热带海洋学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 72-84.doi: 10.11978/2020111CSTR: 32234.14.2020111
中建南盆地北部海底麻坑地貌特征及成因机制
汪灵1,2,3( ), 王彬4, 李健1,2(
), 王彬4, 李健1,2( ), 喻凯琦1,2,3, 赵芳1,2
), 喻凯琦1,2,3, 赵芳1,2
- 1.中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室, 南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 511458
3.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
4.中国石油天然气股份有限公司杭州地质研究院, 浙江 杭州 310023
-
收稿日期:2020-09-22修回日期:2020-12-09出版日期:2021-09-10发布日期:2021-01-13 -
通讯作者:李健 -
作者简介:汪灵(1996—), 女, 江西省井冈山市人, 硕士研究生, 主要从事海底地貌与海洋地球物理方面的研究。email:wangling@scsio.ac.cn -
基金资助:广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0104);国家科技基础资源调查专项(2017FY201406);广东省“珠江人才计划”高层次人才认定项目(2017GC010510)
Morphology characteristics and formation mechanisms of submarine pockmarks in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea
WANG Ling1,2,3( ), WANG Bin4, LI Jian1,2(
), WANG Bin4, LI Jian1,2( ), YU Kaiqi1,2,3, ZHAO Fang1,2
), YU Kaiqi1,2,3, ZHAO Fang1,2
- 1. Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Guangzhou 511458, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. PetroChina Hangzhou Research Institute of Geology, Hangzhou 310023, China
-
Received:2020-09-22Revised:2020-12-09Online:2021-09-10Published:2021-01-13 -
