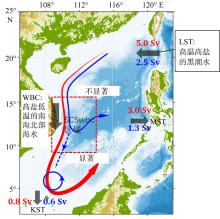
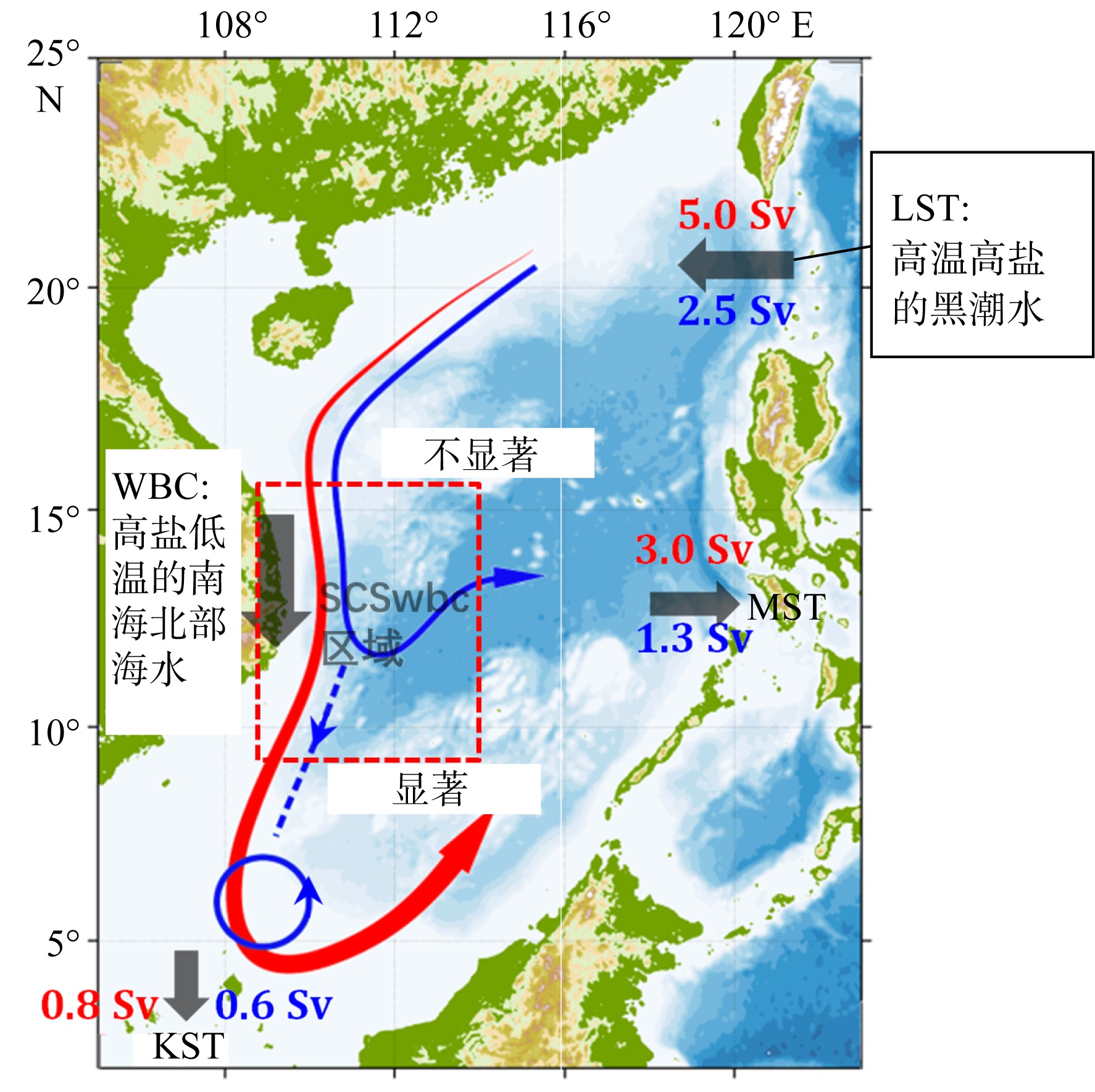
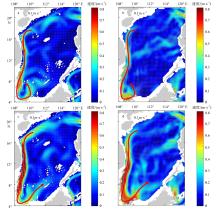
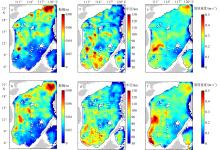
