热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 47-62.doi: 10.11978/2022174CSTR: 32234.14.2022174
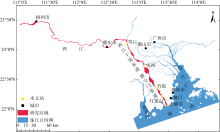
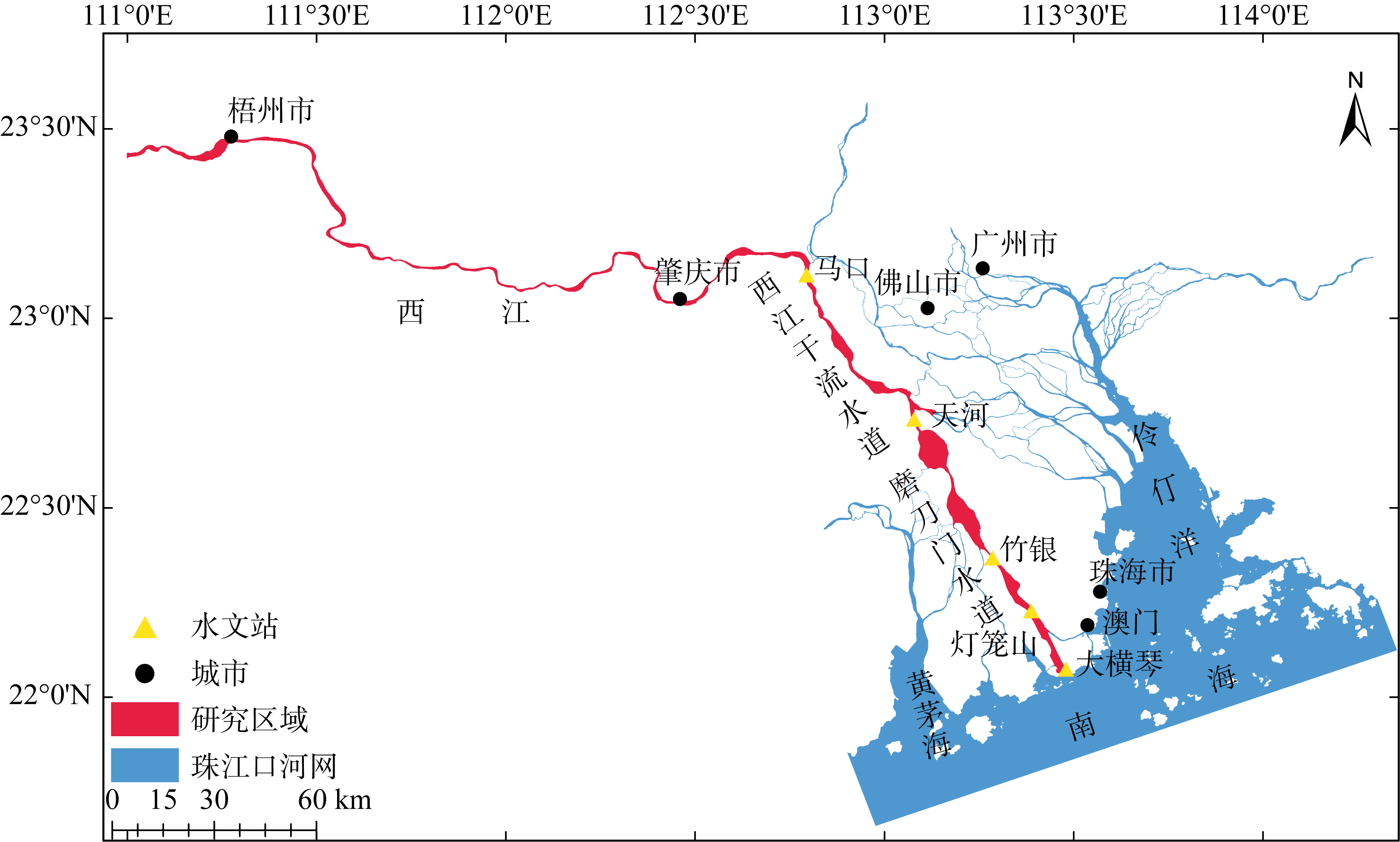
西江感潮河道(马口—磨刀门)的潮波传播特征研究
武家兴1,2,3( ), 王浩丞1,2,3, 张璐1,2,3, 张卓1,2,3(
), 王浩丞1,2,3, 张璐1,2,3, 张卓1,2,3( ), 陈鹏1,2,3, 李玉婷1,2,3
), 陈鹏1,2,3, 李玉婷1,2,3
- 1.南京师范大学, 虚拟地理环境教育部重点实验室, 江苏 南京 210023
2.江苏省地理信息资源开发与利用协同创新中心, 江苏 南京 210023
3.江苏省大规模复杂系统数值模拟重点实验室, 江苏 南京 210023
-
收稿日期:2022-08-03修回日期:2022-09-16出版日期:2023-07-10发布日期:2022-09-21 -
作者简介:武家兴(1996—), 男, 安徽省肥西县人, 硕士研究生, 从事河口海岸动力学研究。email: Wujx06@126.com
-
基金资助:水利部水旱灾害防御重点实验室开放基金(KYFB202112010704); 国家自然科学基金(42171465)
Investigation into the tidal propagation features along the tidal reach of the West River (Makou — Modaomen)
WU Jiaxing1,2,3( ), WANG Haocheng1,2,3, ZHANG Lu1,2,3, ZHANG Zhuo1,2,3(
), WANG Haocheng1,2,3, ZHANG Lu1,2,3, ZHANG Zhuo1,2,3( ), CHEN Peng1,2,3, LI Yuting1,2,3
), CHEN Peng1,2,3, LI Yuting1,2,3
- 1. Key Laboratory of Virtual Geographic Environment, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, China