Contact:LI Jian -
Supported by:Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory(GML2019ZD0104);Special Foundation for National Science and Technology Basic Research Program of China(2017FY201406);Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program(2017GC010510)
摘要:
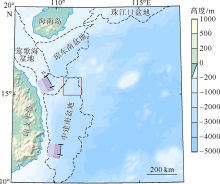
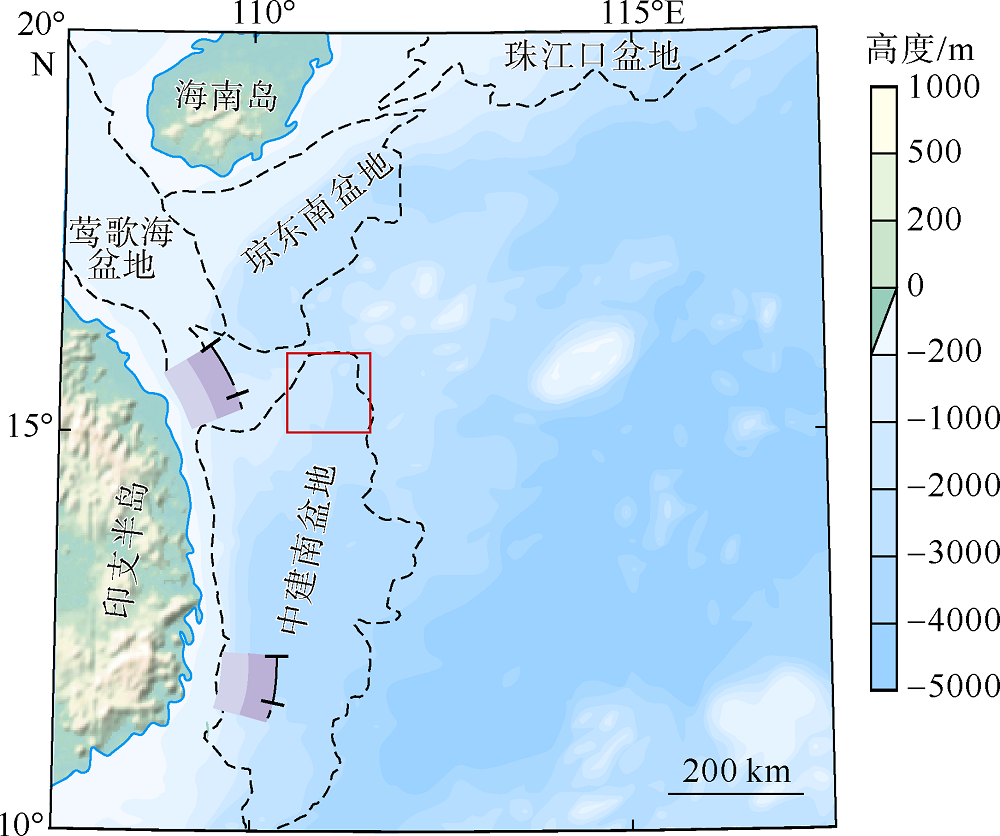
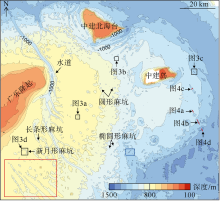
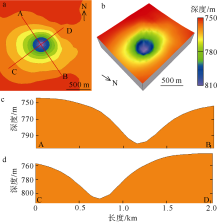
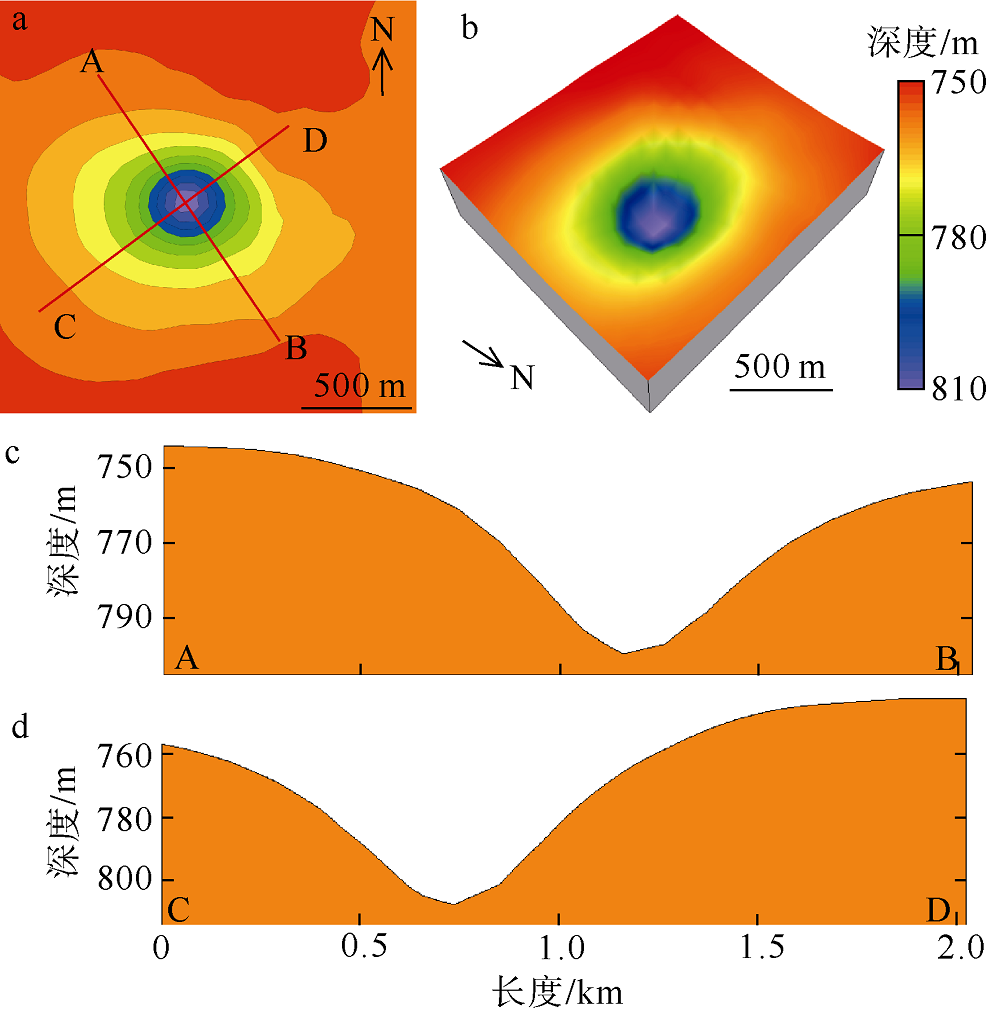
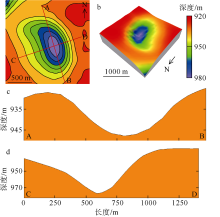
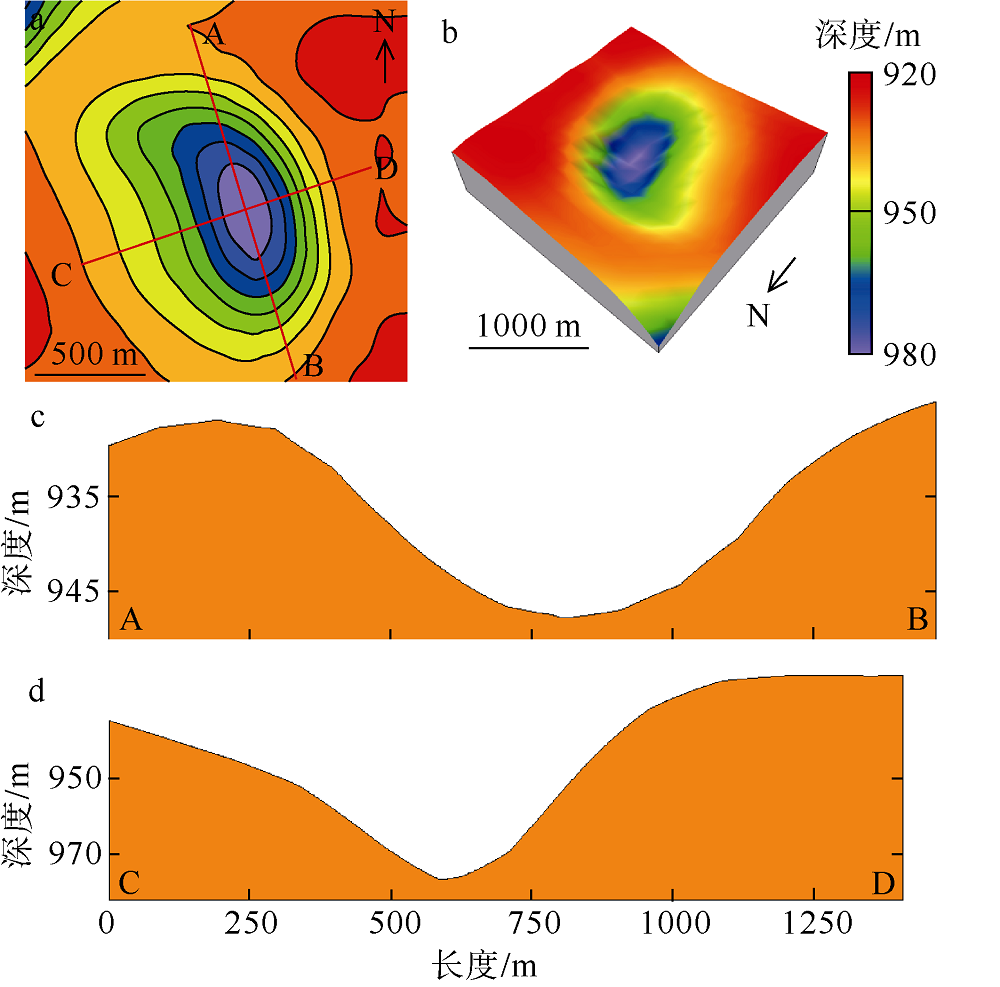
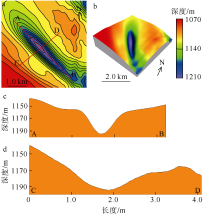
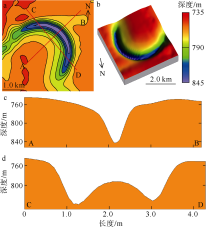
