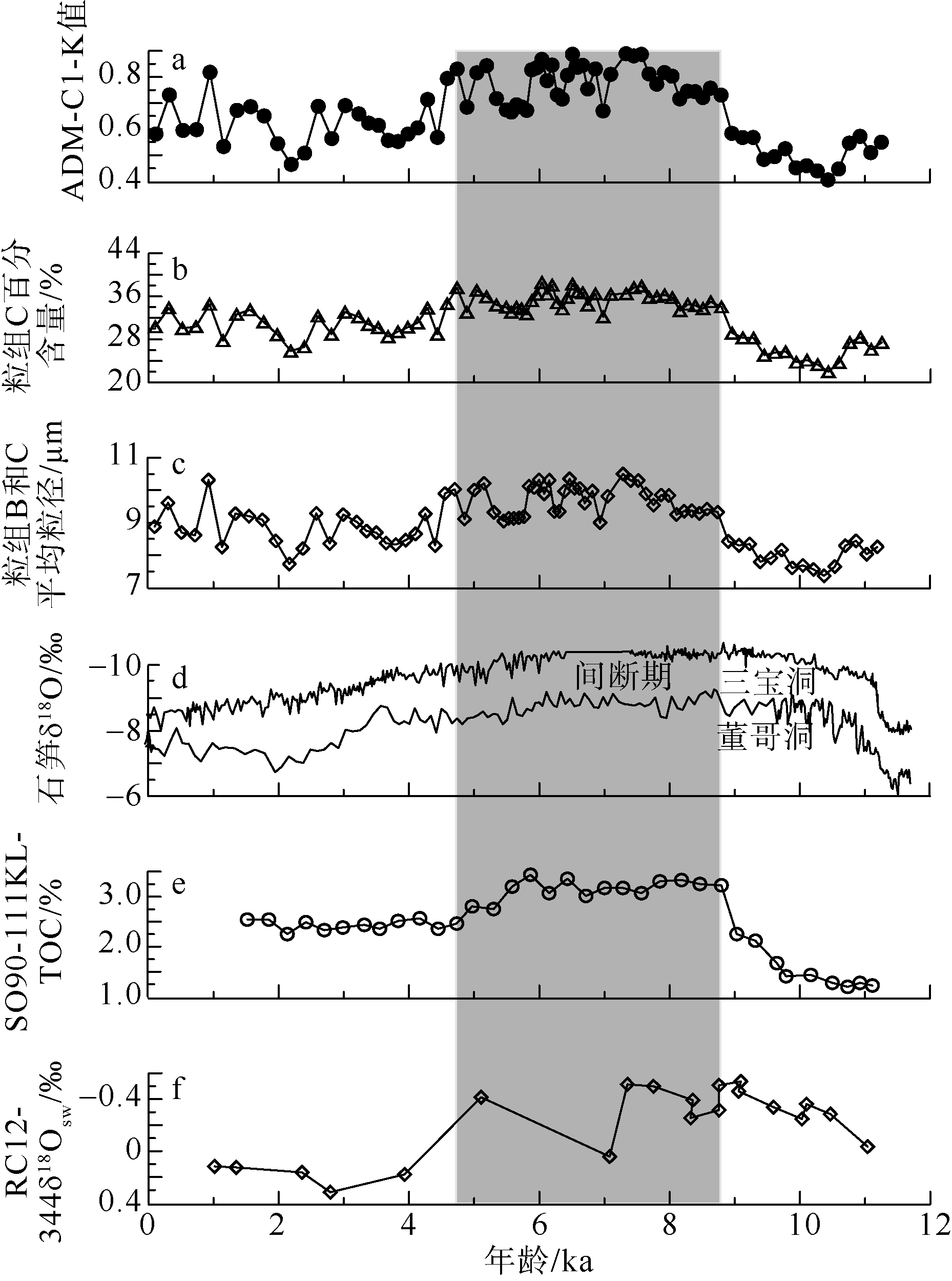
| [1] |
曹鹏, 石学法, 李巍然, 等, 2015. 安达曼海东南部海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 35(5): 57-67
|
|
CAO PENG, SHI XUEFA, LI WEIRAN, et al, 2015. Rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in southeastern Andaman Sea and implications for provenance[J]. Marine Geology #cod#x00026; Quaternary Geology, 35(5): 57-67 (in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
陈敬安, 万国江, 张峰, 等, 2003. 不同时间尺度下的湖泊沉积物环境记录#cod#x02014;#cod#x02014;以沉积物粒度为例[J]. 中国科学: D辑地球科学, 47(10): 954-960
|
|
CHEN JING#cod#x02019;AN, WAN GUOJIANG, ZHANG FENG, et al, 2004. Environmental records of lacustrine sediments in different time scales: Sediment grain size as an example[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 47(10): 954-960 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
葛倩, 初凤友, 叶黎明, 等, 2012. 近3000a来东亚冬季风变化在南海北部陆架泥质区的记录[J]. 海洋学研究, 30(3): 56-62
|
|
GE QIAN, CHU FENGYOU, YE LIMING, et al, 2012. East Asian Winter Monsoon records from the mud area, northern shelf of the South China Sea over the last 3000 years[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 30(3): 56-62 (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
孙千里, 周杰, 肖举乐, 2001. 岱海沉积物粒度特征及其古环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 21(1): 93-95
|
|
SUN QIANLI, ZHOU JIE, XIAO JULE, 2001. Grain-size characteristics of Lake Daihai sediments and its paleaoenvironment significance[J]. Marine Geology #cod#x00026; Quaternary Geology, 21(1): 93-95 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
王伟, 李安春, 徐方建, 等, 2009. 北黄海表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其沉积环境分析[J]. 海洋与湖泊, 40(5): 525-531
|
|
WANG WEI, LI ANCHUN, XU FANGJIAN, et al, 2009. Distribution of surface sediments and sedimentary environment in the north yellow sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 40(5): 525-531 (in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
向荣, 杨作升, SAITO Y, 等, 2006. 济州岛西南泥质区近2300a来环境敏感粒度组分记录的东亚冬季风变化[J]. 中国科学: D辑地球科学, 49(6): 604-614
|
|
XIANG RONG, YANG ZUOSHENG, SAITO Y, et al, 2006. East Asia Winter Monsoon changes inferred from environmentally sensitive grain-size component records during the last 2300 years in mud area southwest off Cheju Island, ECS[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 49(6): 604-614 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
郑洪波, 陈国成, 谢昕, 等, 2008. 南海晚第四纪陆源沉积: 粒度组成、动力控制及反映的东亚季风演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 28(3): 414-424
|