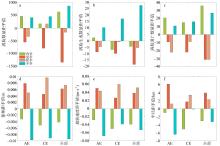
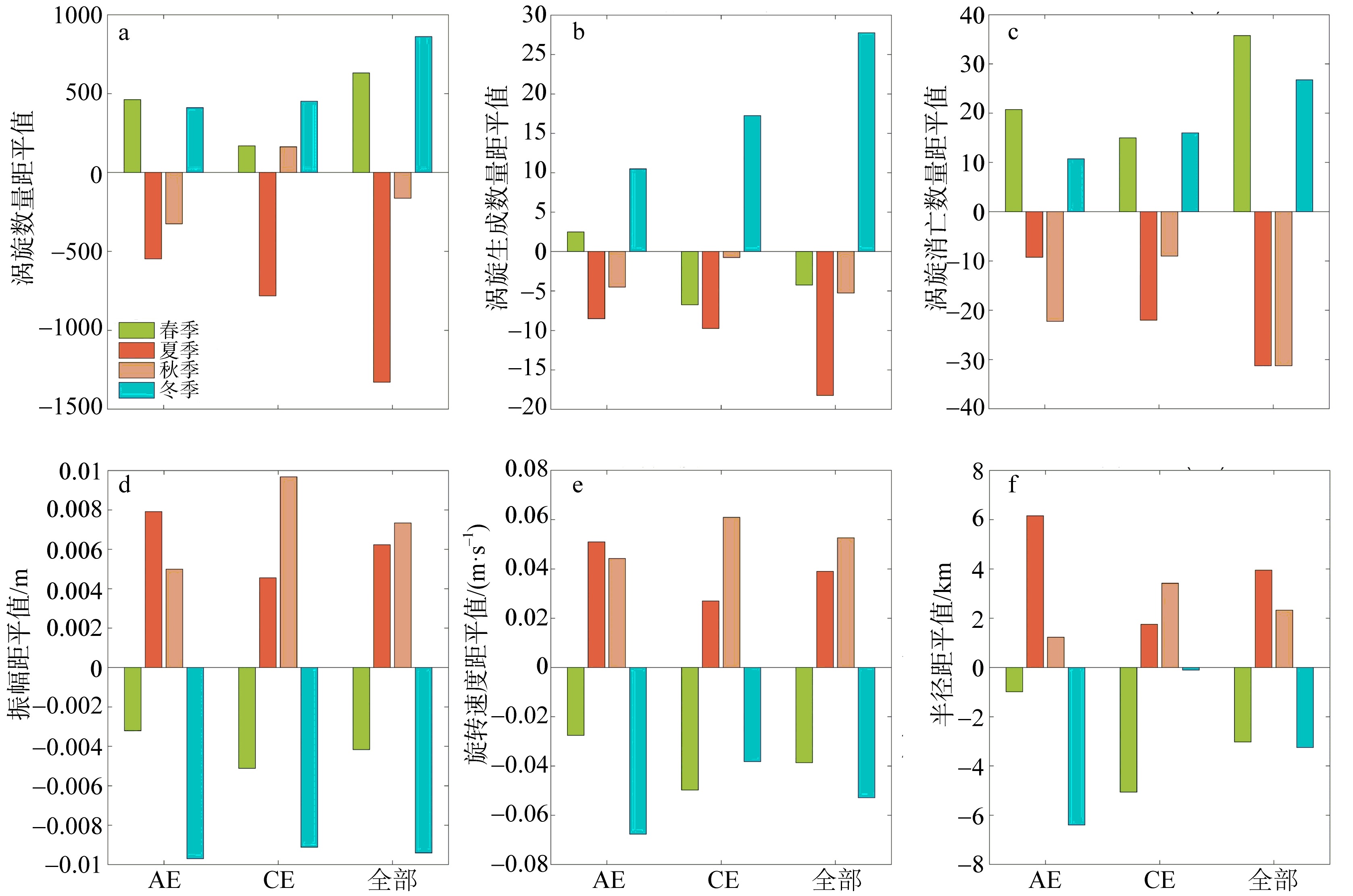
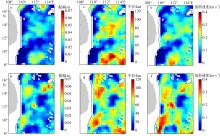
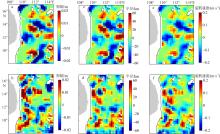