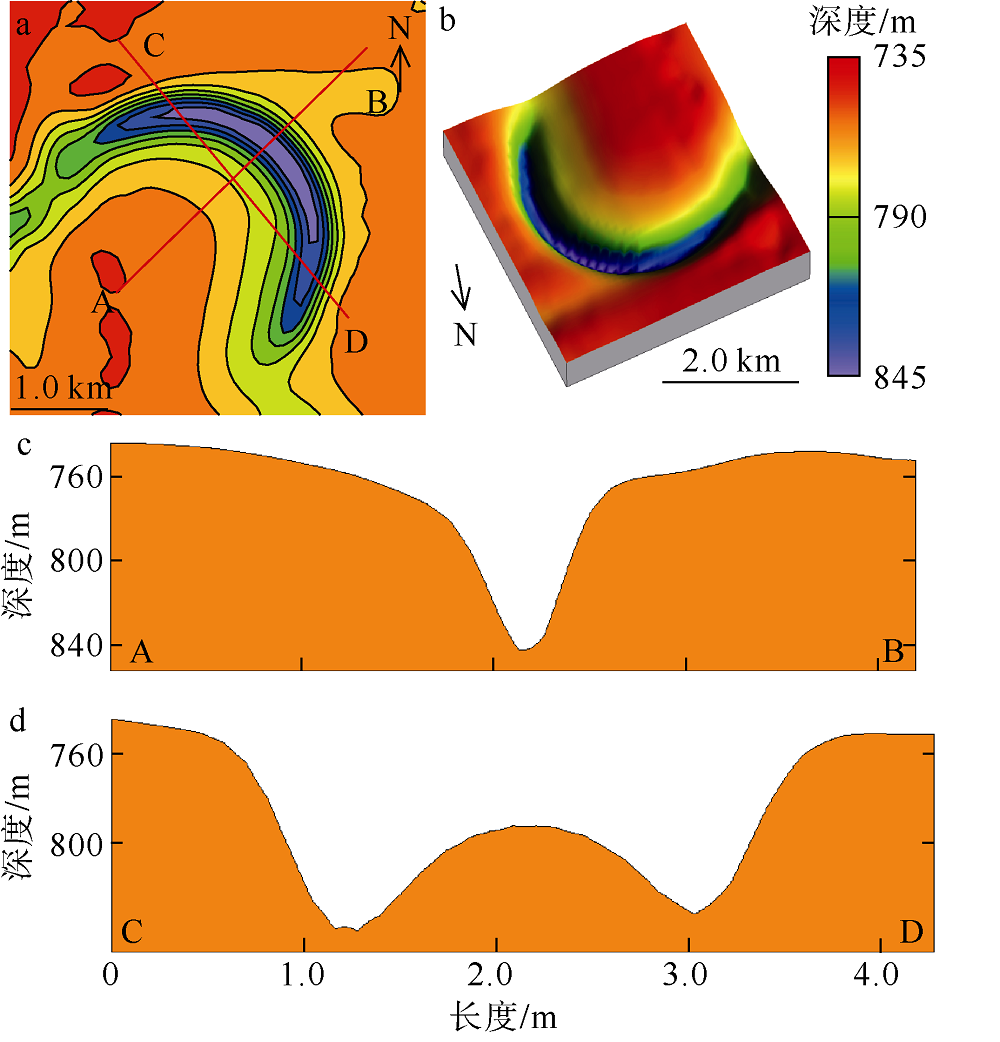
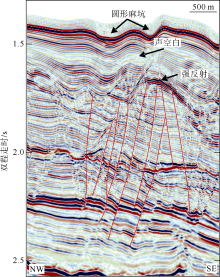
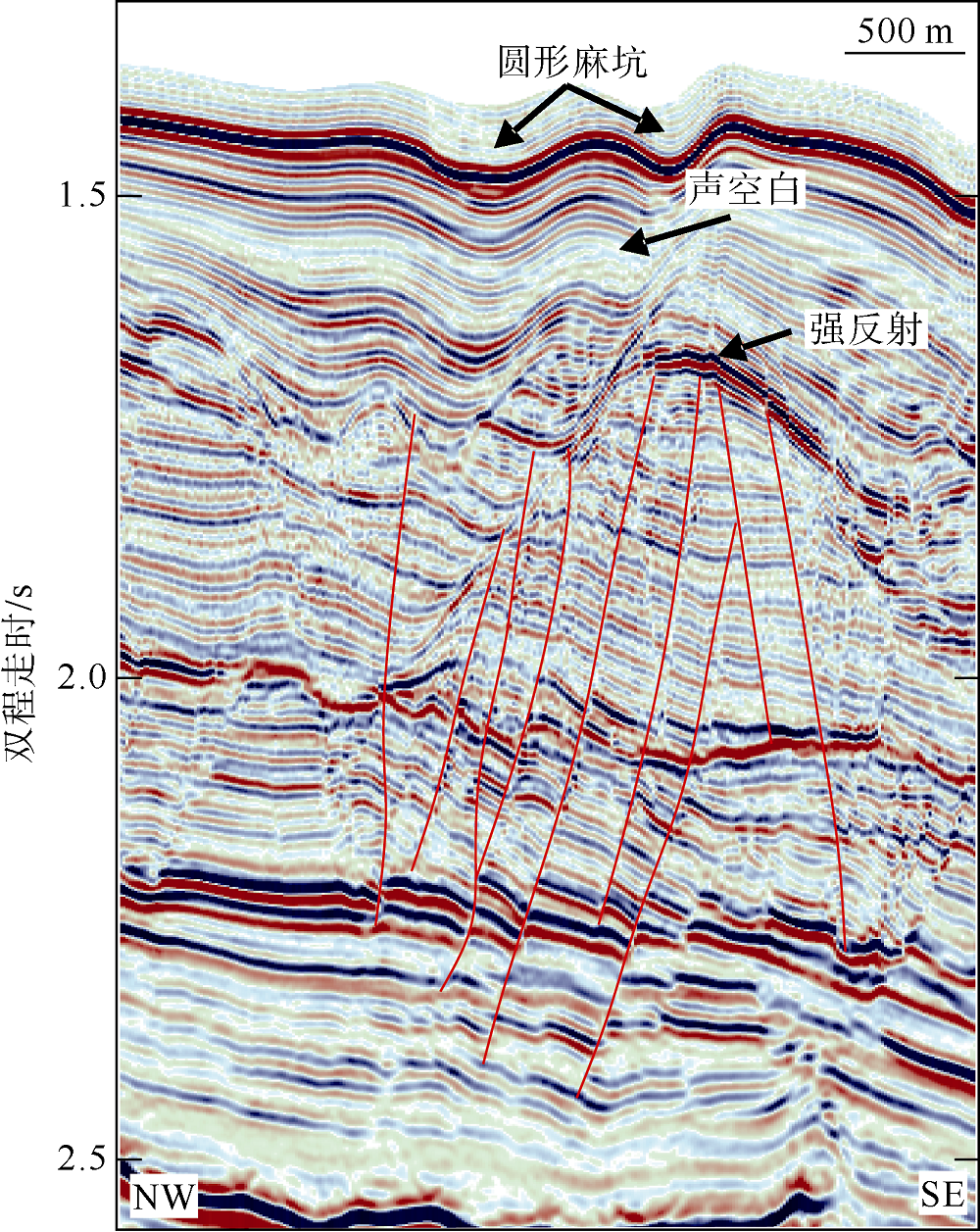
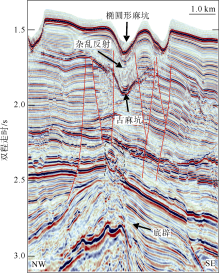
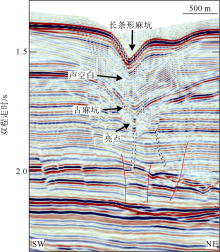
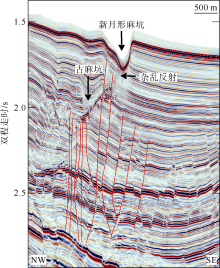
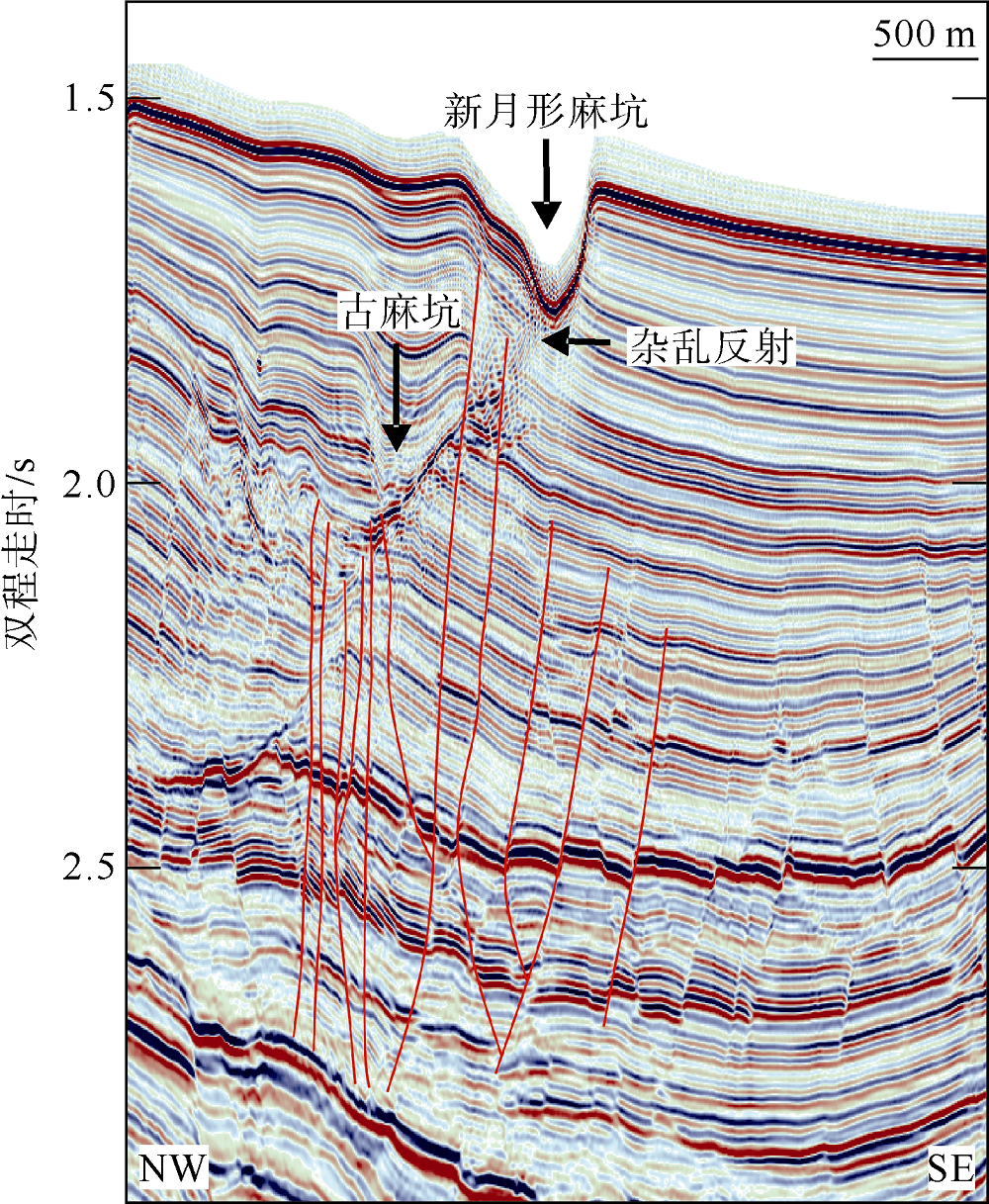
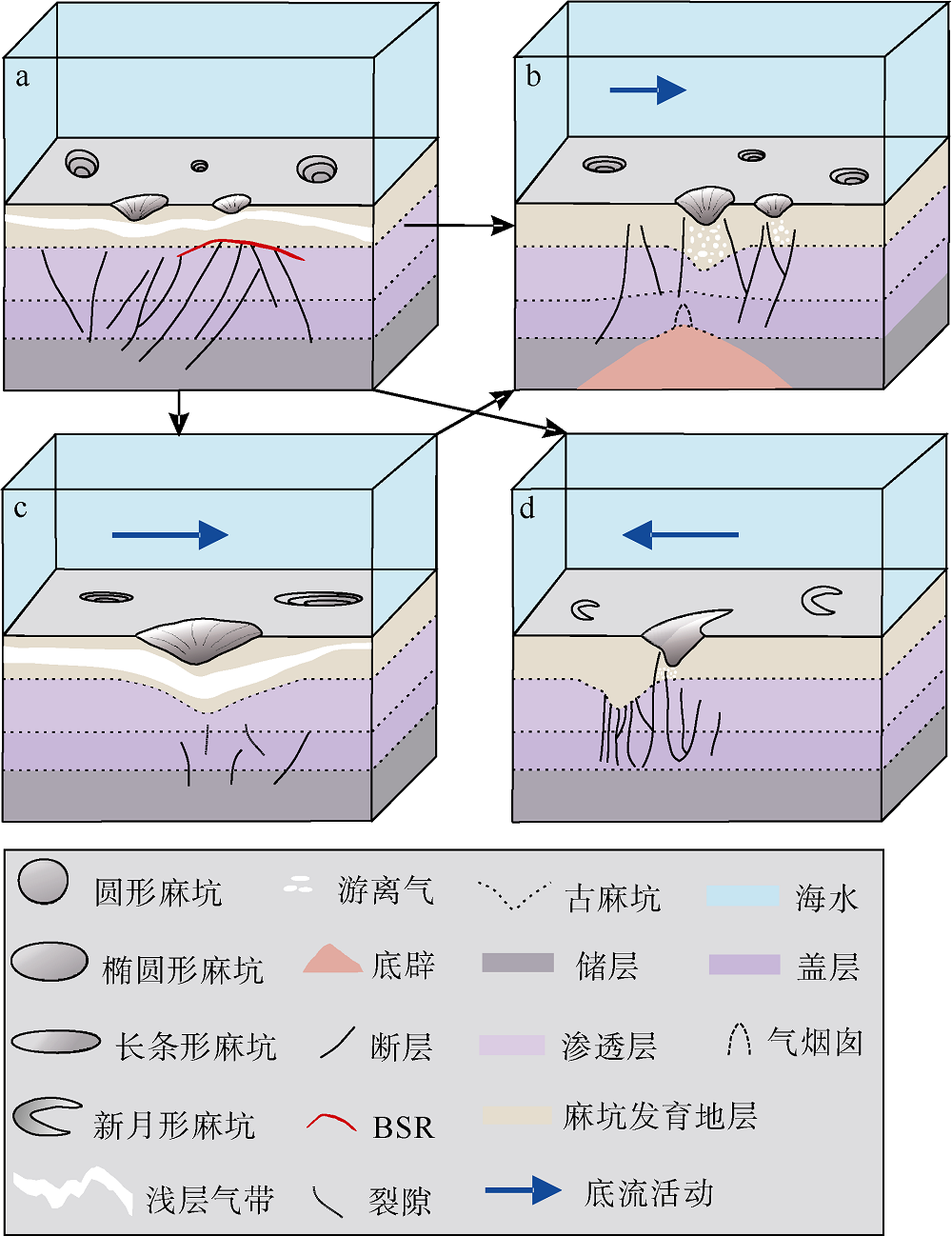
海底麻坑是与流体逸散相关的一种海底凹陷地貌, 在全球海域的陆架、陆坡和深海平原等均有广泛发育。文章利用高分辨率的多波束测深数据和三维地震资料, 在中建南盆地北部识别出330个规模不等的海底麻坑, 按照麻坑形态可将其分为: 圆形、椭圆形、长条形及新月形麻坑。研究区内海底麻坑直径可达1500~7900m, 最大深度可达175m, 其中圆形麻坑规模(直径、深度)小于椭圆形、长条形和新月形麻坑, 表明圆形麻坑处于麻坑发育早期阶段。三维地震资料显示不同类型海底麻坑的下伏地层中均发育有断层、气烟囱、裂隙等流体逸散通道, 为该区域海底麻坑形成提供了有利条件。