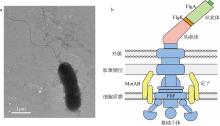
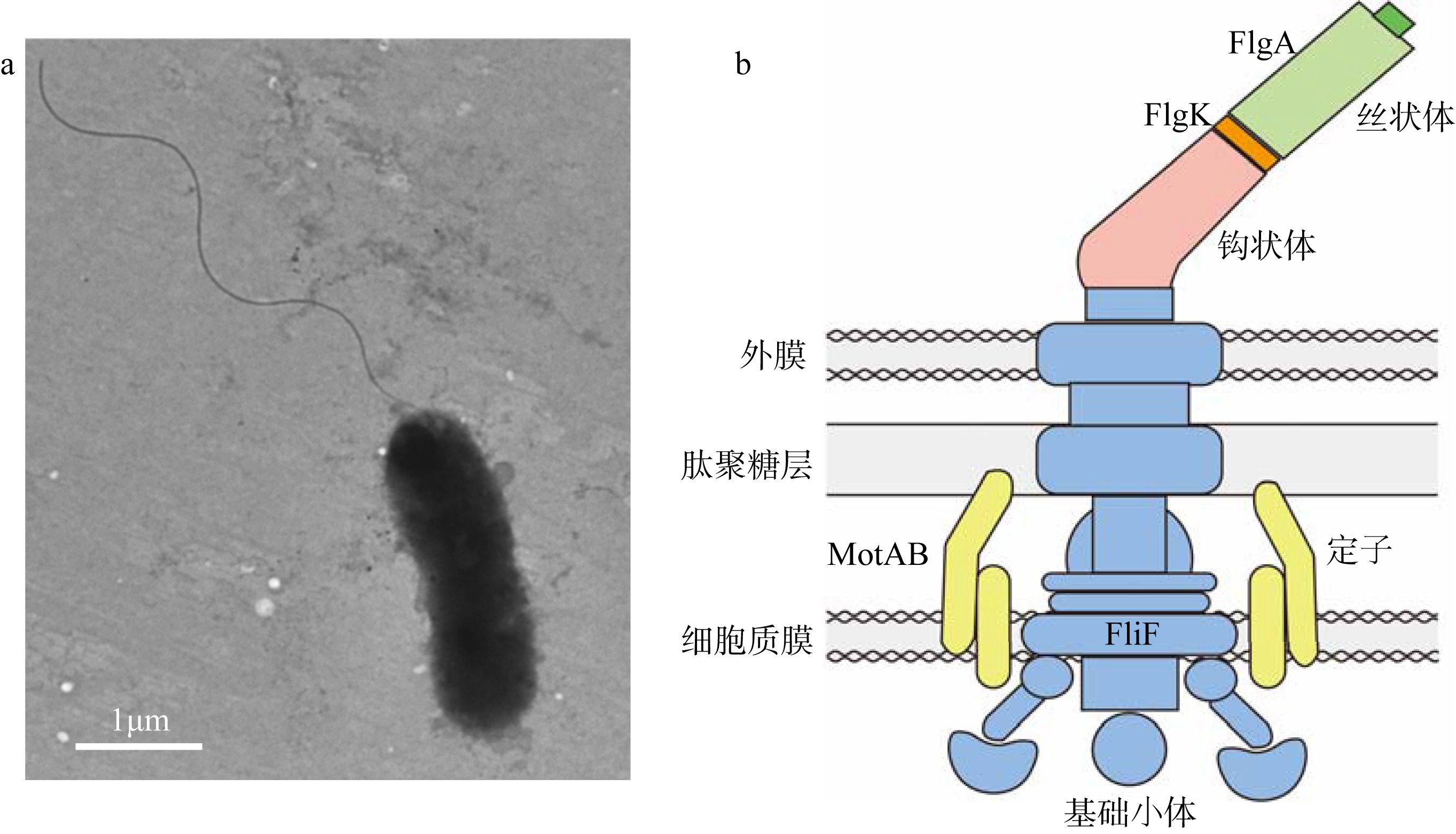
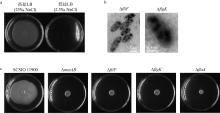
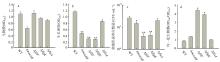
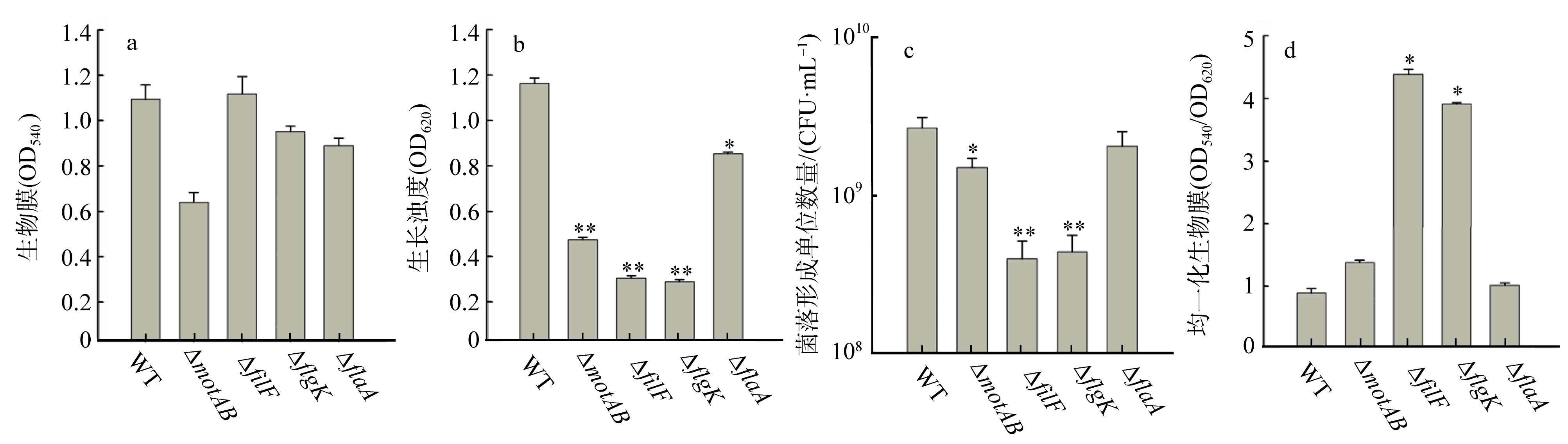
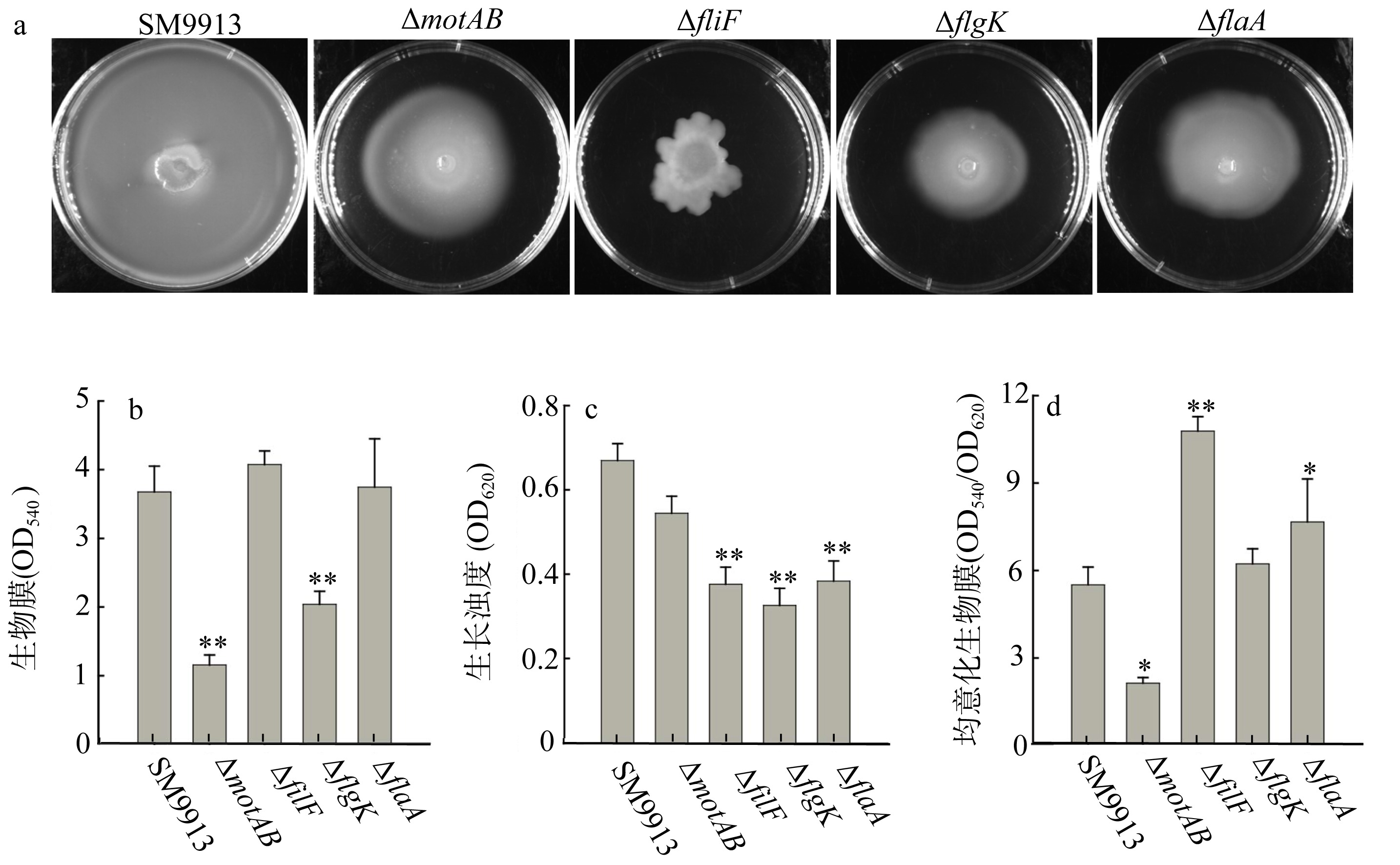
| [1] |
乔毅, 沈辉, 万夕和, 等, 2015. 1株黑鲷致病性假交替单胞菌的鉴定及毒力基因分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 43(4): 229-233.
|
|
QIAO YI, SHEN HUI, WAN XIHE, et al, 2015. Identification and virulence genes analysis of a Pseudoalteromonas strain isolated from diseased Acanthopagrus schlegelii[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 43(4): 229-233 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
王枫林, 王秀华, 张宇哲, 等, 2021. 杀鱼假交替单胞菌2515的抗弧菌效果及在对虾养殖中的应用[J]. 中国水产科学, 28(7): 903-913.
|
|
WANG FENGLIN, WANG XIUHUA, ZHANG YUZHE, et al, 2021. Anti-vibrio effect of Pseudoalteromonas piscicida 2515 and its application in shrimp culture[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 28(7): 903-913. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
席宇, 朱大恒, 刘红涛, 等, 2005. 假交替单胞菌及其胞外生物活性物质研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 32(3): 108-112.
|
|
XI YU, ZHU DAHENG, LIUHONGTAO, et al, 2005. Advances on Pseudoaltermonas species and their extracellular bioactive compounds[J]. Microbiology China, 32(3): 108-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
闫咏, 马家海, 许璞, 等, 2002. 1株引起条斑紫菜绿斑病的柠檬假交替单胞菌[J]. 中国水产科学, 9(4): 353-358.
