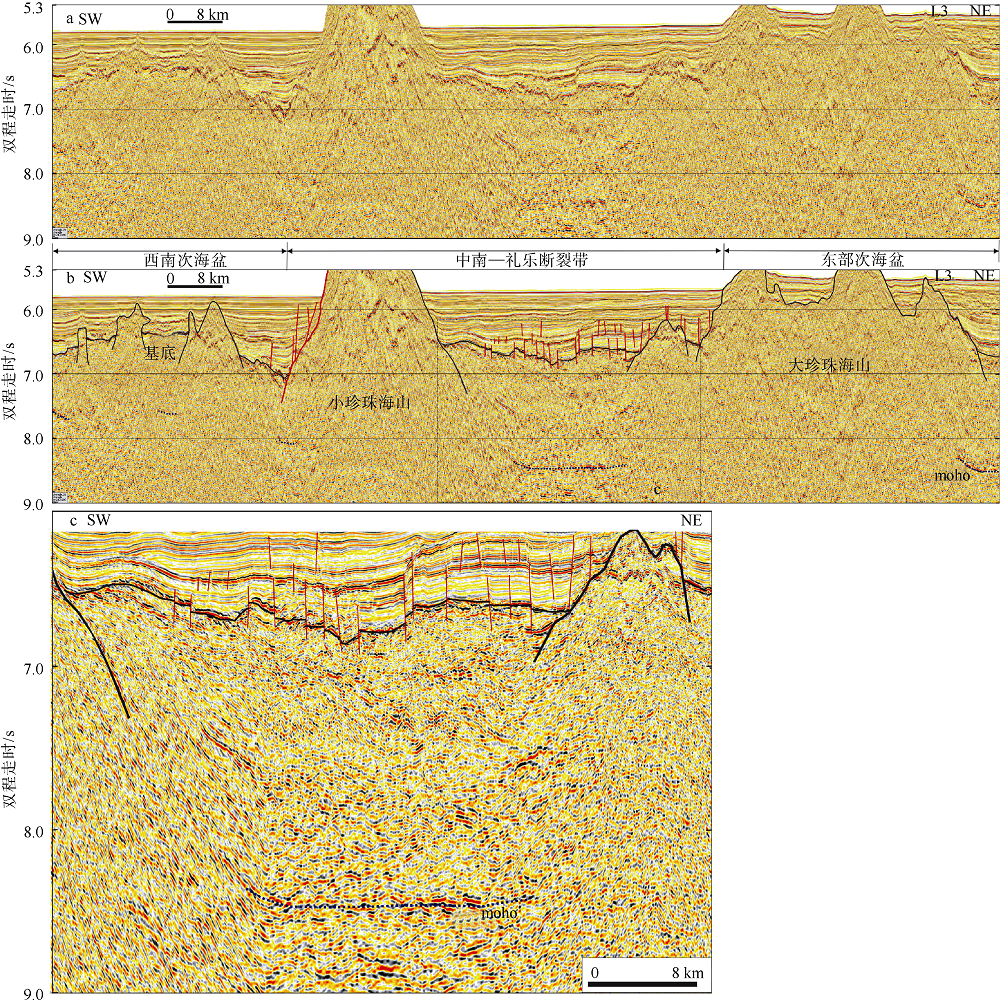
| [1] |
JONES E J W, 2009. 海洋地球物理[M]. 金翔龙, 赵俐红, 孙鹏,等, 译. 北京:海洋出版社: 446-450.
