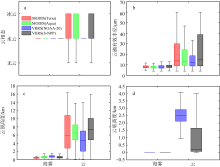
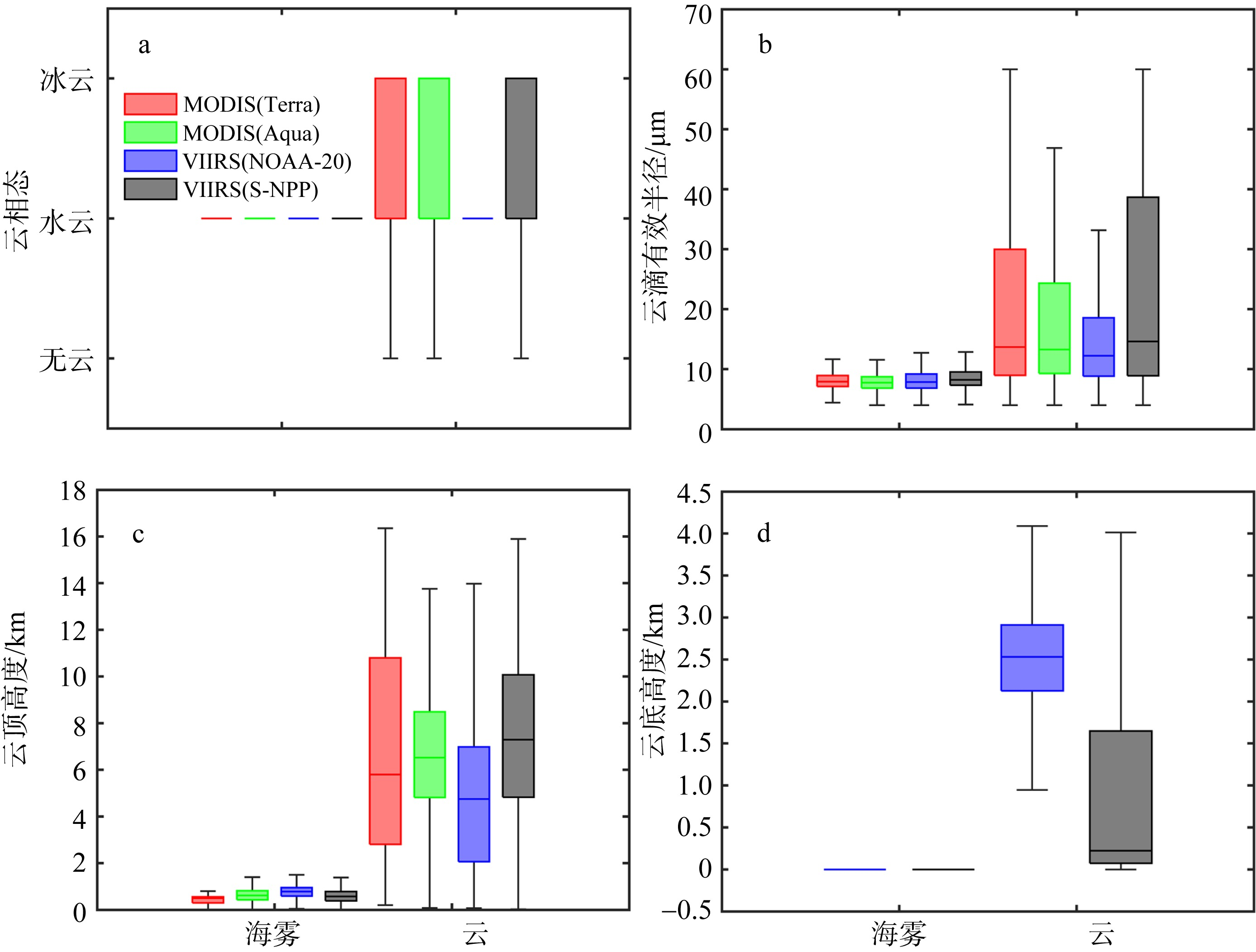
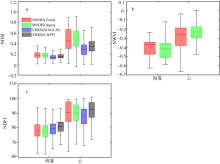
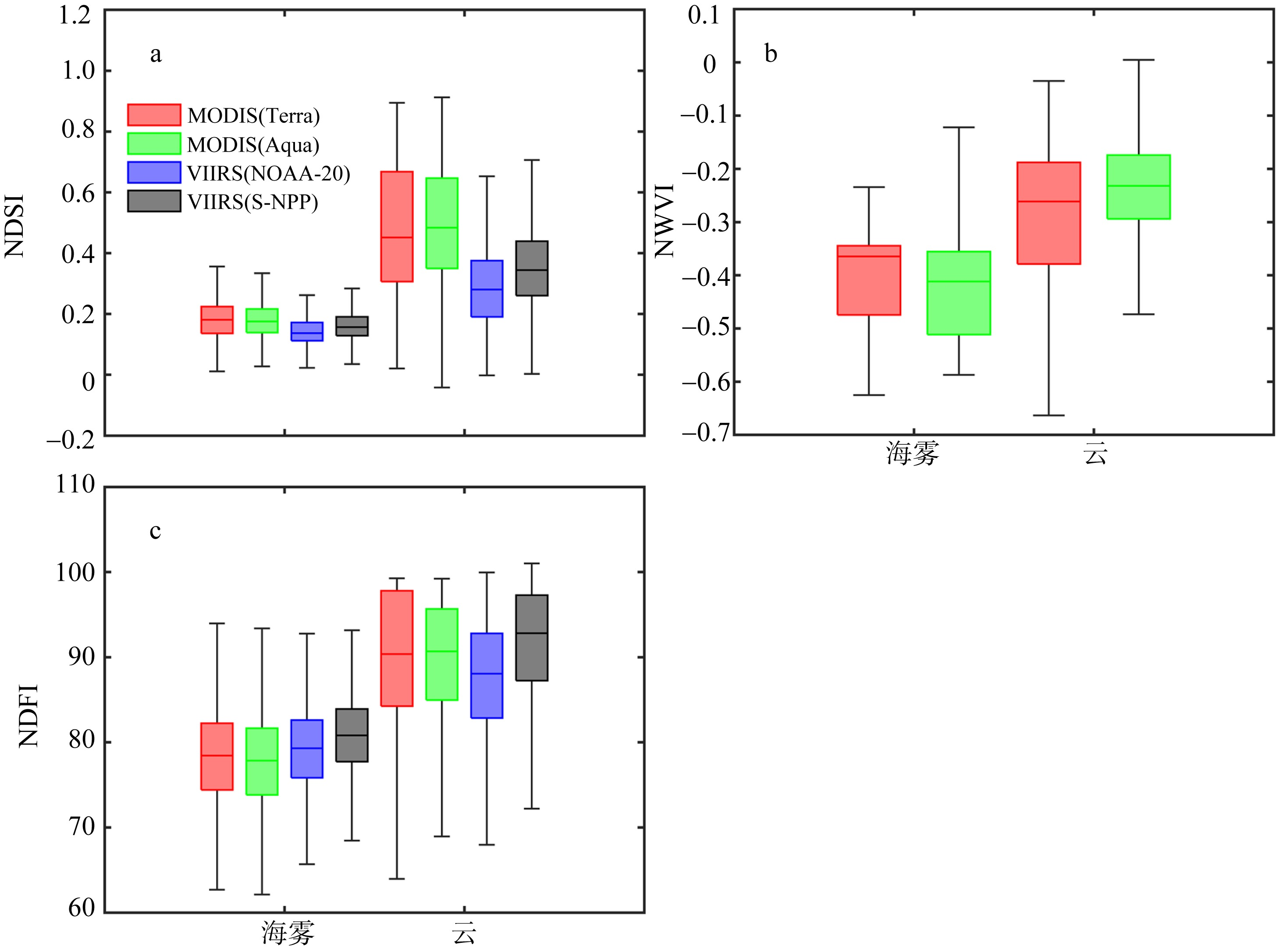
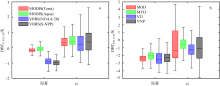
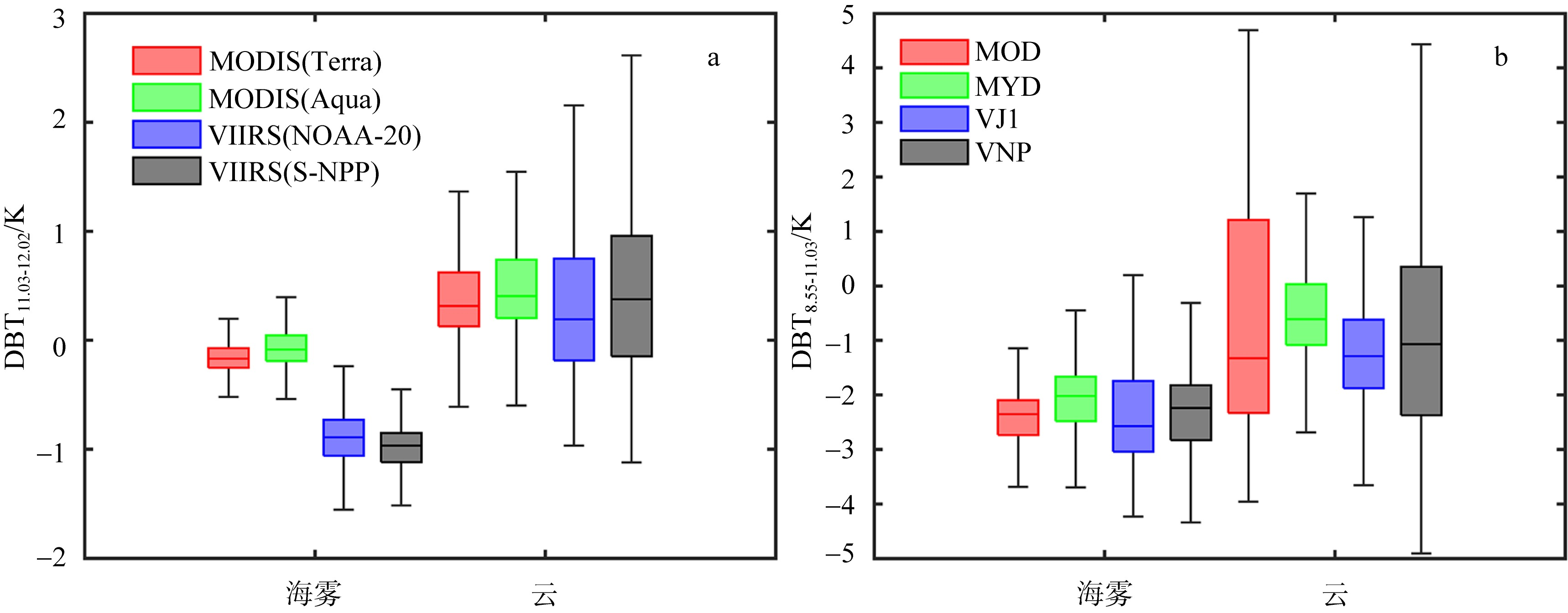
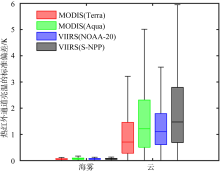
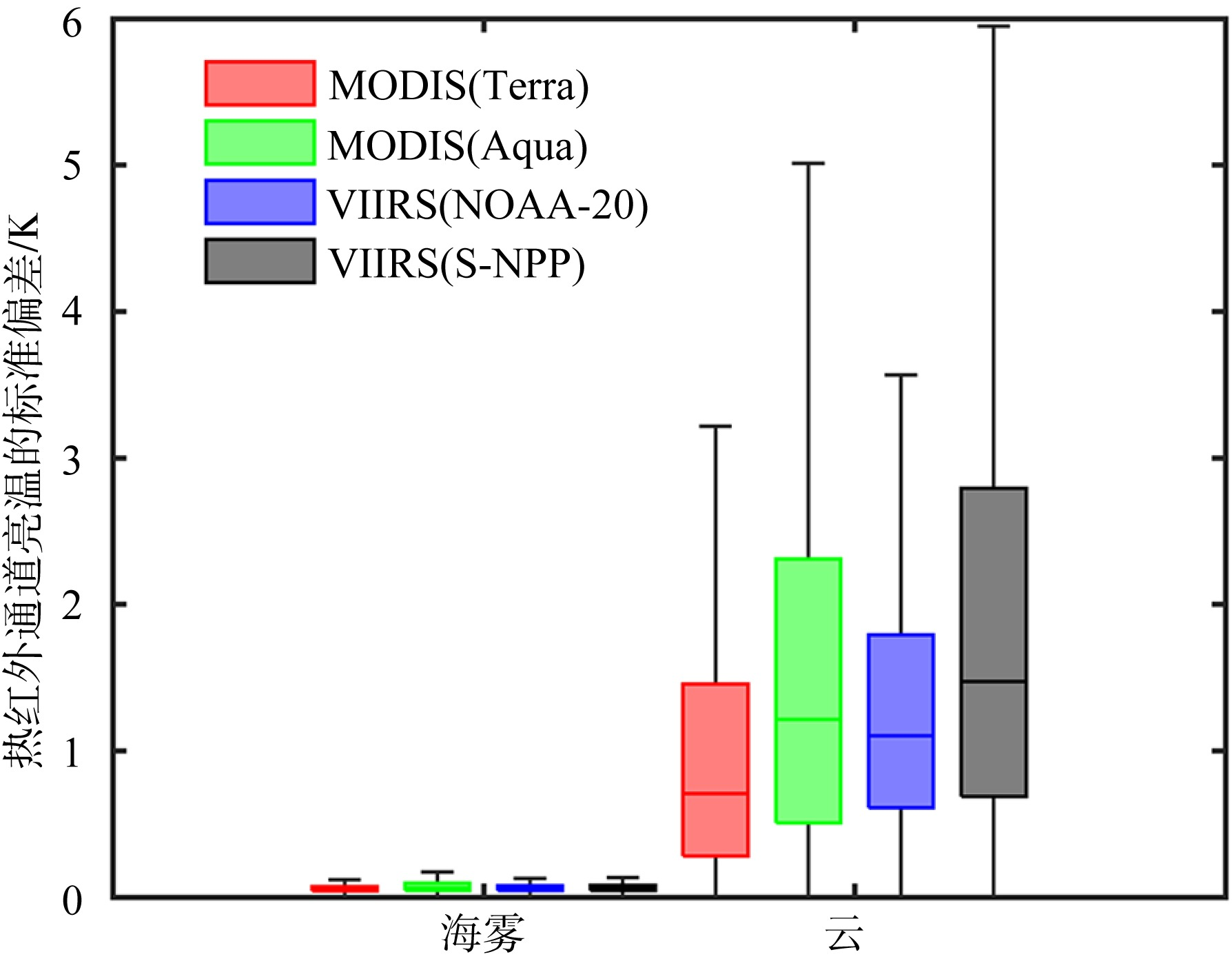
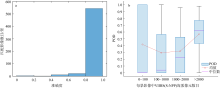
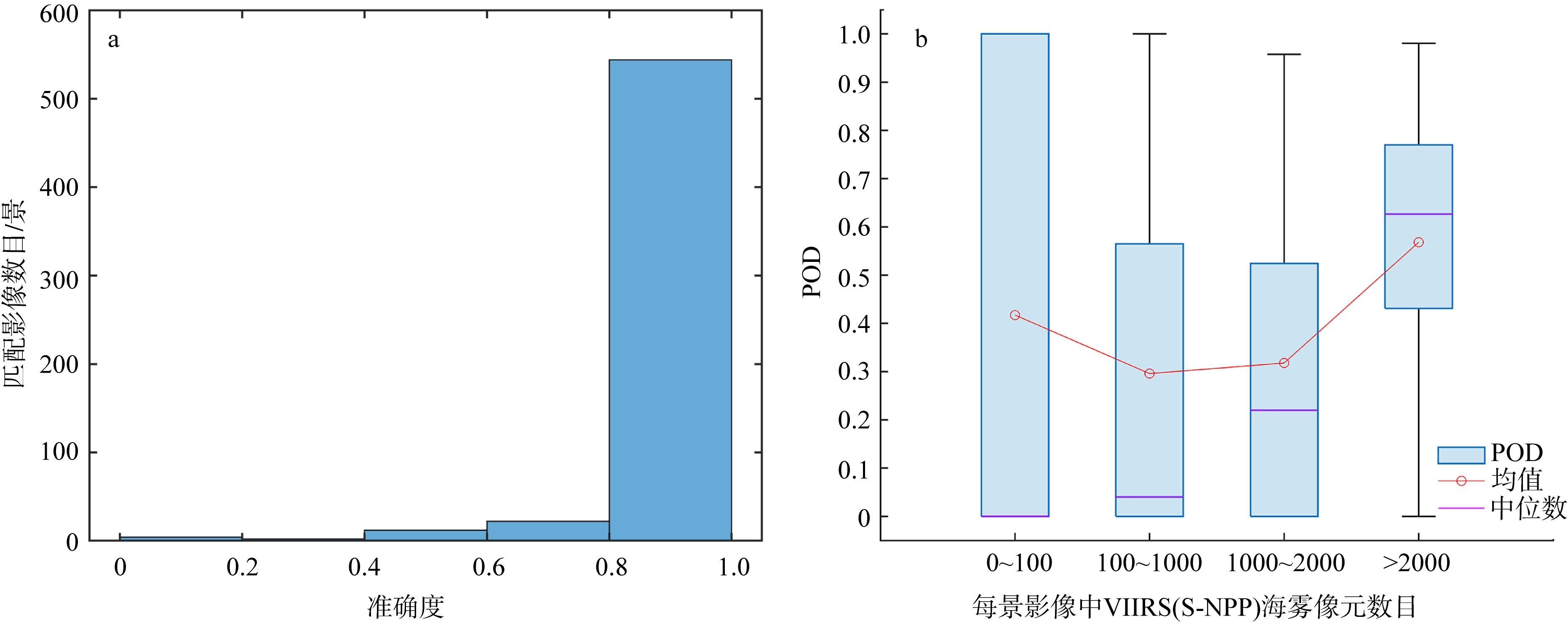
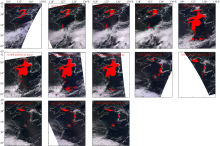
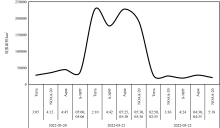
| [1] |
傅刚, 王菁茜, 张美根, 等, 2004. 一次黄海海雾事件的观测与数值模拟研究——以2004年4月11日为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 34(5): 720-726, 926.
|
|
