热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 116-125.doi: 10.11978/2022121CSTR: 32234.14.2022121
铵态氮加富对贝克喜盐草光合作用、谷氨酰胺合成酶和氨基酸成分的影响
江志坚1,2,3,4,5,6( ), Chanaka Isuranga PREMARATHNE1,3, 方扬1,3, 林基桢1,3, 吴云超1,2,4,5,6, 刘松林1,2,4,5,6, 黄小平1,2,3,4,5,6(
), Chanaka Isuranga PREMARATHNE1,3, 方扬1,3, 林基桢1,3, 吴云超1,2,4,5,6, 刘松林1,2,4,5,6, 黄小平1,2,3,4,5,6( )
)
- 1.中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室, 广东 广州 510301
2.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
3.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
4.中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 510301
5.三亚海洋生态环境工程研究院, 海南省热带海洋生物技术重点实验室, 海南 三亚 572100
6.广东省应用海洋生物学重点实验室, 广东 广州 510301
-
收稿日期:2022-05-26修回日期:2022-07-16出版日期:2023-05-10发布日期:2022-07-21 -
作者简介:江志坚(1982—), 男, 广东省清远市人, 研究员, 从事海草生物生态研究。email: jiangzj1982@scsio.ac.cn
-
基金资助:海南省科技专项(ZDYF2021SHFZ254); 国家自然科学基金项目(41735029); 国家自然科学基金项目(41976144); 国家自然科学基金项目(U1901221); 国家自然科学基金项目(42176158); 中国科学院青年创新促进会(2023359); 广东省应用海洋生物学重点实验室运行经费(2020B1212060058)
Effects of ammonium enrichment on the photosynthesis, glutamine synthetase and amino acid composition of seagrass Halophila beccarii Asch
JIANG Zhijian1,2,3,4,5,6( ), Chanaka Isuranga PREMARATHNE1,3, FANG Yang1,3, LIN Jizhen1,3, WU Yunchao1,2,4,5,6, LIU Songlin1,2,4,5,6, HUANG Xiaoping1,2,3,4,5,6(