|
ZHENG HONGBO, CHEN GUOCHENG, XIE XIN, et al, 2008. Grain size distribution and dynamic control of late Quaternary terrigenous sediments in the South China Sea and their implication for East Asian Monsoon evolution[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 28(3): 414-424 (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
AN ZHISHENG, KUKLA G, PORTER S C, et al, 1991. Late Quaternary dust flow on the Chinese loess plateau[J]. CATANA, 18(2): 125-132.
|
| [9] |
BIANCHI G G, MCCAVE I N, 1999. Holocene periodicity in North Atlantic climate and deep-ocean flow south of Iceland[J]. Nature, 397(6719): 515-517.
|
| [10] |
.BOULAY S, COLIN C, TRENTESAUX A, et al, 2003. Mineralogy and sedimentology of Pleistocene sediment in the South China Sea (ODP Site 1144)[C]//PRELL W L, WANG P, BLUM P, et al. Proceedings of Ocean Drilling Program Scientific Results 184. Ocean Drilling Program. College Station, TX: 1-21.
|
| [11] |
BROWN B E, 2007. Coral reefs of the Andaman Sea#cod#x02014;An integrated perspective[J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 45: 173-194.
|
| [12] |
CAO PENG, SHI XUEFA, LI WEIRAN, et al, 2015. Sedimentary responses to the Indian Summer Monsoon variations recorded in the southeastern Andaman Sea slope since 26ka[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 114: 512-525.
|
| [13] |
DIGERFELDT G, OLSSON S, SANDGREN P, 2000. Reconstruction of lake-level changes in lake Xinias, central Greece, during the last 40000 years[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 158(1-2): 65-82.
|
| [14] |
DING ZHONGLI, YU ZHIWEI, RUTTER N W, et al, 1994. Towards an orbital time scale for Chinese loess deposits[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 13(1): 39-70.
|
| [15] |
DONG JINGUO, WANG YONGJIN, CHENG HAI, et al, 2010. A high-resolution stalagmite record of the Holocene East Asian monsoon from Mt Shennongjia, central China[J]. The Holocene, 20(2): 257-264.
|
| [16] |
HU BANGQI, YANG ZUOSHENG, ZHAO MEIXUN, et al, 2012. Grain size records reveal variability of the East Asian Winter Monsoon since the Middle Holocene in the Central Yellow Sea mud area, China[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 55(10): 1656-1668.
|
| [17] |
HUANG JIE, JIANG FUQING, WAN SHIMING, et al, 2016. Terrigenous supplies variability over the past 22,000 yr in the southern South China Sea slope: relation to sea level and monsoon rainfall changes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 117: 317-327.
