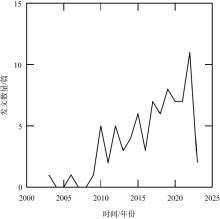
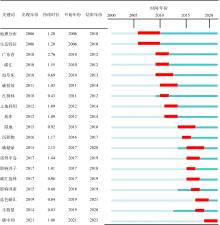
| [1] |
陈超美, 陈悦, 侯剑华, 等, 2009. CiteSpace Ⅱ: 科学文献中新趋势与新动态的识别与可视化[J]. 情报学报, 28(3): 401-421.
|
|
CHEN CHAOMEI, CHEN YUE, HOU JIANHUA, et al, 2009. CiteSpace Ⅱ: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature[J]. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information, 28(3): 401-421 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
陈光程, 2021. 我国成功交易首个“蓝碳”碳汇项目[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 40(3): 555-556.
|
|
CHEN GUANGCHENG, 2021. China’s first “blue carbon” carbon sink project successfully traded[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 40(3): 555-556 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
陈小龙, 狄乾斌, 侯智文, 等, 2023. 海洋碳汇研究进展及展望[J]. 资源科学, 45(8): 1619-1633.
doi: 10.18402/resci.2023.08.10
|
|
CHEN XIAOLONG, DI QIANBIN, HOU ZHIWEN, et al, 2023. Research progress and prospect of marine carbon sink[J]. Resources Science, 45(8): 1619-1633 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.18402/resci.2023.08.10
|
| [4] |
陈瑶瑶, 张雅松, 娄铎, 等, 2019. 广东英罗湾不同潮位红树林-滩涂系统碳密度差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(6): 1134-1140.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.06.008
|
|
CHEN YAOYAO, ZHANG YASONG, LOU DUO, et al, 2019. Carbon density difference of mangrove-shoal system at different tidal levels in Yingluo Bay, Guangdong[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(6): 1134-1140 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
陈悦, 陈超美, 刘则渊, 等, 2015. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究, 33(2): 242-253.
|
|
CHEN YUE, CHEN CHAOMEI, LIU ZEYUAN, et al, 2015. The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains[J]. Studies in Science of Science, 33(2): 242-253 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
高天伦, 2018. 广东省雷州附城主要红树林群落碳储量及其影响因子[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院:16-19.
|
|
GAO TIANLUN, 2018. Carbon storage and influence factors of major mangrove communities in Fucheng, Leizhou peninsula, Guangdong Province[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry: 16-19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
广东省生态环境厅, 2023. 广东省红树林碳普惠方法学[Z]. 广州: 广东省生态环境厅: 8-13.
|
|
DEPARTMENT OF ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT OF GUANGDONG PROVINCE, 2023. Carbon Inclusive Methodology for Mangrove Forests in Guangdong Province[Z]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Provincial Department of Ecology and Environment: 8-13 (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
韩广轩, 王法明, 马俊, 等, 2022. 滨海盐沼湿地蓝色碳汇功能、形成机制及其增汇潜力[J]. 植物生态学报, 46(4): 373-382.
doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2021.0264
|
|
HAN GUANGXUAN, WANG FAMING, MA JUN, et al, 2022. Blue carbon sink function, formation mechanism and sequestration potential of coastal salt marshes[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 46(4): 373-382 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
贺炬成, 2021. 广东省红树林湿地生态系统碳汇研究综述[J]. 中国林业产业, (12): 54-57.
|
|
HE JUCHENG, 2021. Review of carbon sink of mangrove wetland ecosystem in Guangdong Province[J]. China Forestry Industry, (12): 54-57 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
胡懿凯, 徐耀文, 薛春泉, 等, 2019. 广东省无瓣海桑和林地土壤碳储量研究[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 40(6): 95-103.
|
|
HU YIKAI, XU YAOWEN, XUE CHUNQUAN, et al, 2019. Studies on carbon storages of Sonneratia apetala forest vegetation and soil in Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 40(6): 95-103 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
华国栋, 庄礼凤, 李家祥, 等, 2021. 广东台山镇海湾红树林国家湿地公园土壤有机碳含量及其影响因素分析[J]. 林业与环境科学, 37(6): 118-123.
|
|
HUA GUODONG, ZHUANG LIFENG, LI JIAXIANG, et al, 2021. Contents of soil organic carbon of mangrove in Haiwan mangrove national wetland park, Taishan Town, Guangdong and their influencing factors[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science, 37(6): 118-123 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
黄妃本, 陈纯秀, 罗勇, 2015. 碳汇监测与计量技术在广东红树林生态系统的应用研究[J]. 广东林业科技, 31(4): 101-105.