2. Jiangsu Center for Collaborative Innovation in Geographical Information Resource Development and Application, Nanjing 210023, China
3. Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Numerical Simulation of Large Scale Complex Systems, Nanjing 210023, China
-
Received:2022-08-03Revised:2022-09-16Online:2023-07-10Published:2022-09-21 -
Supported by:Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Water and Drought Disaster Defense, Ministry of Water Resources(KYFB202112010704); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42171465)
摘要:
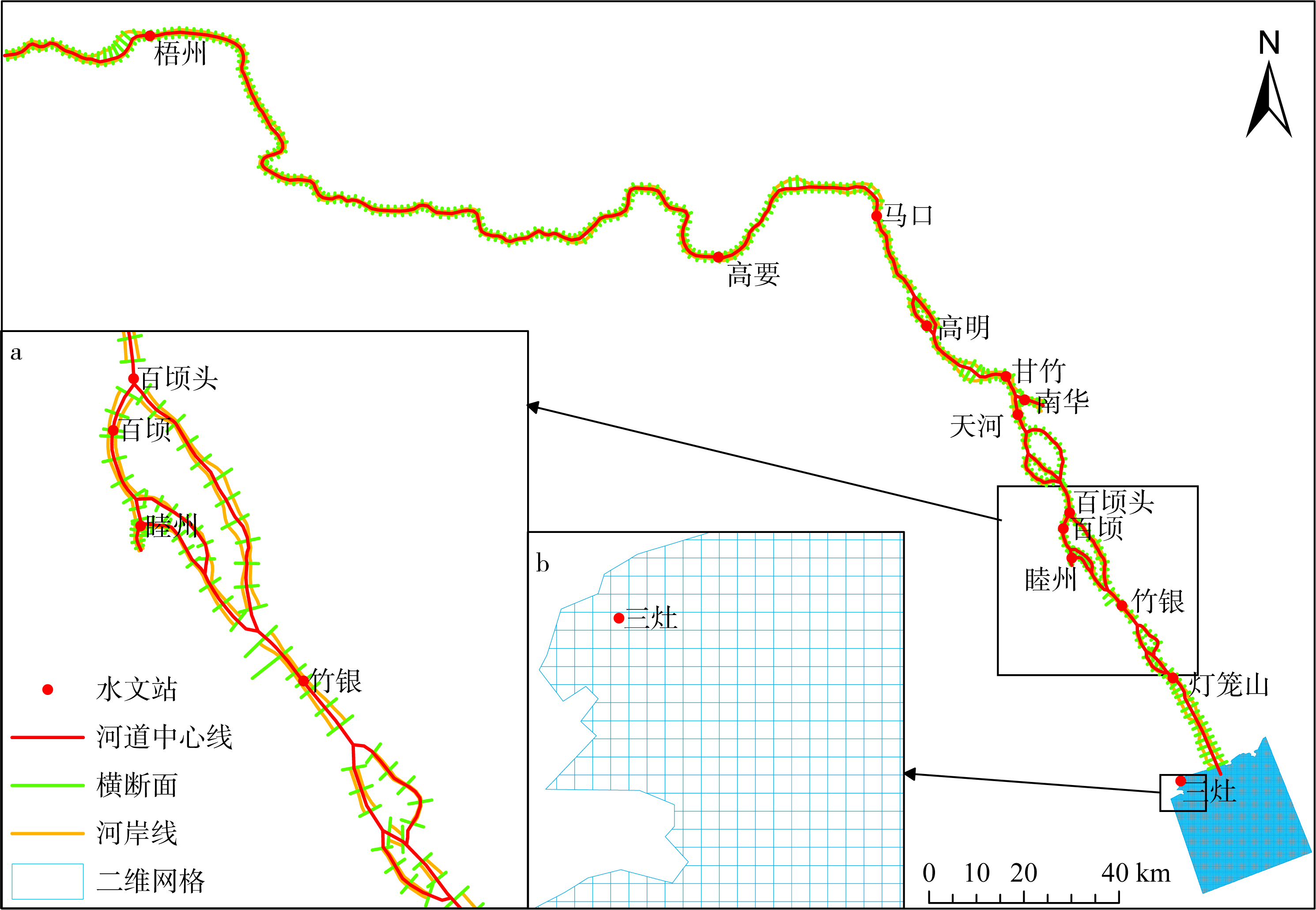
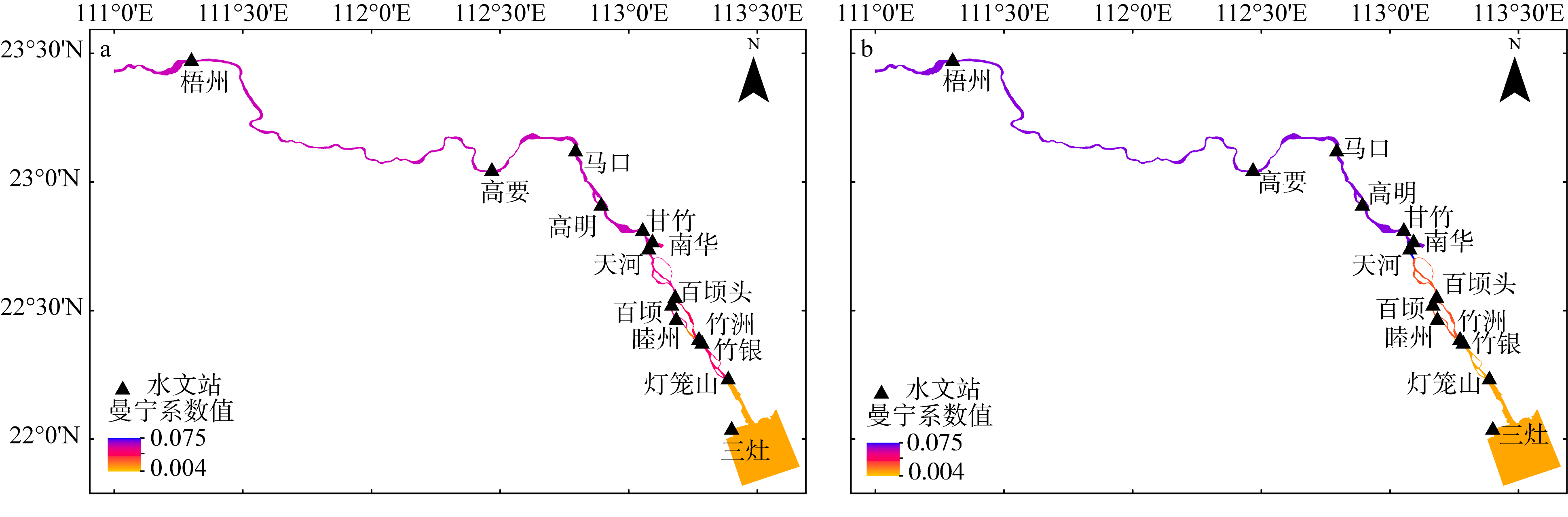
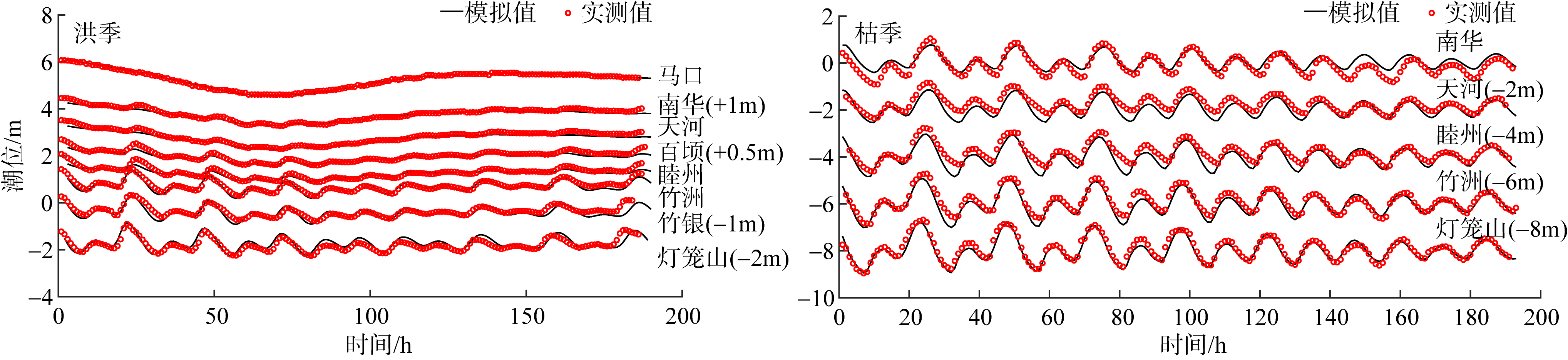
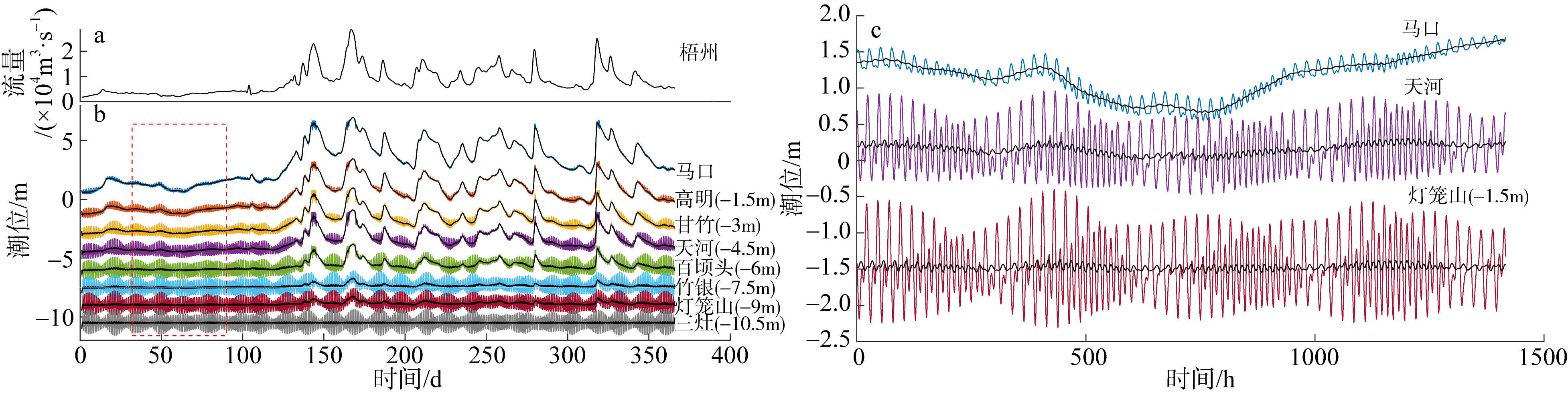
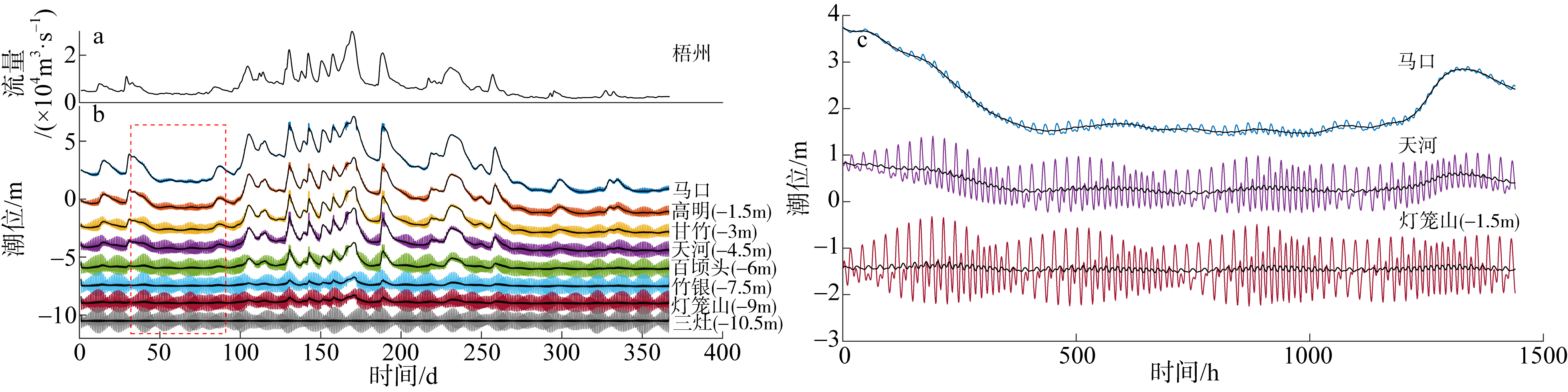
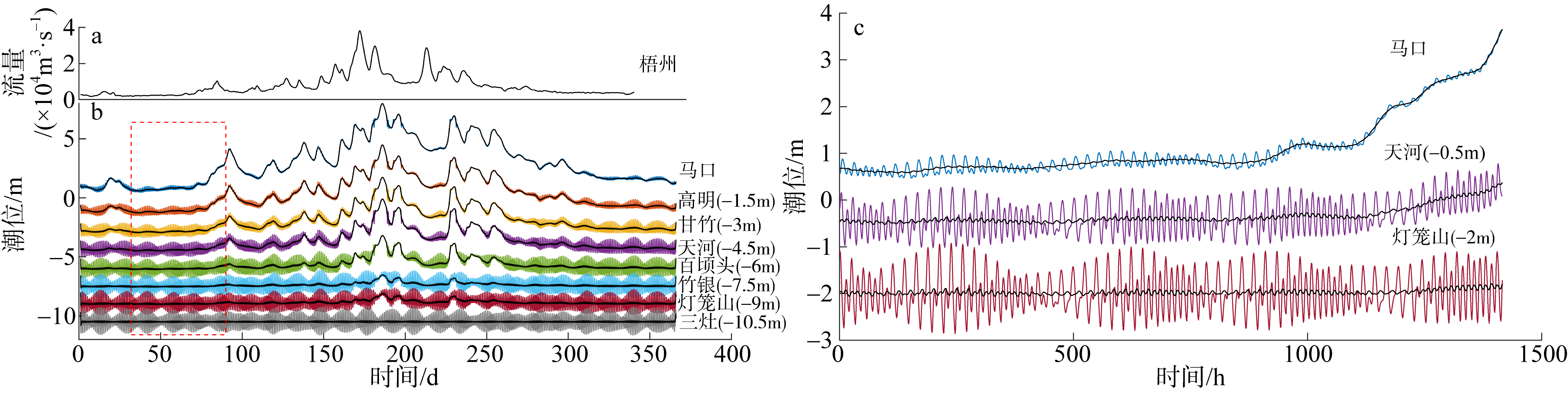
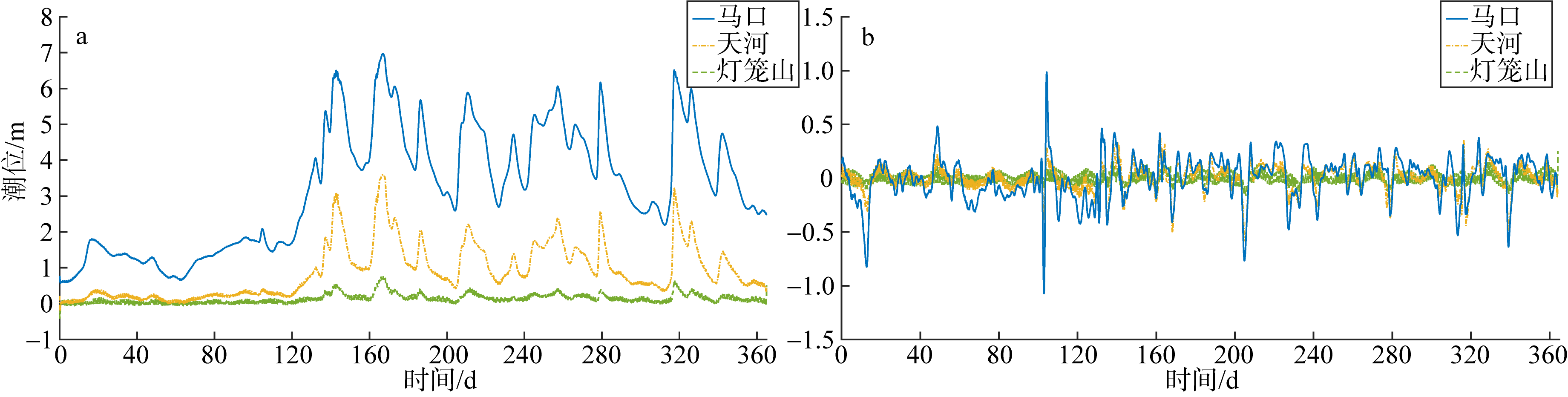
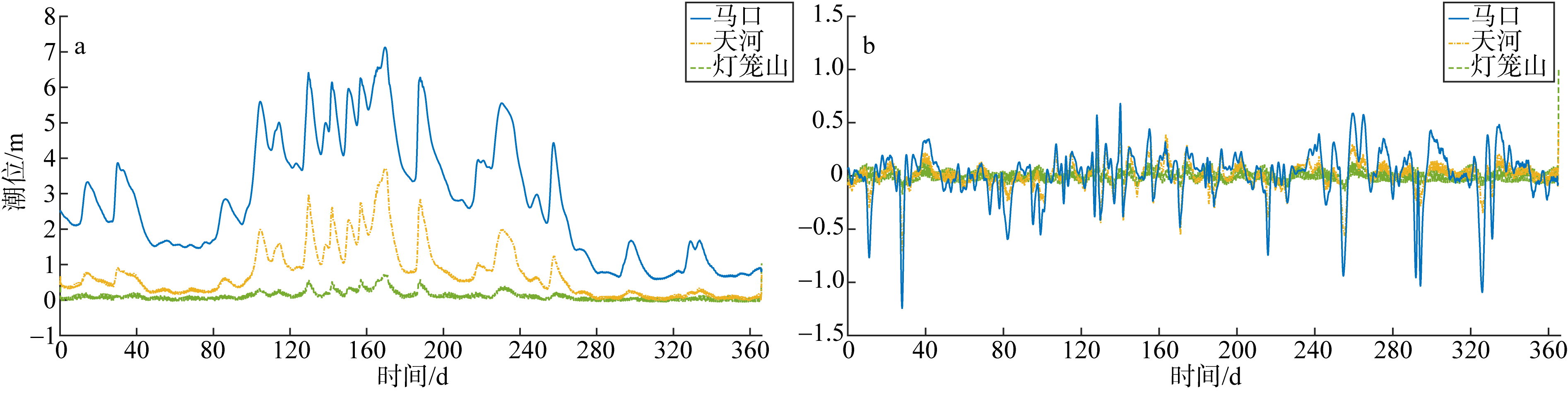
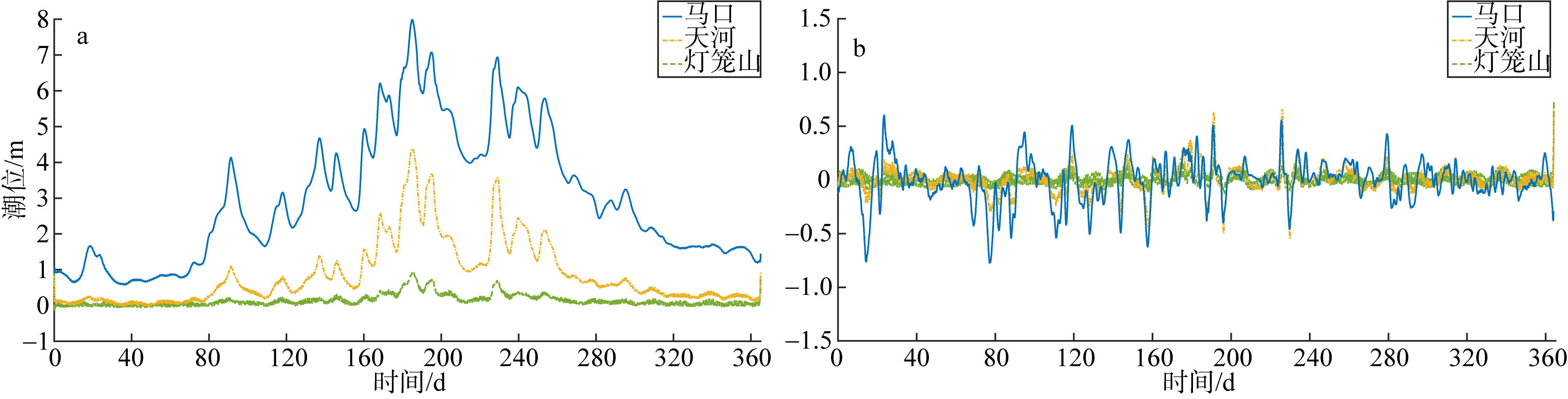
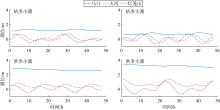
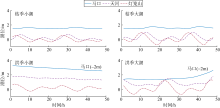
