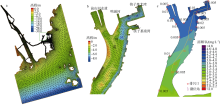
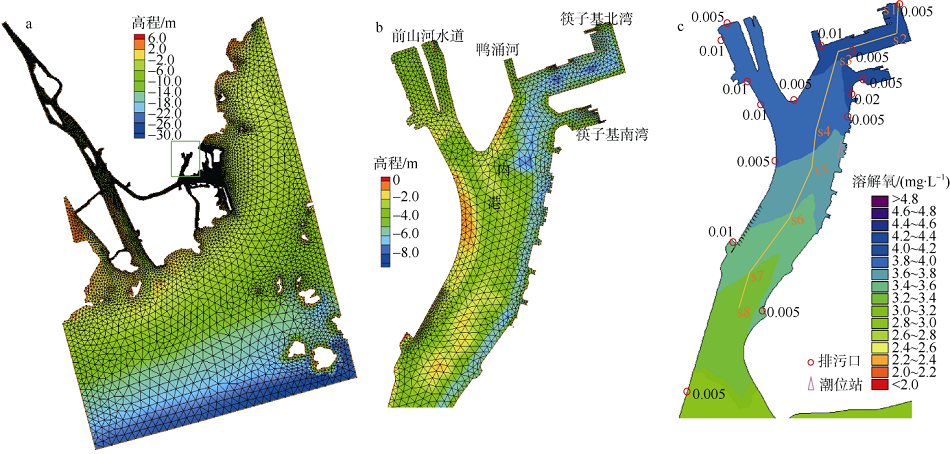
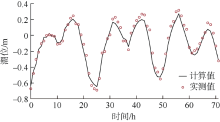
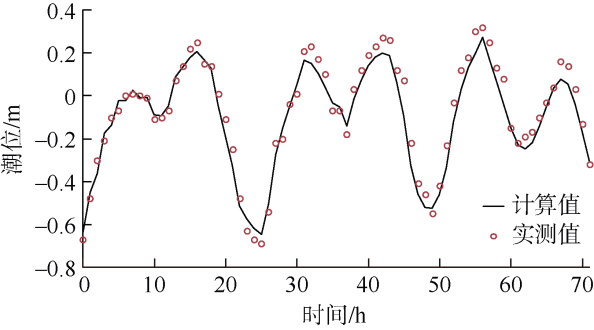
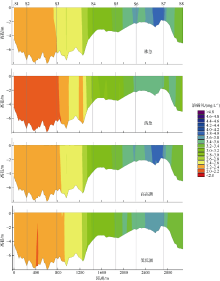
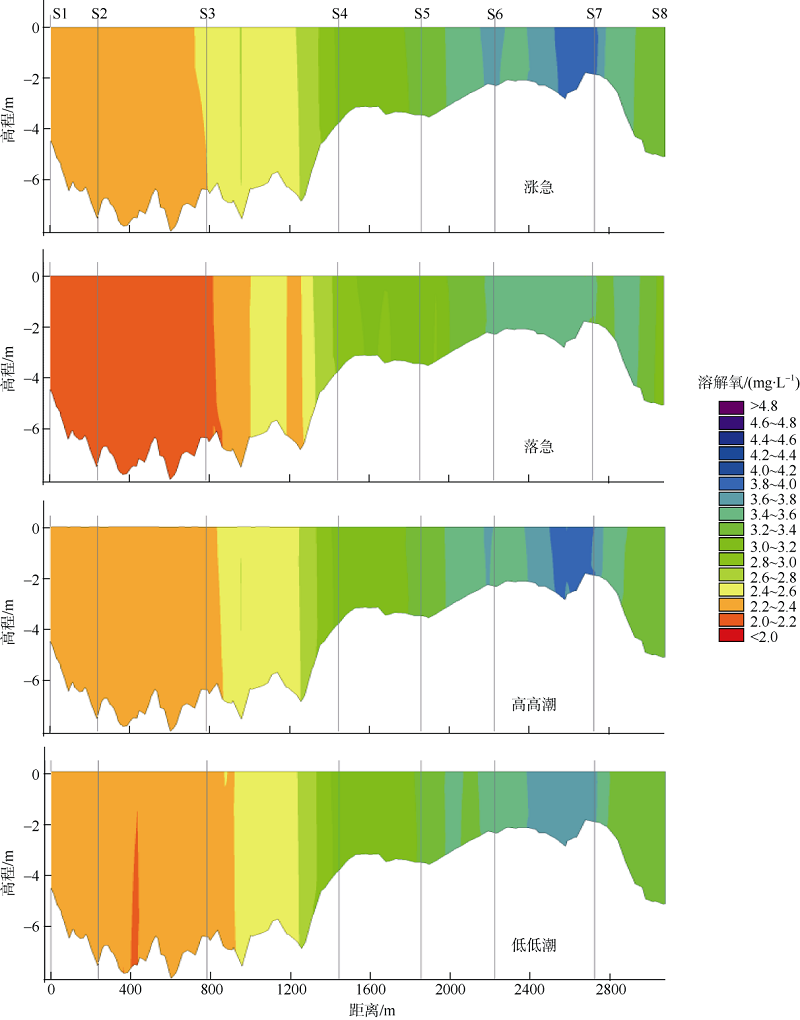
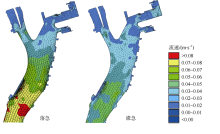
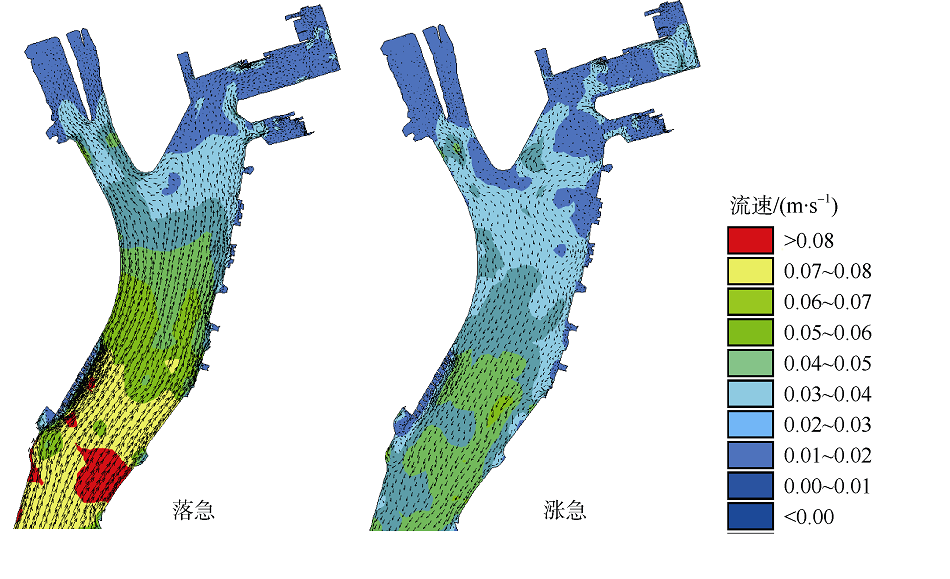