在海底麻坑演化过程中, 底流对海底麻坑的地貌形态具有改造作用。当圆形麻坑下伏地层流体活动强烈时, 流体可沿着运移通道直接向麻坑内壁渗漏, 使得其内壁塌陷, 逐渐演化成椭圆形麻坑。由于椭圆形麻坑处于底流活动影响的早期阶段, 其受底流改造作用较弱。在持续性底流活动的强烈改造作用下, 紧密排列的圆形或椭圆形麻坑逐渐拉伸演变成长条形麻坑。当底流作用于孤立的圆形麻坑时, 在底流的上游侧沉积速率增加, 麻坑在上游侧接受沉积被掩埋, 下游侧地层被侵蚀, 从而形成新月形麻坑。根据研究区海底麻坑成因机制分析, 文章首次提出了一种展示中建南盆地不同类型海底麻坑演化过程模型, 该模型有助于理解中建南盆地流体逸散过程和底流活动, 并且可为其他区域海底麻坑演化过程研究提供参考。
中图分类号:
- P737.22
引用本文
汪灵, 王彬, 李健, 喻凯琦, 赵芳. 中建南盆地北部海底麻坑地貌特征及成因机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 72-84.
WANG Ling, WANG Bin, LI Jian, YU Kaiqi, ZHAO Fang. Morphology characteristics and formation mechanisms of submarine pockmarks in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 72-84.