|
|
JONES E J W, 2009. Marine geophysics[M]. JIN XIANGLONG, ZHAO LIHONG, SUNPENG, et al. Beijing: Ocean Press: 446-450 (in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
李家彪, 丁巍伟, 高金耀, 等, 2011. 南海新生代海底扩张的构造演化模式: 来自高分辨率地球物理数据的新认识[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(12): 3004-3015.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.003
|
|
LI JIABIAO, DING WEIWEI, GAO JINYAO, et al, 2011. Cenozoic evolution model of the sea-floor spreading in South China Sea: new constraints from high resolution geophysical data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(12): 3004-3015 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.003
|
| [3] |
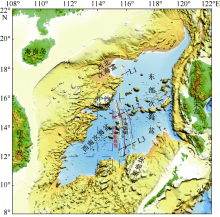
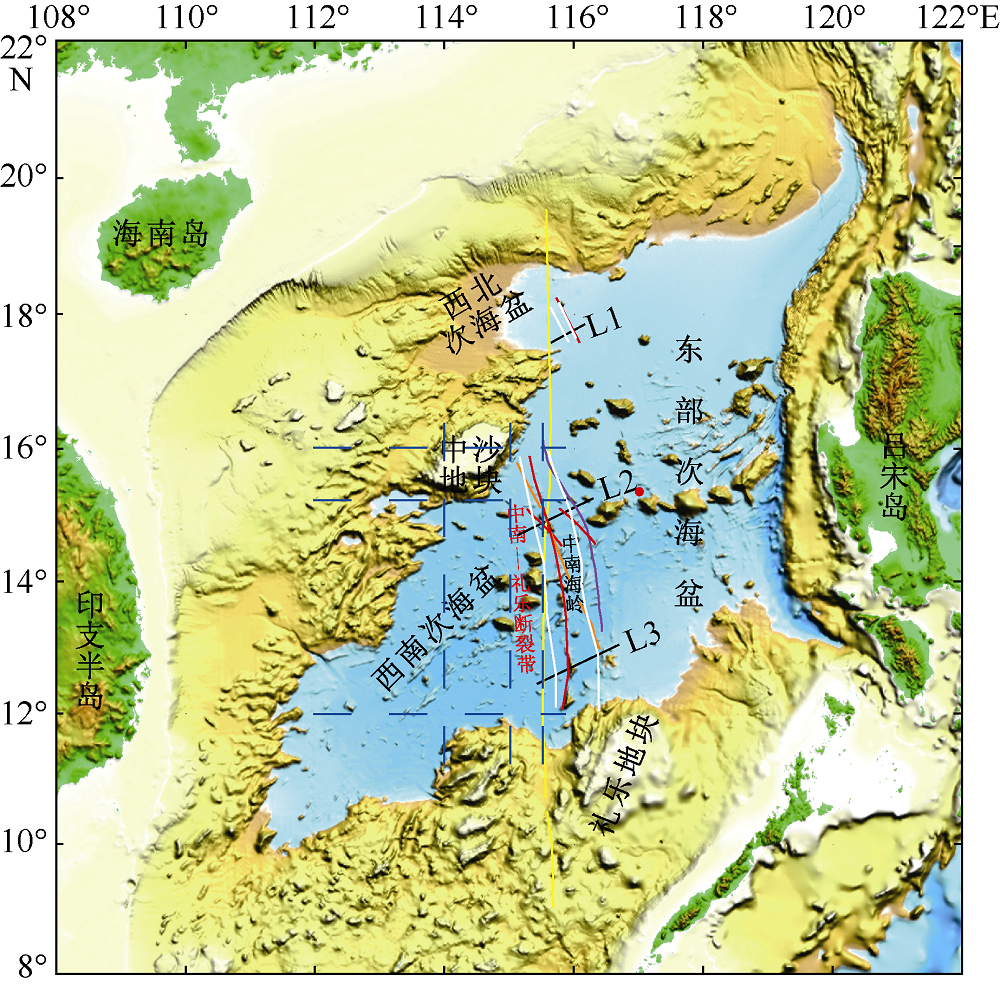
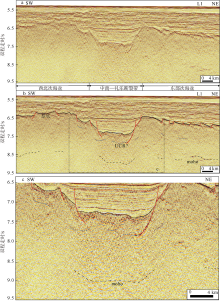
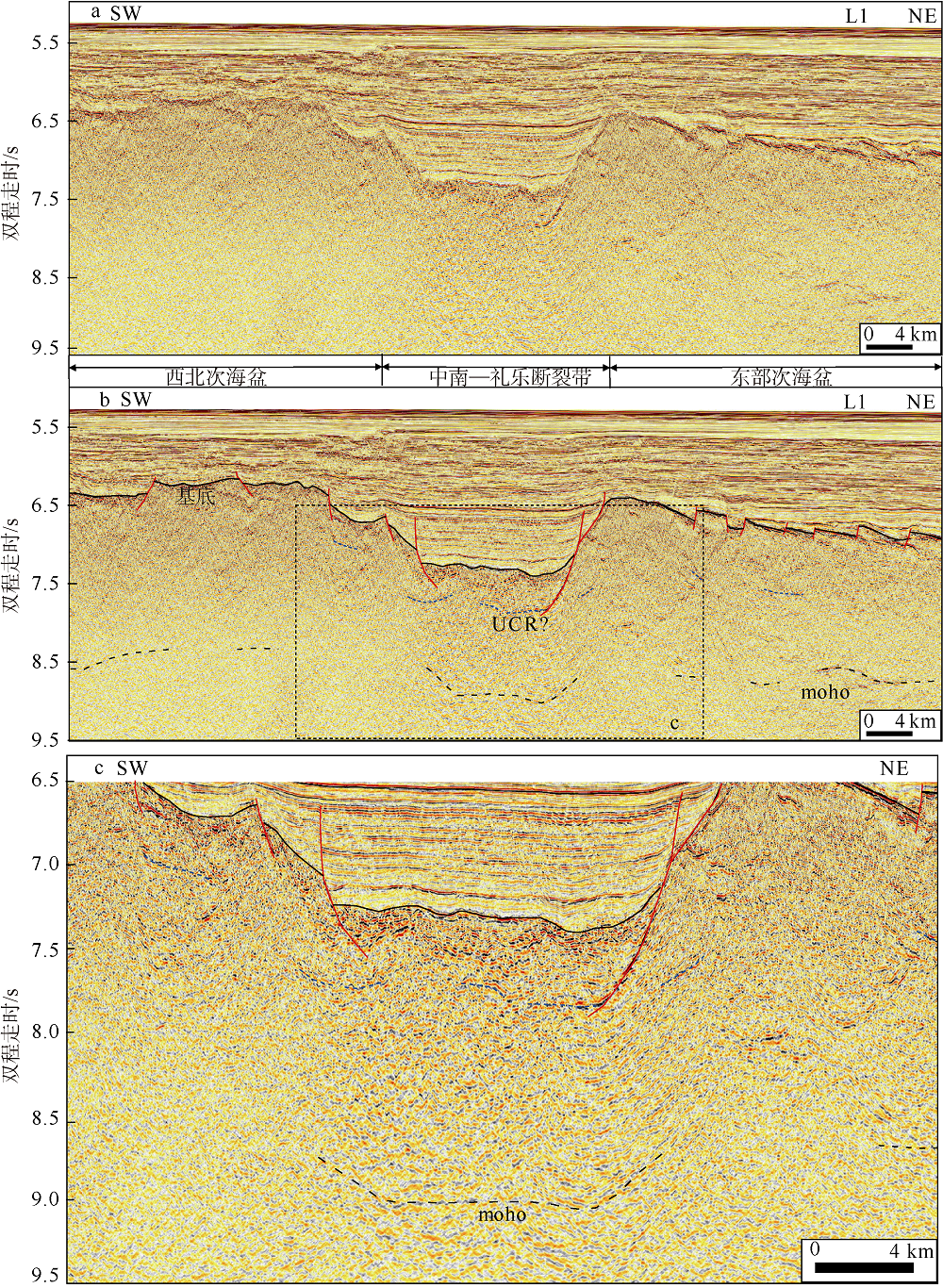
黎雨晗, 刘海龄, 朱荣伟, 等, 2017. 南海中南—司令断裂带的延伸特征及其与南海扩张演化的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪, 37(2): 82-98.
|
|
LI YUHAN, LIU HAILING, ZHU RONGWEI, et al, 2017. Extension of the Zhongnan-siling fault zone in South China Sea and its bearing on seafloor spreading[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 37(2): 82-98 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
王叶剑, 韩喜球, 罗照华, 等, 2009. 晚中新世南海珍贝—黄岩海山岩浆活动及其演化: 岩石地球化学和年代学证据[J]. 海洋学报, 31(4): 93-102.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.04.011