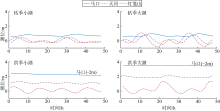
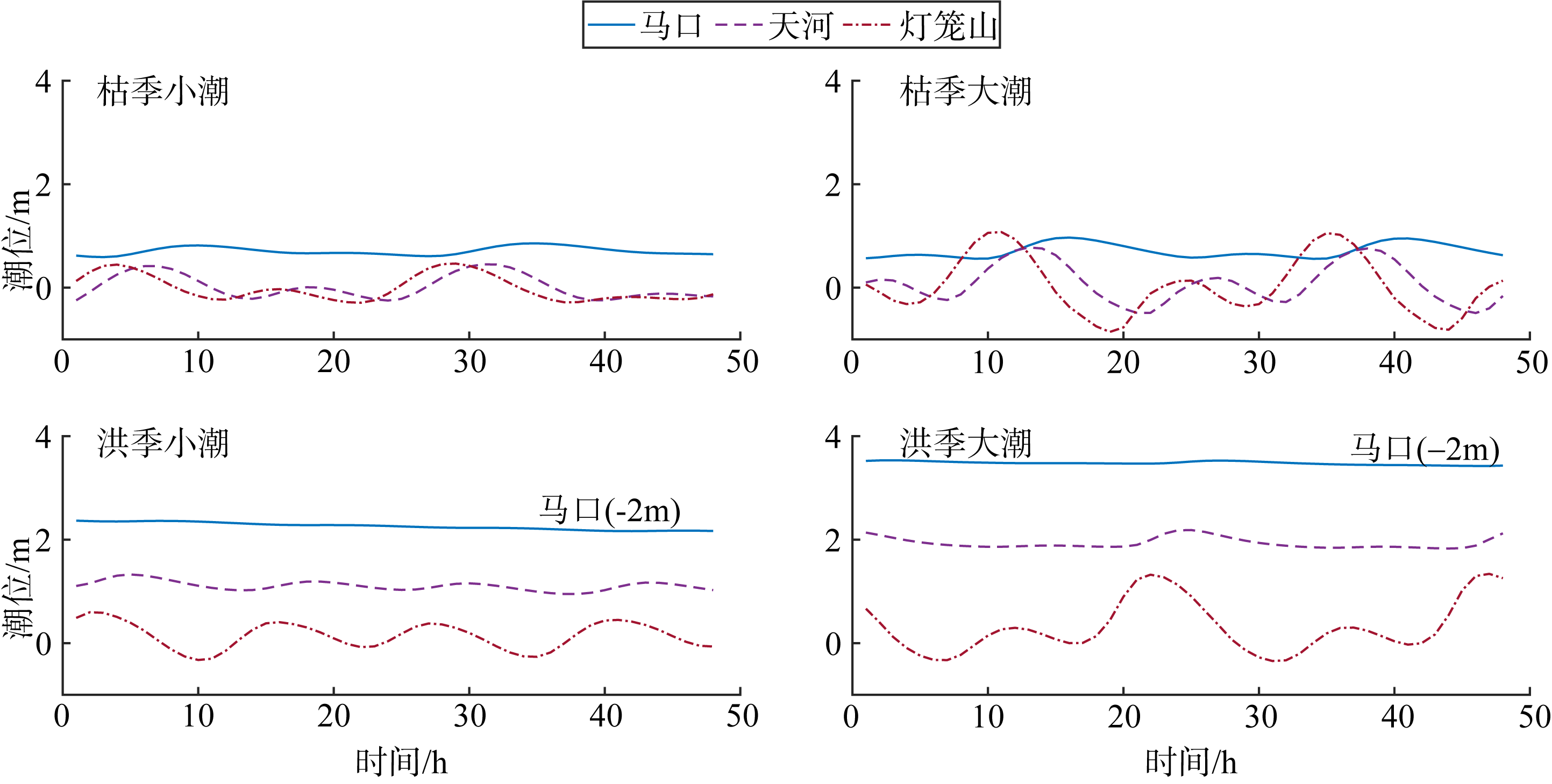
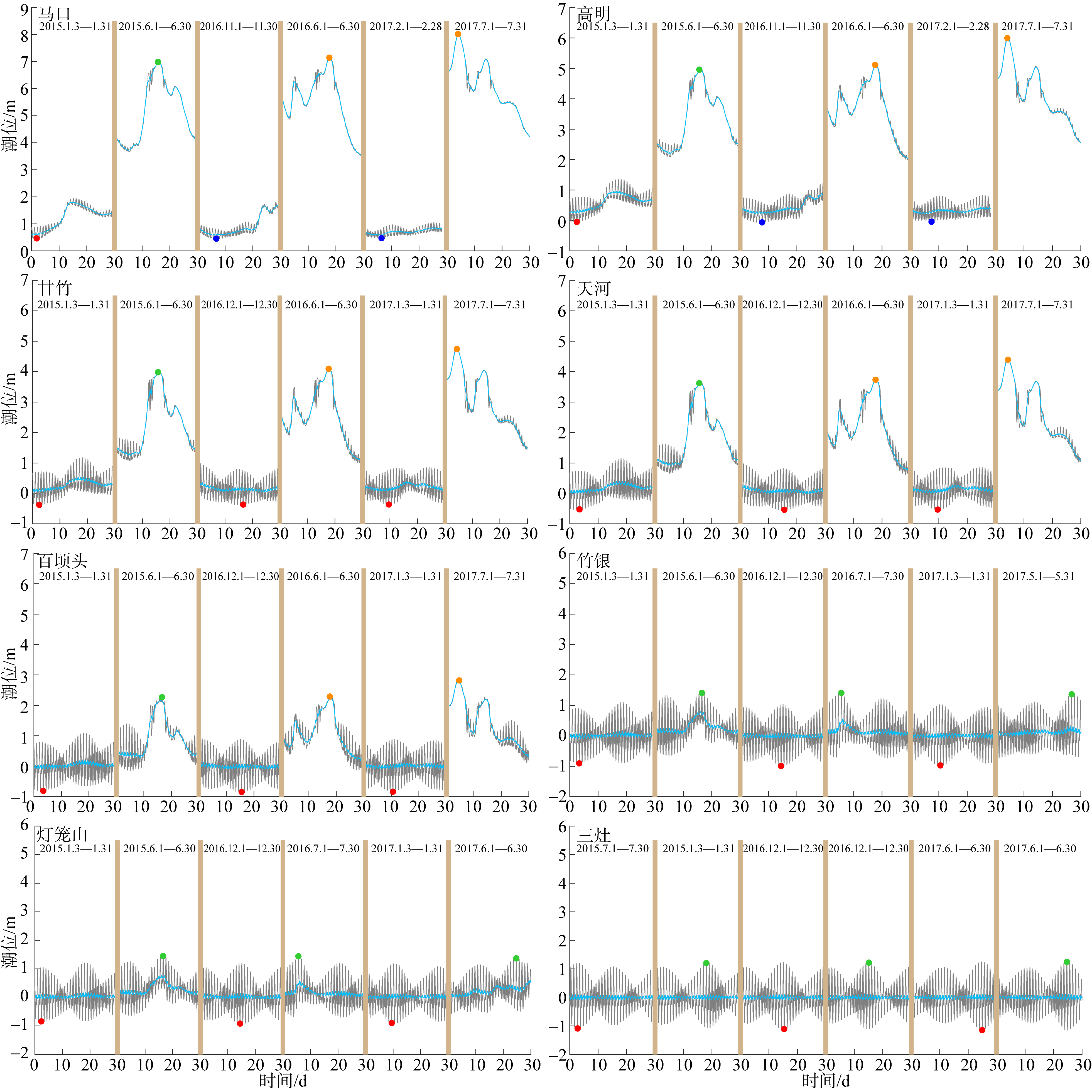
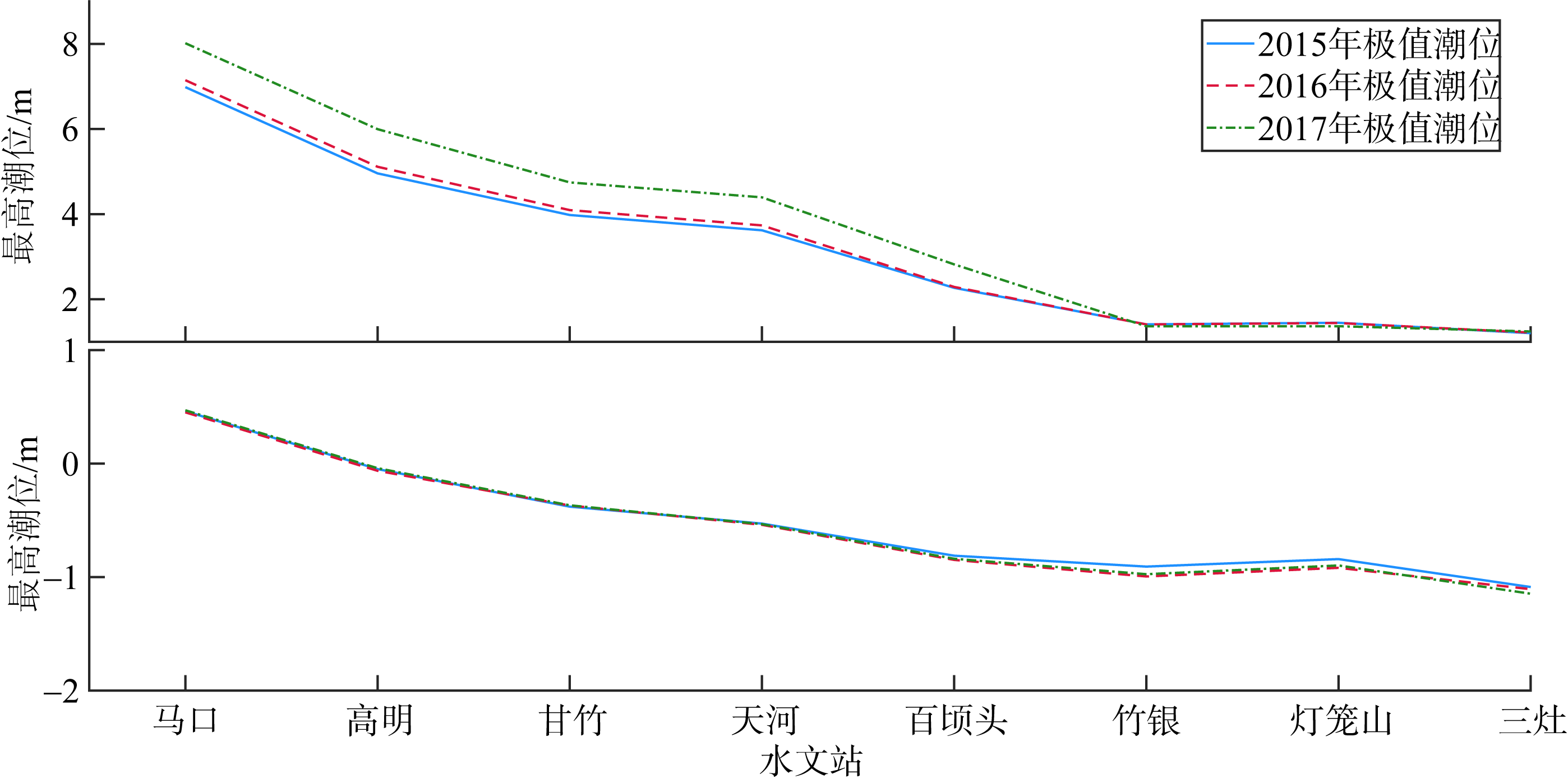
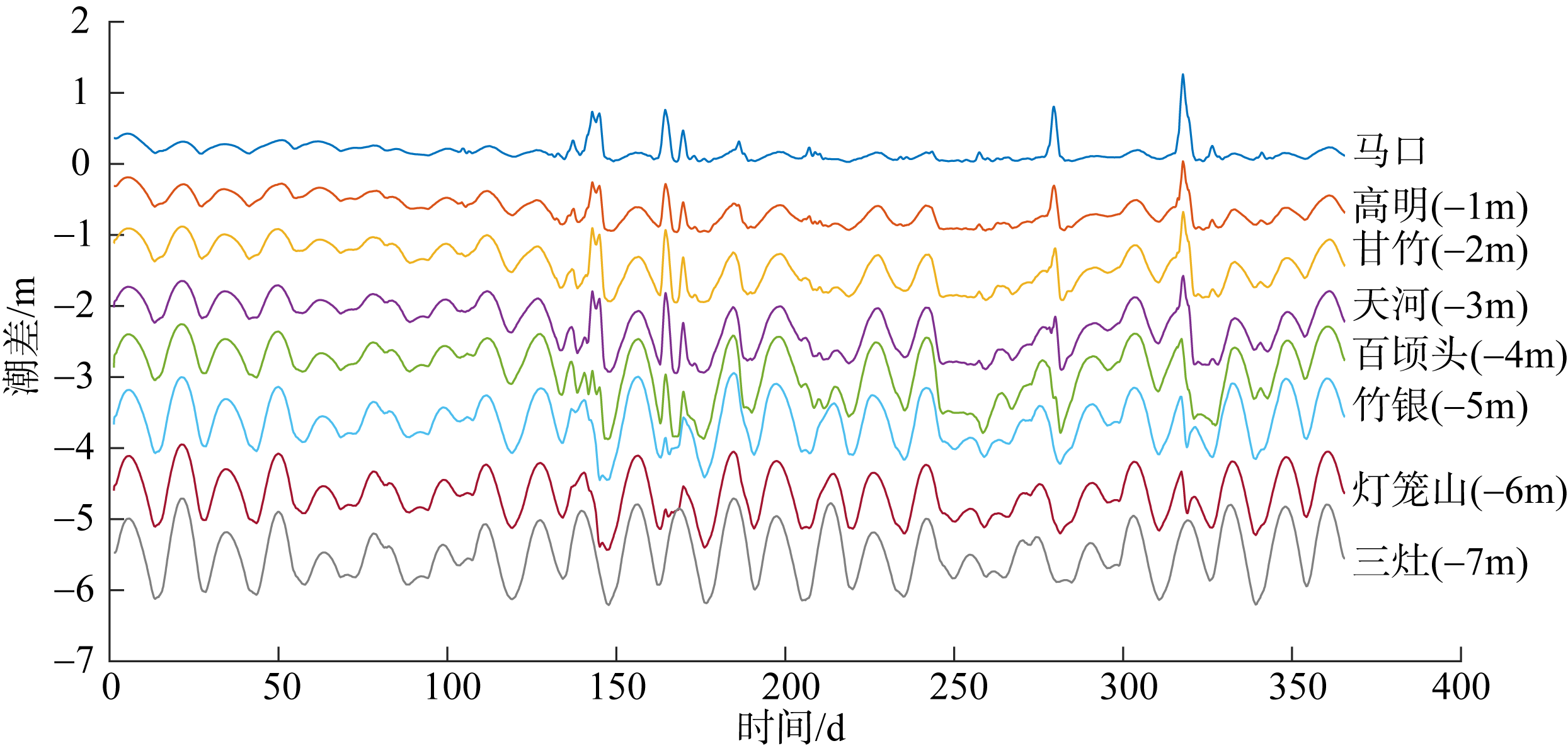
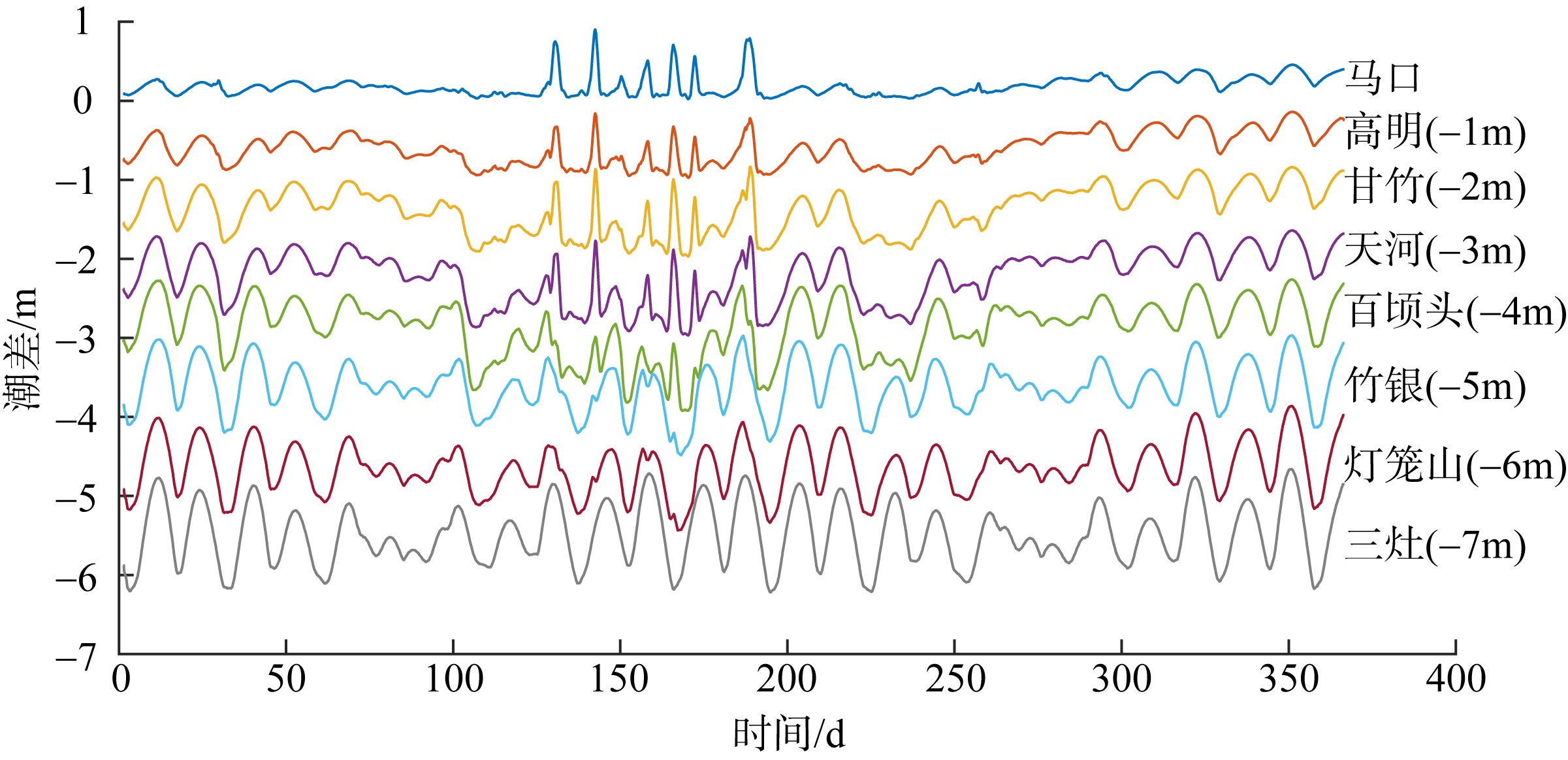
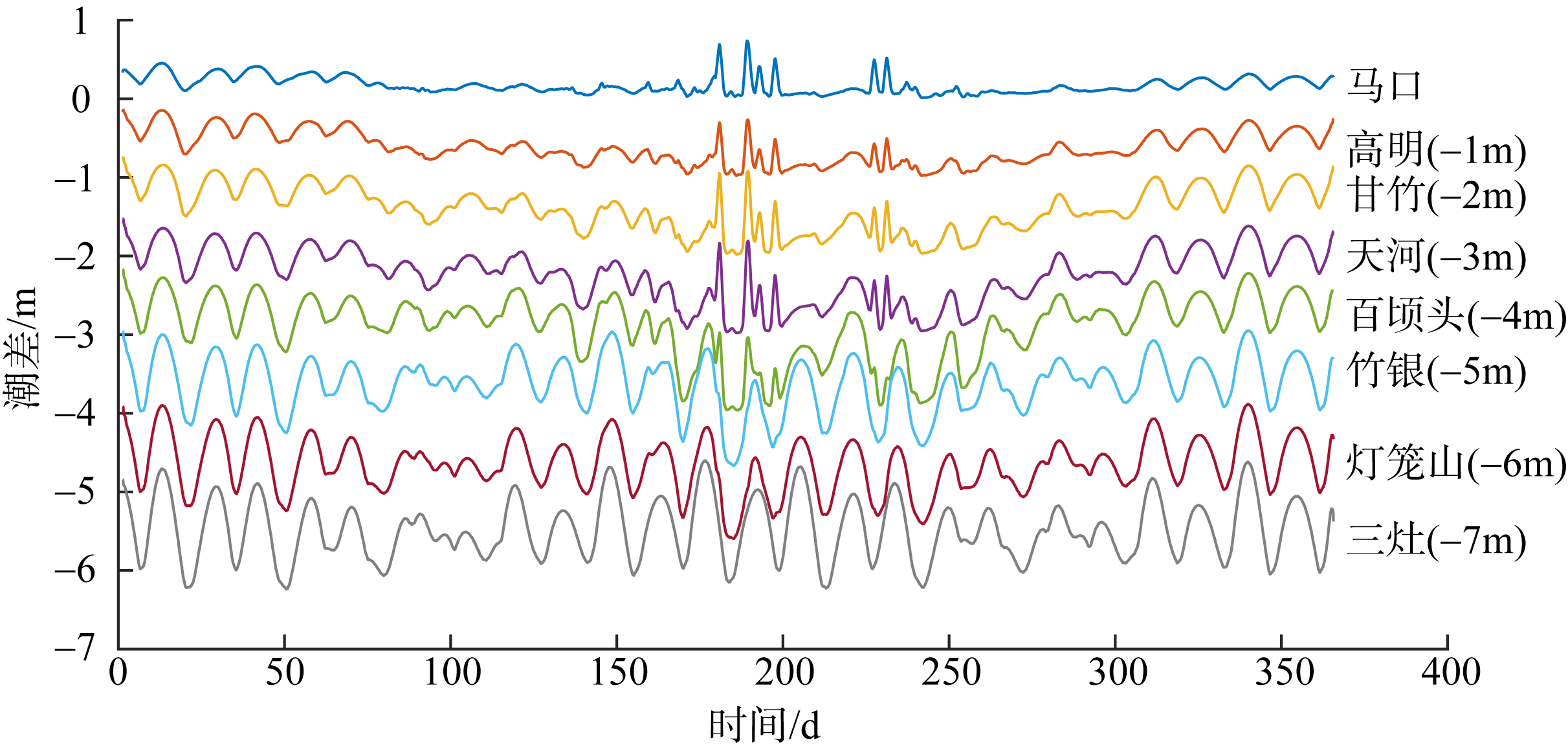
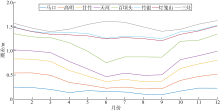
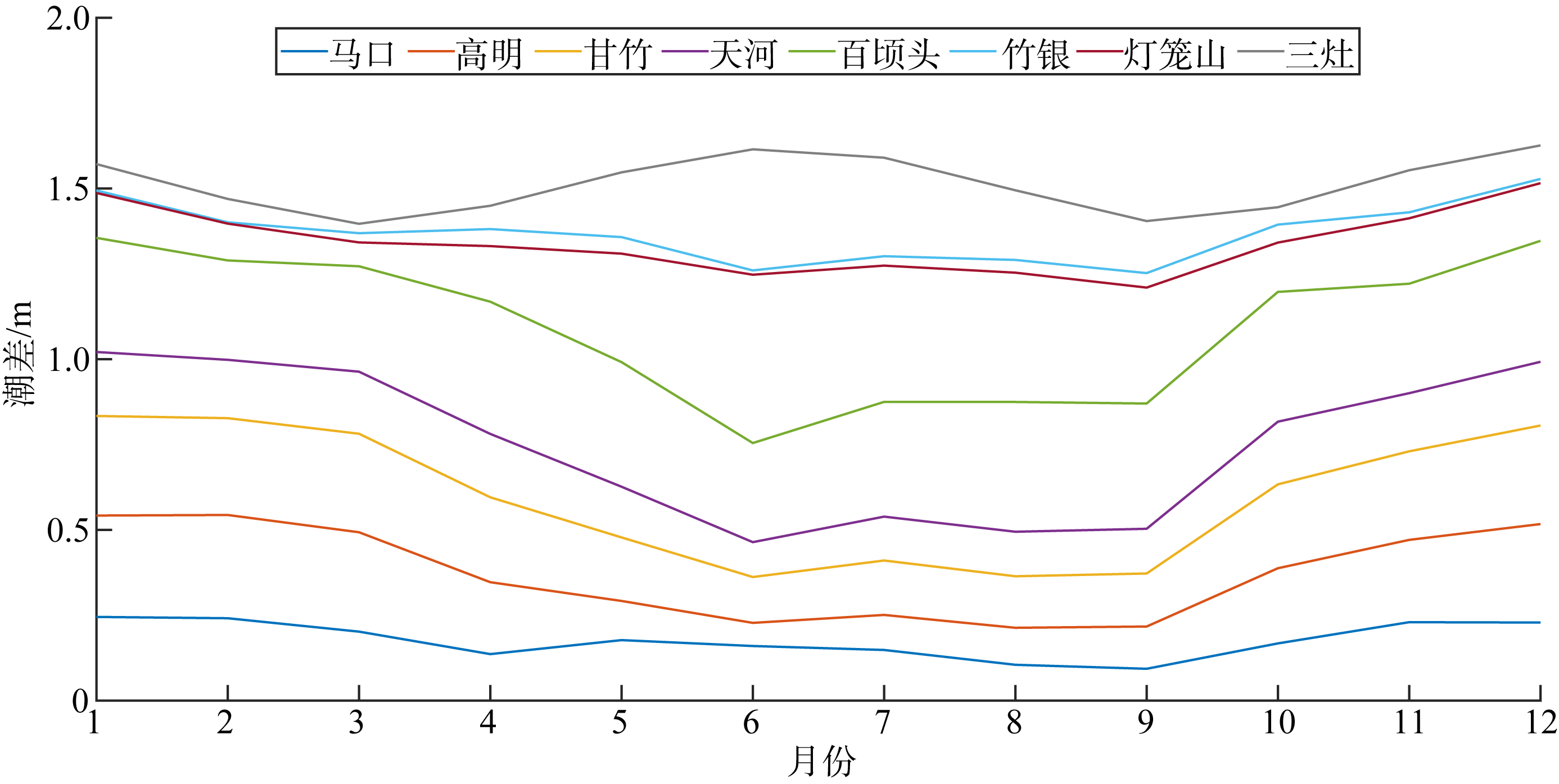
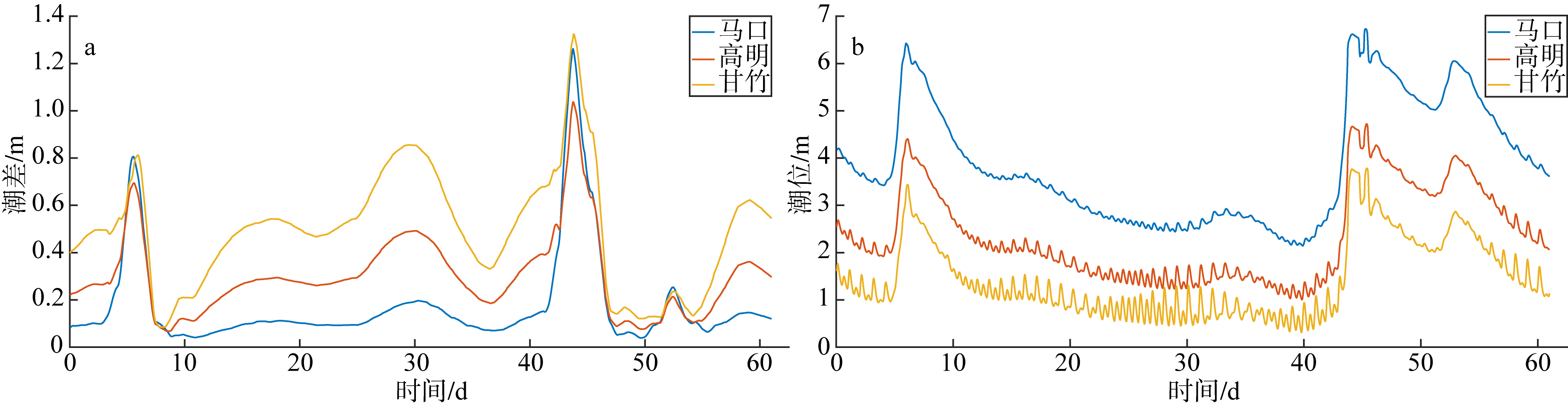
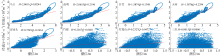
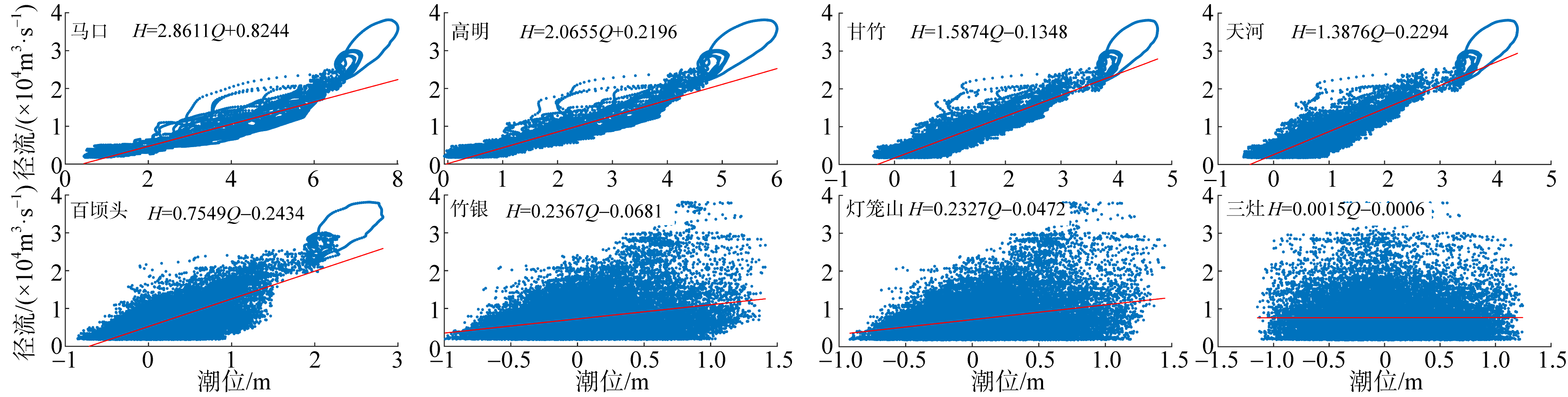
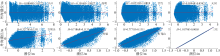
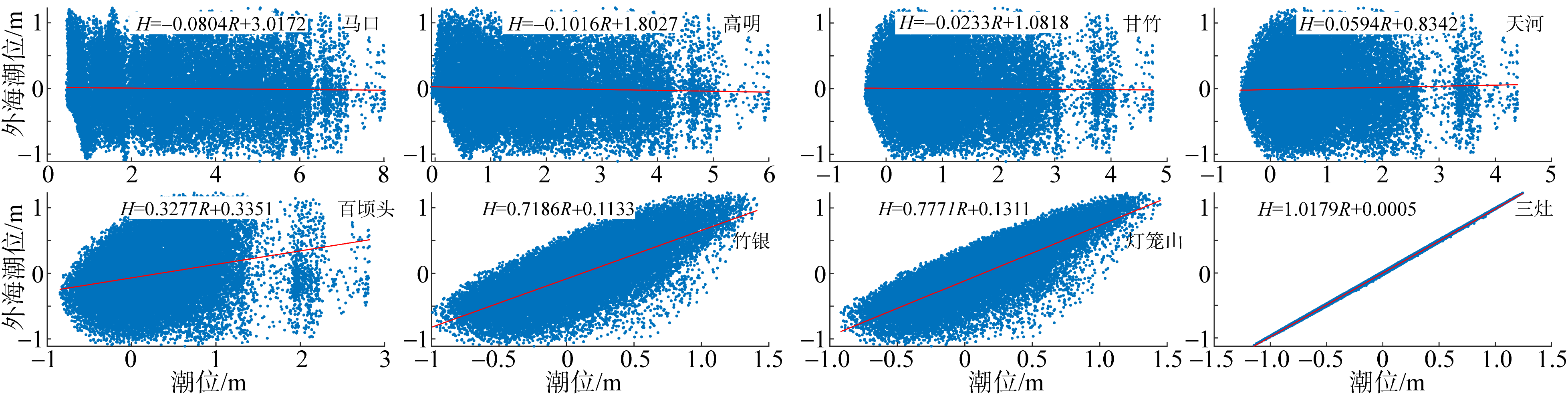
基于2015—2017年梧州站逐日流量时间序列, 应用一维、二维耦合数值模型, 并考虑曼宁系数的洪枯季变化, 模拟了西江感潮河道(马口—磨刀门)潮位的时空变化, 研究了潮波从河口向河道上游传播过程中的潮波变形特征、潮位极值点的时空分布以及潮差的沿程衰减特征。结果表明, 河道水位受径流影响有明显的洪枯季特征; 日均水位呈现大小潮期间的半月周期变化, 半月变化沿河道上溯逐渐增大, 说明外海潮波以一种半月低频分潮的形式向河道上游传播; 受径流影响, 潮汐不对称特征越往上游越明显, 涨潮历时和落潮历时的差异往上游递增。各个水文站的极值潮位受径流影响往上游呈递增趋势, 且在外海潮汐的作用下多发生在大潮期间。河道内潮差从下游往上游呈递减趋势, 季节差异显著, 下游的灯笼山和三灶站有明显的半年周期特征。
引用本文
武家兴, 王浩丞, 张璐, 张卓, 陈鹏, 李玉婷. 西江感潮河道(马口—磨刀门)的潮波传播特征研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 47-62.