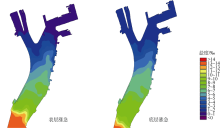
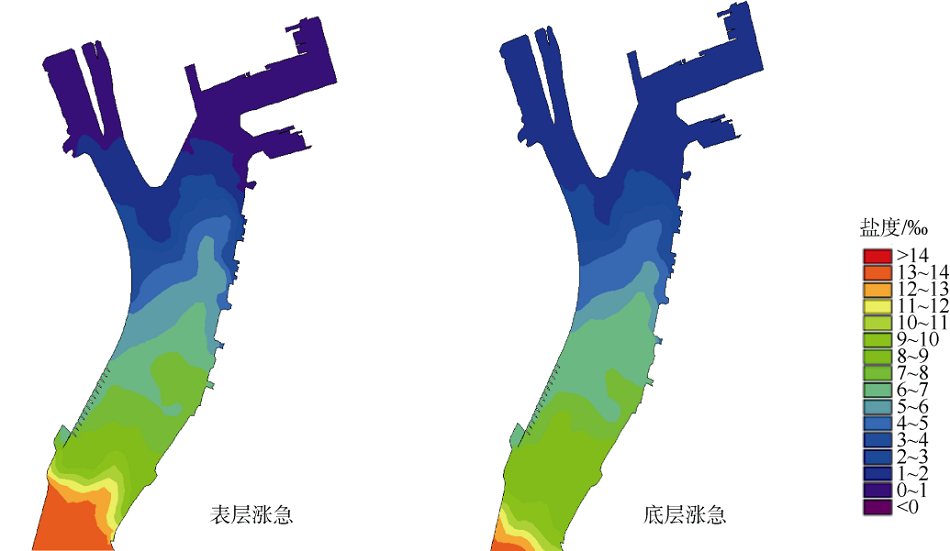
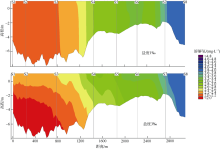
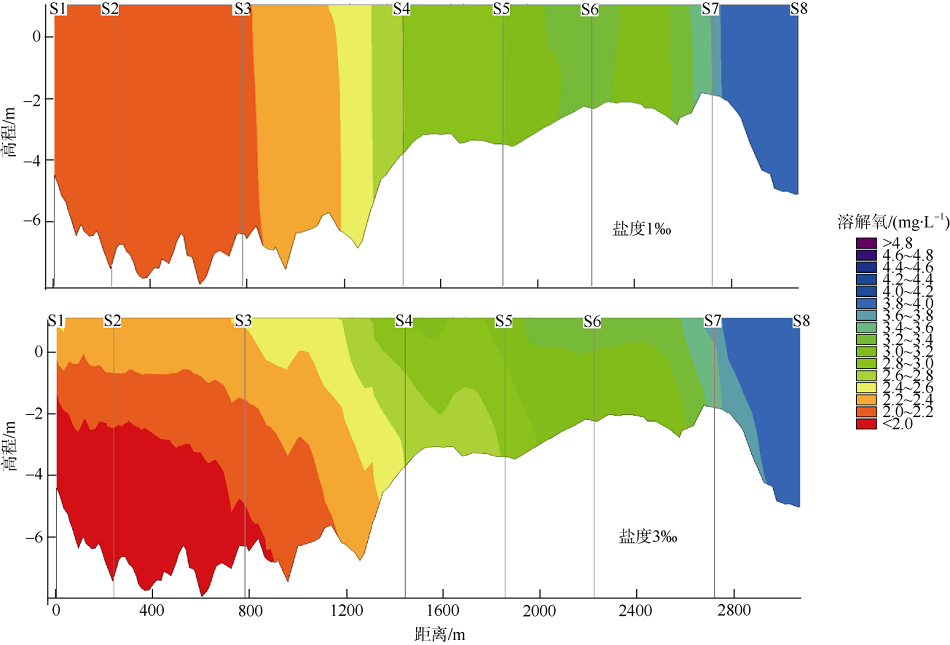
| [1] |
澳门环境保护局, (2017-02). 澳门水质自动监测站年度监测数据报告[EB/OL]. 澳门: 澳门环境保护局: 6-7. https://www.dspa.gov.mo/publish.aspx. Macau Environmental Protection Bureau, (1999-12).
|
|
Annual monitoring data report of Macau water quality automatic monitoring station[EB/OL]. Macao: Macau Environmental Protection Bureau:6-7. https://www.dspa.gov.mo/publish.aspx (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
澳门环境保护局, (2021-06). 澳门环境状况报告[EB/OL]. 澳门: 澳门环境保护局:31-43. https://www.dspa.gov.mo/publish.aspx. Macau Environmental Protection Bureau, (2021-06).
