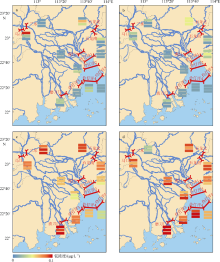
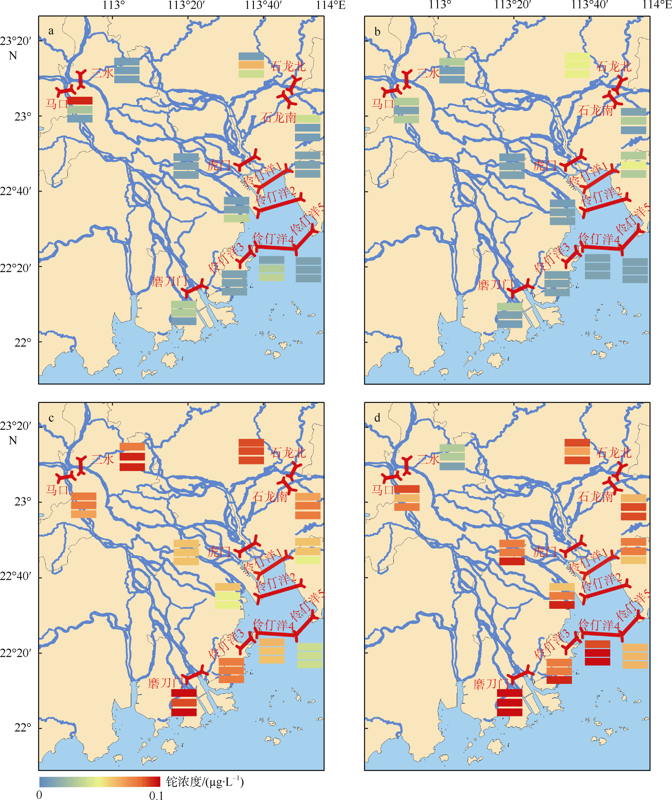
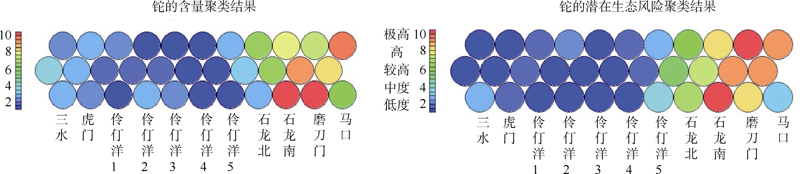
| [1] |
毕建培, 刘晨, 崔凡, 2019. 珠江流域重要饮用水水源地安全状况评估及对策研究[J]. 水利发展研究, 19(8):33-36, 61.
|
| [2] |
陈学鹏, 2009. 铊中毒的危害以及预防[J]. 现代职业安全, (2):104-105.
|
| [3] |
陈小齐, 余明辉, 刘长杰, 等, 2020. 珠江三角洲近年地形不均匀变化对洪季水动力特征的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 31(1):81-90.
|
|
CHEN XIAOQI, YU MINGHUI, LIU CHANGJIE, et al, 2020. Impact of recent uneven channel evolution on hydrodynamic characteristics during flood season in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Advances in Water Science, 31(1):81-90 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
陈永亨, 张平, 吴颖娟, 等, 2013. 广东北江铊污染的产生原因与污染控制对策[J]. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 12(4):26-31.
|
|
CHEN YONGHENG, ZHANG PING, WU YINGJUAN, et al, 2013. The reasons and the control technology for thallium pollution in Beijiang, Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 12(4):26-31 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
高博, 孙可, 任明忠, 等, 2008. 北江表层沉积物中铊污染的生态风险[J]. 生态环境, 17(2):528-532.
|
|
GAO BO, SUN KE, REN MINGZHONG, et al, 2008. Ecological risk assessment of thallium pollution in the surface sediment of Beijiang River[J]. Ecology and Environment, 17(2):528-532 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
广东省环境保护厅, 广东省质量技术监督局, 2017. DB 44/1989—2017 工业废水铊污染物排放标准[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电.
|
| [7] |
胡溪, 毛献忠, 2012. 珠江口磨刀门水道咸潮入侵规律研究[J]. 水利学报, 43(5):529-536.
|
|
HU XI, MAO XIANZHONG, 2012. Study on saltwater intrusion in Modaomen of the Pearl Estuary[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 43(5):529-536 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
解小凡, 刘娟, 王津, 等, 2015. 粤西河流表层沉积物重金属铊的环境地球化学特征及生态风险评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 45(增刊1):1509-06.
|
| [9] |
孔兰, 陈晓宏, 闻平, 等, 2011. 2009/2010年枯水期珠江口磨刀门水道强咸潮分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 26(11):1858-1865.
|
|
KONG LAN, CHEN XIAOHONG, WEN PING, et al, 2011. Analysis on severe saltwater intrusion in Modaomen channel of the Pearl River Estuary in dry season during 2009-2010[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 26(11):1858-1865 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
刘娟, 张平, 陈永亨, 等, 2008. 珠江柱状沉积物中铊化学形态的研究[J]. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 7(1):67-70.