|
|
WANG YEJIAN, HAN XIQIU, LUO ZHAOHUA, et al, 2009. Late Miocene magmatism and evolution of Zhenbei-Huangyan Seamount in the South China Sea: evidence from petrochemistry and chronology[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(4): 93-102 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.04.011
|
| [5] |
阎贫, 王彦林, 刘海龄, 2008. 南海海盆地形与NW向断裂[J]. 热带海洋学报, 27(3): 30-37.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2008.03.006
|
|
YAN PIN, WANG YANLIN, LIU HAILING, 2008. Topography of oceanic basin in South China Sea and NW-directed faults[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 27(3): 30-37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2008.03.006
|
| [6] |
杨胜雄, 邱燕, 朱本铎, 2015. 南海地质地球物理图系[M]. 天津: 中国航海图书出版社.
|
|
YANG SHENGXIONG, QIU YAN, ZHU BENDUO, 2015. Atlas of geology and geophysics of the South China Sea[M]. Tianjin: China Navigation Publications (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
姚伯初, 曾维军, HAYES D E, 等, 1994. 中美合作调研南海地质专报[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社.
|
|
YAO BOCHU, ZENG WEIJUN, HAYES D E, et al, 1994. The geological memoir of South China Sea surveyed jointly by China & USA[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
姚伯初, 1995. 中南—礼乐断裂的特征及其构造意义[J]. 南海地质研究, (7): 1-14.
