热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 108-120.doi: 10.11978/2023074CSTR: 32234.14.2023074
树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥红树林碳储量的影响
- 广东省土地调查规划院, 广东 广州 510075
-
收稿日期:2023-06-05修回日期:2023-08-28出版日期:2024-03-10发布日期:2024-03-26 -
作者简介:周治刚(1977—), 男, 湖北省黄冈市人, 工程师, 从事海洋调查监测相关研究。email: sherlp@163.com
-
基金资助:广东省自然资源生态修复项目专项(440000210000000019650)
Influence of tree species and intertidal elevations on the carbon storage of the Gaoqiao mangrove area in Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province
ZHOU Zhigang( ), YUE Wen(
), YUE Wen( ), LI Huiquan, LIN Yangyang
), LI Huiquan, LIN Yangyang
- Guangdong Provincial Institute of Land Survey and Planning, Guangzhou 510075, China
-
Received:2023-06-05Revised:2023-08-28Online:2024-03-10Published:2024-03-26 -
Supported by:Special Funds for Natural Resource Ecological Restoration Projects in Guangdong Province(440000210000000019650)
摘要:
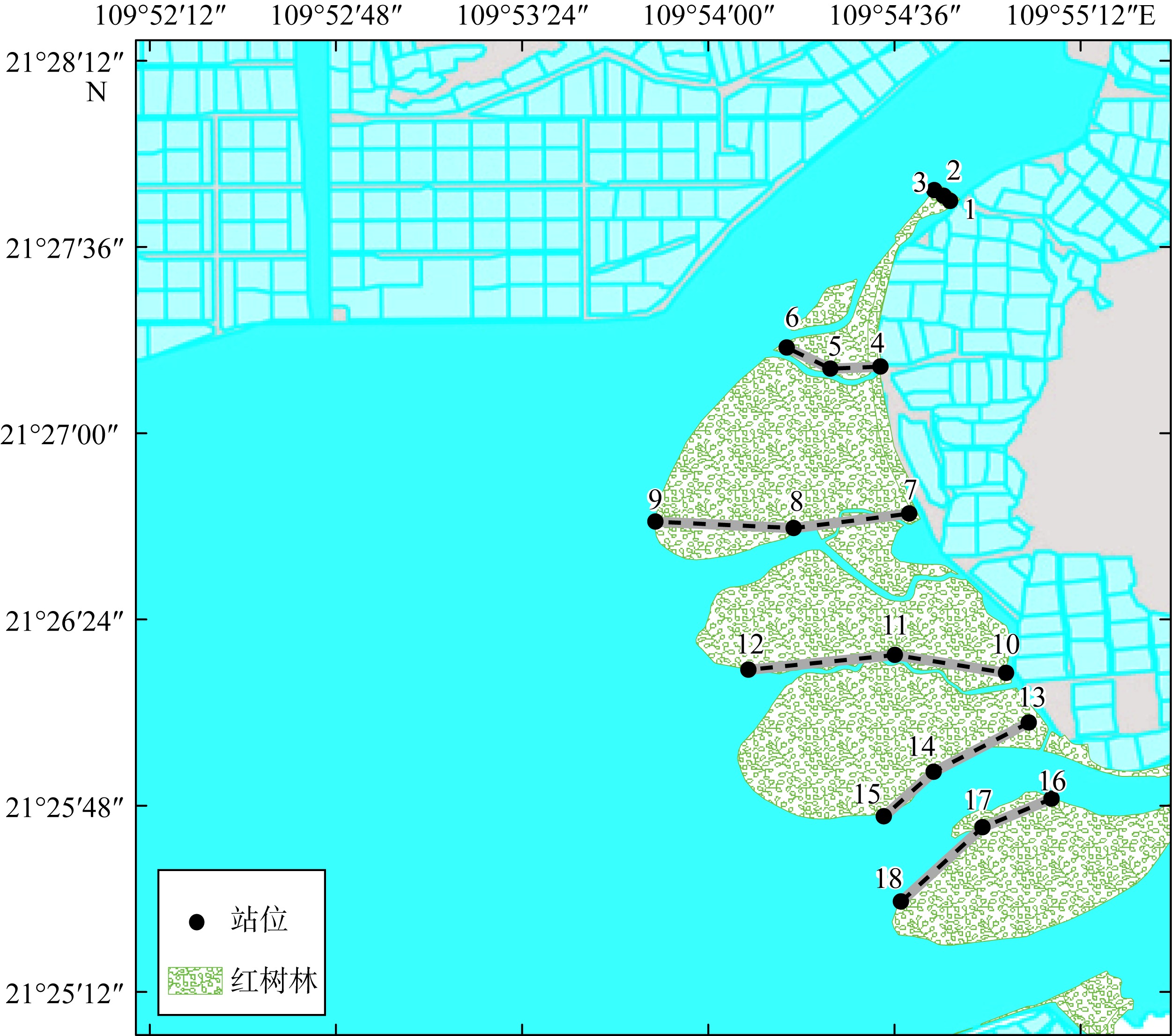
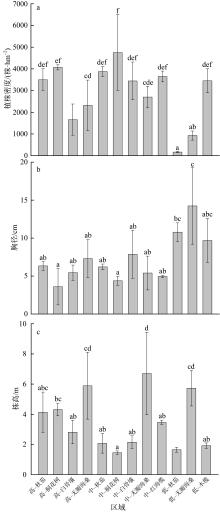
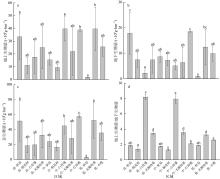
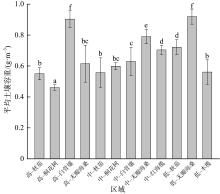
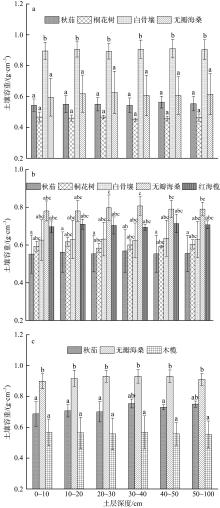
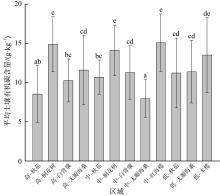