WU Jiaxing, WANG Haocheng, ZHANG Lu, ZHANG Zhuo, CHEN Peng, LI Yuting. Investigation into the tidal propagation features along the tidal reach of the West River (Makou — Modaomen)[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 47-62.
| [1] |
蔡华阳, 杨昊, 郭晓娟, 等, 2018. 珠江磨刀门河口径潮动力耦合条件下余水位的多时空尺度分析[J]. 海洋学报, 40(7): 55-65.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
方新, 2014. 长江感潮河段水位过程预报模型研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
龚文平, 刘欢, 任杰, 等, 2012. 黄茅海河口潮波的传播特征与机理研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 34(3): 41-54.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
郭磊城, 朱春燕, 何青, 等, 2017. 长江河口潮波时空特征再分析[J]. 海洋通报, 36(6): 652-661.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
洪鹏锋, 杜文印, 2019. 强人类活动驱动下珠江磨刀门河口潮汐动力增强原因初探[J]. 人民珠江, 40(9): 28-32.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
黄竞争, 张先毅, 吴峥, 等, 2020. 长江感潮河段潮波传播变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 海洋学报, 42(3): 25-35.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
蒋陈娟, 周佳楠, 杨清书, 2020. 珠江磨刀门河口潮汐动力变化对人类活动的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(6): 66-76.