|
| [18] |
HUANG JIE, LI ANCHUN, WAN SHIMING, 2011. Sensitive grain-size records of Holocene East Asian summer monsoon in sediments of northern South China Sea slope[J]. Quaternary Research, 75(3): 734-744.
|
| [19] |
LIU JIANGUO, XIANG RONG, KAO S J, et al, 2016. Sedimentary responses to sea-level rise and Kuroshio Current intrusion since the Last Glacial Maximum: grain size and clay mineral evidence from the northern South China Sea slope[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 450: 111-121.
|
| [20] |
MENKING K M, BISCHOFF J L, FITZPATRICK J A, et al, 1997. Climatic/hydrologic oscillations since 155,000 yr B.P. at Owens Lake, California, reflected in abundance and stable isotope composition of sediment carbonate[J]. Quaternary Research, 48(1): 58-68.
|
| [21] |
MILLIMAN J D, MEADE R H, 1983. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. The Journal of Geology, 91(1): 1-21.
|
| [22] |
QIAO SHUQING, YANG ZUOSHENG, LIU JINGPU, et al, 2011. Records of late-Holocene East Asian winter monsoon in the East China Sea: key grain-size component of quartz versus bulk sediments[J]. Quaternary International, 230(1-2): 106-114.
|
| [23] |
RASHID H, FLOWER B P, POORE R Z, et al, 2007. A~25ka Indian Ocean monsoon variability record from the Andaman Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 26(19-21): 2586-2597.
|
| [24] |
REIMER P J, BARD E, BAYLISS A, et al, 2013. IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0~50000 years cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 55(4): 1869-1887.
|
| [25] |
ROBINSON R A J, BIRD M I, OO N W, et al, 2007. The Irrawaddy River sediment flux to the Indian Ocean: the original nineteenth-century data revisited[J]. The Journal of Geology, 115(6): 629-640.
|
| [26] |
RODOLFO K S, 1969. Sediments of the Andaman Basin, Northeastern Indian Ocean[J]. Marine geology, 7(5): 371-402.
|
| [27] |
SCHULZ H, VON RAD U, ERLENKEUSER H, et al, 1998. Correlation between Arabian Sea and Greenland climate oscillations of the past 110, 000 years[J]. Nature, 393(6680): 54-57.
|
| [28] |
SHENG ENGUO, YU KEKE, XU HAI, et al, 2015. Late Holocene Indian summer monsoon precipitation history at Lake Lugu, northwestern Yunnan Province, southwestern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 438: 24-33.
|
| [29] |
SUWANNATHATSA S, WONGWISES P, VONGVISE- SSOMJAI S, et al, 2012. Phytoplankton tracking by oceanic model and satellite data in the bay of Bengal and Andaman sea[J]. APCBEE Procedia, 2: 183-189.
|
| [30] |
TALMA A S, VOGEL J C, 1993. A simplified approach to calibrating 14C dates[J]. Radiocarbon, 35(2): 317-322.
|
| [31] |
TU LUYAO, ZHOU XIN, CHENG WENHAN, et al, 2016. Holocene East Asian winter monsoon changes reconstructed by sensitive grain size of sediments from Chinese coastal seas: a review[J]. Quaternary International, doi: 10.1016/j.quaint. 2016.03.024.
|
| [32] |
VARKEY M J, MURTY V S N, SURYANARAYANA A, 1996. Physical oceanography of the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea[J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 34: 1-70.
|
| [33] |
XIAO JULE, ZHENG HONGBO, ZHAO HUA, 1992. Variation of winter monsoon intensity on the Loess Plateau, Central China during the last 130000 years: evidence from the grain size distribution[J]. The Quaternary Research (Daiyonki-Kenkyu), 31(1): 13-19.
|
| [34] |
XIAO SHANGBIN, LI ANCHUN, JIANG FUQING, et al, 2005. Recent 2000 year geological records of mud in the inner shelf of the East China Sea and their climatic implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(5): 466-471.
|
| [35] |
YANG YIPING, ZHANG HUCAI, CHANG FENGQIN, et al, 2016. Vegetation and climate history inferred from a Qinghai Crater Lake pollen record from Tengchong, southwestern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 461: 1-11.
|
| [36] |
YUAN DAOXIAN, CHENG HAI, EDWARDS R L, et al, 2004. Timing, duration, and transitions of the last interglacial Asian monsoon[J]. Science, 304(5670): 575-578.
|
| [37] |
ZHENG XUFENG, LI ANCHUN, KAO S, et al, 2016. Synchronicity of Kuroshio Current and climate system variability since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 452: 247-257.
|
| [38] |
ZHOU XIN, YANG WENQING, XIANG RONG, et al, 2014. Re-examining the potential of using sensitive grain size of coastal muddy sediments as proxy of winter monsoon strength[J]. Quaternary International, 333: 173-178.
