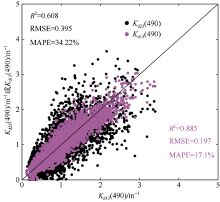
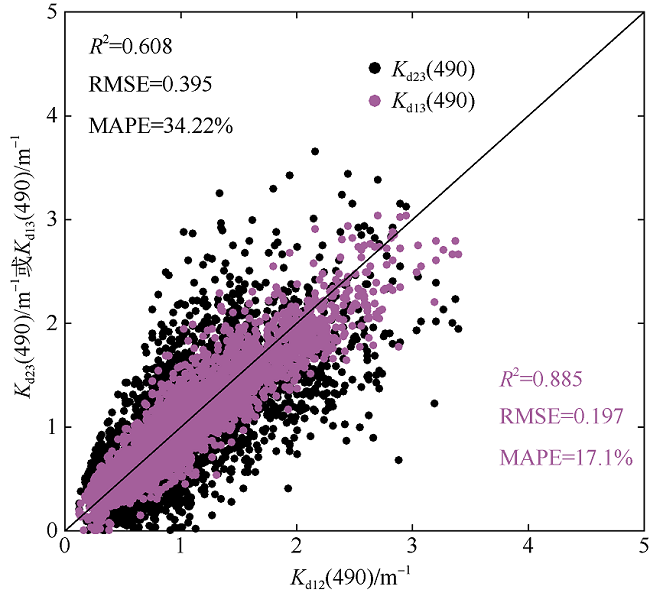
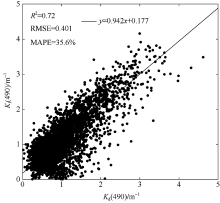
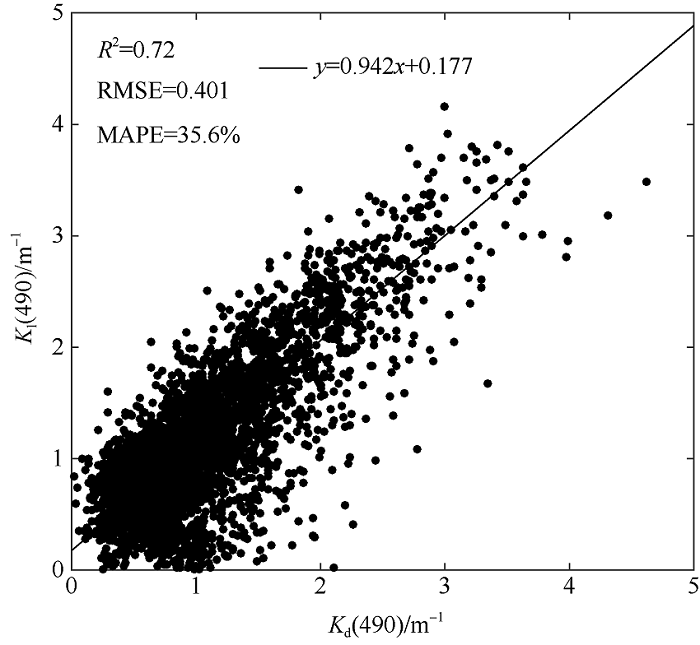
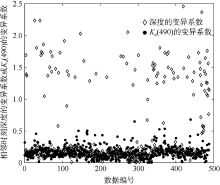
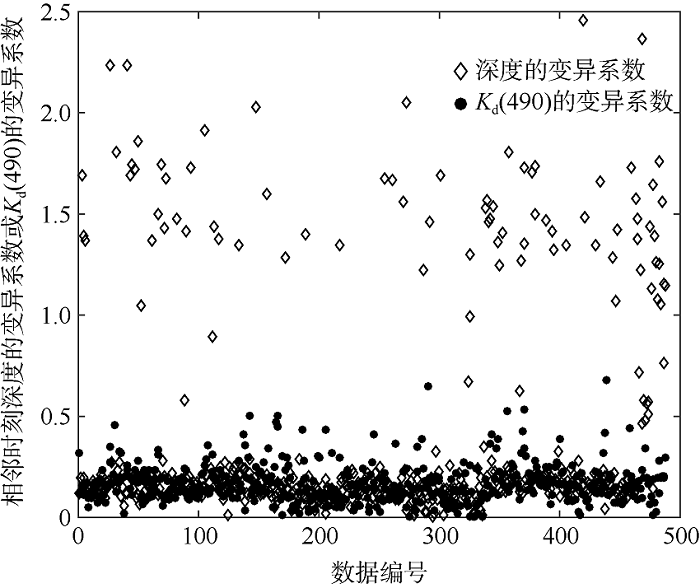
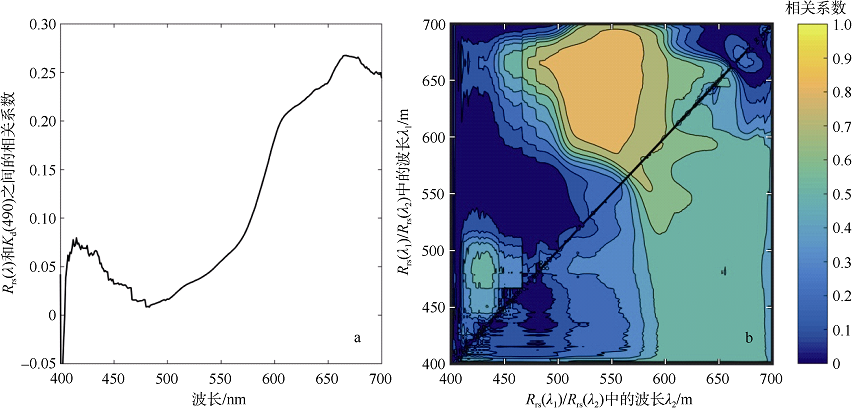
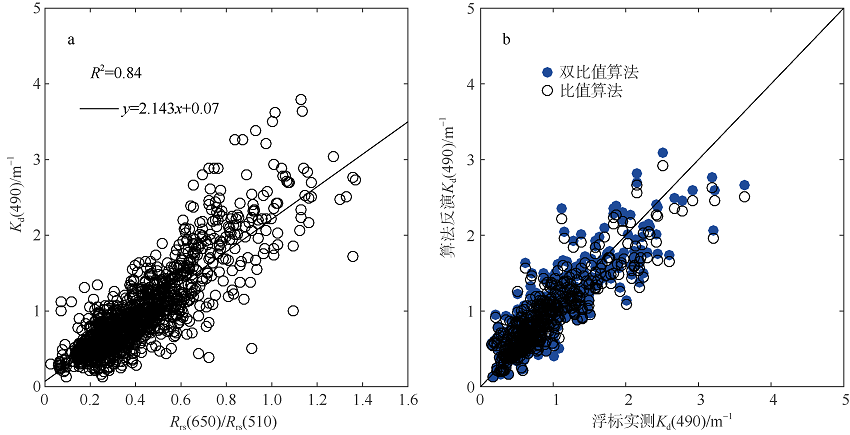