| [1] | 陈端新, 吴时国, 王志君, 等, 2012. 南海北部陆缘深水盆地多边形断层几何特征及成因[J]. 石油学报, 33(4):610-616. |
| CHEN DUANXIN, WU SHIGUO, WANG ZHIJUN, et al, 2012. Geometry and genesis of polygonal faults in epicontinental deepwater basins, northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 33(4):610-616 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 陈玲, 2006. 南海中建南盆地构造样式分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 26(1):53-58. |
| CHEN LING, 2006. Analysis of structural styles of Zhongjiannan basin in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 26(1):53-58 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 邸鹏飞, 黄华谷, 黄保家, 等, 2012. 莺歌海盆地海底麻坑的形成与泥底辟发育和流体活动的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 31(5):26-36. |
| DI PENGFEI, HUANG HUAGU, HUANG BAOJIA, et al, 2012. Seabed pockmark formation associated with mud diapir development and fluid activities in the Yinggehai Basin of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 31(5):26-36 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 高红芳, 白志琳, 郭依群, 2000. 南海西部中建南盆地新生代沉积相及古地理演化[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 14(6):411-416. |
| GAO HONGFANG, BAI ZHILIN, GUO YIQUN, 2000. Cenozoic sedimentary facies and palaeogeographic evolution of Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 14(6):411-416 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 高红芳, 王衍棠, 郭丽华, 2007. 南海西部中建南盆地油气地质条件和勘探前景分析[J]. 中国地质, 34(4):592-598. |
| GAO HONGFANG, WANG YANTANG, GUO LIHUA, 2007. Petroleum geological conditions and prospects in the Zhongjiannan basin in the western South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 34(4):592-598 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 何家雄, 夏斌, 张树林, 等, 2006. 莺歌海盆地泥底辟成因、展布特征及其与天然气运聚成藏关系[J]. 中国地质, 33(6):1336-1344. |
| HE JIAXIONG, XIA BIN, ZHANG SHULIN, et al, 2006. Origin and distribution of mud diapirs in the Yinggehai basin and their relation to the migration and accumulation of natural gas[J]. Geology in China, 33(6):1336-1344 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 何丽娟, 熊亮萍, 汪集旸, 1998. 南海盆地地热特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 12(2):87-90. |
| HE LIJUAN, XIONG LIANGPING, WANG JIYANG, 1998. The geothermal characteristics in South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 12(2):87-90 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 李家彪, 2005. 中国边缘海形成演化与资源效应[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-505. |
| LI JIABIAO, 2005. Evolution of China’s marginal seas and its effect of natural resources[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press: 1-505(in Chinese). | |
| [9] | 李家彪, 丁巍伟, 高金耀, 等, 2011. 南海新生代海底扩张的构造演化模式: 来自高分辨率地球物理数据的新认识[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(12):3004-3015. |
| LI JIABIAO, DING WEIWEI, GAO JINYAO, et al, 2011. Cenozoic evolution model of the sea-floor spreading in South China Sea: new constraints from high resolution geophysical data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(12):3004-3015 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 梁全胜, 刘震, 王德杰, 等, 2006. “气烟囱”与油气勘探[J]. 新疆石油地质, 27(3):288-290. |
| LIANG QUANSHENG, LIU ZHEN, WANG DEJIE, et al, 2006. Gas chimney and hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 27(3):288-290 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 刘金萍, 简晓玲, 王后金, 等, 2020. 南海西部中建南盆地烃源岩热演化史[J]. 地质学刊, 44(1):157-162. |
| LIU JINPING, JIAN XIAOLING, WANG HOUJIN, et al, 2020. Thermal evolution history of hydrocarbon source rock in the Zhongjiannan Basin, western South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geology, 44(1):157-162 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 罗敏, 吴庐山, 陈多福, 2012. 海底麻坑研究现状及进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 28(5):33-42. |
| LUO MIN, WU LUSHAN, CHEN DUOFU, 2012. Research status and progress of seabed pockmarks[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 28(5):33-42 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 孙启良, 2011. 南海北部深水盆地流体逸散系统与沉积物变形[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所). |
| SUN QILIANG, 2011. Focused fliud-flow escape system and sediments deformation in deep-water basins of northern south china sea[D]. Beijing: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 吴时国, 孙启良, 董冬冬, 2008. 深水盆地中多边形断层的几何特征与形成机制探讨[J]. 地质力学学报, 14(3):231-240. |
| WU SHIGUO, SUN QILIANG, DONG DONGDONG, 2008. The geometrical characteristics and formation mechanism of polygonal faults in deep-water basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 14(3):231-240 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 夏少红, 范朝焰, 孙金龙, 等, 2017. 南海北部晚新生代岩浆活动的发育特征与构造意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 37(6):25-33. |
| XIA SHAOHONG, FAN CHAOYAN, SUN JINLONG, et al, 2017. Characteristics of late cenozoic magmatic activities on the northern margin of South China Sea and their tectonic implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 37(6):25-33 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 徐行, 罗贤虎, 许鹤华, 等, 2015. 南海地热流探测、研究与展望[J]. 南海地质研究, (1):1-18. |
| XU XING, LUO XIANHU, XU HEHUA, et al, 2015. The measurement, review and prospect on geothermal studies of the South China Sea[J]. Geological Research of South China Sea, (1):1-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [17] | 杨涛涛, 吕福亮, 王彬, 等, 2013. 琼东南盆地南部深水区气烟囱地球物理特征及成因分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 28(5):2634-2641. |
| YANG TAOTAO, LV FULIANG, WANG BIN, et al, 2013. Geophysical characteristics and genetic mechanism of the gas chimney in deepwater area of southern qiongdongnan basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 28(5):2634-2641 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] | 杨志力, 王彬, 李丽, 等. 南海中建海域麻坑发育特征及成因机制[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020(1):42-49. |
| YANG ZHILI, WANG BIN, LI LI, et al, 2020. Characteristics of pockmarks and their genesis Zhongjian offshore area, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontier, 2020(1):42-49 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [19] | 姚伯初, 万玲, 刘振湖, 2004. 南海海域新生代沉积盆地构造演化的动力学特征及其油气资源[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 29(5):543-549. |
| YAO BOCHU, WAN LING, LIU ZHENHU, 2004. Tectonic dynamics of cenozoic sedimentary basins and hydrocarbon resources in the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science - Journal of China University of Geosciences, 29(5):543-549 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [20] | 姚伯初, 万玲, 吴能友, 2005. 南海新生代构造演化及岩石圈三维结构特征[J]. 地质通报, 24(1):1-8. |
| YAO BOCHU, WAN LING, WU NENGYOU, 2005. Cenozoic tectonic evolution and the 3D structure of the lithosphere of the South China Sea[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 24(1):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [21] | 张功成, 谢晓军, 王万银, 等, 2013. 中国南海含油气盆地构造类型及勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 34(4):611-627. |
| ZHANG GONGCHENG, XIE XIAOJUN, WANG WANYIN, et al, 2013. Tectonic types of petroliferous basins and its exploration potential in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(4):611-627 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [22] | 张伟, 梁金强, 何家雄, 等, 2017. 南海北部陆坡泥底辟/气烟囱基本特征及其与油气和水合物成藏关系[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 33(7):11-23. |
| ZHANG WEI, LIANG JINQIANG, HE JIAXIONG, et al, 2017. Characteristics of mud diapir and gas chimney and their relationship with reservoir forming for petroleum and natural gas hydrate on northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 33(7):11-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [23] | 钟广见, 高红芳, 2005. 中建南盆地新生代层序地层特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 29(3):403-409. |
| ZHONG GUANGJIAN, GAO HONGFANG, 2005. Sequence Characteristics of Cenozoic stratigraphy in Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 29(3):403-409 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [24] |
ANDREASSEN K, HUBBARD A, WINSBORROW M, et al, 2017. Massive blow-out craters formed by hydrate-controlled methane expulsion from the Arctic seafloor[J]. Science, 356(6341):948-953.
