

夏季大亚湾大型底栖动物群落结构*
作者简介:袁涛萍(1976—), 女, 江西省景德镇市人, 博士研究生, 主要从事海洋生物生态的研究。E-mail:yuan@scsio.ac.cn
收稿日期: 2016-04-19
要求修回日期: 2016-05-12
网络出版日期: 2017-01-19
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41206133)
Community structure of macrobenthos in summer in Daya Bay
Received date: 2016-04-19
Request revised date: 2016-05-12
Online published: 2017-01-19
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China (41206133)
Copyright
利用2013年8月在大亚湾海域进行的海洋生态调查所采集的底栖动物样品及环境参数, 研究了夏季大亚湾海域底栖动物种类组成、数量分布、群落结构及其环境影响因子。结果表明, 调查共采集到大型底栖动物153种, 其中环节动物81种、软体动物37种、甲壳动物25种、棘皮动物6种、其他类动物4种; 环节动物种数占总种数的52.94%, 是构成大亚湾大型底栖动物的主要类群。优势种类为短吻铲荚螠和波纹巴菲蛤。底栖动物平均丰度和平均生物量分别为410ind·m-2和84.83g·m-2。等级聚类分析(CLUSTER)将大亚湾的底栖动物分为5个群落。相关性分析表明, 影响夏季大亚湾底栖动物群落结构的主要环境因子为沉积物石油类。BIOENV分析表明, 底栖动物种类丰度与有机质和重金属的铅、铜和镉等环境因素密切相关。
袁涛萍 , 李恒翔 , 李路 , 王卉 , 杨长平 . 夏季大亚湾大型底栖动物群落结构*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017 , 36(1) : 41 -47 . DOI: 10.11978/2016040
The species composition, abundance, biomass and characteristics of macrobenthic fauna in Daya Bay were studied and the main factors that influence the distribution of benthic macrofauna were discussed, based on samples obtained from 32 stations in August 2013. A total of 153 macrobenthic species were identified, including 81 species of polychaete, 37 species of mollusk, 25 species of crustacean, 6 species of echinoderm and 4 species of others. Polychaetes represented the most dominant group and accounted for 52.94% of the total species. The macrobenthos was dominated by Listriolobus brevirostri and Paphia undulata. The average total density and average total biomass of the macrobenthos were 410 ind·m-2 and 84.83 g·m-2, respectively. Cluster analysis showed that the macrobenthic community could be divided into five groups with notable differences. Person correlation analysis was conducted between community characteristic indices and sediment factors, which showed that petroleum hydrocarbon in sediment in Daya Bay was main environmental factor affecting the benthic community structure in summer. BIOENV analysis showed that the benthic species abundance was closely related to organic matters and heavy metals such as lead, copper and cadmium.
Key words: Daya Bay; macrobenthos; community structure; abundance; biomass
Fig. 1 Locations of the sampling stations图1 调查站位示意图 |
 , 式中H′为种类多样性指数, S为样品中的种类总数, Pi为第i种的个体数与总个体数的比值。Margalef 物种丰富度指数D=(S-1)/ log2N。Pielou均匀度J=H/log2S, 式中J为均匀度, H′为种类多样性指数, N为所有物种的总个体数。优势度公式为:
, 式中H′为种类多样性指数, S为样品中的种类总数, Pi为第i种的个体数与总个体数的比值。Margalef 物种丰富度指数D=(S-1)/ log2N。Pielou均匀度J=H/log2S, 式中J为均匀度, H′为种类多样性指数, N为所有物种的总个体数。优势度公式为: 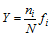 , 式中ni为第i种的总个体数, fi为第i种在各站位出现的频率, 以 Y>0.02 作为优势种。利用PRIMER6.0 软件包对群落结构进行分析, 为减少机会种对大型底栖动物群落结构的干扰, 数据分析时不包括总体样品中相对丰度小于l%且在每个站位样品中相对丰度均小于3%的物种。基于种丰度矩阵、经4次方根转换、Bray-Curtis相似性计算进行组平均连接的等级聚合聚类(CLUSTER)分析大亚湾大型底栖动物群落结构。使用丰度生物量法(abundance-biomass comparison, ABC)对群落的稳定性和受扰动状况进行分析。采用PRIMER软件中的BIOENV方法进行生物-环境相关分析, 以寻找与群落结构相匹配的最佳环境因子组合。运用SPSS 13.0统计分析软件对底栖动物群落特征参数与环境因子进行Pearson相关分析。