|
|
HUANG FEIBEN, CHEN CHUNXIU, LUO YONG, 2015. Study on monitoring and calculation of mangrove ecosystem carbon sinks in Guangdong[J]. Guangdong Forestry Science and Technology, 31(4): 101-105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
黄灵玉, 2015. 广东红树林土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范学院:20-22.
|
|
HUANG LINGYU, 2015. Distribution characteristics and influential factors of soil organic carbon in mangrove wetlands in Guangdong province[D]. Guilin: Guangxi Teachers Education University: 20-22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
黄小平, 黄良民, 李颖虹, 等, 2006. 华南沿海主要海草床及其生境威胁[J]. 科学通报, (S3): 114-119.
|
|
HUANG XIAOPING, HUANG LIANGMIN, LI YINGHONG, et al, 2006. Major seagrass beds and their habitat threats along the coast of South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, (S3): 114-119 (in Chinese).
|
| [15] |
江小芳, 2020. 中国红树林植被和土壤碳储量及其影响因子[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学:25-37.
|
|
JIANG XIAOFANG, 2020. The biomass and soil carbon stocks and their influencing factors of mangrove forests in China[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University: 25-37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
黎夏, 叶嘉安, 王树功, 等, 2006. 红树林湿地植被生物量的雷达遥感估算[J]. 遥感学报, 10(3): 387-396.
|
|
LI XIA, YE JIA’AN, WANG SHUGONG, et al, 2006. Estimating mangrove wetland biomass using radar remote sensing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 10(3): 387-396 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
李政, 严欣恬, 李杨帆, 等, 2022. 构建粤港澳大湾区特色蓝碳交易市场探析[J]. 特区实践与理论, (5): 56-60.
|
|
LI ZHENG, YAN XINTIAN, LI YANGFAN, et al, 2022. Analysis on the construction of a characteristic blue carbon trading market in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Practice and Theory of Seas, (5): 56-60 (in Chinese).
|
| [18] |
廖宝文, 张乔民, 2014. 中国红树林的分布、面积和树种组成[J]. 湿地科学, 12(4): 435-440.
|
|
LIAO BAOWEN, ZHANG QIAOMIN, 2014. Area, distribution and species composition of mangroves in China[J]. Wetland Science, 12(4): 435-440 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
林德明, 陈超美, 刘则渊, 2011. 共被引网络中介中心性的Zipf-Pareto分布研究[J]. 情报学报, 30(1): 76-82.
|
|
LIN DEMING, CHEN CHAOMEI, LIU ZEYUAN, 2011. Study on Zipf-Pareto distribution of the betweenness centrality of a co-citation network[J]. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information, 30(1): 76-82 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [20] |
刘镇杭, 刘大海, 池源, 等, 2023. 基于自然的海岸带蓝碳增汇措施及其技术体系研究[J]. 海岸工程, 42(1): 13-24.
|
|
LIU ZHENHANG, LIU DAHAI, CHI YUAN, et al, 2023. Research on measures and technology system for enhancing coastal blue carbon sink based on natural endowment[J]. Coastal Engineering, 42(1): 13-24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [21] |
吕华当, 2016. 广东: 海洋生物固碳养殖初见成效[J]. 海洋与渔业, (5): 18.
|
|
LYU HUADANG, 2016. Guangdong: Initial results of carbon sequestration aquaculture of marine organisms[J]. Ocean and Fishery, (5): 18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [22] |
覃国铭, 张靖凡, 周金戈, 等, 2023. 广东省红树林土壤碳储量及固碳潜力研究[J]. 热带地理, 43(1): 23-30.
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003606
|
|
QIN GUOMING, ZHANG JINGFAN, ZHOU JINGE, et al, 2023. Soil carbon stock and potential carbon storage in the mangrove forests of Guangdong[J]. Tropical Geography, 43(1): 23-30 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003606
|
| [23] |
任玉正, 刘松林, 罗红雪, 等, 2023. 海草床退化与修复对其沉积物有机碳储存的影响过程[J]. 科学通报, 68(22): 2961-2972.
|
|
REN YUZHENG, LIU SONGLIN, LUO HONGXUE, et al, 2023. Influence processes of seagrass degradation and restoration on sediment organic carbon storage[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 68(22): 2961-2972 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [24] |
生态环境部, 2021. 关于统筹和加强应对气候变化与生态环境保护相关工作的指导意见[R]. 北京: 生态环境部:5-6.
|
|
MINISTRY OF ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT, 2021. Guiding Opinions on Co-ordinating and Strengthening the Work Related to Climate Change Response and Ecological Environment Protection[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Ecology and Environment: 5-6 (in Chinese).