|
|
Report on the state of the environment in Macao[EB/OL]. Macao: Macau Environmental Protection Bureau: 31-43. https://www.dspa.gov.mo/publish.aspx (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
蔡树群, 郑舒, 韦惺, 2013. 珠江口水动力特征与缺氧现象的研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(5):1-8.
|
|
CAI SHUQUN, ZHENG SHU, WEI XING, 2013. Progress on the hydrodynamic characteristics and the hypoxia phenomenon in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(5):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
邓思思, 朱志伟, 2013. 河流底泥耗氧量测量方法及耗氧量影响因素[J]. 水利水运工程学报, (4):60-66.
|
|
DENG SISI, ZHU D Z, 2013. A review of methods for sediment oxygen demand measurement and its influencing factors[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, (4):60-66 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
龚依琳, 2019. 基于ECOLab的澜沧江小湾水库水质模拟研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学: 15-30.
|
|
GONG YILIN, 2019. Water quality simulation study of Xiaowan reservoir in Lancang river based on Ecolab model[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology: 15-30 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
罗琳, 李适宇, 王东晓, 2008. 珠江河口夏季缺氧现象的模拟[J]. 水科学进展, 19(5):729-735.
|
|
LUO LIN, LI SHIYU, WANG DONGXIAO, 2008. Modelling of hypoxia in the Pearl River estuary in summer[J]. Advances in Water Science, 19(5):729-735 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
麻素挺, 林海转, 苏园, 等, 2019. 典型河口区低溶解氧现象及形成机理研究——以鳌江为例[J]. 环境科技, 32(5):28-34.
|
|
MA SUTING, LIN HAIZHUAN, SU YUAN, et al, 2019. Preliminary study on low DO phenomenon and formation mechanism in Typical Estuary Area—Take Aojiang River as an example[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(5):28-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
王海龙, 丁平兴, 沈健, 2010. 河口/近海区域低氧形成的物理机制研究进展[J]. 海洋科学进展, 28(1):115-125.
|
|
WANG HAILONG, DING PINGXING, SHEN JIAN, 2010. Advances in the study on physical mechanism of hypoxia formation in Estuary and Coastal Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 28(1):115-125 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
王巧宁, 2012. 大规模藻华区低氧对海洋生物的影响研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所):3-25.
|
|
WANG QIAONING. 2012. The effects of hypoxia on the marine organisms in large-scale algal bloom area[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences):3-25 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
王松朵, 董洪哲, 王玥, 等, 2020. 2016年夏季长江口邻近海域溶解氧的周日变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 59(S1):56-62.
|
|
WANG SONGDUO, DONG HONGZHE, WANG YUE, et al, 2020. Diurnal variation characteristics and influencing factors of dissolved oxygen in the Yangtze River Estuary adjacent sea area in summer of 2016[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 59(S1):56-62 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
许晓飞, 王晓娟, 刘凤霞, 等, 2015. 感潮河段盐度和缺氧水体时空分布规律研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(9):2900-2909.
|
|
XU XIAOFEI, WANG XIAOJUAN, LIU FENGXIA, et al, 2015. Temporal and spatial distribution of salinity and hypoxia in a tidal river[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(9):2900-2909 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
张恒, 李适宇, 2009. 生化过程对夏季珠江口底层缺氧影响的模拟研究[C]// 中国环境科学学会2009年学术年会论文集. 武汉: 中国环境科学学会: 376-280.
|
|
ZHANG HENG, LI SHIYU, 2009. Simulation of the effects of biochemical processes on anoxia at the bottom of the Pearl River estuary in summer[C]// Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences. Wuhan: Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences: 376-280 (in Chinese).
|
| [13] |
张恒, 李适宇, 2010. 基于改进的RCA水质模型对珠江口夏季缺氧及初级生产力的数值模拟研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(1):20-31.