doi: 10.1126/science.aal4500 |
| [25] |
ANDRESEN K J, HUUSE M, CLAUSEN O R, 2008. Morphology and distribution of Oligocene and Miocene pockmarks in the Danish North Sea - implications for bottom current activity and fluid migration[J]. Basin Research, 20(3):445-466.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2008.00362.x |
| [26] |
ANDRESEN K J, HUUSE M, 2011. ‘Bulls-eye’ pockmarks and polygonal faulting in the Lower Congo Basin: Relative timing and implications for fluid expulsion during shallow burial[J]. Marine Geology, 279(1-4):111-127.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.10.016 |
| [27] |
BARAZA J, ERCILLA G, NELSON C H, 1999. Potential geologic hazards on the eastern Gulf of Cadiz slope (SW Spain)[J]. Marine Geology, 155(1-2):191-215.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00147-9 |
| [28] |
BETZLER C, LINDHORST S, HÜBSCHER C, et al, 2011. Giant pockmarks in a carbonate platform (Maldives, Indian Ocean)[J]. Marine Geology, 289(1-4):1-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.09.004 |
| [29] |
BÖTTNER C, BERNDT C, REINARDY B T I, et al, 2019. Pockmarks in the Witch Ground Basin, Central North Sea[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 20(4):1698-1719.
doi: 10.1029/2018GC008068 |
| [30] |
BULAT J, LONG D, 2001. Images of the seabed in the Faroe-Shetland Channel from commercial 3D seismic data[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 22(5-6):345-367.
doi: 10.1023/A:1016343431386 |
| [31] |
CATHLES L M, SU ZHEN, CHEN DUOFU, 2010. The physics of gas chimney and pockmark formation, with implications for assessment of seafloor hazards and gas sequestration[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 27(1):82-91.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.09.010 |
| [32] | CHAND S, THORSNES T, RISE L, et al, 2012. Multiple episodes of fluid flow in the SW Barents Sea (Loppa High) evidenced by gas flares, pockmarks and gas hydrate accumulation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 331- 332:305-314. |
| [33] | CHEN DUANXIN, WU SHIGUO, WANG XIUJUAN, et al, 2011. Seismic expression of polygonal faults and its impact on fluid flow migration for gas hydrates formation in deep water of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geological Research, 2011: 283-284. |
| [34] | CHEN JIANGXIN, SONG HAIBIN, GUAN YONGXIAN, et al, 2015. Morphologies, classification and genesis of pockmarks, mud volcanoes and associated fluid escape features in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 122:106-117. |
| [35] |
CHEN JIANGXIN, SONG HAIBIN, GUAN YONGXIAN, et al, 2018. Geological and oceanographic controls on seabed fluid escape structures in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 168:38-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.04.027 |
| [36] |
ÇIFÇI G, DONDURUR D, ERGÜN M, 2003. Deep and shallow structures of large pockmarks in the Turkish shelf, Eastern Black Sea[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 23(3-4):311-322.
doi: 10.1007/s00367-003-0138-x |
| [37] |
DANDAPATH S, CHAKRABORTY B, KARISIDDAIAH S M, et al, 2010. Morphology of pockmarks along the western continental margin of India: employing multibeam bathymetry and backscatter data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 27(10):2107-2117.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.09.005 |
| [38] |
FAULKNER D R, JACKSON C A L, LUNN R J, et al, 2010. A review of recent developments concerning the structure, mechanics and fluid flow properties of fault zones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 32(11):1557-1575.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2010.06.009 |
| [39] |
GAN JIANPING, LIU ZHIQIANG, HUI C R, 2016. A three-layer alternating spinning circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(8):2309-2315.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-16-0044.1 |
| [40] |
GELETTI R, DEL BEN A, BUSETTI M, et al, 2008. Gas seeps linked to salt structures in the Central Adriatic Sea[J]. Basin Research, 20(4):473-487.
doi: 10.1111/bre.2008.20.issue-4 |
| [41] | GENG MINGHUI, SONG HAIBIN, GUAN YONGXIAN, et al, 2017. Characteristics and generation mechanism of gullies and mega-pockmarks in the Zhongjiannan Basin, western South China Sea[J]. Interpretation, 5(3): SM49-SM59. |
| [42] |
GOFF J A, 2019. Modern and fossil pockmarks in the new England mud patch: implications for submarine groundwater discharge on the middle shelf[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(21):12213-12220.
doi: 10.1029/2019GL084881 |
| [43] |
HAMMER Ø, WEBB K E, DEPREITER D, 2009. Numerical simulation of upwelling currents in pockmarks, and data from the Inner Oslofjord, Norway[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 29(4):269-275.
doi: 10.1007/s00367-009-0140-z |
| [44] |
HARRINGTON P K, 1985. Formation of pockmarks by pore-water escape[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 5(3):193-197.
doi: 10.1007/BF02281638 |
| [45] |
HASIOTIS T, PAPATHEODOROU G, KASTANOS N, et al, 1996. A pockmark field in the Patras Gulf (Greece) and its activation during the 14/7/93 seismic event[J]. Marine Geology, 130(3-4):333-344.
doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(95)00131-X |
| [46] |
HILLMAN J I T, GORMAN A R, PECHER I A, 2015. Geostatistical analysis of seafloor depressions on the southeast margin of New Zealand’s South Island - Investigating the impact of dynamic near seafloor processes on geomorphology[J]. Marine Geology, 360:70-83.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.11.016 |
| [47] |
HO S, HOVLAND M, BLOUET J P, et al, 2018. Formation of linear planform chimneys controlled by preferential hydrocarbon leakage and anisotropic stresses in faulted fine-grained sediments, Offshore Angola[J]. Solid Earth Discussion, doi: 10.5194/se-2018-34.
doi: 10.5194/se-2018-34 |
| [48] |
HOVLAND M, GARDNER J V, JUDD A G, 2002. The significance of pockmarks to understanding fluid flow processes and geohazards[J]. Geofluids, 2(2):127-136.
doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00028.x |
| [49] |
HOVLAND M, JENSEN S, INDREITEN T, 2012. Unit pockmarks associated with Lophelia coral reefs off mid-Norway: more evidence of control by ‘fertilizing’ bottom currents[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 32(5-6):545-554.
doi: 10.1007/s00367-012-0284-0 |
| [50] |
HUSTOFT S, MIENERT J, BÜNZ S, et al, 2007. High-resolution 3D-seismic data indicate focussed fluid migration pathways above polygonal fault systems of the mid-Norwegian margin[J]. Marine Geology, 245(1-4):89-106.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.07.004 |
| [51] | JUDD A G, HOVLAND M, 2007. Seabed fluid flow: The impact of geology, biology and the marine environment[M]. Cambridge, UK, Cambridge University Press: 492. |
| [52] |
KELLEY J T, DICKSON S M, BELKNAP D F, et al, 1994. Giant sea-bed pockmarks: evidence for gas escape from Belfast Bay, Maine[J]. Geology, 22(1):59-62.
