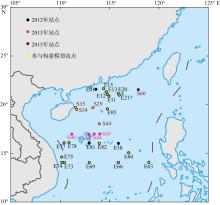
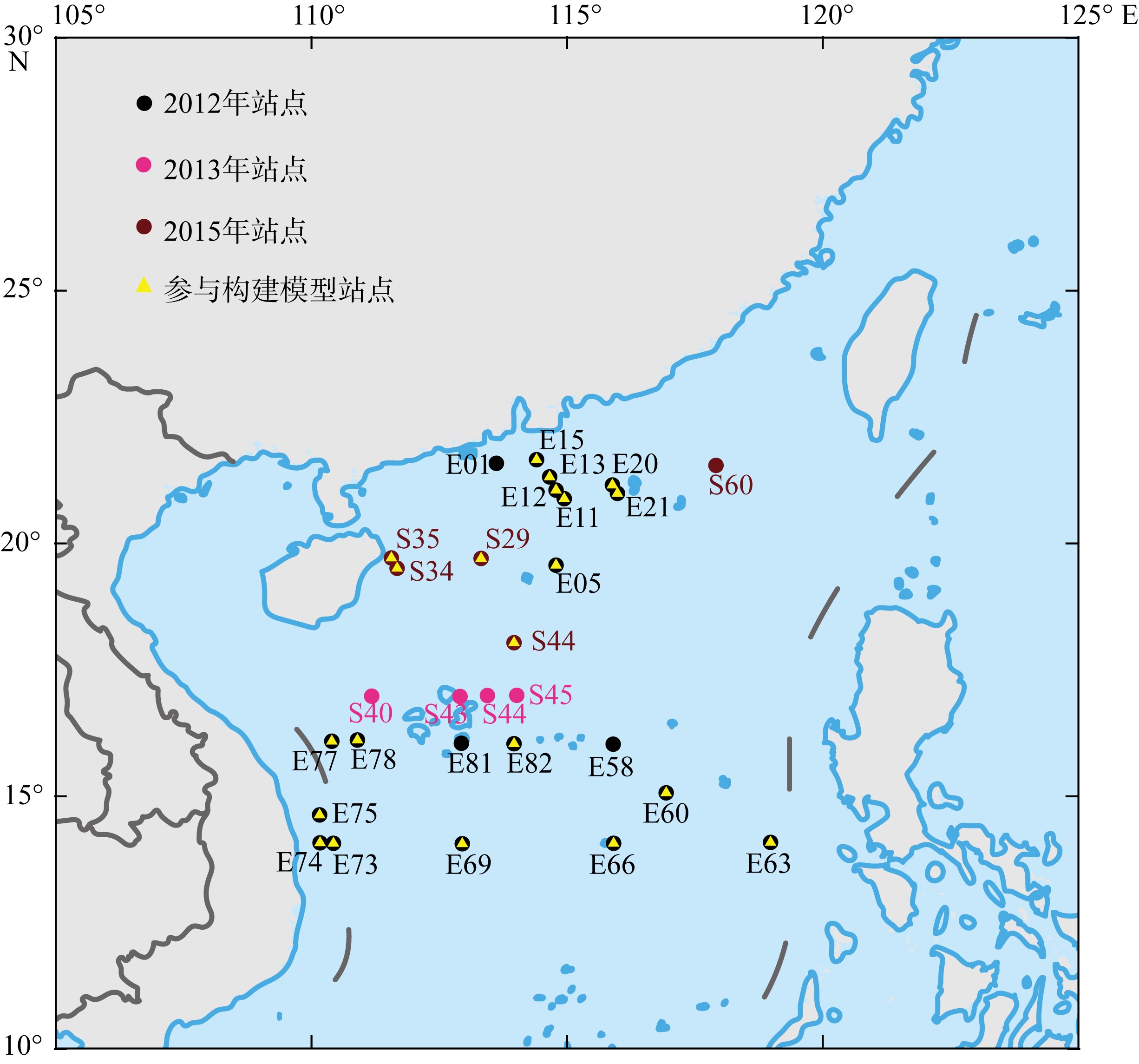
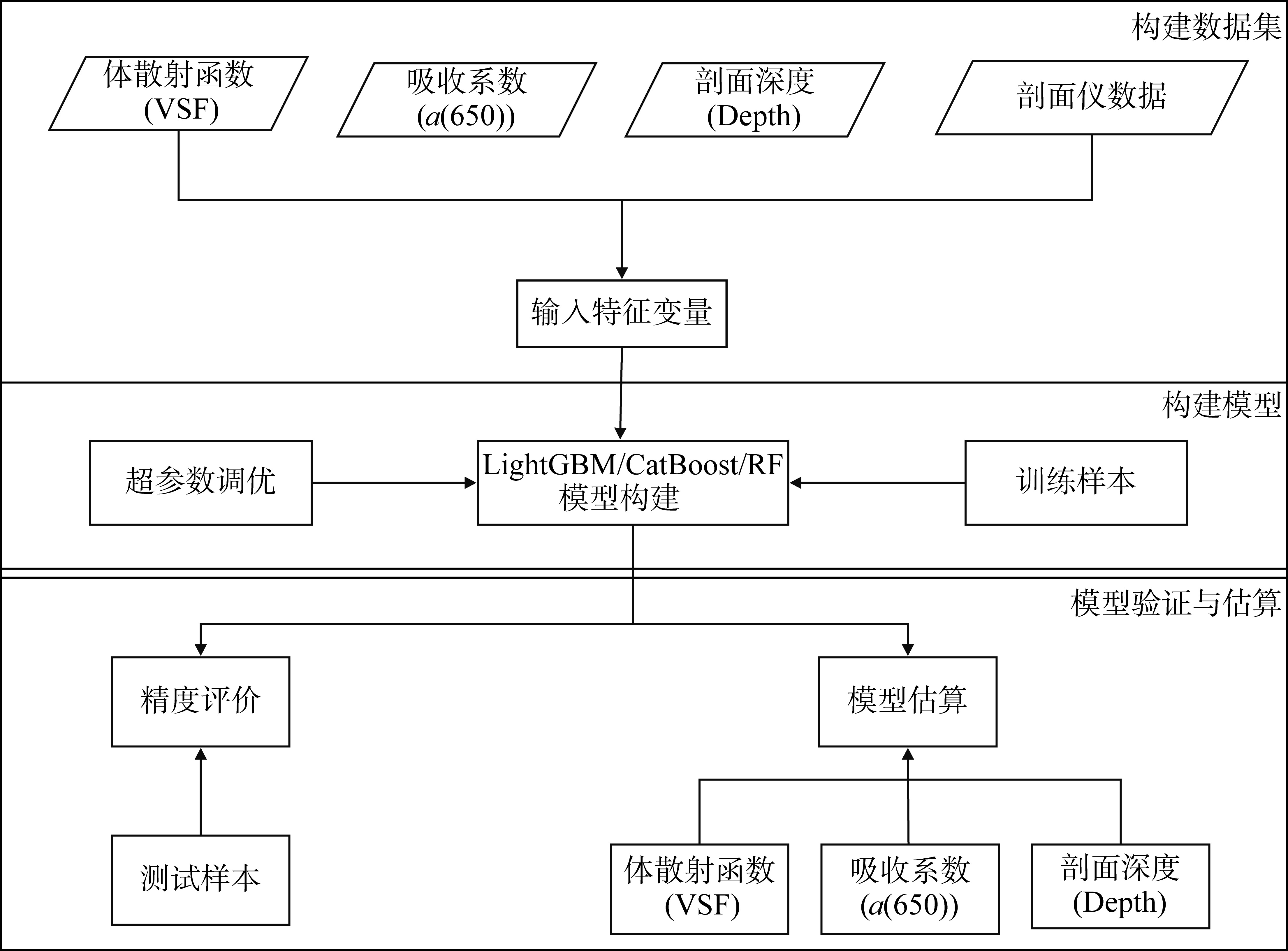
| [1] |
曹渝昆, 朱萌, 2019. 基于主成分分析和LightGBM的风电场发电功率超短期预测[J]. 上海电力学院学报, 35(6): 562-566.
|
|
CAO YUKUN, ZHU MENG, 2019. Ultra-short-term prediction of wind farm power generation based on principal component analysis and LightGBM[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Electric Power, 35(6): 562-566. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
宫鹏, 王德兴, 袁红春, 等, 2021. 基于LightGBM的南太平洋长鳍金枪鱼渔场预报模型研究[J]. 水产科学, 40(5): 762-767.
