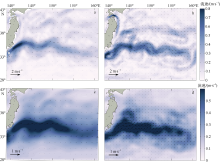
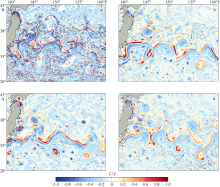
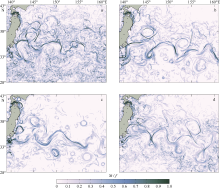
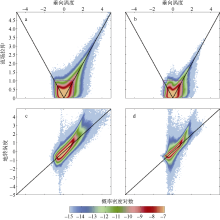
| [1] |
胡冬, 陈希, 赵艳玲, 等, 2018. 两个西边界流延伸体区域中尺度涡统计特征分析[J]. 海洋学报, 40(6):15-28.
|
|
HU DONG, CHEN XI, ZHAO YANLING, et al, 2018. Statistical characteristics of mesoscale eddies in the two western boundary current extension regions[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 40(6):15-28 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
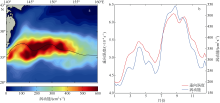
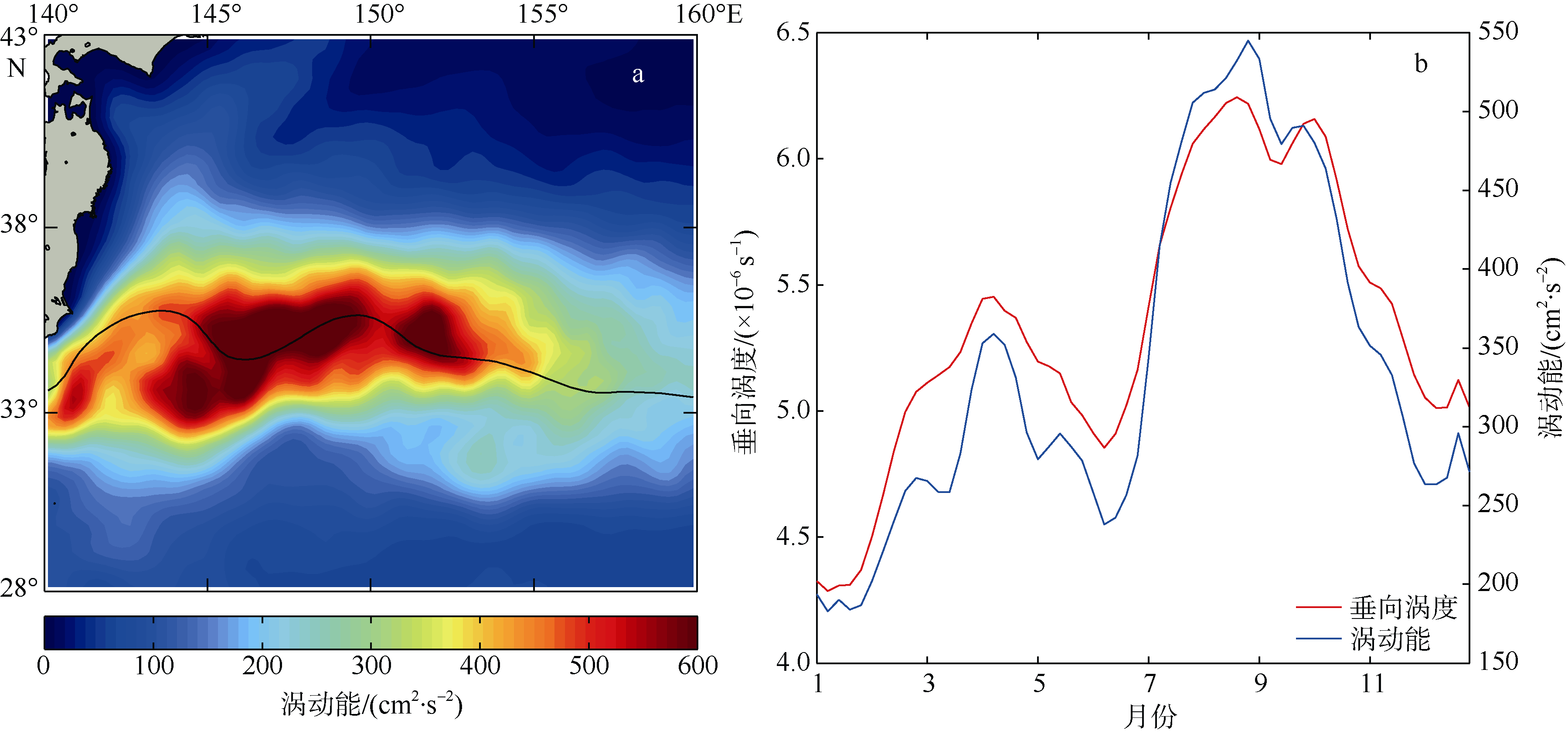
李宏杰, 徐永生, 2017. 北太平洋副热带逆流区涡旋动能谱的季节性变化及其机制[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 48(5):932-943.