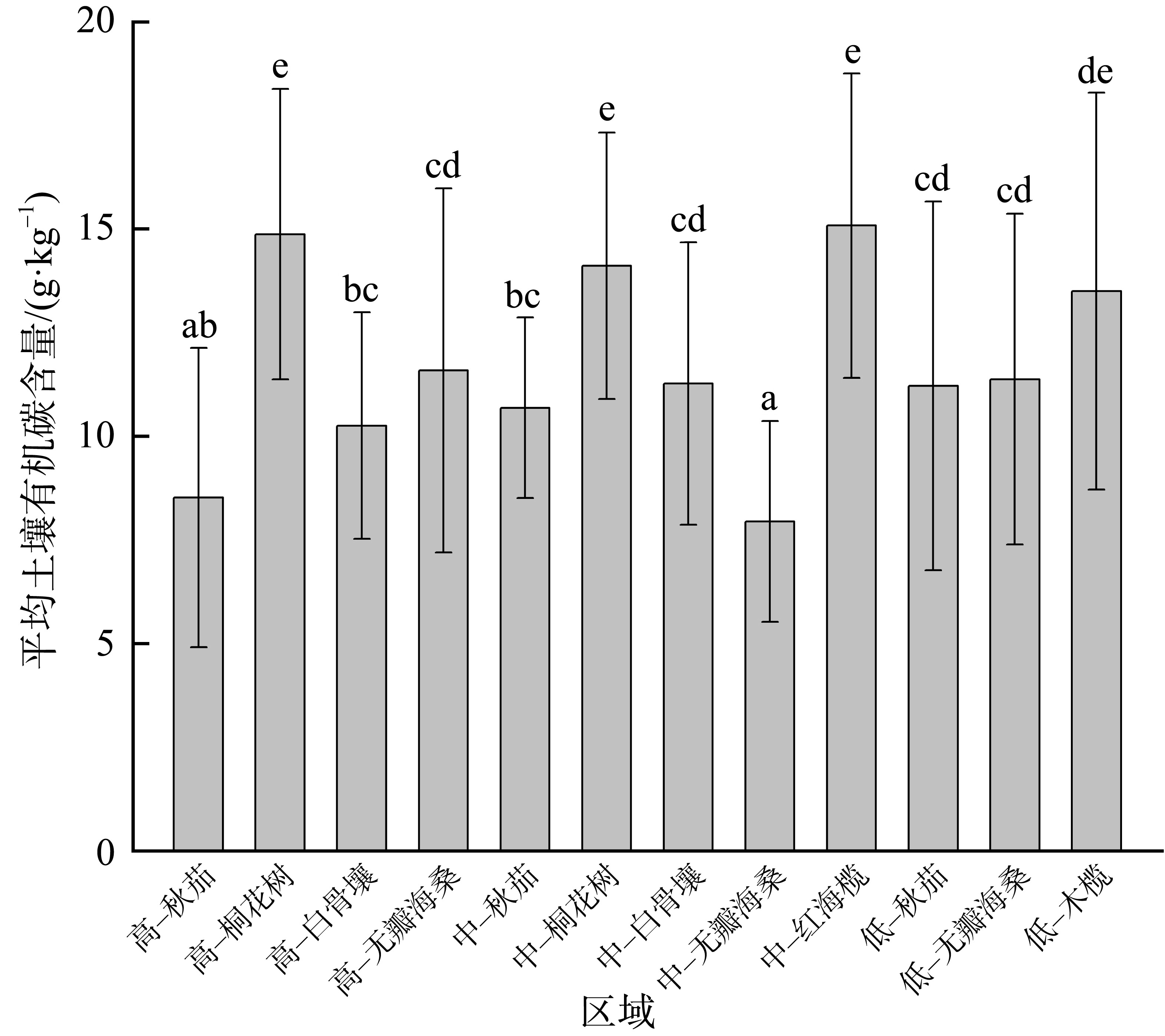
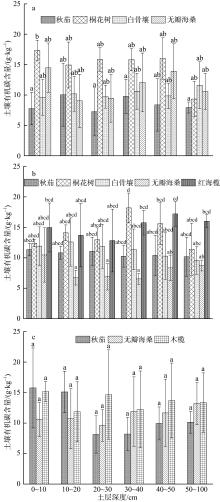
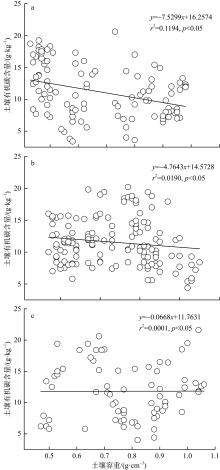
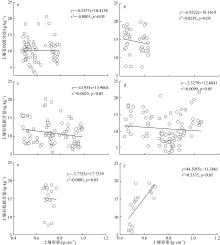
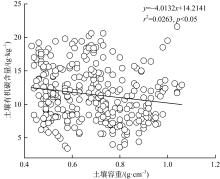
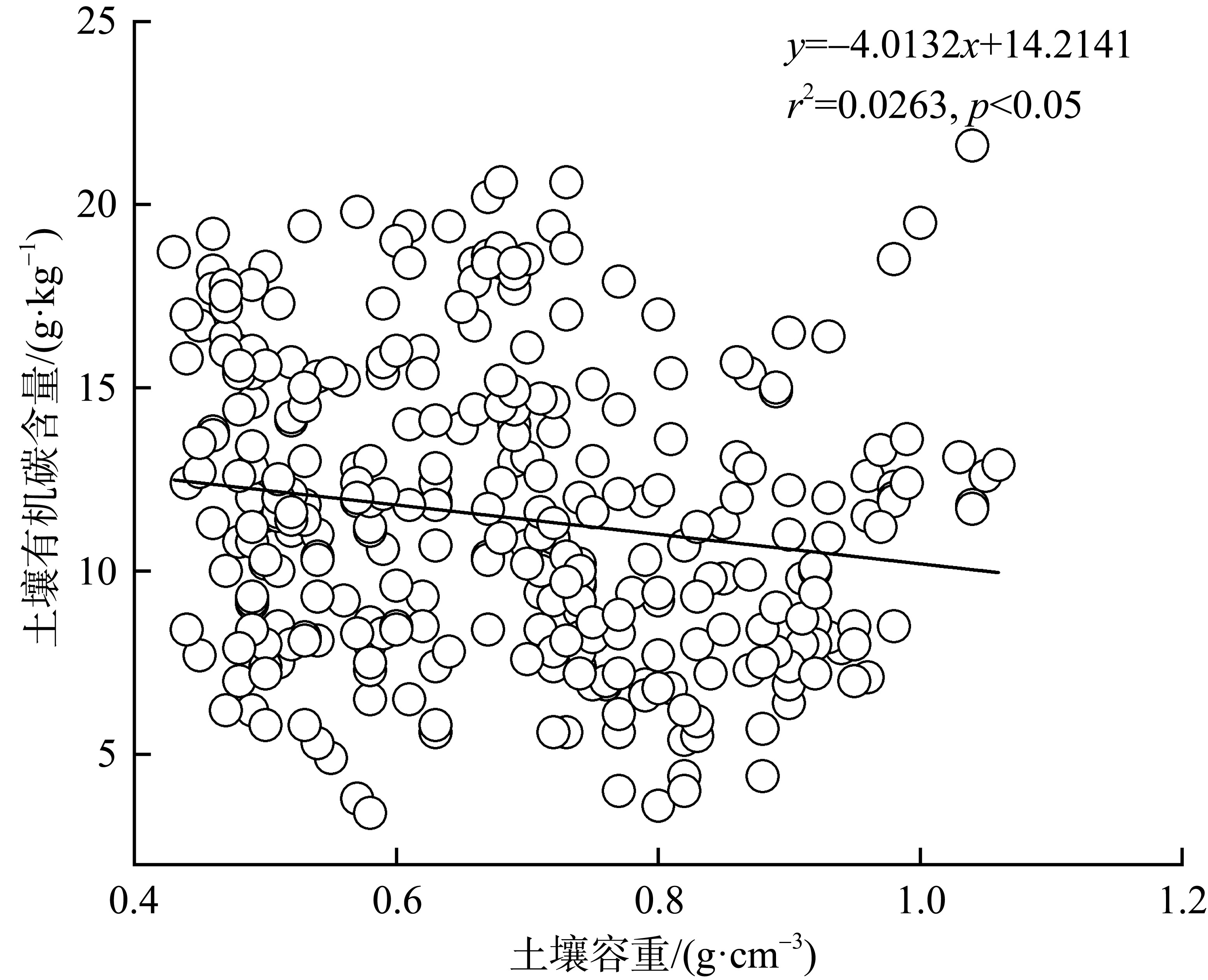
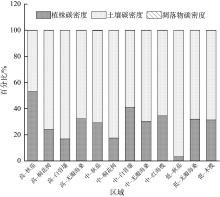
红树林位于海洋与陆地的交界处, 其高效的碳汇能力易受多方面因素的影响。文章通过分析植物生长指标、生物量、植被碳储量和土壤碳储量以及土壤容重等参数, 研究了树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥区红树林群落碳汇功能的单独作用和耦合效应。结果表明, 高桥红树林的固碳总量为4.98×1010g, 碳密度为107.76×106g·hm-2, 土壤碳积累是该红树林固碳的重要贡献。不同潮滩红树林的碳储量受树种差异的影响显著, 且低潮滩的红树林碳储量显著高于高潮滩和中潮滩, 而潮滩高程仅对无瓣海桑群落的碳储量具有显著影响。无论是植物碳库还是土壤碳库, 中潮滩红海榄群落和低潮滩无瓣海桑群落的碳密度最高。红树群落的土壤有机碳含量在垂直方向分布均匀, 各土层间无显著差异。在高潮滩和中潮滩, 土壤有机碳含量的垂直分布受树种影响, 大部分桐花树群落的土壤有机碳含量显著高于同土层的秋茄群落、白骨壤群落和无瓣海桑群落, 而树种对低潮滩各土层有机碳含量无显著影响。虽然树种类型和潮滩高程可影响土壤容重与土壤有机碳含量间的作用关系, 但线性拟合结果以负相关关系为主。
引用本文
周治刚, 岳文, 李辉权, 林阳阳. 树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥红树林碳储量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 108-120.
ZHOU Zhigang, YUE Wen, LI Huiquan, LIN Yangyang. Influence of tree species and intertidal elevations on the carbon storage of the Gaoqiao mangrove area in Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 108-120.
