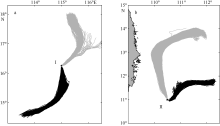
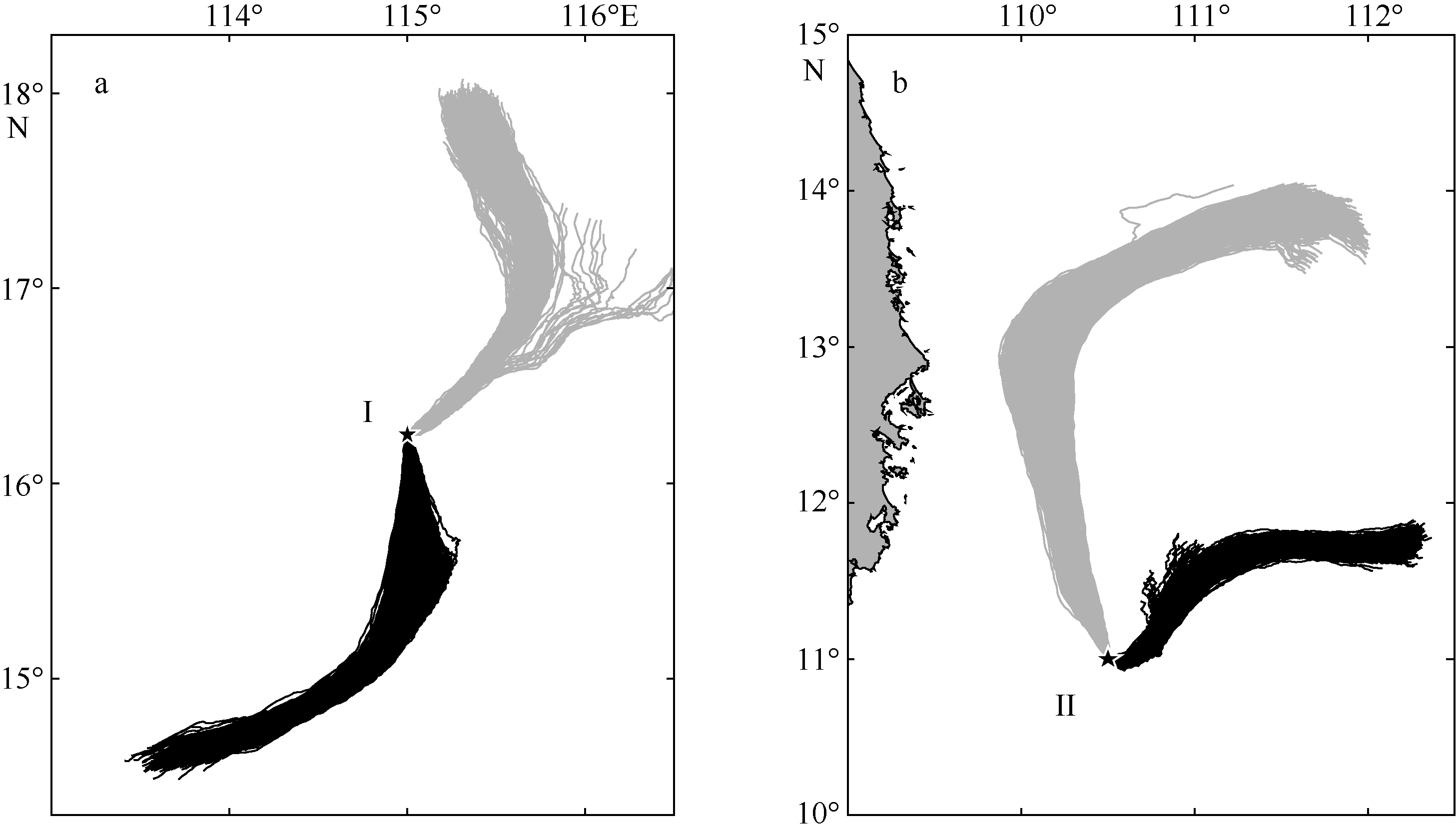
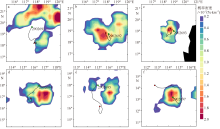
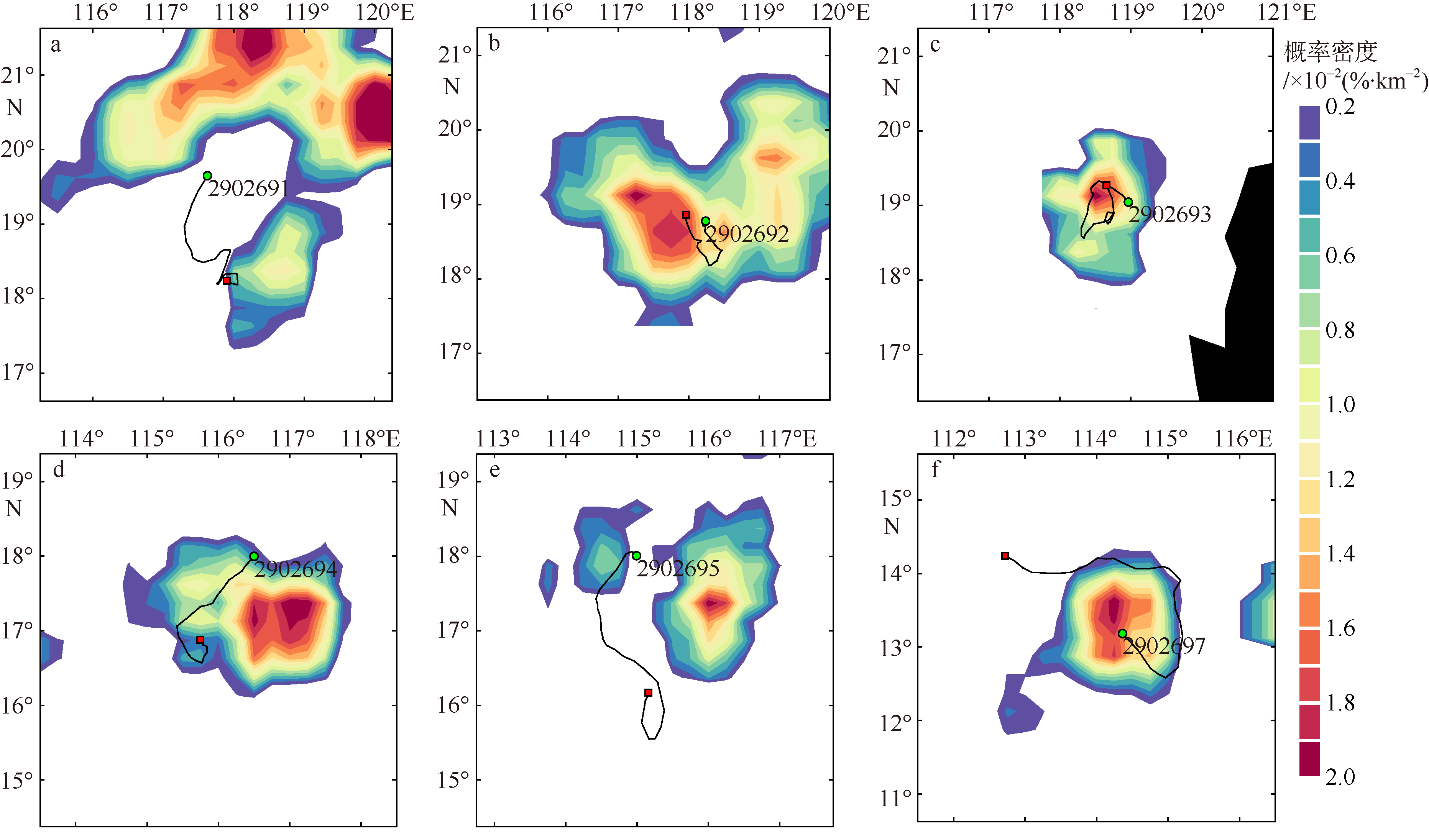
| 1 |
李立, 吴日升, 郭小钢, 2000. 南海的季节环流—TOPEX/ POSEIDON卫星测高应用研究[J]. 海洋学报, 22(6): 13-26.
|
|
LI LI, WU RISHENG, GUO XIAOGANG, 2000. Seasonal circulation in the South China Sea - A TOPEX/POSEIDON satellite altimetry study[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 22(6): 13-26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 2 |
刘秦玉, 杨海军, 刘征宇, 2000. 南海Sverdrup环流的季节变化特征[J]. 自然科学进展, 10(11): 1035-1039.
|
|
LIU QINYU, YANG HAIJUN, LIU ZHENGYU, 2000. The Sverdrup currents in the South China Sea[J]. Process in Nature Science, 10(11): 1035-1039 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 3 |
侍茂崇, 江明顺, 许建平, 等, 2001. 南海西南部环流[C]//中国海洋文集—南海海流数值计算及中尺度特征研究. 北京: 海洋出版社, 57-63.