|
|
GONG PENG, WANG DEXING, YUAN HONGCHUN, et al, 2021. Fishing ground forecast model of albacore tuna based on LightGBM in the South Pacific Ocean[J]. Fisheries Science, 40(5): 762-767. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
卢雪梅, 苏华, 2020. 基于OLCI数据的福建近海悬浮物浓度遥感反演[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(8): 2819-2827.
|
|
LU XUEMEI, SU HUA, 2020. Retrieving total suspended matter concentration in Fujian coastal waters using OLCI data[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(8): 2819-2827. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
徐磊, 吴鹏, 徐明生, 等, 2021. 基于卷积神经网络与LightGBM的短期风电功率预测方法[J]. 水电能源科学, 39(2): 209-212+199.
|
|
XU LEI, WU PENG, XU MINGSHENG, et al, 2021. Short-term wind power prediction based on Convolution Neural Network and LightGBM algorithm[J]. Water Resources and Power, 39(2): 209-212+199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
张天一, 苏华, 杨欣, 等, 2020. 基于LightGBM的全球海洋次表层温盐遥感预测[J]. 遥感学报, 24(10): 1255-1269.
|
|
ZHANG TIANYI, SU HUA, YANG XIN, et al, 2020. Remote sensing prediction of global subsurface thermohaline and the impact of longitude and latitude based on LightGBM[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing(Chinese), 24(10): 1255-1269. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
赵文静, 曹文熙, 胡水波, 等, 2018. MODIS-Aqua漫射衰减产品Kd(490)在南海海域的精度对比[J]. 光学精密工程, 26(1): 14-24.
|
|
ZHAO WENJING, CAO WENXI, HU SHUIBO, et al, 2018. Comparison of diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance products derived from MODIS-Aqua in the South China Sea[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 26(1): 14-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.3788/OPE.
|
| [7] |
AUSTIN R, PETZOLD T J, 1981. The determination of the diffuse attenuation coefficient of sea water using the Coastal Zone Color Scanner[C]// Oceanography from space. Springer: 239-256.
|
| [8] |
BENGIL F, MCKEE D, BEŞIKTEPE S T, et al, 2016. A bio-optical model for integration into ecosystem models for the Ligurian Sea[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 149: 1-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2016.10.007
|
| [9] |
BREIMAN L, 2001. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 45: 5-32.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324
|
| [10] |
CASTILLO-RAMIREZ A, SANTAMARIA-DEL-ANGEL E, GONZALEZ-SILVERA A, et al, 2020. A New Algorithm to Estimate Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient from Secchi Disk Depth[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(8): 558.
doi: 10.3390/jmse8080558
|
| [11] |
DOROGUSH A V, ERSHOV V, GULIN A, 2018. CatBoost: gradient boosting with categorical features support[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1810. 11363.
|
| [12] |
GORDON H R, 1989. Can the Lambert-Beer law be applied to the diffuse attenuation coefficient of ocean water?[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 34(8): 1389.
doi: 10.4319/lo.1989.34.8.1389
|
| [13] |
GORDON H R, SMITH R C, ZANEVELD J R V, 1980. Introduction to Ocean Optics[C]// Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series. 14-55. 10.1117/12.958262.
doi: 10.1117/12.958262
|
| [14] |
HUANG C, YAO L, HUANG T, et al, 2017. Wind and rainfall regulation of the diffuse attenuation coefficient in large, shallow lakes from long‐term MODIS observations using a semianalytical model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 122(13): 6748-6763.
doi: 10.1002/jgrd.v122.13
|
| [15] |
KE G, MENG Q, FINLEY T, et al, 2017. LightGBM: a highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree[M]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, California, USA: Curran Associates Inc.: 3149-3157.
|
| [16] |
KIRK J T O, 1981. Monte-carlo study of the nature of the underwater light-field in, and the relationships between optical-properties of, turbid yellow waters[J]. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 32(4): 517-532.
doi: 10.1071/MF9810517
|
| [17] |
KIRK J T O, 1994. Estimation of the absorption and the scattering coefficients of natural-waters by use of underwater irradiance measurements[J]. Applied Optics, 33(15): 3276-3278.
doi: 10.1364/AO.33.003276
|
| [18] |
KULLENBERG G, 1968. Scattering of light by sargasso sea water[J]. Deep-Sea Research, 15(4): 423-424.