|
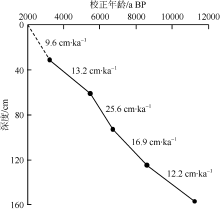
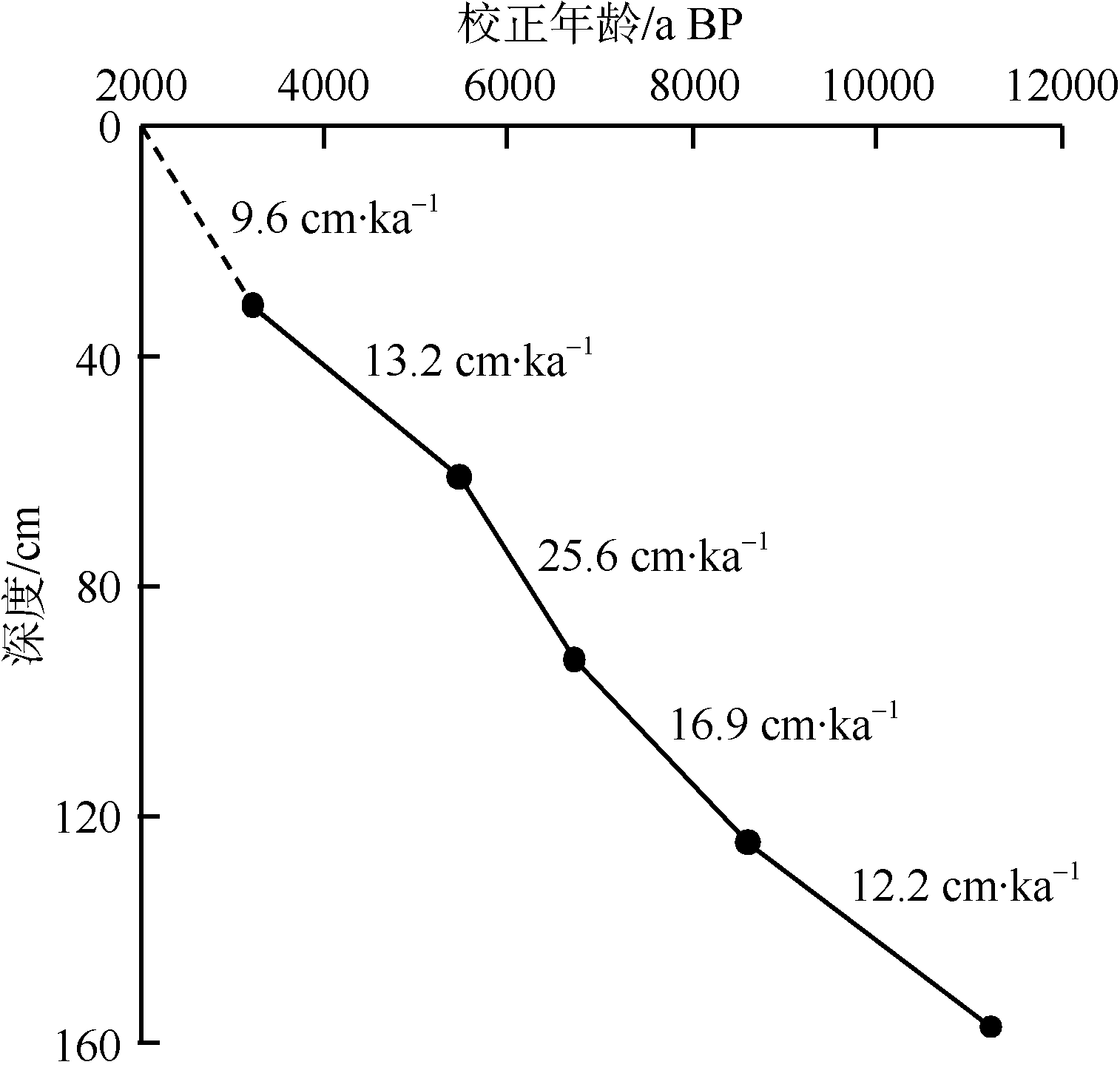
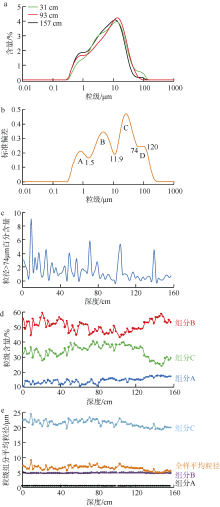
 ), 向荣1(
), 向荣1( ), 刘升发3, 杨艺萍1,2, 刘建国1
), 刘升发3, 杨艺萍1,2, 刘建国1