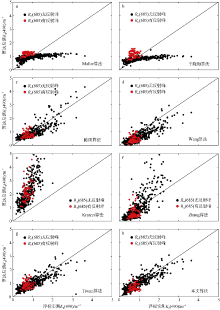
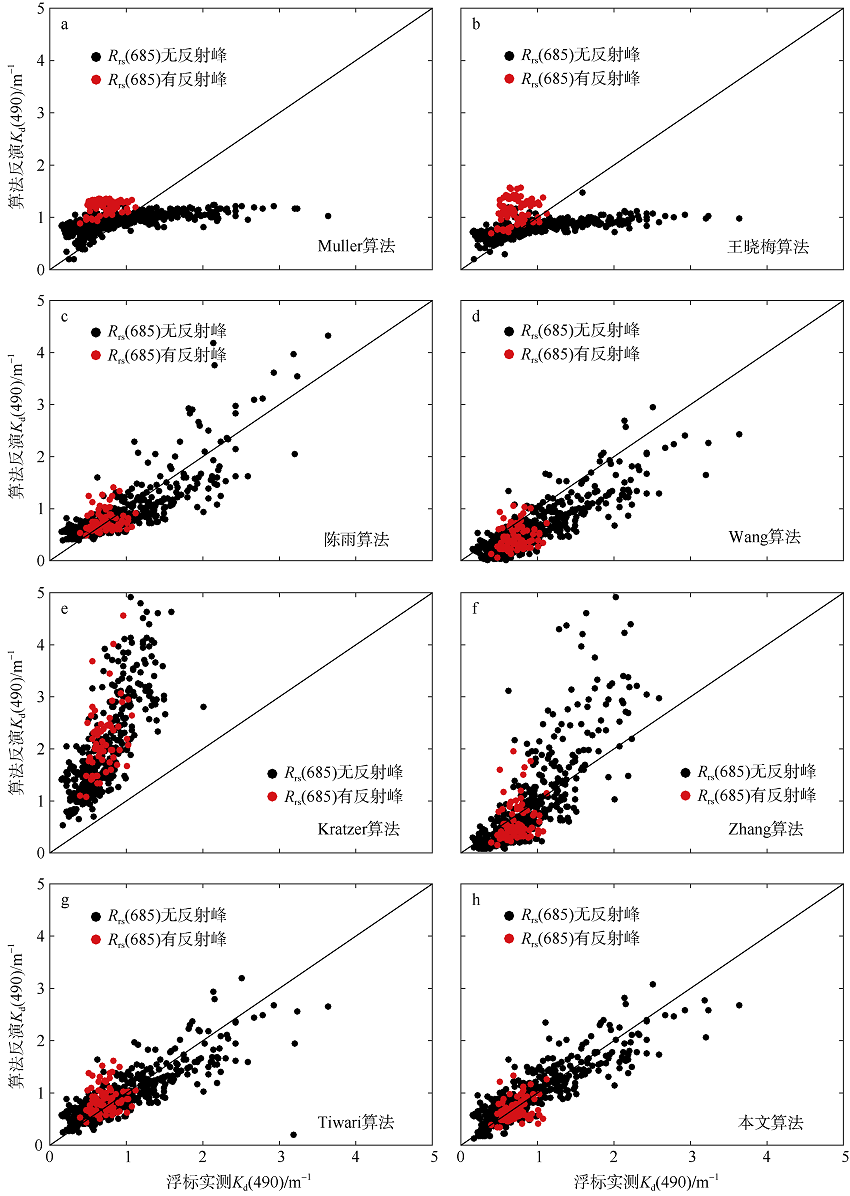
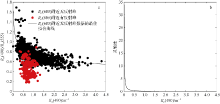
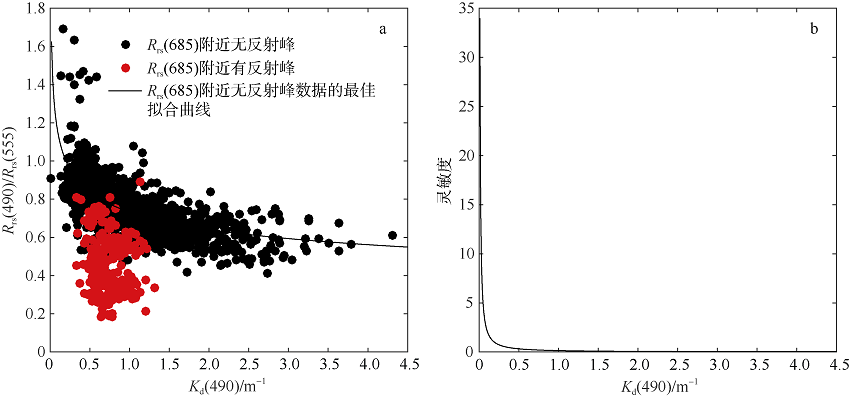
| [1] |
艾威, 李茂田, 刘晓强, 等, 2018. 长江口南槽最大浑浊带枯季大小潮悬沙峰特征及其动力机制[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 49(4):769-778.
|
|
AI WEI, LI MAOTIAN, LIU XIAOQIANG, et al, 2018. Hydrodynamics of SSC peak in dry season of the south passage of Changjiang River estuary[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 49(4):769-778 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
曹沛奎, 严肃庄, 1996. 长江口悬沙锋及其对物质输移的影响[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (1):85-94.