FU GANG, WANG JINGQIAN, ZHANG MEIGEN, et al, 2004. An observational and numerical study of a sea fog event over the Yellow Sea on 11 April, 2004[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 34(5): 720-726, 926 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
耿丹, 刘婷婷, 李超, 2022. 结合FY-4A卫星及随机森林的日间沿海海雾识别模型的研究[J]. 海洋预报, 39(3): 83-93.
|
|
GENG DAN, LIU TINGTING, LI CHAO, 2022. Research on a daytime sea fog identification model based on FY-4A satellite data and random forest algorithm[J]. Marine Forecasts, 39(3): 83-93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
郝姝馨, 郝增周, 黄海清, 等, 2021. 基于Himawari-8数据的夜间海雾识别[J]. 海洋学报, 43(11): 166-180.
|
|
HAO SHUXIN, HAO ZENGZHOU, HUANG HAIQING, et al, 2021. Nighttime sea fog recognition based on Himawari-8 data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 43(11): 166-180 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
胡晨悦, 丘仲锋, 廖廓, 等, 2022. 福建海雾的CALIOP遥感监测及基于Himawari-8的云下雾光谱特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报: 1-10.
|
|
HU CHENYUE, QIU ZHONGFENG, LIAOKUO, et al, 2022. CALIOP remote sensing monitoring of Fujian sea fog and spectral characteristics analysis of cloud fog based on Himawari-8[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography: 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
刘照民, 康琮, 2011. 琼州海峡船舶雾航安全管理[J]. 中国海事, (2): 28-30.
|
|
LIU ZHAOMIN, KANG ZONG, 2011. Safety control of ships navigating in the Qiongzhou Strait in foggy weather[J]. China Maritime Safety, (2): 28-30 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
史得道, 黄彬, 吴振玲, 2018. 2016年春季一次黄渤海明显海雾过程的大气海洋特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 35(5): 85-92.
|
|
SHI DEDAO, HUANG BIN, WU ZHENLING, 2018. Analysis of atmosphere and sea characteristics under an obvious sea fog process over the Bohai and Yellow Sea in spring 2016[J]. Marine Forecasts, 35(5): 85-92 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
苏婧, 2019. 基于主被动遥感的海雾探测方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东):19-21.
|
|
SU JING, 2019. Research on sea fog detection method based on active and passive remote sensing[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China): 19-21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
张苏平, 鲍献文, 2008. 近十年中国海雾研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 359-366.
|
|
ZHANG SUPING, BAO XIANWEN, 2008. The main advances in sea fog research in China[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 38(3): 359-366 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
AMEUR Z, AMEUR S, ADANE A, et al, 2004. Cloud classification using the textural features of Meteosat images[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(21): 4491-4503. DOI: 10.1080/01431160410001735120.