|
|
YAO BOCHU, 1995. Characteristics and tectonic meaning of Zhongnan-Liyue fault[J]. Geological Research of South China Sea, (7): 1-14 (in Chinese).
|
| [9] |
BARCKHAUSEN U, ENGELS M, FRANKE D, et al, 2014. Evolution of the South China Sea: revised ages for breakup and seafloor spreading[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 599-611.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.02.022
|
| [10] |
BARCKHAUSEN U, ROESER H A, 2004. Seafloor spreading anomalies in the South China Sea revisited[M]//CLIFT P, KUHNT W, WANG P, et al. Continent‐Ocean Interactions Within East Asian Marginal Seas. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 149: 121-125.
|
| [11] |
BRIAIS A, PATRIAT P, TAPPONNIER P, 1993. Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading stages in the South China Sea: implications for the tertiary tectonics of Southeast Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 98(B4): 6299-6328.
doi: 10.1029/92JB02280
|
| [12] |
DING WEIWEI, SUN ZHEN, DADD K, et al, 2018. Structures within the oceanic crust of the central South China Sea basin and their implications for oceanic accretionary processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 488: 115-125.
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2018.02.011
|
| [13] |
FRANKE D, 2013. Rifting, lithosphere breakup and volcanism: Comparison of magma-poor and volcanic rifted margins[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 43: 63-87.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.11.003
|
| [14] |
FRANKE D, SAVVA D, PUBELLIER M, et al, 2014. The final rifting evolution in the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 704-720.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.11.020
|
| [15] |
LI CHUNFENG, LIN JIAN, KULHANEK D K, et al, 2015. Expedition 349 summary[C]//Proceedings of the International Ocean Discovery Program. doi: 10.14379/iodp.proc.349.101. 2015.
|
| [16] |
LI CHUNFENG, SONG TAORAN, 2012. Magnetic recording of the Cenozoic oceanic crustal accretion and evolution of the South China Sea basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(24): 3165-3181.
doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5063-9
|
| [17] |
LI CHUNFENG, XU XING, LIN JIAN, et al, 2014. Ages and magnetic structures of the South China Sea constrained by deep tow magnetic surveys and IODP Expedition 349[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 15(12): 4958-4983.
doi: 10.1002/2014GC005567
|
| [18] |
LI CHUNFENG, ZHOU ZUYI, LI JIABIAO, et al, 2008. Magnetic zoning and seismic structure of the South China Sea ocean basin[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 29(4): 223-238.
doi: 10.1007/s11001-008-9059-4
|
| [19] |
RUAN AIGUO, WEI XIAODONG, NIU XIONGWEI, et al, 2016. Crustal structure and fracture zone in the Central Basin of the South China Sea from wide angle seismic experiments using OBS[J]. Tectonophysics, 688: 1-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.09.022
|
| [20] |
SCHLÜTER H U, HINZ K, BLOCK M, 1996. Tectono- stratigraphic terranes and detachment faulting of the South China Sea and Sulu Sea[J]. Marin Geology, 130(1-2): 39-51, 58-78.
doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(95)00137-9
|
| [21] |
SIBUET J C, YEH Y C, LEE C S, 2016. Geodynamics of the South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 692: 98-119.
doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.02.022
|
| [22] |
TAYLOR B, HAYES D E, 1980. The tectonic evolution of the South China Basin[M]//HAYES D E. The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 23: 89-104.
|
| [23] |
TAYLOR B, HAYES D E, 1983. Origin and history of the South China Sea basin[M]//HAYES D E. The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands: Part 2. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 27: 23-56.
|
| [24] |
TONGKUL F, 1993. Tectonic control on the development of the Neogene basins in Sabah, East Malaysia[C]//Proceedings Symposium on the Tectonic Framework and Energy Resources of the Western Margin of the Pacific Basin. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: Geological Society of Malaysia: 95-103.
|
| [25] |
TONGKUL F, 1994. The geology of northern Sabah, Malaysia: its relationship to the opening of the South China Sea basin[J]. Tectonophysics, 235(1-2): 131-147.
doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(94)90021-3
|
 ), 汪俊, 高红芳, 孙桂华, 孙美静, 聂鑫, 朱荣伟
), 汪俊, 高红芳, 孙桂华, 孙美静, 聂鑫, 朱荣伟
 ), Jun WANG, Hongfang GAO, Guihua SUN, Meijing SUN, Xin NIE, Rongwei ZHU
), Jun WANG, Hongfang GAO, Guihua SUN, Meijing SUN, Xin NIE, Rongwei ZHU