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0059:GSBPEF>2.3.CO;2 |
| [53] |
KING L H, MACLEAN B, 1970. Pockmarks on the Scotian Shelf[J]. GSA Bulletin, 81(10):3141-3148.
doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1970)81[3141:POTSS]2.0.CO;2 |
| [54] |
LØSETH H, WENSAAS L, ARNTSEN B, et al, 2011. 1000m long gas blow-out pipes[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 28(5):1047-1060.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.10.001 |
| [55] |
LU YINTAO, LUAN XIWU, LYU F, et al, 2017. Seismic evidence and formation mechanism of gas hydrates in the Zhongjiannan Basin, Western margin of the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 84:274-288.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.04.005 |
| [56] |
MAZZINI A, SVENSEN H H, FORSBERG C F, et al, 2017. A climatic trigger for the giant Troll pockmark field in the northern North Sea[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 464:24-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.02.014 |
| [57] |
MICHEL G, DUPRÉ S, BALTZER A, et al, 2017. Pockmarks on the South Aquitaine Margin continental slope: the seabed expression of past fluid circulation and former bottom currents[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 349(8):391-401.
doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2017.10.003 |
| [58] |
MORGAN D A, CARTWRIGHT J A, IMBERT P, 2015. Perturbation of polygonal fault propagation by buried pockmarks and the implications for the development of polygonal fault systems[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 65:157-171.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.03.024 |
| [59] |
MOSS J L, CARTWRIGHT J, MOORE R, 2012. Evidence for fluid migration following pockmark formation: examples from the Nile Deep Sea Fan[J]. Marine Geology, 303-306:1-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.01.010 |
| [60] |
NELSON C S, HEALY T R, 1984. Pockmark-like structures on the Poverty Bay sea bed — possible evidence for submarine mud volcanism[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 27(2):225-230.
doi: 10.1080/00288306.1984.10422530 |
| [61] |
NELSON H, THOR D R, SANDSTROM M W, et al, 1979. Modern biogenic gas-generated craters (sea-floor “pockmarks”) on the Bering Shelf, Alaska[J]. GSA Bulletin, 90(12):1144-1152.
doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1979)90<1144:MBGCSP>2.0.CO;2 |
| [62] |
PAULL C K, USSLER III W, BOROWSKI W S, 1999. Freshwater ice rafting: an additional mechanism for the formation of some high-latitude submarine pockmarks[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 19(1-2):164-168.
doi: 10.1007/s003670050104 |
| [63] |
PAULL C K, USSLER III W, HOLBROOK W S, et al, 2008. Origin of pockmarks and chimney structures on the flanks of the Storegga Slide, offshore Norway[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 28(1):43-51.
doi: 10.1007/s00367-007-0088-9 |
| [64] |
PILCHER R, ARGENT J, 2007. Mega-pockmarks and linear pockmark trains on the West African continental margin[J]. Marine Geology, 244(1-4):15-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.05.002 |
| [65] |
RIBOULOT V, CATTANEO A, SULTAN N, et al, 2013. Sea-level change and free gas occurrence influencing a submarine landslide and pockmark formation and distribution in deepwater Nigeria[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 375:78-91.
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.05.013 |
| [66] |
RIBOULOT V, THOMAS Y, BERNÉ S, et al, 2014. Control of Quaternary sea-level changes on gas seeps[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(14):4970-4977.
doi: 10.1002/2014GL060460 |
| [67] |
SERIÉ C, HUUSE M, SCHØDT N H, 2012. Gas hydrate pingoes: deep seafloor evidence of focused fluid flow on continental margins[J]. Geology, 40(3):207-210.
doi: 10.1130/G32690.1 |
| [68] |
SOTER S, 1999. Macroscopic seismic anomalies and submarine pockmarks in the Corinth - Patras rift, Greece[J]. Tectonophysics, 308(1-2):275-290.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00090-6 |
| [69] | SULTAN N, MARSSET B, KER S, et al, 2010. Hydrate dissolution as a potential mechanism for pockmark formation in the Niger delta[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 115(B8):B08101. |
| [70] | SULTAN N, RIBOULOT V, KER S, et al, 2011. Dynamics of fault-fluid-hydrate system around a shale-cored anticline in deepwater Nigeria[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 116(B12):B12110. |
| [71] |
SUN QILIANG, WU SHIGUO, HOVLAND M, et al, 2011. The morphologies and genesis of mega-pockmarks near the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 28(6):1146-1156.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.03.003 |
| [72] | SUN QILIANG, WU SHIGUO, CARTWRIGHT J, et al, 2012. Shallow gas and focused fluid flow systems in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 315- 318:1-14. |
| [73] |
WAGHORN K A, PECHER I, STRACHAN L J, et al, 2018. Paleo-fluid expulsion and contouritic drift formation on the Chatham Rise, New Zealand[J]. Basin Research, 30(1):5-19.
doi: 10.1111/bre.12237 |
| [74] |
WEI JIANGONG, PAPE T, SULTAN N, et al, 2015. Gas hydrate distributions in sediments of pockmarks from the Nigerian margin - Results and interpretation from shallow drilling[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 59:359-370.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.09.013 |
| [75] |
YE JIANLIANG, WEI JIANGONG, LIANG JINQIANG, et al, 2019. Complex gas hydrate system in a gas chimney, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 104:29-39.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.03.023 |
| [76] |
ZHANG YANWEI, LIU ZHIFEI, ZHAO YULONG, et al, 2014. Mesoscale eddies transport deep-sea sediments[J]. Scientific Reports, 4(1):5937.
doi: 10.1038/srep05937 |
| [1] | 丁巍伟, 李家彪, 李军, 韩喜彬. 南海珠江口外海底峡谷形成的控制因素及过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(6): 63-72. |
|
||