|
|
LIU JUAN, ZHANG PING, CHEN YONGHENG, et al, 2008. Determination of thallium chemical form in sediment core from Pearl River[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 7(1):67-70 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
刘娟, 王津, 陈永亨, 等, 2015. 粤西某河流沉积物铊污染的铅同位素示踪研究[J]. 地质学报, 89(S1):278-279.
|
| [12] |
刘敬勇, 常向阳, 涂湘林, 等, 2010. 广东某硫酸废渣堆渣场周围土壤铊污染的地累积指数评价[J]. 土壤通报, 41(5):1231-1236.
|
|
LIU JINGYONG, CHANG XIANGYANG, TU XIANGLIN, et al, 2010. Applying the index geoaccumulation to assessment of soil thallium pollution in soil around a thallium-containing slag pile site near a sulphuric acid plant in Guangdong province[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 41(5):1231-1236 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
宋美英, 2014. 珠江河口水体和沉积物中重金属的分布特征及风险评估[D]. 广州: 暨南大学.
|
|
SONG MEIYING, 2014. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in water and sediments of the Pearl River Estuary[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
孙加龙, (2018-09-01). 粤港澳大湾区水环境整治的思路及对策研究[EB/OL]. http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_539f650f01030uo9.html. SUN JIALONG. (2018-09-01).
|
| [15] |
唐天均, 2018. 粤港澳湾区水环境保护对策和建议[J]. 广东化工, 45(2):153-154.
|
|
TANG TIANJUN, 2018. Measures and suggestions of water environment protection in Guangdong- Hong Kong-Macao greater bay area[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 45(2):153-154 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
万军, 李新, 关杨, 等, 2019. 坚持共保共享绿色发展建设粤港澳美丽大湾区[J]. 环境保护, 47(7):8-11.
|
|
WAN JUN, LI XIN, GUAN YANG, et al, 2019. Strive for collaborative protecting, shared growth and green development, build a beautiful bay area of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao[J]. Environmental Protection, 47(7):8-11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
中华人民共和国卫生部, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2007. GB 5749-2006 生活饮用水卫生标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
| [18] |
朱金格, 包芸, 胡维平, 等, 2010. 近50年来珠江河网区水动力对地形的响应[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 49(4):129-133.
|
|
ZHU JINGE, BAO YUN, HU WEIPING, et al, 2010. Impact of channel evolution on hydrodynamics in the Pearl River Delta in the last 50 years[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 49(4):129-133 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
BANKS D, REIMANN C, RØYSET O, et al, 1995. Natural concentrations of major and trace elements in some Norwegian bedrock groundwaters[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 10(1):1-16.
doi: 10.1016/0883-2927(94)00046-9
|
| [20] |
CHEAM V, LAWSON G, LECHNER J, et al, 1996. Thallium and cadmium in recent snow and firn layers in the Canadian Arctic by atomic fluorescence and absorption spectrometries[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 355(3-4):332-335.
|
| [21] |
CLEVEN R, FOKKERT L, 1994. Potentiometric stripping analysis of thallium in natural waters[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 289(2):215-221.
doi: 10.1016/0003-2670(94)80105-3
|
| [22] |
DALL'AGLIO M, FORNASERI M, BRONDI M, 1994. New data on thallium in rocks and natural waters from central and southern Italy: Insights into applications[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 37:103-112.
|
| [23] |
FLEGAL A R, PATTERSON C C, 1985. Thallium concentrations in seawater[J]. Marine Chemistry, 15(4):327-331.
doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(85)90043-X
|
| [24] |
HAKANSON L, 1980. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8):975-1001.
doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
|
| [25] |
KASKI S, VENNA J, KOHONEN T, 1992. Coloring that reveals high-dimensional structures in data[C]// Proceedings of the 6th international conference on neural information processing. Perth, WA, Australia: IEEE, 2:729-734.
|
| [26] |
KOHONEN T, 2001. Self-organizing maps[M]. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer.
|
| [27] |
LIN T S, NRIAGU J, 1999. Thallium speciation in the Great Lakes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(19):3394-3397.
doi: 10.1021/es981096o
|
| [28] |
LUO F, 1994. Determination of sub-ppb levels of thallium in natural water by STPF AAS after preconcentration using a polyerethane plastic foam column[J]. Atomic Spectroscopy, (15):216-219.
|
| [29] |
MÜLLER B, BERG M, YAO ZHIPING, et al, 2005. How polluted is the Yangtze River? Water quality downstream from the Three Gorges Dam[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 402(2-3):232-247.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.04.049
|
| [30] |
QU BIN, SILLANPÄÄ M, ZHANG YULAN, et al, 2015. Water chemistry of the headwaters of the Yangtze River[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(8):6443-6458.
doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4174-4
|
 ), 利锋1, 张超1, 董汉英2(
), 利锋1, 张超1, 董汉英2( ), 杨清书3, 余明辉4, 文汝兵1, 杨玉洁1
), 杨清书3, 余明辉4, 文汝兵1, 杨玉洁1
 ), LI Feng1, ZHANG Chao1, DONG Hanying2(
), LI Feng1, ZHANG Chao1, DONG Hanying2( ), YANG Qingshu3, YU Minghui4, WEN Rubing1, YANG Yujie1
), YANG Qingshu3, YU Minghui4, WEN Rubing1, YANG Yujie1