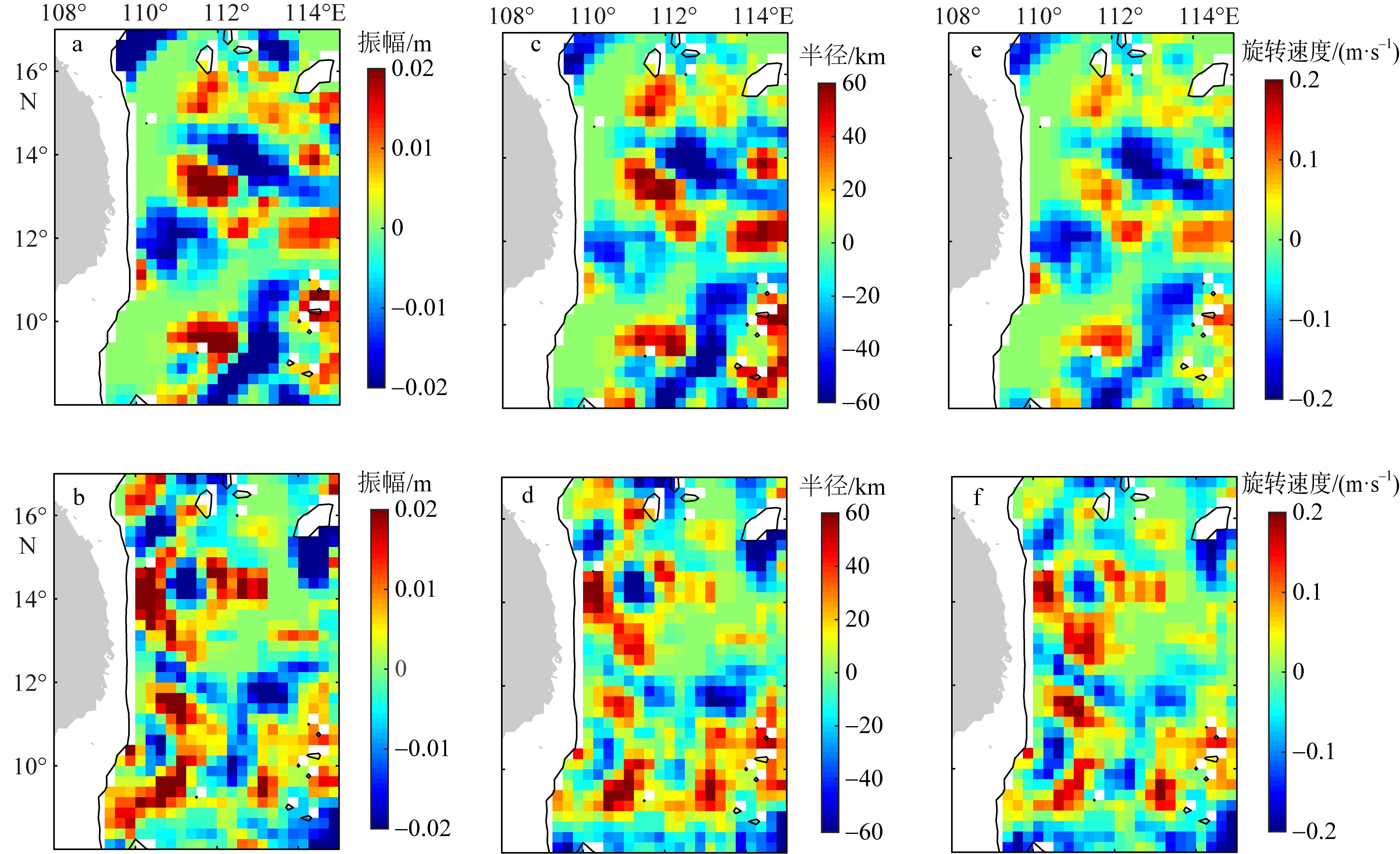
| [1] |
林鹏飞, 王凡, 陈永利, 等, 2007. 南海中尺度涡的时空变化规律Ⅰ. 统计特征分析[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 2007(3): 14-22.
|
|
LIN PENGFEI, WANG FAN, CHEN YONGLI, et al, 2007. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics on eddies in the South China Sea I. statistical analyses. Haiyang Xuebao, 29(3): 14-22. (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
王东晓, 王强, 蔡树群, 等, 2019. 南海中深层动力格局与演变机制研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49(12): 1919-1932. (in Chinese)
|
| [3] |
CAI SHUQUN, SU JILAN, GAN ZIJUN, et al, 2002. The numerical study of the South China Sea upper circulation characteristics and its dynamic mechanism, in winter[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 22(15): 2247-2264.
doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00073-0
|
| [4] |
CEBALLOS L, DI LORENZO E, HOYOS C, et al, 2009. North Pacific Gyre Oscillation Synchronizes Climate Fluctuations in the Eastern and Western Boundary Systems[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(19): 5163-5174.
doi: 10.1175/2009JCLI2848.1
|
| [5] |
CHELTON D B, SCHLAX M G, SAMELSON R M, 2011. Global observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 91(2): 167-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2011.01.002
|
| [6] |
CHEN CHANGLIN, WANG GUIHUA, 2014. Interannual variability of the eastward current in the western South China Sea associated with the summer Asian monsoon[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(9): 5745-5754.
doi: 10.1002/2014JC010309
|
| [7] |
CHEN GENGXIN, GAN JIANPING, XIE QIANG, et al, 2012. Eddy heat and salt transports in the South China Sea and their seasonal modulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C5).
|
| [8] |
CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, CHU XIAOQING, 2011. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: Mean properties, spatiotemporal variability, and impact on thermohaline structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(C6).
|
| [9] |
CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, ZHANG QILONG, et al, 2010. The eddy pair off eastern Vietnam: Interannual variability and impact on thermohaline structure[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 30(7): 715-723.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.11.013
|
| [10] |
CHEN GENGXIN, XUE HUIJIE, 2014. Westward intensification in marginal seas[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 64(3): 337-345.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-014-0691-z
|
| [11] |
CHU P C, EDMONS N L, FAN C, 1999. Dynamical mechanisms for the South China Sea seasonal circulation and thermohaline variabilities[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 29(11): 2971-2989.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1999)029<2971:DMFTSC>2.0.CO;2
|
| [12] |
CHU XIAOQING, DONG CHANMING, QI YIQUAN, 2017. The influence of ENSO on an oceanic eddy pair in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(3): 1643-1652.
doi: 10.1002/2016JC012642
|
| [13] |
CHU XIAOQING, XUE HUJIE, QI YIQUAN, et al, 2014. An exceptional anticyclonic eddy in the South China Sea in 2010[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(2): 881-897.
doi: 10.1002/2013JC009314
|
| [14] |
DU YUNYAN, DI WU, LIANG FUYUAN, et al, 2016. Major migration corridors of mesoscale ocean eddies in the South China Sea from 1992 to 2012[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 158: 173-181.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.01.013
|
| [15] |
FANG WENDONG, FANG GUOHONG, SHI PING, et al, 2002. Seasonal structures of upper layer circulation in the southern South China Sea from in situ observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107(C11): 23-1-23-12.
|
| [16] |
FENG BAOXIN, LIU HAILONG, LIN PENGFEI, 2020. Effects of Kuroshio intrusion optimization on the simulation of mesoscale eddies in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 39(3): 12-24.
|
| [17] |
GAN JIANPING, LI H, CURCHITSER E N, et al, 2006. Modeling South China Sea circulation: Response to seasonal forcing regimes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C6).