), Chanaka Isuranga PREMARATHNE1,3, FANG Yang1,3, LIN Jizhen1,3, WU Yunchao1,2,4,5,6, LIU Songlin1,2,4,5,6, HUANG Xiaoping1,2,3,4,5,6( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
5. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Biotechnology of Hainan Province, Sanya Institute of Ocean Eco-Environmental Engineering, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sanya 572100, China
6. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2022-05-26Revised:2022-07-16Online:2023-05-10Published:2022-07-21 -
Supported by:Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund(ZDYF2021SHFZ254); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41735029); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976144); National Natural Science Foundation of China(U1901221); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42176158); Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS(2023359); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China(2020B1212060058)
摘要:
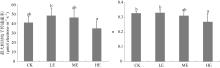
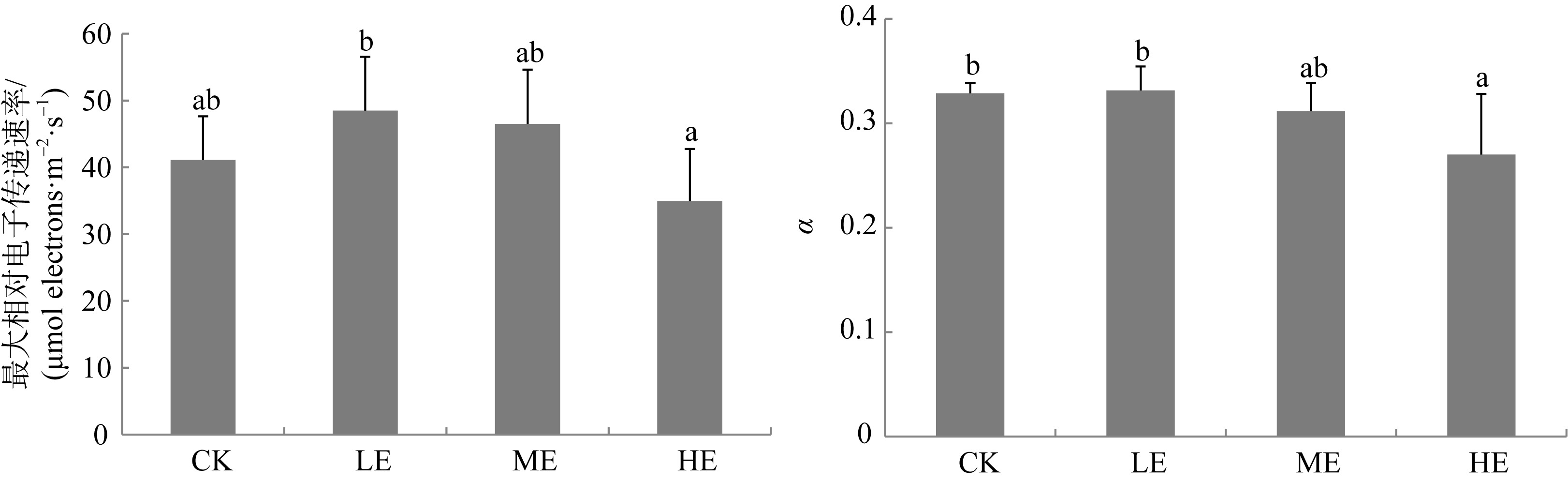
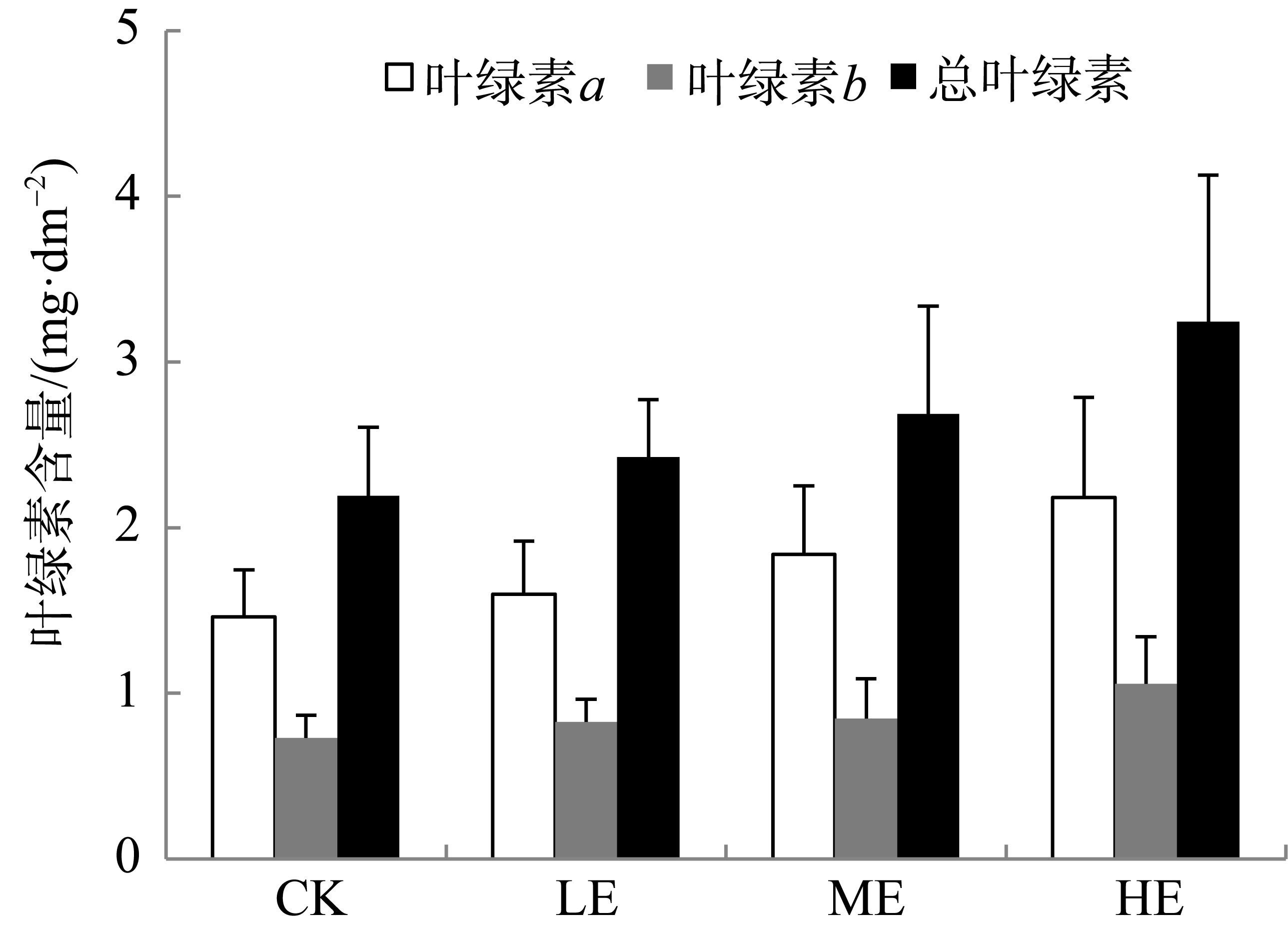
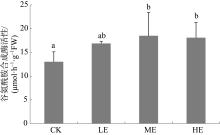
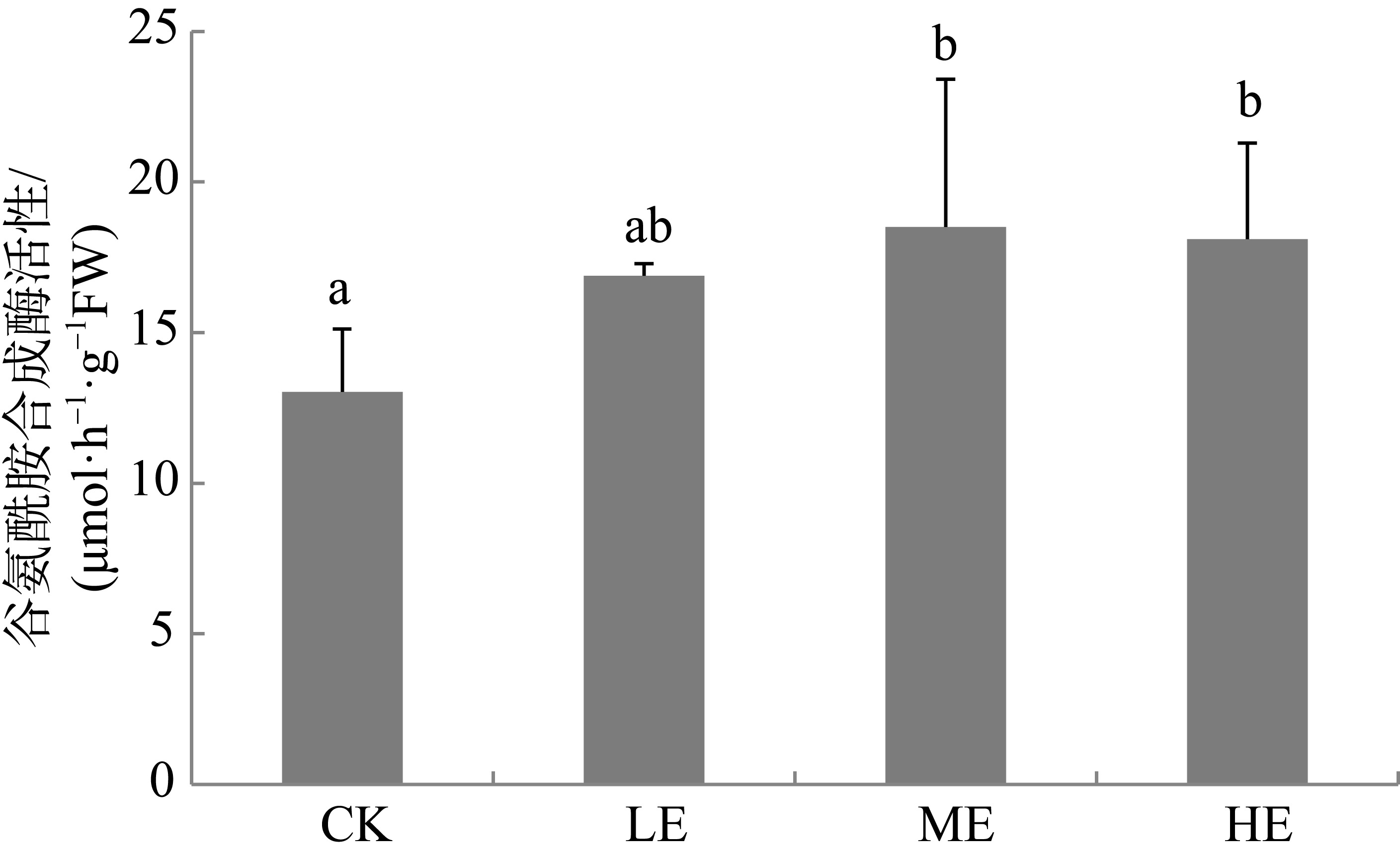
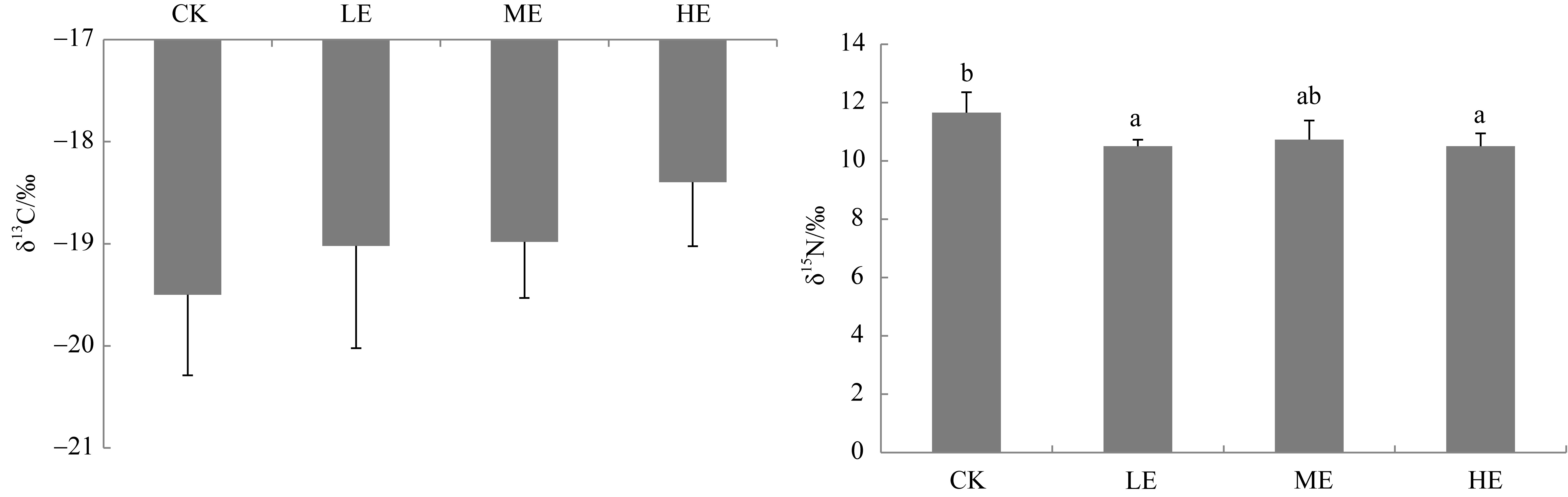
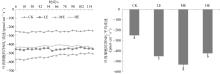
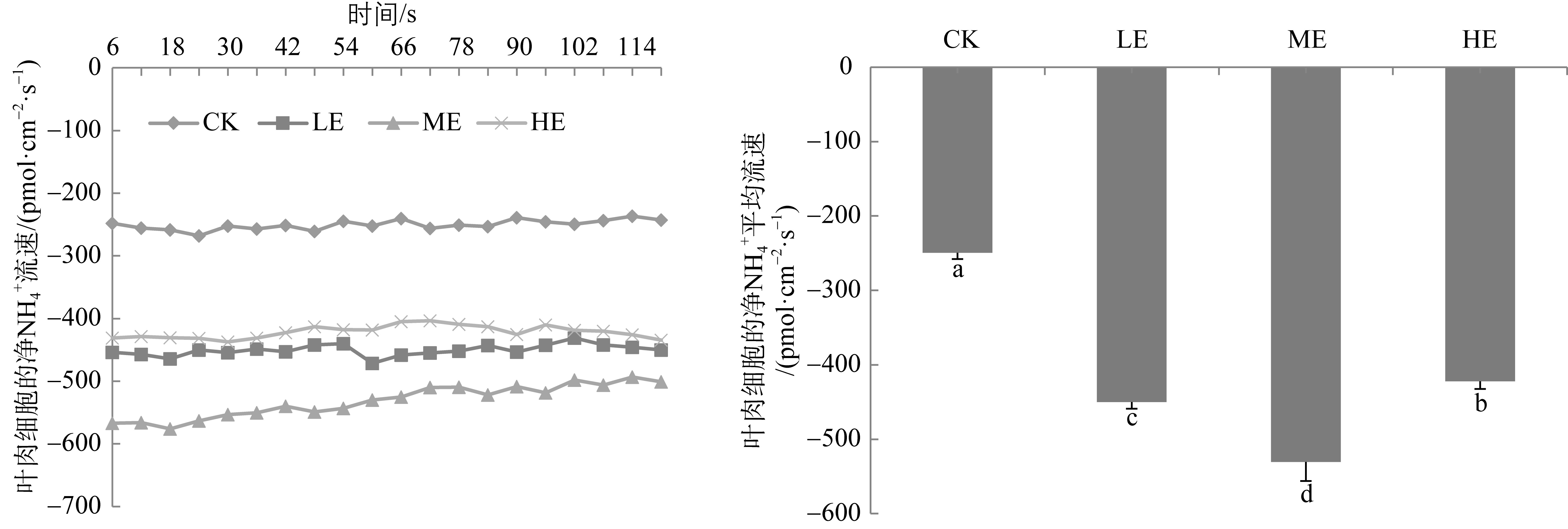
海草贝克喜盐草(Halophila beccarii)由于体型小, 其重要性一直被忽视, 且近海氮负荷增加导致其处于加速退化状态。目前贝克喜盐草对铵毒害的生理响应尚不清楚。基于室内模拟实验, 设置了四种铵态氮梯度(对照; 25、50和100μmol·L-1), 结合叶绿素荧光技术、非损伤微测技术和靶向代谢组学, 探讨了铵态氮加富对贝克喜盐草光合作用、叶绿素、叶肉细胞铵离子流速、谷氨酰胺合成酶活性以及营养成分的影响。结果表明, 贝克喜盐草叶片的最大相对电子传递速率呈现低铵态氮加富>中铵态氮加富>对照>高铵态氮加富的变化趋势, 高铵态氮加富显著降低了最大相对电子传递速率和光能利用效率, 进而减少碳库用于铵态氮的同化。同时, 铵态氮加富显著增加了铵离子内流流速和谷氨酰胺合成酶活性, 把过多的铵同化成氨基酸。但是, 铵态氮加富却降低了氨基酸成分, 这可能是由于氨基酸被用来合成有机物如关键次生代谢物, 以进一步调节和适应铵毒害作用。因此, 适度的铵营养盐增加可促进贝克喜盐草的光合作用和生长, 而高浓度的铵营养盐则对贝克喜盐草产生毒害作用。
引用本文
江志坚, Chanaka Isuranga PREMARATHNE, 方扬, 林基桢, 吴云超, 刘松林, 黄小平. 铵态氮加富对贝克喜盐草光合作用、谷氨酰胺合成酶和氨基酸成分的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 116-125.