doi: 10.11978/2019137 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2019137 |
|
| [8] |
赖锡军, 姜加虎, 黄群, 2008. 洞庭湖地区水系水动力耦合数值模型[J]. 海洋与湖沼, (1): 74-81.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李传奇, 侯贵兵, 2010. 一维二维水动力模型耦合的城市洪水模拟[J]. 水利水电技术, 41(3): 83-85.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
路川藤, 2009. 长江口潮波传播[D]. 南京: 南京水利科学研究院.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
路川藤, 罗小峰, 陈志昌, 2010. 长江口不同径流量对潮波传播的影响[J]. 人民长江, 41(12): 45-48.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
马玉婷, 蔡华阳, 杨昊, 等, 2022. 珠江磨刀门河口水位分布演变特征及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(2): 52-64.
doi: 10.11978/2021072 |
|
|
|
| [13] |
欧素英, 田枫, 郭晓娟, 等, 2016. 珠江三角洲径潮相互作用下潮能的传播和衰减[J]. 海洋学报, 38(12): 1-10.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
欧素英, 杨清书, 杨昊, 等, 2017. 河口三角洲径流和潮汐相互作用模型及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(5): 1-8.
doi: 10.11978/2016131 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2016131 |
|
| [15] |
秦莉真, 张蔚, 官明开, 等, 2019. 不同周期分潮簇对复杂河网潮位分布的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(1): 27-34.
doi: 10.11978/2018044 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2018044 |
|
| [16] |
宋永港, 朱建荣, 吴辉, 2011. 长江河口北支潮位与潮差的时空变化和机理[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (6): 10-19.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
宋云平, 朱建荣, 2021. 长江口余水位时空变化的数值模拟和分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (4): 121-133.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
唐启邦, 欧素英, 蔡华阳, 等, 2020. 珠江磨刀门河口水位与海平面、上游流量的联合分布关系异变研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(5): 1080-1092.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
童朝锋, 司家林, 张蔚, 等, 2020. 伶仃洋洪季潮波传播变形及不对称性规律分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(1): 36-52.
doi: 10.11978/2019061 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2019061 |
|
| [20] |
王彪, 朱建荣, 李路, 2011. 长江河口涨落潮不对称性动力成因分析[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 33(3): 19-27.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