|
| [18] |
GAN JIANPING, QU TANGDONG, 2008. Coastal jet separation and associated flow variability in the southwest South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 55(1): 1-19.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2007.09.008
|
| [19] |
GONADUWAGE L P, CHEN GENGXIN, PRIYADARSHANA T, et al, 2021. Interannual variability of summertime eddy-induced heat transport in the Western South China Sea and its formation mechanism[J]. Climate Dynamics, 57(1-2): 451-468.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-021-05719-7
|
| [20] |
HE QINGYOU, ZHAN HAIGANG, CAI SHUQUN, et al, 2018. A New Assessment of Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea: Surface Features, Three‐Dimensional Structures, and Thermohaline Transports[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(7): 4906-4929.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014054
|
| [21] |
HU JIANYU, KAWAMURA H, HONG H, et al, 2000. A Review on the Currents in the South China Sea: Seasonal Circulation, South China Sea Warm Current and Kuroshio Intrusion[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 56(6): 607-624.
doi: 10.1023/A:1011117531252
|
| [22] |
KURIAN JAISON, COLAS FRANCOISX, CAPET XAVIER, et al, 2011. Eddy properties in the California Current System[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(C08027).
|
| [23] |
LI HONG, XU FANGHUA, ZHOU WEI, et al, 2017. Development of a global gridded Argo data set with Barnes successive corrections[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(2): 866-889.
doi: 10.1002/2016JC012285
|
| [24] |
LI W, LIU Q, FANG W, et al, 2022. Interannual variability of eddy kinetic energy in the South China Sea related to two types of winter circulation events[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology (in press).
|
| [25] |
MASON E, PASCUAL A, MCWILLIAMS J, 2014. A New Sea Surface Height-Based Code for Oceanic Mesoscale Eddy Tracking[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 31(5): 1181-1188.
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-14-00019.1
|
| [26] |
MASUMOTO Y, SASAKI H, KOMORI N, et al, 2004. A Fifty-year Eddy-Resolving Simulation of the World Ocean-Preliminary Outcomes of OFES(OGCM for the Earth Simulator)[J]. Journal of the Earth Simulator, 1: 35-56.
|
| [27] |
PENVEN P, ECHEVIN V, PASAPERA J, et al, 2005. Average circulation, seasonal cycle, and mesoscale dynamics of the Peru Current System: A modeling approach[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110(C10).
|
| [28] |
QU TANGDONG, 2000. Upper-Layer Circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 30(6): 1450-1460.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2000)030<1450:ULCITS>2.0.CO;2
|
| [29] |
QUAN QI, XUE HUIJIE, QIN HUILING, et al. 2016. Features and variability of the South China Sea western boundary current from 1992 to 2011[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 66(6): 795-810.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-016-0951-1
|
| [30] |
STAMMER D, 1997. Global Characteristics of Ocean Variability Estimated from Regional TOPEX/POSEIDON Altimeter Measurements[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 27(8): 1743-1769.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1997)027<1743:GCOOVE>2.0.CO;2
|
| [31] |
TAGUCHI B, XIE SHANG-PING, SCHNEIDER N, et al, 2007. Decadal Variability of the Kuroshio Extension: Observations and an Eddy-Resolving Model Hindcast[J]. Journal of Climate, 20(11): 2357-2377.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI4142.1
|
| [32] |
WANG GUIHUA, CHEN D, SU JILAN, 2006a. Generation and life cycle of the dipole in the South China Sea summer circulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C6).
|
| [33] |
WANG GUIHUA, CHEN D, SU JILAN, 2008. Winter Eddy Genesis in the Eastern South China Sea due to Orographic Wind Jets[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 38(3): 726-732.
doi: 10.1175/2007JPO3868.1
|
| [34] |
WANG GUIHUA, SU JILAN, CHU P, 2003. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea observed with altimeter data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(21).
|
| [35] |
WANG MINYANG, DU YAN, QIU BO, et al, 2017. Mechanism of seasonal eddy kinetic energy variability in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(4): 3240-3252.