|
|
LI HONGJIE, XU YONGSHENG, 2017. Seasonal variation in eddy kinetic energy spectrum and its mechanism in the north Pacific subtropical countercurrent[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 48(5):932-943 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
罗士浩, 经志友, 齐义泉, 等, 2016. 南海北部次中尺度过程数值研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 35(5):10-19.
|
|
LUO SHIHAO, JING ZHIYOU, QI YIQUAN, et al, 2016. Numerical study on sub-mesoscale processes in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 35(5):10-19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
张菀伦, 刘志亮, 王世红, 2017. 南黄海涡动能及其谱特征的季节性变化[J]. 海洋科学, 41(3):130-137.
|
|
ZHANG WANLUN, LIU ZHILIANG, WANG SHIHONG, 2017. Seasonal variations of eddy kinetic energy and its spectral characteristics in the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 41(3):130-137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
郑瑞玺, 经志友, 罗士浩, 2018. 南海北部反气旋涡旋边缘的次中尺度动力过程分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(3):19-25.
|
|
ZHENG RUIXI, JING ZHIYOU, LUO SHIHAO, 2018. Analysis of sub-mesoscale dynamic processes in the periphery of anticyclonic eddy in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(3):19-25 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
BOCCALETTI G, FERRARI R, FOX-KEMPER B, 2007. Mixed layer instabilities and restratification[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 37(9):2228-2250.
|
| [7] |
BRACCO A, LIU GUANGPENG, SUN DAOXUN, 2019. Mesoscale-submesoscale interactions in the Gulf of Mexico: From oil dispersion to climate[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 119:63-72.
|
| [8] |
CALLIES J, FERRARI R, KLYMAK J M, et al, 2015. Seasonality in submesoscale turbulence[J]. Nature Communications, 6(1):6862.
|
| [9] |
CAPET X, MCWILLIAMS J C, MOLEMAKER M J, et al, 2008a. Mesoscale to submesoscale transition in the California Current System. Part II: frontal processes[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 38(1):44-64.
|
| [10] |
CAPET X, MCWILLIAMS J C, MOLEMAKER M J, et al, 2008b. Mesoscale to submesoscale transition in the California Current System. Part III: energy balance and flux[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 38(10):2256-2269.
|
| [11] |
CHELTON D B, DESZOEKE R A, SCHLAX M G, et al, 1998. Geographical variability of the first baroclinic Rossby radius of deformation[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 28(3):433-460.
|
| [12] |
D’ASARO E, LEE C, RAINVILLE L, et al, 2011. Enhanced turbulence and energy dissipation at ocean fronts[J]. Science, 332(6027):318-322.
doi: 10.1126/science.1201515
pmid: 21393512
|
| [13] |
DUCET N, LE TRAON P Y, REVERDIN G, 2000. Global high - resolution mapping of ocean circulation from TOPEX/ Poseidon and ERS-1 and-2[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 105(C8):19477-19498.
|
| [14] |
FERRARI R, WUNSCH C, 2009. Ocean circulation kinetic energy: reservoirs, sources, and sinks[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 41:253-282.
|
| [15] |
GULA J, MOLEMAKER M J, MCWILLIAMS J C, 2016. Submesoscale dynamics of a Gulf Stream frontal eddy in the South Atlantic Bight[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(1):305-325.
|
| [16] |
GULA J, BLACIC T M, TODD R E, 2019. Submesoscale coherent vortices in the Gulf Stream[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(5):2704-2714.
|
| [17] |
LARGE W G, MCWILLIAMS J C, DONEY S C, 1994. Oceanic vertical mixing: a review and a model with a nonlocal boundary layer parameterization[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 32(4):363-403.
|
| [18] |
LEMARIÉ F, KURIAN J, SHCHEPETKIN A F, et al, 2012. Are there inescapable issues prohibiting the use of terrain-following coordinates in climate models?[J]. Ocean Modelling, 42:57-79.
|
| [19] |
MAHADEVAN A, 2016. The impact of submesoscale physics on primary productivity of plankton[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 8:161-184.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015912
pmid: 26394203
|
| [20] |
MCWILLIAMS J C, 2016. Submesoscale currents in the ocean[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 472(2189):20160117.