|
|
SHI MAOCHONG, JIANG MINGSHUN, XU JIANPING, et al, 2001. The currents in the southwest of the South China Sea[C]//Chinese Ocean Anthology. Beijing: Ocean Press: 57-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 4 |
王东晓, 肖劲根, 舒业强, 等, 2016. 南海深层环流与经向翻转环流的研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 46(10): 1317-1323.
|
|
WANG DONGXIAO, XIAO JINGEN, SHU YEQIANG, et al, 2016. Progress on deep circulation and meridional overturning circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 59(9): 1827-1833.
|
| 5 |
BATCHELOR G K, 1952. The effect of homogeneous turbulence on material lines and surfaces[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 213(1114): 349-366.
|
| 6 |
CHAO S Y, SHAW P T, WU S Y, 1996. Deep water ventilation in the South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I Oceanographic Research Papers, 43(4): 445-466.
|
| 7 |
CHEN C T A, HUANG M H, 1996. A mid-depth front separating the South China Sea water and the Philippine sea water[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 52(1): 17-25.
|
| 8 |
DALE W, 1956. Wind and drift currents in the South China Sea[J]. Malayan Journal of Tropical Geography, 8:1-31.
|
| 9 |
GILLE S T, 2003. Float observations of the southern ocean. Part I: estimating mean fields, bottom velocities, and Topographic Steering[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 33(6): 1167-1181.
|
| 10 |
KINDERMAN A J, MONAHAN J F, 1977. Computer generation of random variables using the ratio of uniform deviates[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 3(3): 257-260.
|
| 11 |
LACASCE J H, 2000. Floats and f/H[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 58(1): 61-95.
|
| 12 |
LI L, QU T, 2006. Thermohaline circulation in the deep South China Sea basin inferred from oxygen distributions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 111(C5): 101-112.
|
| 13 |
MADDEN R A, JULIAN P R, 1994. Observations of the 40~50-Day Tropical Oscillation - A review[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 122(5): 814-837.
|
| 14 |
MAO J, CHAN J C L, 2005. Intraseasonal Variability of the South China Sea Summer Monsoon[J]. Journal of Climate, 18(13): 2388-2402.
|
| 15 |
OLLITRAULT M, RANNOU J P, 2013. ANDRO: An Argo-based deep displacement dataset[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 30(4): 759-788.
|
| 16 |
QU T D, MITSUDERA H, YAMAGATAY T, 2000. Intrusion of the North Pacific waters into the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 105(C3): 6415-6424.
|
| 17 |
QU T D, DU Y, SASAKI H, 2006. South China Sea throughflow: A heat and freshwater conveyor[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(23): L23617.
|
| 18 |
ROACH C J, BALWADA D, SPEER K, 2016. Horizontal mixing in the Southern Ocean from Argo float trajectories[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121(8): 5570-5586.
|
| 19 |
ROEMMICH D, GILSON J, 2009b. The 2004—2008 mean and annual cycle of temperature, salinity, and steric height in the global ocean from the Argo program[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 82(2): 81-100.
|
| 20 |
ROEMMICH D, JOHNSON G, RISER S, et al, 2009a. The Argo program: Observing the global oceans with profiling floats[J]. Oceanography, 22(2): 34-43.
|
| 21 |
SHAW P T, CHAO S Y, 1994. Surface circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 41(11-12): 1663-1683.
|
| 22 |
THE ARGO SCIENCE TEAM, 1998. On the design and implementation of argo - An initial plan for a global array of profiling floats[R]. Melbourne, Australia: GODAE International Project office, c/o Bureau of Meteorology, Office ICPO Report No. 21. GODAE Report No 5.
|
| 23 |
WYRTKI K, 1961. Physical Oceanography of the Southeast Asian Waters[C]//Scripps Institution of Oceanography. La Jolla, California: 2.
|
| 24 |
XIE S P, XIE Q, WANG D, 2003. Summer upwelling in the South China Sea and its role in regional climate variations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 108(C8): 3250-3261.
|
| 25 |
YANG QING, TIAN JIWEI, ZHAO WEI, 2010. Observation of Luzon Strait transport in summer 2007[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 57(5): 670-676.
|
| 26 |
YUAN D L, 2002. A numerical study of the South China Sea deep circulation and its relation to the Luzon Strait transport[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 21(2): 187-202.
|
| 27 |
ZILBERMAN N V, ROEMMICH D H, GILLE S T, 2013. The mean and the time variability of the shallow meridional overturning circulation in the tropical South Pacific Ocean[J]. Journal of Climate, 26(2): 4069-4087.
|
 ), Yan DU1,2(
), Yan DU1,2( ), Yifan XIA1,2
), Yifan XIA1,2