|
|
CAO PEIKUI, YAN SUZHUANG, 1996. Suspended sediments front and its impacts on the materials transport of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (1):85-94 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
陈雨, 沈芳, 2014. 长江口邻近海域冬季漫衰减系数及其遥感反演[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (4):27-34.
|
|
CHEN YU, SHEN FANG, 2014. Diffuse attenuation coefficient of remote sensing inversion in Yangtze River Estuary’s adjacent sea area in winter[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (4):27-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
何文珊, 陆健健, 2001. 高浓度悬沙对长江河口水域初级生产力的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 9(4):24-27.
|
|
HE WENSHAN, LU JIANJIAN, 2001. Effects of high-density suspended sediments on primary production at the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 9(4):24-27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
胡连波, 张亭禄, 2012. 一种东中国海水体漫衰减系数Kd(490)的反演方法[J]. 海洋技术, 31(4):60-63.
|
|
HU LIANBO, ZHANG ZHANG, 2012. A method to derive the diffuse attenuation coefficient Kd(490) in the East China Sea[J]. Ocean Technology, 31(4):60-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
乐成峰, 李云梅, 查勇, 等, 2009. 太湖水体漫射衰减系数的光学特性及其遥感反演模型[J]. 应用生态学报, 20(2):337-343.
|
|
LE CHENGFENG, LI YUNMEI, ZHA YONG, et al, 2009. Optical properties and remote sensing retrieval model of diffuse attenuation coefficient of Taihu Lake water body[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20(2):337-343 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
李素菊, 吴倩, 王学军, 等, 2002. 巢湖浮游植物叶绿素含量与反射光谱特征的关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 14(3):228-234.
|
|
LI SUJU, WU QIAN, WANG XUEJUN, et al, 2002. Correlations between reflectance spectra and contents of chlorophyll-a in Chaohu Lake[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 14(3):228-234 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
丘仲锋, 崔廷伟, 何宜军, 2011. 基于水体光谱特性的赤潮分布信息MODIS遥感提取[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 31(8):2233-2237.
|
|
QIU ZHONGFENG, CUI TINGWEI, HE YIJUN, 2011. Retrieve of red tide distributions from MODIS data based on the characteristics of water spectrum[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 31(8):2233-2237 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
沈焕庭, 贺松林, 潘定安, 等, 1992. 长江河口最大浑浊带研究[J]. 地理学报, 47(5):472-479.
|
|
SHEN HUANTING, HE SONGLIN, PAN DINGAN, et al, 1992. A study of turbidity maximum in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 47(5):472-479 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
沈明, 段洪涛, 曹志刚, 等, 2017. 适用于多种卫星数据的太湖水体漫衰减系数估算算法[J]. 湖泊科学, 29(6):1473-1484.
|
|
SHEN MING, DUAN HONGTAO, CAO ZHIGANG, et al, 2017. Remote sensing estimation algorithm of diffuse attenuation coefficient applicable to different satellite data in Lake Taihu, China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 29(6):1473-1484 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
孙德勇, 李云梅, 王桥, 等, 2009. 基于实测高光谱的太湖水体悬浮物浓度遥感估算研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 28(2):124-128.
|
|
SUN DEYONG, LI YUNMEI, WANG QIAO, et al, 2009. Study on remote sensing estimation of suspended matter concentrations based on in situ hyperspectral data in Lake Tai waters[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 28(2):124-128 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
唐军武, 王晓梅, 宋庆君, 等, 2004. 黄、东海二类水体水色要素的统计反演模式[J]. 海洋科学进展, 22(S1):1-7.
|
|
TANG JUNWU, WANG XIAOMEI, SONG QINGJUN, et al, 2004. Statistical inversion models for case Ⅱ water color elements in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 22(S1):1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
唐军武, 丁静, 田纪伟, 等, 2005. 黄东海二类水体三要素浓度反演的神经网络模型[J]. 高技术通讯, 15(3):83-88.
|
|
TANG JUNWU, DING JING, TIAN JIWEI, et al, 2005. Neural network models for the retrieval of chlorophyll, total suspended matter, and gelbstoff concentrations of case-Ⅱ waters in Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 15(3):83-88 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
王晓梅, 唐军武, 丁静, 等, 2005. 黄海、东海二类水体漫衰减系数与透明度反演模式研究[J]. 海洋学报, 27(5):38-45.