表2
不同红树林树种的地上及地下生物量模型"
| 树种 | 地上生物量模型 | 地下生物量模型 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 秋茄(Kandelia obovata) | Ba=0.0341(d2h)1.03 | Bu=0.0483(d2h)0.834 | Hoque等( |
| 无瓣海桑(Sonneratia apetala) | Ba=0.280(d2h)0.693 | Bu=0.038(d2h)0.759 | Ren等( |
| 桐花树(Aegiceras corniculatum) | lgBa=1.496+0.465lg(d2h) | lgBu=0.967+0.303lg(d2h) | Tam等( |
| 白骨壤(Avicennia marina) | lgBa=2.113lgd-0.511 | lgBu=1.171lgd+0.106 | Comley等( |
| 木榄(Bruguiera gymnorrhiza) | Ba=0.168d2.31 | Bu=0.0188(d2h)0.909 | Clough等( |
| 红海榄(Rhizophora stylosa) | Ba=0.2206d2.4292 | Bu=0.261d1.86 | Tamai等( |
| [1] |
曹庆先, 2010. 北部湾沿海红树林生物量和碳贮量的遥感估算[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院:99-104.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈鹭真, 林鹏, 王文卿, 2006. 红树植物淹水胁迫响应研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 26(2): 586-593.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈玮琪, 洪华生, 张珞平, 等, 2007. 中国红树林生态系统服务的能值价值[J]. 资源科学, 29(1): 147-154.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈小花, 陈宗铸, 雷金睿, 等, 2022. 清澜港红树林湿地典型群落类型沉积物活性有机碳组分分布特征[J]. 生态学报, 42(11): 4572-4581.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
陈瑶瑶, 张雅松, 娄铎, 等, 2019. 广东英罗湾不同潮位红树林-滩涂系统碳密度差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(6): 1134-1140.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.06.008 |
|
|
|
| [6] |
陈玉军, 李婷, 朱立安, 等, 2022. 淹水梯度对红树林湿地土壤微生物生物量与酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 42(6): 68-75.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
成家隆, 吕瑜良, 陈玉军, 等, 2015. 水东湾红树林不同生长位置生长差异性研究[J]. 生态科学, 34(6): 30-35.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
高天伦, 管伟, 毛静, 等, 2017. 广东省雷州附城主要红树林群落碳储量及其影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(6): 985-990.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
胡倩芳, 2009. 不同高程下白骨壤+秋茄人工红树林生长、生理及其更新能力的比较研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学:15-32.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
胡懿凯, 2019. 淇澳岛不同恢复类型红树林碳密度和固碳速率比较研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学:17-23.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
黄诚智, 曾德华, 2019. 4种红树树种在三亚河红树林自然保护区的生长和生理生化响应[J]. 热带林业, 47(1): 34-37.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
黄灵玉, 2015. 广东红树林土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范学院.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
黄星, 袁菁菁, 马基仪, 等, 2022. 沙井港不同湿地植被群落沉积物中有机碳含量与分布特征[J]. 科技技术创新, (2): 25-28.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
来洪运, 王咏雪, 章翊涵, 等, 2021. 浙江苍南沿浦湾秋茄人工林早期生长特征研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 34(4): 156-165.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
李林锋, 吴小凤, 刘素青, 2015. 湛江5种红树林树种光合作用特性及光合固碳能力研究[J]. 广西植物, 35(6): 825-832.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
李燕, 赵志忠, 王鸿平, 等, 2018. 海南东寨港红树林湿地沉积物有机碳的分布特征[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 45(2): 268-273.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
廖宝文, 2010. 三种红树植物对潮水淹浸与水体盐度适应能力的研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院:17-41.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
罗美娟, 2012. 红树植物桐花树幼苗对潮汐淹水胁迫的响应研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院:15-23.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
孙学超, 黄展鹏, 张琼锐, 等, 2022. 珠海淇澳岛人工次生无瓣海桑纯林的植被碳储量变化[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 54(4): 89-100.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
辛琨, 颜葵, 李真, 等, 2014. 海南岛红树林湿地土壤有机碳分布规律及影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 51(5): 1078-1086.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
许大全, 张玉忠, 张荣铣, 1992. 植物光合作用的光抑制[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 28(4): 237-243.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
张莉, 2013. 海南清澜港红树林土壤有机碳及其与土壤因子关系研究[D]. 洛阳: 河南科技大学:29-30.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
张莉, 郭志华, 李志勇, 2013. 红树林湿地碳储量及碳汇研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(4): 1153-1159.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
郑鹏, 史红文, 邓红兵, 等, 2012. 武汉市65个园林树种的生态功能研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 30(5): 468-475.
|
|
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1142.2012.50468 |
|
| [25] |
周莉, 李保国, 周广胜, 2005. 土壤有机碳的主导影响因子及其研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 20(1): 99-105.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2005.01.0099 |
|
|
|
| [26] |
朱耀军, 赵峰, 郭菊兰, 等, 2017. 广东湛江高桥红树林湿地沉积柱粒度特征[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 39(11): 9-17.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.4155/cmt.12.20 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3326 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/0378-1127(89)90034-0 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1071/BT04162 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1007/s00248-003-1063-2 pmid: 15692862 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1007/s004420050489 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2013.03.023 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1146/ecolsys.1974.5.issue-1 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1007/s10265-005-0221-7 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.04.074 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.846556 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00029126 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1007/BF02348582 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136742 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105423 |
| [1] | 张彤, 凌娟, 岳维忠, 王友绍, 程皓, 孙红岩, 黄小芳, 梁童茵, 周卫国, 董俊德. 基于CiteSpace的广东省典型蓝碳生态系统碳汇研究进展的可视化分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 58-68. |
|
||