|
|
ZHANG HENG, LI SHIYU, 2010. A numerical study on hypoxia and primary production in the Pearl River Estuary in summer using the modified RCA water quality model[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 29(1):20-31 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
张华, 李艳芳, 唐诚, 等, 2016. 渤海底层低氧区的空间特征与形成机制[J]. 科学通报, 61(14):1612-1620.
|
|
ZHANG HUA, LI YANFANG, TANG CHENG, et al, 2016. Spatial characteristics and formation mechanisms of bottom hypoxia zone in the Bohai Sea during summer[J]. China Academic Journal, 61(14):1612-1620 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
CHEN GUANGHAO, LEONG I M, LIU JIAN, et al, 1999. Study of oxygen uptake by tidal river sediment[J]. Water Research, 33(13):2905-2912.
doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00527-2
|
| [16] |
CHI LIANBAO, SONG XIUXIAN, YUAN YONGQUAN, et al, 2017. Distribution and key influential factors of dissolved oxygen off the Changjiang River Estuary (CRE) and its adjacent waters in China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 125(1-2):440-450.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.09.063
|
| [17] |
DANISH HYDRAULIC INSTITUTE (DHI), 2012. WQ TEMPLATES scientific description[R]. Denmark: DHI.
|
| [18] |
DIAZ R J, 2001. Overview of hypoxia around the world[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30(2):275-281.
doi: 10.2134/jeq2001.302275x
|
| [19] |
DIAZ R J, ROSENBERG R, 2008. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems[J]. Science, 321(5891):926-929.
doi: 10.1126/science.1156401
|
| [20] |
GRAY J S, WU R S S, OR Y Y, 2002. Effects of hypoxia and organic enrichment on the coastal marine environment[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 238:249-279.
doi: 10.3354/meps238249
|
| [21] |
GUO XIAOYI, XU BOCHAO, BURNETT W C, et al, 2020. Does submarine groundwater discharge contribute to summer hypoxia in the Changjiang (Yangtze) River Estuary?[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 719:137450.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137450
|
| [22] |
HETLAND R D, DIMARCO S F, 2008. How does the character of oxygen demand control the structure of hypoxia on the Texas-Louisiana continental shelf?[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 70(1-2):49-62.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2007.03.002
|
| [23] |
LI XIUQIN, LU CHUQIAN, ZHANG YAFENG, et al, 2020. Low dissolved oxygen in the Pearl River estuary in summer: long-term spatio-temporal patterns, trends, and regulating factors[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 151:110814.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110814
|
| [24] |
RABALAIS N N, DÍAZ R J, LEVIN L A, et al, 2010. Dynamics and distribution of natural and human-caused hypoxia[J]. Biogeosciences, 7(2):585-619.
doi: 10.5194/bg-7-585-2010
|
| [25] |
WANG XIULIN, CUI ZHENGGUO, GUO QUAN, et al, 2009. Distribution of nutrients and eutrophication assessment in the Bohai Sea of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 27(1):177-183.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-009-0177-x
|
| [26] |
WISEMAN W J, RABALAIS N N, TURNER R E, et al, 1997. Seasonal and interannual variability within the Louisiana coastal current: stratification and hypoxia[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 12(1-4):237-248.
doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(96)00100-5
|
| [27] |
ZHANG HAIYAN, ZHAO LIANG, SUN YAO, et al, 2017. Contribution of sediment oxygen demand to hypoxia development off the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 192:149-157.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2017.05.006
|
| [28] |
ZHANG J, GILBERT D, GOODAY A J, et al, 2010. Natural and human-induced hypoxia and consequences for coastal areas: synjournal and future development[J]. Biogeosciences, 7(5):1443-1467.
doi: 10.5194/bg-7-1443-2010
|
 ), JIANG Ran1, YANG Liling1,2, LIU Bingjun3
), JIANG Ran1, YANG Liling1,2, LIU Bingjun3