|
| [21] |
MENSA J A, GARRAFFO Z, GRIFFA A, et al, 2013. Seasonality of the submesoscale dynamics in the Gulf Stream region[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 63(8):923-941.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-013-0633-1
|
| [22] |
MOLEMAKER M J, MCWILLIAMS J C, DEWAR W K, 2015. Submesoscale instability and generation of mesoscale anticyclones near a separation of the California Undercurrent[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 45(3):613-629.
|
| [23] |
QIU BO, SCOTT R B, CHEN SHUIMING, 2008. Length scales of eddy generation and nonlinear evolution of the seasonally modulated South Pacific Subtropical Countercurrent[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 38(7):1515-1528.
|
| [24] |
QIU BO, CHEN SHUIMING, KLEIN P, et al, 2016. Reconstructability of three-dimensional upper-ocean circulation from SWOT sea surface height measurements[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(3):947-963.
|
| [25] |
RENAULT L, MCWILLIAMS J C, PENVEN P, 2017. Modulation of the Agulhas Current retroflection and leakage by oceanic current interaction with the atmosphere in coupled simulations[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 47(8):2077-2100.
|
| [26] |
RENAULT L, MCWILLIAMS J C, GULA J, 2018. Dampening of submesoscale currents by air-sea stress coupling in the Californian Upwelling System[J]. Scientific Reports, 8(1):13388.
pmid: 30190530
|
| [27] |
ROCHA C B, GILLE S T, CHERESKIN T K, et al, 2016. Seasonality of submesoscale dynamics in the Kuroshio Extension[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(21):11304-11311.
|
| [28] |
SASAKI H, KLEIN P, QIU BO, et al, 2014. Impact of oceanic- scale interactions on the seasonal modulation of ocean dynamics by the atmosphere[J]. Nature Communications, 5(1):5636.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6636
|
| [29] |
SASAKI H, KLEIN P, SASAI Y, et al, 2017. Regionality and seasonality of submesoscale and mesoscale turbulence in the North Pacific Ocean[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 67(9):1195-1216.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-017-1083-y
|
| [30] |
SCOTT R B, WANG FAMING, 2005. Direct evidence of an oceanic inverse kinetic energy cascade from satellite altimetry[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 35(9):1650-1666.
doi: 10.1175/JPO2771.1
|
| [31] |
SHCHERBINA A Y, D’ASARO E, LEE C M, et al, 2013. Statistics of vertical vorticity, divergence, and strain in a developed submesoscale turbulence field[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(17):4706-4711.
doi: 10.1002/grl.50919
|
| [32] |
THOMAS L N, TANDON A, MAHADEVAN A, 2008. Submesoscale processes and dynamics[M]// HECHT M W, HASUMI H. Ocean modeling in an eddying regime. American: American Geophysical Union: 17-38.
|
| [33] |
THOMAS L N, TAYLOR J R, FERRARI R, et al, 2013. Symmetric instability in the Gulf Stream[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 91:96-110.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.02.025
|
| [34] |
THOMPSON A F, LAZAR A, BUCKINGHAM C, et al, 2016. Open-ocean submesoscale motions: a full seasonal cycle of mixed layer instabilities from gliders[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(4):1285-1307.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-15-0170.1
|
| [35] |
ZHANG ZHENGGUANG, QIU BO, 2018. Evolution of Submesoscale Ageostrophic motions through the life cycle of oceanic Mesoscale Eddies[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(21):11847-11855.
doi: 10.1029/2018GL080399
|
| [36] |
ZHANG ZHENGGUANG, QIU BO, KLEIN P, et al, 2019. The influence of geostrophic strain on oceanic ageostrophic motion and surface chlorophyll[J]. Nature Communications, 10(1):2838.
pmid: 31253812
|
| [37] |
ZHANG ZHIWEI, TIAN JIWEI, QIU BO, et al, 2016. Observed 3D structure, generation, and dissipation of oceanic mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1):24349.
|
| [38] |
ZHANG ZHIWEI, ZHANG YUCHEN, QIU BO, et al, 2020. Spatiotemporal characteristics and generation mechanisms of submesoscale currents in the northeastern South China Sea revealed by numerical simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 152(2).
|
| [39] |
ZHONG YISEN, BRACCO A, TIAN JIWEI, et al, 2017. Observed and simulated submesoscale vertical pump of an anticyclonic eddy in the South China Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 7(1):44011.
|
 ), 经志友1, 闫桐1, 郑瑞玺1,2, 曹海锦3, 齐义泉3
), 经志友1, 闫桐1, 郑瑞玺1,2, 曹海锦3, 齐义泉3
 ), JING Zhiyou1, YAN Tong1, ZHENG Ruixi1,2, CAO Haijin3, QI Yiquan3
), JING Zhiyou1, YAN Tong1, ZHENG Ruixi1,2, CAO Haijin3, QI Yiquan3