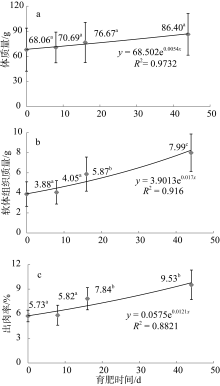
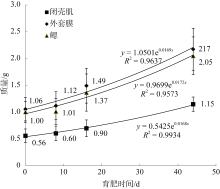
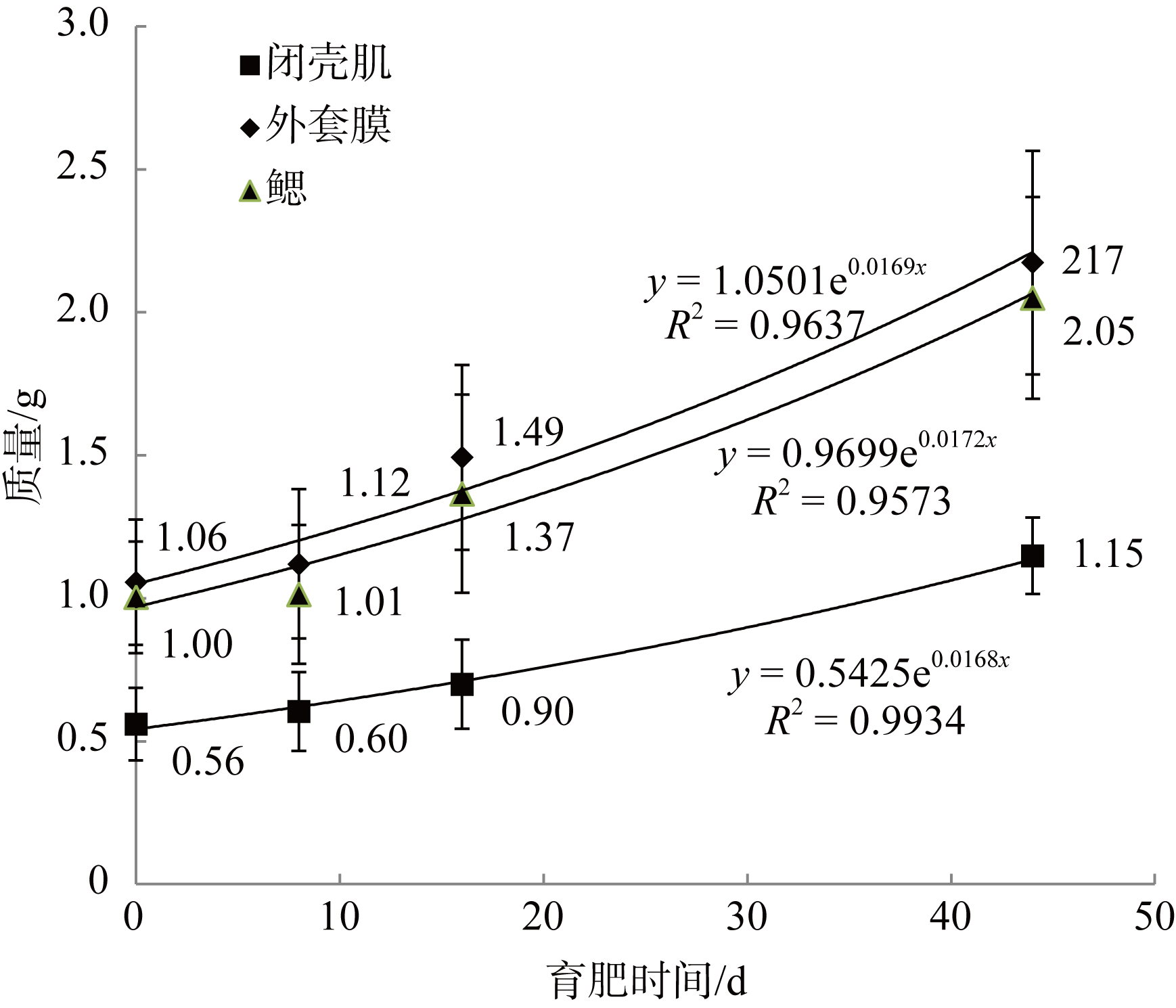
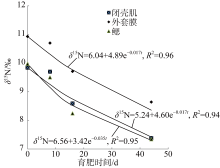
| [1] |
白富进, 2010. 湛江港近江牡蛎中碳氮同位素时空分布及其对无机氮响应的初步研究[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学: 5-6.