|
| [10] |
BADARINATH K V S, KHAROL S K, SHARMA A R, et al, 2009. Fog over Indo-Gangetic Plains—A study using multisatellite data and ground observations[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2(3): 185-195. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2009.2019830.
|
| [11] |
BENDIX J, CERMAK J, THIES B, 2004. New perspectives in remote sensing of fog and low stratus-TERRA/AQUA-MODIS and MSG[C/OL]. Cape Town, South Africa:3rd Int. Conf. on Fog, Fog Collection and Dew, 11-15 Oct. 2004 [2023-02-08]. https://www.researchgate.net/deref/https%3A%2F%2Fwww.researchgate.net%2Fpublication%2F228860444_New_perspectives_in_remote_sensing_of_fog_and_low_stratus-TERRAAQUA-MODIS_and_MSG?_tp=eyJjb250ZXh0Ijp7ImZpcnN0UGFnZSI6InB1YmxpY2F0aW9uIiwicGFnZSI6InB1YmxpY2F0aW9uIiwicHJldmlvdXNQYWdlIjoicHVibGljYXRpb24ifX0
|
| [12] |
CERMAK J, BENDIX J, 2011. Detecting ground fog from space - a microphysics-based approach[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(12): 3345-3371. DOI: 10.1080/01431161003747505.
|
| [13] |
DOZIER J, PAINTER T H, 2004. Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing of alpine snow properties[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 32(1): 465-494. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120404.
|
| [14] |
HAN J H, SUH M S, YU H Y, et al, 2020. Development of fog detection algorithm using GK2A/AMI and ground data[J]. Remote Sensing, 12(19): 3181. DOI: 10.3390/rs12193181.
|
| [15] |
JEON J, KIM S, YANG CHANSU, 2016. Fundamental research on spring season daytime sea fog detection using MODIS in the Yellow Sea[J]. Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(4): 339-351.
doi: 10.7780/kjrs.2016.32.4.1
|
| [16] |
LIU LIANGMING, WEN XIONGFEI, GONZALEZ A, et al, 2011. An object-oriented daytime land-fog-detection approach based on the mean-shift and full lambda-schedule algorithms using EOS/MODIS data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(17): 4769-4785. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2010.489067.
|
| [17] |
QU J J, GAO WEI, KAFATOS M, et al, 2006. Earth science satellite remote sensing[M]. Beijing, China: Tsinghua University Press.
|
| [18] |
THIES B, NAUSS T, BENDIX J, 2008. Precipitation process and rainfall intensity differentiation using Meteosat Second Generation Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 113(D23). DOI: 10.1029/2008JD010464.
|
| [19] |
WEN XIONGFEI, HU DUNMEI, DONG XINYI, et al, 2014. An object-oriented daytime land fog detection approach based on NDFI and fractal dimension using EOS/MODIS data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(13): 4865-4880. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2014.930564.
|
| [20] |
WU DONG, LU BO, ZHANG TIANCHE, et al, 2015. A method of detecting sea fogs using CALIOP data and its application to improve MODIS-based sea fog detection[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 153: 88-94. DOI: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2014.09.021.
|
| [21] |
WU XIAOJING, LI SANMEI, 2014. Automatic sea fog detection over Chinese adjacent oceans using Terra/MODIS data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(21): 7430-7457. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2014.968685.
|
| [22] |
YUAN YIBO, QIU ZHONGFENG, SUN DEDONG, et al, 2016. Daytime sea fog retrieval based on GOCI data: a case study over the Yellow Sea[J]. Optics Express, 24(2): 787-801. DOI: 10.1364/OE.24.000787.
pmid: 26832463
|
| [23] |
ZHANG SUPING, YI LI, 2013. A comprehensive dynamic threshold algorithm for daytime sea fog retrieval over the Chinese adjacent seas[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 170(11): 1931-1944. DOI: 10.1007/s00024-013-0641-6.
|
 ), 胡晨悦1, 丘仲锋1(
), 胡晨悦1, 丘仲锋1( ), 赵冬至1, 吴到懋2, 廖廓3
), 赵冬至1, 吴到懋2, 廖廓3
 ), HU Chenyue1, QIU Zhongfeng1(
), HU Chenyue1, QIU Zhongfeng1( ), ZHAO Dongzhi1, WU Daomao2, LIAO Kuo3
), ZHAO Dongzhi1, WU Daomao2, LIAO Kuo3