JIANG Zhijian, Chanaka Isuranga PREMARATHNE, FANG Yang, LIN Jizhen, WU Yunchao, LIU Songlin, HUANG Xiaoping. Effects of ammonium enrichment on the photosynthesis, glutamine synthetase and amino acid composition of seagrass Halophila beccarii Asch[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 116-125.
表1
铵态氮加富对贝克喜盐草叶片氨基酸成分的影响"
| 氨基酸 | 对照 | 25μmol·L-1 NH+ 4 | 50μmol·L-1 NH+ 4 | 100μmol·L-1 NH+ 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量/(μg·g-1) | 占比/% | 含量/(μg·g-1) | 占比/% | 含量/(μg·g-1) | 占比/% | 含量/(μg·g-1) | 占比/% | |
| 甘氨酸 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 丙氨酸 | 2101.7±710.2A | 10.35 | 1538.0±524.9AB | 9.88 | 1537.1±412.8AB | 9.54 | 1062.9±272.8B | 9.48 |
| γ-氨基丁酸 | 148.5±85.5A | 0.73 | 92.8±34.9AB | 0.60 | 100.2±53.1AB | 0.62 | 61.1±42.2B | 0.54 |
| 丝氨酸 | 254.7±70.4 | 1.25 | 218.1±62.1 | 1.40 | 218.9±55.3 | 1.36 | 154.8±46.2 | 1.38 |
| 脯氨酸 | 44.4±12.4 | 0.22 | 37.5±20.4 | 0.24 | 36.0±7.5 | 0.22 | 25.9±13.7 | 0.23 |
| 缬氨酸 | 299.0±93.9 | 1.47 | 203.2±49.6 | 1.31 | 224.7±107.4 | 1.39 | 154.8±72.7 | 1.38 |
| 苏氨酸 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 异亮氨酸 | 347.7±112.2 | 1.71 | 271.5±93.0 | 1.74 | 293.7±134.6 | 1.82 | 204.6±85.0 | 1.82 |
| 亮氨酸 | 75.1±20.8 | 0.37 | 49.2±9.5 | 0.32 | 61.4±40.3 | 0.38 | 36.3±19.7 | 0.32 |
| 天冬酰胺 | 14022.5±3810.7 | 69.04 | 11103.8±2500.6 | 71.34 | 11339.8±5312.9 | 70.38 | 7923.3±4034.9 | 70.64 |
| 鸟氨酸 | 2.3±1.0 | 0.01 | 3.3±1.7 | 0.02 | 2.8±1.5 | 0.02 | 1.8±0.9 | 0.02 |
| 天冬氨酸 | 506.9±114.1A | 2.50 | 392.8±65.9AB | 2.52 | 370.1±147.3AB | 2.30 | 285.4±124.3B | 2.54 |
| 高半胱氨酸 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 谷氨酰胺 | 2233.8±787.1A | 11.00 | 1429.1±570.5A | 9.18 | 1685.2±970.4AB | 10.46 | 1114.8±671.0B | 9.94 |
| 赖氨酸 | 11.1±2.4 | 0.05 | 14.6±8.9 | 0.09 | 10.2±6.3 | 0.06 | 6.4±4.5 | 0.06 |
| 谷氨酸 | 156.4±12.5 | 0.77 | 133.9±18.2 | 0.86 | 154.2±44.0 | 0.96 | 124.1±44.6 | 1.11 |
| 甲硫氨酸 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 组氨酸 | 16.9±3.0 | 0.08 | 13.3±2.8 | 0.09 | 12.4±9.8 | 0.08 | 11.0±6.7 | 0.10 |
| 苯丙氨酸 | 46.5±11.9A | 0.23 | 38.6±4.8AB | 0.25 | 39.1±19.3AB | 0.24 | 28.7±11.0B | 0.26 |
| 精氨酸 | 1.9±0.4 | 0.01 | 2.4±0.9 | 0.02 | 2.0±0.8 | 0.01 | 2.0±1.1 | 0.02 |
| 酪氨酸 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 色氨酸 | 41.6±14.9A | 0.20 | 23.1±7.7AB | 0.15 | 24.5±19.1B | 0.15 | 18.1±12.9B | 0.16 |
| 总氨基酸 | 20311.0±5768.9 | 100.00 | 15565.3±3627.4 | 100.00 | 16112.4±7267.6 | 100.00 | 11216.1±5384.5 | 100.00 |
| [1] |
陈启明, 刘松林, 张弛, 等, 2020. 海南典型热带海草床4种代表性鱼类的生长特征及其对海草资源量变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(5): 62-70.
doi: 10.11978/2020007 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020007 |
|
| [2] |
黄小平, 江志坚, 张景平, 等, 2018. 全球海草的中文命名[J]. 海洋学报, 40(4): 127-133.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
李玲兰, 江志坚, 方扬, 等, 2020. 海草组学研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 65: 4063-4072.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
邱广龙, 苏治南, 范航清, 等, 2020. 贝克喜盐草的生物学和生态学特征及其保护对策[J]. 海洋环境科学, 39(1): 121-126.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
邱广龙, 苏治南, 钟才荣, 等, 2016. 濒危海草贝克喜盐草在海南东寨港的分布及其群落基本特征[J]. 广西植物, 36(7): 882-889.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
舒展, 张晓素, 陈娟, 等, 2010. 叶绿素含量测定的简化[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 46(4): 399-402.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
王道儒, 吴钟解, 陈春华, 等, 2012. 海南岛海草资源分布现状及存在威胁[J]. 海洋环境科学, 31(1): 34-38.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1002/lno.10084 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1111/mae.2010.31.issue-4 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00325 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1071/PP01185 pmid: 32689481 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.12.005 pmid: 25576003 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2007.06.024 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1111/cobi.12951 pmid: 28464290 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1038/ngeo1477 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2018.11.001 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b04647 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.3354/meps140285 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e01035 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00194 |
| [27] |
doi: S0025-326X(17)30661-6 pmid: 28818604 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aal1956 pmid: 28209895 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134068 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.1999.44.5.1204 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2007.06.016 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2007.05.006 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0755 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1002/aqc.v29.9 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/0304-3770(80)90025-X |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1038/nature16548 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119077 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.10.003 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsab031 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2005.02.006 |
| [48] |
doi: S0141-1136(17)30531-7 pmid: 29519535 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1007/s002270000433 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2007.06.012 |
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.104986 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2022.107837 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(00)00196-9 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(00)00195-7 |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1007/s13280-018-1115-y |
| [57] |
doi: 10.3354/meps157159 |
| [58] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.571363 |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1007/s12237-016-0103-3 |
| [60] |
doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105965 |
| [61] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905620106 |
| [1] | 吴雪萍, 叶红霞, 姚又菊, 刘浩翔, 李瑞华, 童潼. 3个地区可口革囊星虫营养成分及重金属含量的分析与评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 92-107. |
| [2] | 巫楚君, 潘剑宇, 蔡冰娜, 陶曙红. 黄鳍金枪鱼酶解物免疫活性及其氨基酸分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 128-134. |
| [3] | 李云凯, 陈子昂, 贡艺, 陈新军. 海洋动物营养生态位研究方法及其应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(4): 143-156. |
| [4] | 周洁, 施祺, 余克服. 三亚造礁石珊瑚虫黄藻光合作用效率的日周期及其调控因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(1): 81-89. |
| [5] | 区又君,李加儿. 野生波纹唇鱼Cheilinus undulates营养成分分析与评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(3): 97-102. |
|
||