|
|
BAI FUJIN, 2010. Preliminary study the spatial and temporal distribution of carbon and nitrogen isotope in Ostrea rivularis Gould and the response to inorganic nitrogen, Zhanjiang Harbor[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University: 5-6 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
才让卓玛, 2015. 香港牡蛎产地溯源指纹信息筛选的研究[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学: 4-5.
|
|
CAIYANG ZHUOMA, 2015. Study on the screening of fingerprint information for geographical origin traceability of Crassostrea hongkongensis[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University: 4-5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
贾真, 佘智彩, 彭业韶, 等, 2019. 香港牡蛎不同育肥方式的育肥效果[J]. 水产科学, 38(4): 514-520.
|
|
JIA ZHEN, SHE ZHICAI, PENU YESHAO, et al, 2019. Effects of Hongkong oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis fattening in onshore ponds and in offshore sea[J]. Fisheries Science, 38(4): 514-520 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
刘小琳, RUTAKUMWA E S, 徐靖昂, 等, 2021. 舟山外海重要海洋动物的碳氮稳定同位素特征和食物网营养结构[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 40(5): 415-423.
|
|
LIU XIAOLIN, RUTAKUMWA E S, XU JINGANG, et al, 2021. Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope characteristics and nutrient structure of food web of important marine animals near Zhoushan islands[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University(Natural Science), 40(5): 415-423 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
陆亚楠, 张瑞, 张虎, 等, 2022. 应用稳定同位素技术研究江苏近海食物网营养结构的季节性变化[J]. 海洋学报, 44(2): 1-10.
|
|
LU YANAN, ZHANG RUI, ZHANG HU, et al, 2022. Seasonal variation in the trophic structure of food webs in coastal waters of Jiangsu Province based on stable isotope techniques[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 44(2): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
潘英, 李坚明, 黄伟德, 等, 2021. 广西牡蛎产业现状分析及发展策略[J]. 南方农业学报, 52(9): 2608-2618.
|
|
PAN YING, LI JIANMING, HUANG WEIDE, et al, 2021. Analysis of current situations, existing problems of oyster industry and its developmental suggestions in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 52(9): 2608-2618 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
祁剑飞, 宁岳, 曾志南, 等, 2015. 冬季单体牡蛎池塘育肥初步实验[J]. 福建水产, 37(5): 406-410.
|
|
QI JIANFEI, NING YUE, ZENG ZHINAN, et al, 2015. Study on winter fattening of single-seed Portuguese oyster (Crassostrea angulata) in semi closed ponds[J]. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, 37(5): 406-410 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
权伟, 应苗苗, 周庆澔, 等, 2018. 基于稳定碳同位素技术的养殖贝类碳源分析[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 27(2): 175-180.
|
|
QUAN WEI, YING MIAOMIAO, ZHOU QINGHAO, et al, 2018. Carbon source analysis of bivalve-culture based on stable carbon isotope technique[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 27(2): 175-180 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
徐军, 张敏, 谢平, 2010. 氮稳定同位素基准的可变性及对营养级评价的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 22(1): 8-20.
|
|
XU JUN, ZHANG MIN, XIE PING, 2010. Variability of stable nitrogen isotopic baselines and its consequence for trophic modeling[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 22(1): 8-20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.18307/2010.0102
|
| [10] |
严雪瑜, 覃波忠, 黄伟德, 等, 2021. 不同育肥海区香港牡蛎的营养评价及基因表达相关性分析[J]. 食品工业科技, 43(13): 276-283.
|
|
YAN XUEYU, QIN BOZHONG, HUANG WEIDE, et al, 2021. Correlation analysis between nutritional evaluation and gene expression of Crassostrea hongkongensis in different fattening sea areas[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 43(13): 276-283 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
於锋, 罗帮, 陈雪芬, 等, 2016. 广西茅尾海的香港巨牡蛎(Crassostrea hongkongensis)在不同养殖区的性腺发育变化[J]. 渔业科学进展, 37(3): 134-142.
|
|
YU FENG, LUO BANG, CHEN XUEFEN, et al, 2016. Gonad development of oyster(Crassostrea hongkongensis) at different cultural sites in Maowei bay, Guangxi, China[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 37(3): 134-142 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
于瑞海, 李海昆, 2021. 我国三倍体牡蛎育苗、养殖现状及发展对策[J]. 科学养鱼, (11): 2-4 (in Chinese).