doi: 10.1002/2017JC012711
|
| [36] |
WANG QIANG, ZENG LILI, SHU YEQIANG, et al, 2019. Energetic Topographic Rossby Waves in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 49(10): 2697-2714.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-18-0247.1
|
| [37] |
WANG QIANG, ZENG LILI, SHU YEQIANG, et al, 2020. Interannual variability of South China Sea winter circulation: response to Luzon Strait transport and El Nino wind[J]. Clim Dyn, 54: 1145-1159.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-019-05050-2
|
| [38] |
WANG XIDONG, LI WEI, QI YIQUAN, et al, 2012. Heat, salt and volume transports by eddies in the vicinity of the Luzon Strait[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 61: 21-33.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2011.11.006
|
| [39] |
WANG YONGGANG, FANG GUOHONG, WEI ZEXUN, et al, 2006b. Interannual variation of the South China Sea circulation and its relation to El Niño, as seen from a variable grid global ocean model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C11).
|
| [40] |
WU CHAU-RON, CHANG C, 2005. Interannual variability of the South China Sea in a data assimilation model[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(17).
|
| [41] |
WU CHAN-RON, SHAW PING-TUNG, CHAO SHENN-YU, 1998. Seasonal and interannual variations in the velocity field of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 1998, 54(4): 361-372.
doi: 10.1007/BF02742620
|
| [42] |
WU CHAU-RON, SHAW PING-TUNG, CHAO SHENN-YU, 1999. Assimilating altimetric data into a South China Sea model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104(C12): 29987-30005.
doi: 10.1029/1999JC900260
|
| [43] |
XIU PENG, CHAI FEI, SHI LEI, et al, 2010. A census of eddy activities in the South China Sea during 1993-2007[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C3).
|
| [44] |
XU LIXIAO, LI PEILIANG, XIE SHANG-PING, et al, 2016. Observing mesoscale eddy effects on mode-water subduction and transport in the North Pacific[J]. Nature communications, 7: 10505.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms10505
pmid: 26829888
|
| [45] |
XUE HUIJIE, CHAI FEI, PERTTIGREW N, et al, 2004. Kuroshio intrusion and the circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109(C2).
|
| [46] |
YAN XIAOMEI, KANG DUJUAN, CURCHITSER E, et al, 2019. Energetics of Eddy-Mean Flow Interactions along the Western Boundary Currents in the North Pacific[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 49(3): 789-810.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-18-0201.1
|
| [47] |
YANG HAIYUAN, WU LIXIN, LIU HAILONG, 2013. Eddy energy sources and sinks in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118(9): 4716-4726.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20343
|
| [48] |
ZHANG NINGNING, LIU GUOQIANG, LIU QINYAN, et al, 2020. Spatiotemporal Variations of Mesoscale Eddies in the Southeast Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 125(8): e2019JC15712.
|
| [49] |
ZHENG SHAOJUN, FENG MING, DU YAN, et al, 2018. Interannual Variability of Eddy Kinetic Energy in the Subtropical Southeast Indian Ocean Associated With the El Niño-Southern Oscillation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(2): 1048-1061.
doi: 10.1002/2017JC013562
|
| [50] |
ZHUANG WEI, XIE SHANG-PING, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2010. Intraseasonal variability in sea surface height over the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C4)
|
| [51] |
ZU TINGTING, XUE HUIJIE, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2019. Interannual variation of the South China Sea circulation during winter: intensified in the southern basin[J]. Climate Dynamics, 52(3-4): 1917-1933.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-018-4230-3
|
| [52] |
ZU TINGTING, WANG DONGXIAO, WANG QIANG, et al, 2020. A revisit of the interannual variation of the South China Sea upper layer circulation in summer: correlation between the eastward jet and northward branch[J]. Climate Dynamics, 54(1-2): 457-471.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-019-05007-5
|
 ), 李汶莲1,3, 石睿1, 陈举1, 李春晖4, 谢强5
), 李汶莲1,3, 石睿1, 陈举1, 李春晖4, 谢强5
 ), LI Wenlian1,3, SHI Rui1, CHEN Ju1, LI Chunhui4, XIE Qiang5
), LI Wenlian1,3, SHI Rui1, CHEN Ju1, LI Chunhui4, XIE Qiang5