热带海洋学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 1-8.doi: 10.11978/2016131CSTR: 32234.14.2016131
• • 下一篇
河口三角洲径流和潮汐相互作用模型及应用
- 中山大学河口海岸研究所, 河口水利技术国家地方联合工程实验室, 广东 广州 510275
The development and application of river-tide harmonic model
Suying OU( ), Qingshu YANG, Hao YANG, Shuai HU
), Qingshu YANG, Hao YANG, Shuai HU
- Institute of Estuarine and Coastal Research, Sun Yat-sen University, State and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Estuarine Hydraulic Technology, Guangzhou 510275, China
摘要:
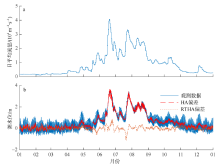
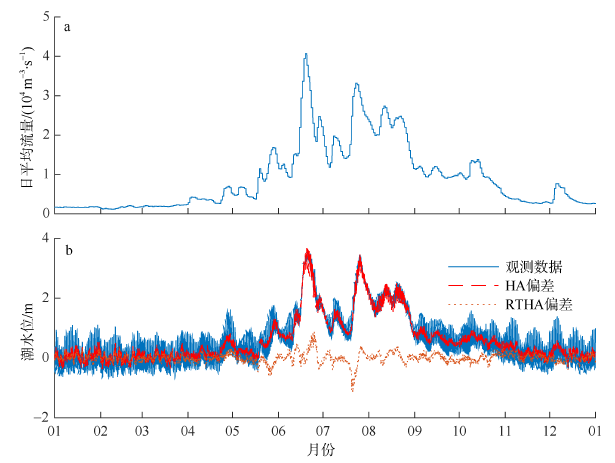
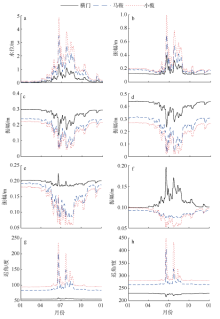
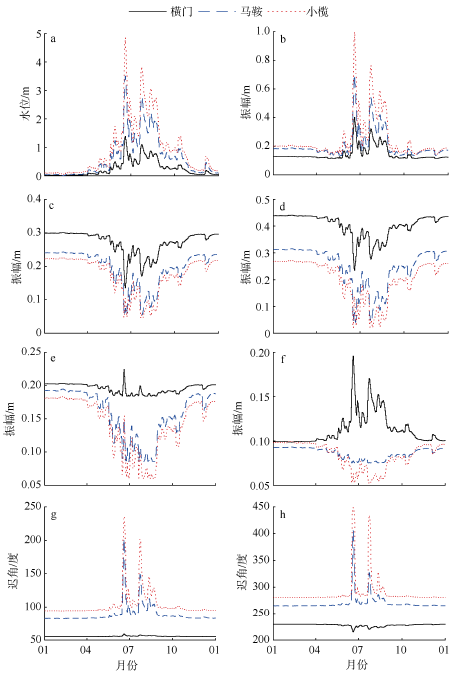
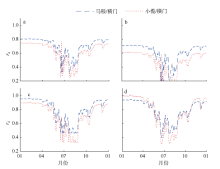
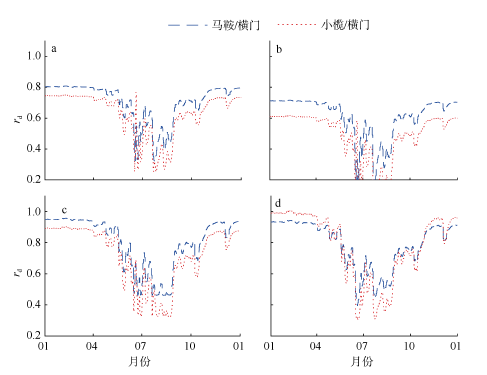
受径流影响和调制, 径优型河口潮汐的非线性作用强, 潮汐调和分析和预报误差大。文章在调和分析方法的基础上, 结合河口三角洲内径潮相互作用机理, 假定河道地形变化微弱, 采用实测潮水位和上游径流量, 建立径流和潮汐调和分析(river-tidal harmonic analysis, 简称RTHA)模型, 用于分析和研究珠江三角洲的径流和潮汐的相互作用过程。结果表明, 对于珠江河口年尺度的潮水位数据, RTHA模型分析和预报的标准误差0.12~0.17 m, 方差贡献(相关指数)为91% ~98%, 特别是在径流作用强的河口三角洲中上段, RTHA模型结果远高于传统的调和分析和预报结果, 可以以较高精度分离径流和潮汐信号。利用该回归模型对珠江径流影响下非线性潮汐的变化进行研究, 结果发现, 珠江径流量的洪枯季变化引起河口全日分潮、半日分潮、三分之一分潮的振幅洪季小、枯季大, 口门段四分之一分潮的振幅洪季大、枯季小; 洪季全日分潮、半日分潮传播速度变小(位相增大), 分潮振幅沿程衰减幅度显著增大, 自枯季的10%~30%迅速增加到洪季的70%~80%。