|
| [13] |
周晖, 陈刚, 古滨河, 等, 2013. 饲料中的玉米蛋白质对军曹鱼幼鱼蛋白质生长的贡献率[J]. 动物营养学报, 25(11): 2633-2642.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2013.11.016
|
|
ZHOU HUI, CHEN GANG, GU BINHE, et al, 2013. Contribution rate of dietary corn protein to protein growth of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum L.)[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 25(11): 2633-2642 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
邹琰, 刘广斌, 张天文, 等, 2021. 我国太平洋牡蛎主要养殖模式[J]. 科学养鱼, (11): 63-64 (in Chinese).
|
| [15] |
CAUT S, ANGULO E, COURCHAMP F, 2008. Caution on isotopic model use for analyses of consumer diet[J]. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 86(5): 438-445.
doi: 10.1139/Z08-012
|
| [16] |
DEUDERO S, CABANELLAS M, BLANCO A, et al, 2009. Stable isotope fractionation in the digestive gland, muscle and gills tissues of the marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 368(2): 181-188.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2008.10.008
|
| [17] |
FENG JIE, TIAN XIANGLI, DONG SHUANGLIN, et al, 2018. Trophic interaction in a Portunus rituberculatus polyculture ecosystem based on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analysis[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 17(6): 1432-1440.
doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3655-y
|
| [18] |
HESSLEIN R H, HALLARD K A, RAMLAL P, 1993. Replacement of sulfur, carbon, and nitrogen in tissue of growing broad whitefish (Coregonus nasus) in response to a change in diet traced by δ34S, δ13C, and δ15N[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 50(10): 2071-2076.
doi: 10.1139/f93-230
|
| [19] |
MARTÍNEZ DEL RIO C, WOLF B O, 2005. Mass balance models for animal isotopic ecology[M]//STARCK M A, WANG T, Physiological and ecological adaptations to feeding in vertebrates. Enfield: Science Publishers: 141-174.
|
| [20] |
MARTÍNEZ DEL RIO C, WOLF N, CARLETON S A, et al, 2009. Isotopic ecology ten years after a call for more laboratory experiments[J]. Biological Reviews, 84(1): 91-111.
doi: 10.1111/brv.2009.84.issue-1
|
| [21] |
MCCORMACK S A, TREBILCO R, MELBOURNE-THOMAS J, et al, 2019. Using stable isotope data to advance marine food web modelling[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 29: 277-296.
doi: 10.1007/s11160-019-09552-4
|
| [22] |
NABAES JODAR D N, CUSSAC V E, BECKER L A, 2020. Into the wild: escaped farmed rainbow trout show a dispersal-associated diet shift towards natural prey[J]. Hydrobiologia, 847: 105-120.
doi: 10.1007/s10750-019-04075-2
|
| [23] |
PETERSON B J, FRY B, 1987. Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 18: 293-320.
doi: 10.1146/ecolsys.1987.18.issue-1
|
| [24] |
PIOLA R F, MOORE S K, SUTHERS I M, 2006. Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analysis of three types of oyster tissue in an impacted estuary[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 66(1-2): 255-266.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2005.08.013
|
| [25] |
POST D M, 2002. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions[J]. Ecology, 83(3): 703-718.
doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[0703:USITET]2.0.CO;2
|
| [26] |
SOLETCHNIK P, LE MOINE O, GOULLETQUER P, et al, 2001. Optimisation of the traditional Pacific cupped oyster (Crassostrea gigas Thunberg) culture on the French Atlantic coastline: autumnal fattening in semi-closed ponds[J]. Aquaculture, 199(1-2): 73-91.
doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00554-3
|
| [27] |
ZHOU HUI, CHEN GANG, GU BINHE, et al, 2016. Relative contribution of alternative proteins to the growth of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum (Linnaeus)[J]. Aquaculture Research, 47(5): 1639-1651.
doi: 10.1111/are.12625
|
| [28] |
ZHOU HUI, GU BINHE, 2020. Using stable isotope analysis to assess the relationship among dietary protein sources, growth, nutrient turnover and incorporation in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. Aquaculture Nutrion, 26(5): 1443-1452.
|
 ), 汤保贵1(
), 汤保贵1( ), 伍栩民1, 彭梓峰1, 钟培贵2, 于鸽3, 孔繁森1
), 伍栩民1, 彭梓峰1, 钟培贵2, 于鸽3, 孔繁森1
 ), TANG Baogui1(
), TANG Baogui1( ), WU Xumin1, PENG Zifeng1, ZHONG Peigui2, YU Ge3, KONG Fansen1
), WU Xumin1, PENG Zifeng1, ZHONG Peigui2, YU Ge3, KONG Fansen1