, 式中ni为第i种的总个体数, fi为第i种在各站位出现的频率, 以 Y>0.02 作为优势种。利用PRIMER6.0 软件包对群落结构进行分析, 为减少机会种对大型底栖动物群落结构的干扰, 数据分析时不包括总体样品中相对丰度小于l%且在每个站位样品中相对丰度均小于3%的物种。基于种丰度矩阵、经4次方根转换、Bray-Curtis相似性计算进行组平均连接的等级聚合聚类(CLUSTER)分析大亚湾大型底栖动物群落结构。使用丰度生物量法(abundance-biomass comparison, ABC)对群落的稳定性和受扰动状况进行分析。采用PRIMER软件中的BIOENV方法进行生物-环境相关分析, 以寻找与群落结构相匹配的最佳环境因子组合。运用SPSS 13.0统计分析软件对底栖动物群落特征参数与环境因子进行Pearson相关分析。Tab. 1 Dominant species and their Y value of water in Daya Bay表1 夏季大亚湾底栖动物优势种及优势度 |
| 优势种 | 出现率/% | 平均密度/(ind·m-2) | 所占比例/% | 优势度Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 短吻铲荚螠 | 56.3 | 22.38 | 27.27 | 0.15 |
| 波纹巴菲蛤 | 50.0 | 7.67 | 9.34 | 0.02 |
Fig. 2 Horizontal distributions of macrobenthic abundance and biomass in Daya Bay in summer图2 夏季大亚湾大型底栖动物的丰度(a)以及生物量(b)水平分布 |
Fig. 3 Three biodiversity indices of macrobenthos in Daya Bay in summer图3 大亚湾大型底栖动物物种多样性指数 |
Fig. 4 CLUSTER analysis of macrobenthic community in Daya Bay图4 大亚湾大型底栖动物群落的CLUSTER划分 |
Fig. 5 ABC curves of macrobenthic groups in Daya Bay in summer图5 夏季大亚湾大型底栖动物ABC曲线 |
Tab. 2 Pearson correlations between community characteristics indices of macrobenthos and environmental factors表2 大型底栖动物群落特征指数与沉积环境因子的相关性 |
| 环境因子 | 丰度 | 生物量 | 种类数 | 香浓-威纳指数H′ | 均匀度J | 丰富度指数D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黏土+粉砂 | -0.017 | 0.133 | 0.032 | 0.026 | -0.079 | -0.015 |
| 中值粒径 | -0.052 | 0.176 | 0.015 | 0.030 | -0.008 | 0.015 |
| 有机质 | -0.327 | -0.241 | -0.211 | -0.185 | 0.042 | -0.119 |
| 石油类 | -0.168 | -0.183 | -0.420* | -0.408* | 0.038 | -0.351* |
| 硫化物 | -0.041 | -0.092 | 0.176 | -0.224 | -0.171 | -0.217 |
| 铜(Cu) | -0.108 | -0.129 | -0.347 | -0.342 | -0.049 | -0.253 |
| 铅(Pb) | -0.252 | -0.219 | -0.242 | 0.220 | 0.045 | -0.105 |
| 锌(Zn) | 0.128 | 0.082 | 0.249 | 0.242 | 0.014 | 0.195 |
| 镉(Cd) | -0.020 | -0.183 | -0.170 | -0.173 | 0.009 | -0.103 |
| 铬(Cr) | -0.322 | -0.177 | -0.194 | -0.158 | 0.322 | 0.158 |
| 汞(Hg) | -0.128 | -0.080 | 0.055 | 0.114 | 0.106 | 0.159 |
| 砷(As) | -0.263 | -0.312 | -0.305 | -0.233 | 0.268 | 0.101 |
注: *表示显著相关(p<0.05) |
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China,Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China,2008a.GB/T 12763.6-2007, Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press (in Chinese).
|
| [14] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2008b. GB 17378.5-2007 海洋监测规范第5部分: 沉积物分析[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2008b. GB 17378.5-2007, The specification for marine monitoring—Part 5: sediment analysis[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press (in Chinese).
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |