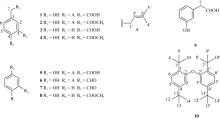
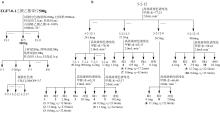
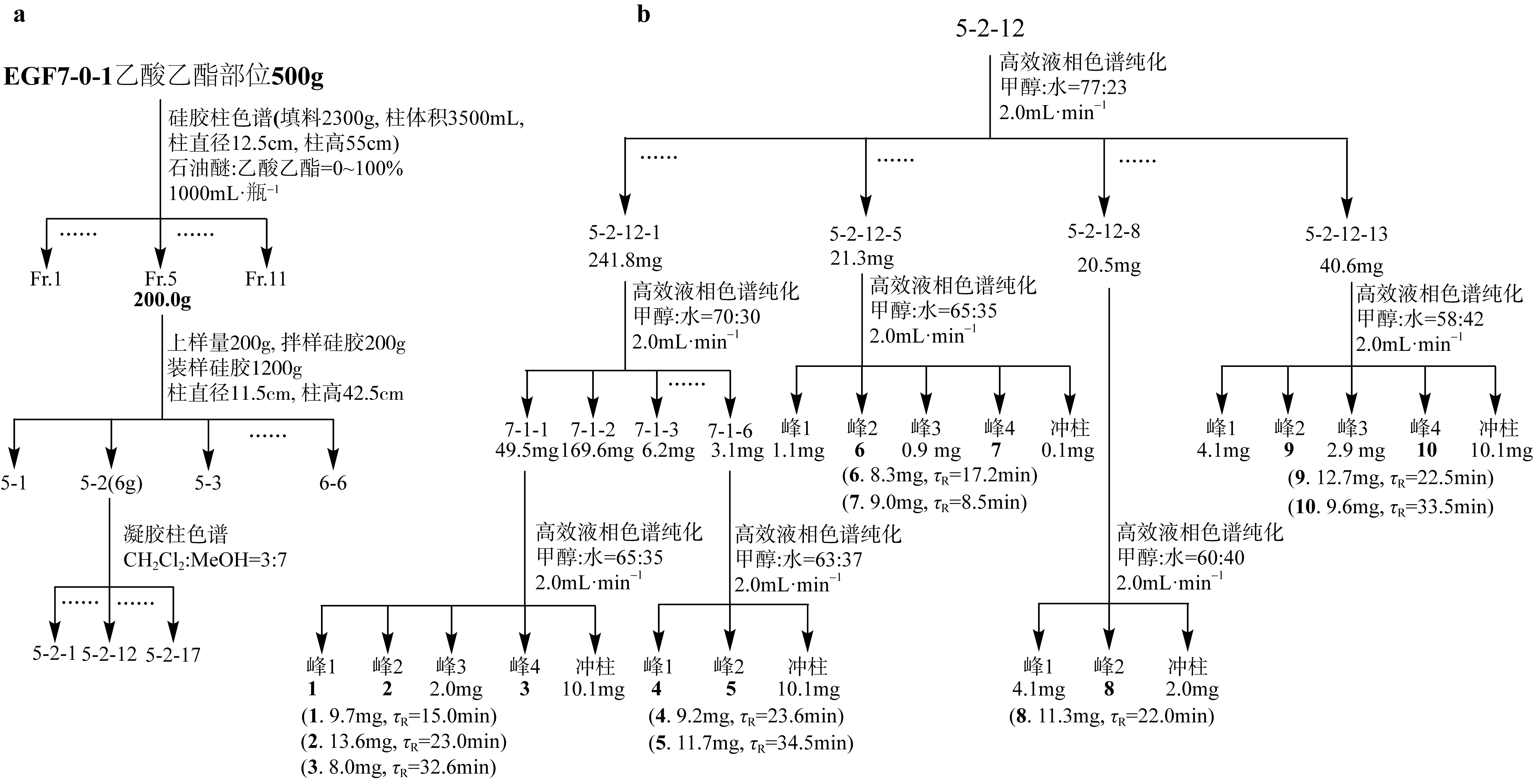
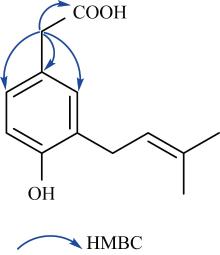
| [1] |
安昶亮, 孔凡栋, 马青云, 等, 2019. 海洋真菌Aspergillus sp. SCS-KFD66的次级代谢产物研究[J]. 中草药, 50(13): 3001-3007.
|
|
AN CHANGLIANG, KONG FANDONG, MA QINGYUN, et al, 2019. Secondary metabolites from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCS-KFD66[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 50(13): 3001-3007 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
曹雷雷, 天海妍, 王友绍, 等, 2015. 红树植物无瓣海桑果实的化学成分研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(1): 77-82.
|
|
CAO LEILEI, TIAN HAIYAN, WANG YOUSHAO, et al, 2015. Chemical constituents in the fruits of mangrove plant Sonneratia apetala Buch. Ham.[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 34(1): 77-82 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
陈若兰, 黎子洋, 巫惠珍, 等, 2022. 一株红树植物内生真菌Pseudallescheria boydii L32的代谢产物[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 61(4): 60-64.
|
|
CHEN RUOLAN, LI ZIYANG, WU HUIZHEN, et al, 2022. The metabolites of a mangrove endophytic fungus Pseudallescheria boydii L32[J]. Journal of Sun Yat-sen University, 61(4): 60-64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
黎咏怡, 蔡金旋, 方越, 等, 2022. 南海软珊瑚共附生真菌Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3中色酮、蒽醌及其二聚体类化合物[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 61(4): 70-78.
|
|
LI YONGYI, CAI JINXUAN, FANG YUE, et al, 2022. Xanthones, anthraquinone and their dimers from soft coral-associated symbiotic and epiphytic fungi Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3[J]. Journal of Sun Yat-sen University, 61(4): 70-78 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
刘炳新, 韦霞, 肖细姬, 等, 2021. 南海软珊瑚共附生真菌 Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3苯甲醛类化合物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(4): 63-69.
doi: 10.11978/2020085
|
|
LIU BINGXIN, WEI XIA, XIAO XIJI, et al, 2021. Research on benzaldehydes from the soft coral-associated symbiotic fungus Aspergillus sp. EGF15-0-3[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 40(4): 63-69 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
吕海宁, 陈辉, 屈晶, 等, 2015. 内生真菌Trichoderma harzianum次生代谢产物研究[J]. 中国现代中药, 17(5): 427-430.
|
|
LYU HAINING, CHEN HUI, QU JING, et al, 2015. Study on secondary metabolites of endophytic fungi Trichoderma harzianum[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 17(5): 427-430 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
马丽丽, 田新朋, 李桂菊, 等, 2021. 海洋微生物来源天然产物研究现状与态势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(5): 134-146.
doi: 10.11978/2020104
|
|
MA LILI, TIAN XINPENG, LI GUIJU, et al, 2021. Research status and development trends of natural products from marine microorganisms[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 40(5): 134-146 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2020104
|
| [8] |
温建辉, 倪付勇, 赵祎武, 等, 2015. 山银花化学成分研究[J]. 中草药, 46(13): 1883-1886.
|
|
WEN JIANHUI, NI FUYONG, ZHAO YIWU, et al, 2015. Chemical constituents from flower buds of Lonicera confuse[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 46(13): 1883-1886 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
张树军, 刘焕, 李军, 等, 2015. 蒙古苍耳全草化学成分研究[J]. 中草药, 46(3): 329-333.
|
|
ZHANG SHUJUN, LIU HUAN, LI JUN, et al, 2015. Study on chemical constituents from whole herbs of Xanthium mongolicum[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 46(3): 329-333 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
BIRCH A J, MAUNG M, 1967. The synthesis of ortho-isopentenyl phenols[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 8(34): 3275-3276.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)89868-3
|
| [11] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2021. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 38(2): 362-413.
doi: 10.1039/d0np00089b
pmid: 33570537
|
| [12] |
FAN HAO, SHI ZHIMIAN, LEI YANHU, et al, 2022. Rare carbon-bridged citrinin dimers from the starfish-derived symbiotic fungus Penicillium sp. GGF16-1-2[J]. Marine Drugs, 20(7): 443.
doi: 10.3390/md20070443
|
| [13] |
VATCHARIN R, NACHAMON R, SARANYOO K, et al, 2014. γ-Butyrolactone, cytochalasin, cyclic carbonate, eutypinic acid, and phenalenone derivatives from the soil fungus Aspergillus sp. PSU-RSPG185[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 77(11): 2375-2382.
doi: 10.1021/np500324b
|
| [14] |
WEI XIA, WANG FANGTING, SI-TU MEI XIA, et al, 2022. Pyranodipyran derivatives with tyrosyl DNA phosphodiesterase 1 inhibitory activities and fluorescent properties from Aspergillus sp. EGF 15-0-3[J]. Marine Drugs, 20(3): 211.
doi: 10.3390/md20030211
|
| [15] |
XU QIANQIAN, QIAO YUBEN, et al, 2021. New polyketides with anti-inflammatory activity from the fungus Aspergillus rugulosa[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12: 700573.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.700573
|
 ), 何嘉鸿1, 韦霞2, 陈乐怡1, 陈欣琪1, 张翠仙1(
), 何嘉鸿1, 韦霞2, 陈乐怡1, 陈欣琪1, 张翠仙1( )
)
 ), HE Jiahong1, WEI Xia2, CHEN Leyi1, CHEN Xinqi1, ZHANG Cuixain1(
), HE Jiahong1, WEI Xia2, CHEN Leyi1, CHEN Xinqi1, ZHANG Cuixain1( )
)