|
|
YAN YONG, MA JIAHAI, XU PU, et al, 2002. Pseudoalteromonas citrea, the causative agent of green-spot disease of Porphyrae yezoensis[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 9(4): 353-358. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
张驰, 王劲松, 杨金龙, 等, 2022. 海假交替单胞菌(Pseudoalteromonas marina) pilZ基因缺失抑制厚壳贻贝附着变态[J]. 海洋学报, 44(4): 95-103.
|
|
ZHANG CHI, WANG JINSONG, ZHANG JUNBO, et al, 2022. Knockout of Pseudoalteromonas marina pilZ gene inhibited the settlement and metamorphosis of Mytilus coruscus[J]. Haiyang xuebao, 44(4): 95-103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
ALEXIEV A, KRUSOR M L, JOSPIN G, et al, 2016. Draft genome sequences of two Pseudoalteromonas strains isolated from roots and leaf blades of the seagrass Zostera marina[J]. Genome Announcements, 4(1): e00010-16.
|
| [7] |
ANTUNES J, LEAO P, VASCONCELOS V, 2019. Marine biofilms: diversity of communities and of chemical cues[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 11(3): 287-305.
doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12694
pmid: 30246474
|
| [8] |
BEURMANN S, VIDEAU P, USHIJIMA B, et al, 2015. Complete genome sequence of Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain OCN003, isolated from Kāne'ohe Bay, O'ahu, Hawaii[J]. Genome Announcements, 3(1): e01396-14.
|
| [9] |
BOWMAN J P J M D, 2007. Bioactive compound synthetic capacity and ecological significance of marine bacterial genus Pseudoalteromonas[J]. Marine Drugs, 5(4): 220-241.
doi: 10.3390/md504220
|
| [10] |
CHEN YUN, CHAI YUNRONG, GUO JIAN-HUA, et al, 2012. Evidence for cyclic di-GMP-mediated signaling in Bacillus subtilis[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 194(18): 5080-5090.
doi: 10.1128/JB.01092-12
|
| [11] |
D’ACUNTO B, FRUNZO L, KLAPPER I, et al, 2019. Mathematical modeling of dispersal phenomenon in biofilms[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 307: 70-87.
doi: S0025-5564(17)30068-8
pmid: 30076852
|
| [12] |
FLEMMING H C, WINGENDER J, 2010. The biofilm matrix[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8(9): 623-633.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2415
|
| [13] |
FLEMMING H C, WINGENDER J, SZEWZYK U, et al, 2016. Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 14(9): 563-575.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.94
|
| [14] |
FLEMMING H C, WUERTZ S, 2019. Bacteria and archaea on earth and their abundance in biofilms[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 17(4): 247-260.
doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0158-9
|
| [15] |
GAUTHIER G, GAUTHIER M, CHRISTEN R J, et al, 1995. Phylogenetic analysis of the genera Alteromonas, Shewanella, and Moritella using genes coding for small-subunit rRNA sequences and division of the genus Alteromonas into two genera, Alteromonas (emended) and Pseudoalteromonas gen. nov., and proposal of twelve new species combinations[J]. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 45(4): 755-761.
doi: 10.1099/00207713-45-4-755
|
| [16] |
GONZÀLEZ Y, VENEGAS D, MENDOZA-HERNANDEZ G, et al, 2010. Na+-and H+-dependent motitility in the coral pathogen Vibrio shilonii[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 312(2010): 142-150.
doi: 10.1111/fml.2010.312.issue-2
|
| [17] |
GIVAN S A, ZHOU MINGYI, BROMERT K, et al, 2015. Genome sequences of Pseudoalteromonas strains ATCC BAA-314, ATCC 70018, and ATCC 70019[J]. Genome Announcements, 3(3): e00390-15.
|
| [18] |
HOLMSTRÖM C, KJELLEBERG S, 1999. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents[J]. FEMF Microbiology Ecology, 30(4): 285-293.
|
| [19] |
JARRELL K F, MCBRIDE M J J N R M, 2008. The surprisingly diverse ways that prokaryotes move[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 6(6): 466-476.