王文才, 李一平, 杜薇, 等, 2017. 长江感潮河段潮汐变化特征[J]. 水资源保护, 33(6): 121-124.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
谢梅芳, 张萍, 杨昊, 等, 2021. 珠江“伶仃洋河口湾—虎门—潮汐通道”的潮波传播特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(4): 1-13.
doi: 10.11978/2020076 |
|
|
|
| [23] |
杨昊, 欧素英, 傅林曦, 等, 2020. 珠江磨刀门河口日均水位变化及影响因子辨识[J]. 水利学报, 51(7): 869-881.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
杨明远, 严以新, 孔俊, 等, 2008. 珠江口水流泥沙运动模拟研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [25] |
杨易, 贺涛, 2021. 近年珠江三角洲洪季余水位和潮差的演变特征研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, (7): 19-23.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
杨正东, 朱建荣, 王彪, 等, 2012. 长江河口潮位站潮汐特征分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (3): 111-119.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
袁小婷, 2019. 近40年长江河口潮汐动力变化特征[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
袁小婷, 程和琴, 郑树伟, 等, 2019. 近期长江大通至南京河段潮动力变化趋势与机制[J]. 海洋通报, 38(5): 553-561.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
张大伟, 李丹勋, 陈稚聪, 等, 2010. 溃堤洪水的一维、二维耦合水动力模型及应用[J]. 水力发电学报, 29(2): 149-154.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
张赛赛, 2019. 长江口潮差的时空变化及其环境意义[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
张先毅, 杨昊, 黄竞争, 等, 2020. 强人类活动驱动下珠江磨刀门河口径潮动力的季节性异变特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(5): 1043-1054.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
周倩倩, 苏炯恒, 梅胜, 等, 2019. 1D/1D及1D/2D耦合水动力模型构建方法研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 30(5): 21-25.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000594 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2020.103634 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1007/s12237-014-9819-0 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124701 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1002/2014JC009791 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.06.007 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20297 |
| [1] | 谢梅芳, 张萍, 杨昊, 傅林曦, 王恒, 蔡华阳, 杨清书. 珠江“伶仃洋河口湾-虎门-潮汐通道”的潮波传播特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(4): 1-13. |
|
||