|
|
WANG XIAOMEI, TANG JUNWU, DING JING, et al, 2005. The retrieval algorithms of diffuse attenuation and transparency for the case-Ⅱ waters of the Huanghai Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 27(5):38-45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
杨跃忠, 曹文熙, 孙兆华, 等, 2009. 海洋高光谱辐射实时观测系统的研制[J]. 光学学报, 29(1):102-107.
|
|
YANG YUEZHONG, CAO WENXI, SUN ZHAOHUA, et al, 2009. Development of real-time hyperspectral radiation sea-observation system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 29(1):102-107 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
张清凌, 陈楚群, 施平, 2003. 南沙群岛海域水体漫衰减系数Kd(490)的特性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 22(1):9-16.
|
|
ZHANG QINGLING, CHEN CHUQUN, SHI PING, 2003. Characteristics of Kd(490) around Nansha Islands in South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 22(1):9-16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
AUSTIN R W, 1974. The remote sensing of spectral radiance from below the ocean surface[M] //JERLOV N G, NIELSEN E S. Optical Aspects of Oceanography. New York: Academic Press, 14:317-344.
|
| [18] |
CHEN JUN, CUI TINGWEI, TANG JUNWU, et al, 2014. Remote sensing of diffuse attenuation coefficient using MODIS imagery of turbid coastal waters: A case study in Bohai Sea[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 140:78-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.08.031
|
| [19] |
GOMES A C C, BERNARDO N, DO CARMO A C, et al, 2018. Diffuse attenuation coefficient retrieval in CDOM dominated inland water with high chlorophyll-a concentrations[J]. Remote Sensing, 10(7):1063.
doi: 10.3390/rs10071063
|
| [20] |
GORDON H R, 1989. Dependence of the diffuse reflectance of natural waters on the sun angle[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 34(8):1484-1489.
|
| [21] |
GORDON H R, BROWN O B, EVANS R H, et al, 1988. A semianalytic radiance model of ocean color[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 93(D9):10909-10924.
|
| [22] |
GORDON H R, BROWN O B, JACOBS M M, 1975. Computed relationships between the inherent and apparent optical properties of a flat homogeneous ocean[J]. Applied Optics, 14(2):417-427.
doi: 10.1364/AO.14.000417
pmid: 20134901
|
| [23] |
IOCCG, 2000. Remote Sensing of Ocean Colour in Coastal, and Other Optically-Complex, Waters[R]// SATHYENDRANATH S. Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group, No. 3. Dartmouth, Canada: IOCCG.
|
| [24] |
JIANG DALIN, MATSUSHITA B, SETIAWAN F, et al, 2019. An improved algorithm for estimating the Secchi disk depth from remote sensing data based on the new underwater visibility theory[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 152:13-23.
|
| [25] |
KRATZER S, BROCKMANN C, MOORE G, 2008. Using MERIS full resolution data to monitor coastal waters - A case study from Himmerfjarden, a fjord-like bay in the northwestern Baltic Sea[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112(5):2284-2300.
|
| [26] |
KRATZER S, HÄKANSSON B, SAHLIN C, 2003. Assessing Secchi and photic zone depth in the Baltic Sea from satellite data[J]. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 32(8):577-585.
doi: 10.1579/0044-7447-32.8.577
|
| [27] |
LEE ZHONGPING, CARDER K L, ARNONE R A, 2002. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters[J]. Applied Optics, 41(27):5755-5772.
pmid: 12269575
|
| [28] |
LEE ZHONGPING, DARECKI M, CARDER K L, et al, 2005a. Diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance: An evaluation of remote sensing methods[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 110(C2):C02017.
|
| [29] |
LEE ZHONGPING, DU KEPING, ARNONE R, 2005b. A model for the diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 110(C2):C02016.
|
| [30] |
LEE ZHONGPING, SHANG SHAOLING, HU CHUANMIN, et al, 2015. Secchi disk depth: A new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 169:139-149.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.08.002
|
| [31] |
LEE ZHONGPING, SHANG SHAOLING, STAVN R, 2018. AOPs are not additive: on the biogeo-optical modeling of the diffuse attenuation coefficient[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5:8.