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1900
|
| [20] |
LEE R D, JOSPIN G, LANG J M, et al, 2015. Draft genome sequence of Pseudoalteromonas tetraodonis strain UCD-SED8 (Phylum Gammaproteobacteria)[J]. Genome Announcements, 3(6): e01276-15.
|
| [21] |
LI BAIYUAN, WANG PENGXIA, ZENG ZHENSHUN, et al, 2016. Complete genome sequence of Pseudoalteromonas rubra SCSIO 6842, harboring a putative conjugative plasmid pMBL6842[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 224: 66-67.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.03.010
|
| [22] |
LIU TAO, GUO ZHANGWEI, ZENG ZHENSHUN, et al, 2018. Marine bacteria provide lasting anticorrosion activity for steel via biofilm-induced mineralization[J]. ACS Applied Material & Interfaces, 10(46): 40317-40327
|
| [23] |
MEDIGUE C, KRIN E, PASCAL G, et al, 2005. Coping with cold: the genome of the versatile marine antarctica bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125[J]. Genome Research, 15(10): 1325-1335.
doi: 10.1101/gr.4126905
|
| [24] |
MI ZIHAO, YU ZICHAO, SU HAINAN, et al, 2015. Physiological and genetic analyses reveal a mechanistic insight into the multifaceted lifestyles of Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM9913 adapted to the deep-sea sediment[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 17(10): 3795-806.
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12823
|
| [25] |
PALLEN M J, MATZKE N J, 2006. From the origin of species to the origin of bacterial flagella[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 4(10): 784-790.
pmid: 16953248
|
| [26] |
PARK H J, SHIN S C, KIM D, 2012. Draft genome sequence of Arctic marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas issachenkonii PAMC 22718[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 194(15): 4140.
doi: 10.1128/JB.00744-12
|
| [27] |
PRATT L A, KOLTER R, 1998. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli biofilm formation: roles of flagella, motility, chemotaxis and type I pili[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 30(2): 285-293.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01061.x
|
| [28] |
QIN QILONG, LI YANG, ZHANG YANJIAO, et al, 2011. Comparative genomics reveals a deep-sea sediment-adapted life style of Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM9913[J]. ISME Journal, 5(2): 274-284.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.103
|
| [29] |
WANG PENGXIA, YU ZICHAO, LI BAI, et al, 2015. Development of an efficient conjugation-based genetic manipulation system for Pseudoalteromonas[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 14: 11.
doi: 10.1186/s12934-015-0194-8
|
| [30] |
WANG PENGXIA, ZENG ZHENSHUN, WANG WEIQUAN, et al, 2017. Dissemination and loss of a biofilm-related genomic island in marine Pseudoalteromonas mediated by integrative and conjugative elements[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 19(11): 4620-4637.
doi: 10.1111/emi.2017.19.issue-11
|
| [31] |
YANG JUN, ZENG ZAOHAI, YANG MANJUN, et al, 2018. NaCl promotes antibiotic resistance by reducing redox states in Vibrio alginolyticus[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 20(11): 4022-4036.
doi: 10.1111/emi.2018.20.issue-11
|
| [32] |
ZENG ZHENSHUN, DAI SHIKUN, XIE YUNCHANG, et al, 2014. Genome sequences of two Pseudoalteromonas strains isolated from the South China Sea[J]. Genome Announcements, 2(2): e00305-14.
|
 ), 蔡兴盛1, 古嘉瑜1,2, 王晓雪1,2
), 蔡兴盛1, 古嘉瑜1,2, 王晓雪1,2
 ), CAI Xingsheng1, GU Jiayu1,2, WANG Xiaoxue1,2
), CAI Xingsheng1, GU Jiayu1,2, WANG Xiaoxue1,2