|
| [19] |
LEE M E, LEWIS M R, 2003. A new method for the measurement of the optical volume scattering function in the upper ocean[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 20(4): 563-571.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2003)20<563:ANMFTM>2.0.CO;2
|
| [20] |
LEE ZP, DARECKI M, CARDER K L, et al, 2005. Diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance: An evaluation of remote sensing methods[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 110(C2): 9.
|
| [21] |
LEE Z P, DU KEPING, ARNONE R, 2005. A model for the diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 110(C2): 10.
|
| [22] |
LEE ZP, SHANG SHAOLING, DU KEPING, et al, 2018. Resolving the long-standing puzzles about the observed Secchi depth relationships[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 63(6): 2321-2336.
doi: 10.1002/lno.v63.6
|
| [23] |
LEWIS M R, WEI JIANWEI, VAN DOMMELEN R, et al, 2011. Quantitative estimation of the underwater radiance distribution[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 116(C7): 14.
|
| [24] |
LI CAI, CAO WENXI, YANG YUEZHONG, et al, 2015. The optical scattering property: spatial and angle variability in Northern South China Sea[C]// The International Conference on Photonics and Optical Engineering (icPOE 2014). SPIE: 93-106.
|
| [25] |
LI CAI, CAO WENXI, YU JING, et al, 2012. An instrument for in situ measuring the volume scattering function of water: design, calibration and primary experiments[J]. Sensors (Basel), 12(4): 4514-4533.
doi: 10.3390/s120404514
|
| [26] |
PETZOLD T J, 1972. Volume scattering functions for selected ocean waters[M]. Scripps Institution of Oceanography La Jolla Ca Visibility Lab.
|
| [27] |
POPE R M, FRY E S, 1997. Absorption spectrum (380-700 nm) of pure water. Ⅱ. Integrating cavity measurements[J]. Applied Optics, 36(33): 8710-8723.
doi: 10.1364/AO.36.008710
|
| [28] |
PREISENDORFER R W, 1976. Hydrologic optics[C]// US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
|
| [29] |
PROKHORENKOVA L, GUSEV G, VOROBEV A, et al, 2018. CatBoost: Unbiased boosting with categorical features[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 31.
|
| [30] |
PYO J, KWON Y S, AHN J H, et al, 2021. Sensitivity analysis and optimization of a radiative transfer numerical model for turbid lake water[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(4): 709.
doi: 10.3390/rs13040709
|
| [31] |
RAYMOND C, SMITH C, KAREN, et al, 1978. Optical classification of natural waters 1[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 23(2): 260-267.
doi: 10.4319/lo.1978.23.2.0260
|
| [32] |
SIEGEL D A, DICKEY T D, 1987. Observations of the vertical structure of the diffuse attenuation coefficient spectrum[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part a-Oceanographic Research Papers, 34(4): 547-563.
doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(87)90005-7
|
| [33] |
SULLIVAN J M, TWARDOWSKI M S, ZANEVELD J R V, et al, 2006. Hyperspectral temperature and salt dependencies of absorption by water and heavy water in the 400-750 nm spectral range[J]. Applied Optics, 45(21): 5294-5309.
pmid: 16826267
|
| [34] |
TWARDOWSKI M, ZHANG X D, VAGLE S, et al, 2012. The optical volume scattering function in a surf zone inverted to derive sediment and bubble particle subpopulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 117(C7): 18.
|
| [35] |
TYLER J E, 1961. Scattering properties of distilled and natural waters[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 6(4): 451-456.
doi: 10.4319/lo.1961.6.4.0451
|
| [36] |
WANG GUIFANG, CAO WENXI, YANG DINGTIAN, et al, 2008. Variation in downwelling diffuse attenuation coefficient in the northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 26: 323-333.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-008-0323-x
|
 ), 李彩1,3(
), 李彩1,3( ), 周雯1,3, 刘聪1, 许占堂1,3, 曹文熙1,3, 杨跃忠1,3
), 周雯1,3, 刘聪1, 许占堂1,3, 曹文熙1,3, 杨跃忠1,3
 ), LI Cai1,3(
), LI Cai1,3( ), Zhou Wen1,3, LIU Cong1, XU Zhantang1,3, CAO Wenxi1,3, YANG Yuezhong1,3
), Zhou Wen1,3, LIU Cong1, XU Zhantang1,3, CAO Wenxi1,3, YANG Yuezhong1,3