|
| [32] |
MAJOZI N P, SALAMA M S, BERNARD S, et al, 2014. Remote sensing of euphotic depth in shallow tropical inland waters of Lake Naivasha using MERIS data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 148:178-189.
|
| [33] |
MOREL A, PRIEUR L, 1977. Analysis of variations in ocean color[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(4):709-722.
|
| [34] |
MUELLER J L, TREES C C, 1997. Revised SeaWiFS prelaunch algorithm for the diffuse attenuation coefficient Kd(490)[R]. NASA SeaWiFS technical report series, TM-104566. Greenbelt, Maryland: Goddard Space Flight Space Center.
|
| [35] |
ORGANELLI E, BARBIEUX M, CLAUSTRE H, et al, 2017. Two databases derived from BGC-Argo float measurements for marine biogeochemical and bio-optical applications[J]. Earth System Science Data, 9(2):861-880.
|
| [36] |
PLATT T, SATHYENDRANATH S, CAVERHILL C M, et al, 1988. Ocean primary production and available light: Further algorithms for remote sensing[J]. Deep Sea Research Part A: Oceanographic Research Papers, 35(6):855-879.
|
| [37] |
SAULQUIN B, HAMDI A, GOHIN F, et al, 2013. Estimation of the diffuse attenuation coefficient KdPAR using MERIS and application to seabed habitat mapping[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 128:224-233.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.10.002
|
| [38] |
SHEN MING, DUAN HONGTAO, CAO ZHIGANG, et al, 2017. Determination of the downwelling diffuse attenuation coefficient of lake water with the sentinel-3A OLCI[J]. Remote Sensing, 9(12):1246.
|
| [39] |
SUN DEYONG, QIU ZHONGFENG, LI YUNMEI, et al, 2014. New strategy to improve estimation of diffuse attenuation coefficient for highly turbid inland waters[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(9):3350-3371.
|
| [40] |
TIWARI S P, SHANMUGAM P, 2014. A robust algorithm to determine diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance from satellite data in coastal oceanic waters[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 7(5):1616-1622.
|
| [41] |
WANG MENGHUA, SON S, HARDING L W Jr, 2009. Retrieval of diffuse attenuation coefficient in the Chesapeake Bay and turbid ocean regions for satellite ocean color applications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 114(C10):C10011.
|
| [42] |
WERDELL P J, BAILEY S W, 2005. An improved in-situ bio-optical data set for ocean color algorithm development and satellite data product validation[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 98(1):122-140.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.07.001
|
| [43] |
ZANEVELD J R V, BOSS E, BARNARD A, 2001. Influence of Surface Waves on Measured and Modeled Irradiance Profiles[J]. Applied Optics, 40(9):1442-1449.
doi: 10.1364/ao.40.001442
pmid: 18357135
|
| [44] |
ZHANG TINGLU, FELL F, 2007. An empirical algorithm for determining the diffuse attenuation coefficient Kd in clear and turbid waters from spectral remote sensing reflectance[J]. Limnology & Oceanography Methods, 5(12):457-462.
|
| [45] |
ZHAO JUN, BARNES B, MELO N, et al, 2013. Assessment of satellite-derived diffuse attenuation coefficients and euphotic depths in south Florida coastal waters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 131:38-50.
|
| [46] |
ZHAO JUN, CAO WENXI, WANG GUIFEN, et al, 2009. The variations in optical properties of CDOM throughout an algal bloom event[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 82(2):225-232.
|
 ), 王桂芬3, 许占堂1(
), 王桂芬3, 许占堂1( ), 杨跃忠1,4, 周雯1, 郑文迪1,2, 曾凯1,2, 邓霖1,2
), 杨跃忠1,4, 周雯1, 郑文迪1,2, 曾凯1,2, 邓霖1,2
 ), WANG Guifen3, XU Zhantang1(
), WANG Guifen3, XU Zhantang1( ), Yang Yuezhong1,4, ZHOU Wen1, ZHENG Wendi1,2, ZENG Kai1,2, DENG Lin1,2
), Yang Yuezhong1,4, ZHOU Wen1, ZHENG Wendi1,2, ZENG Kai1,2, DENG Lin1,2