|
| [25] |
仝川, 罗敏, 陈鹭真, 等, 2023. 滨海蓝碳湿地碳汇速率测定方法及中国的研究现状和挑战[J]. 生态学报, 43(17): 6937-6950.
|
|
TONG CHUAN, LUO MIN, CHEN LUZHEN, et al, 2023. Methods of carbon sink rate measurement of coastal blue carbon wetland ecosystems, current situation and challenges in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(17): 6937-6950 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [26] |
肖明, 陈嘉勇, 李国俊, 2011. 基于CiteSpace研究科学知识图谱的可视化分析[J]. 图书情报工作, 55(6): 91-95.
|
|
XIAO MING, CHEN JIAYONG, LI GUOJUN, 2011. Visualization analysis on the research of mapping knowledge domains based on CiteSpace[J]. Library and Information Service, 55(6): 91-95 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [27] |
许方宏, 张进平, 张倩媚, 等, 2012. 广东湛江高桥三个天然红树林的土壤碳库[J]. 价值工程, 31(15): 5-6.
|
|
XU FANGHONG, ZHANG JINPING, ZHANG QIANMEI, et al, 2012. Carbon storage of three natural mangrove forests in Gaoqiao, Zhanjiang[J]. Value Engineering, 31(15): 5-6 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [28] |
杨熙, 何静, 郭治明, 2023. 南海区海草床生态调查研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社:19-45.
|
|
YANG XI, HE JING, GUO ZHIMING, 2023. Ecological investigation of seagrass beds in the South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press: 19-45 (in Chinese).
|
| [29] |
杨熙, 余威, 何静, 等, 2022. 海南黎安港海草床碳储量评估[J]. 海洋科学, 46(11): 116-125.
|
|
YANG XI, YU WEI, HE JING, et al, 2022. Carbon storage in the seagrass beds of Li’an Bay, Hainan[J]. Marine Sciences, 46(11): 116-125 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [30] |
张莉, 郭志华, 李志勇, 2013. 红树林湿地碳储量及碳汇研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(4): 1153-1159.
|
|
ZHANG LI, GUO ZHIHUA, LI ZHIYONG, 2013. Carbon storage and carbon sink of mangrove wetland: Research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(4): 1153-1159 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [31] |
邹建明, 王树功, 朱远辉, 2010. 广东低碳生态示范省建设背景下的红树林保护与恢复: 2010中国可持续发展论坛暨中国可持续发展研究会学术年会[C]. 济南: 2010中国可持续发展论坛2010年专刊 (二).
|
|
ZOU JIANMING, WANG SHUGONG, ZHU YUANHUI, 2010. Mangrove conservation and restoration in the context of the construction of Low-carbon Ecological Demonstration Province in Guangdong: 2010 China sustainable development forum and annual conference of China society for sustainable development[C]. Jinan: 2010 China Sustainable Development Forum 2010 Special Issue (Ⅱ) (in Chinese).
|
| [32] |
CHEN SHUNYANG, CHEN SHIQUAN, CHEN BIN, et al, 2022. Implication of macroalgal bloom to soil organic carbon stock in seagrass meadows - A case study in South Hainan, China[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9: 870228.
|
| [33] |
COLLIER C J, LAVERY P S, MASINI R J, et al, 2007. Morphological, growth and meadow characteristics of the seagrass Posidonia sinuosa along a depth- related gradient of light availability[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 337: 103-115.
|
| [34] |
COSTANZA R, D’ARGE R, DE GROOT R, et al, 1997. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital[J]. Nature, 387(6630): 253-260.
|
| [35] |
FOURQUREAN J W, DUARTE C M, KENNEDY H, et al, 2012. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock[J]. Nature Geoscience, 5(7): 505-509.
|
| [36] |
FOURQUREAN J W, RUTTEN L M, 2004. The impact of Hurricane Georges on soft-bottom, back reef communities: site- and species-specific effects in south Florida seagrass beds[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 75(2): 239-257.
|
| [37] |
GAO B, WALTER M T, STEENHUIS T S, et al, 2005. Investigating raindrop effects on transport of sediment and non-sorbed chemicals from soil to surface runoff[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 308(1-4): 313-320.
|
| [38] |
INTERGOVERNMENTAL PANEL ON CLIMATE CHANGE, 2019. Special report on the ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate[R]. Geneva: IPCC: 497-500.
|
| [39] |
LAVERY P S, MATEO M Á, SERRANO O, et al, 2013. Variability in the carbon storage of seagrass habitats and its implications for global estimates of blue carbon ecosystem service[J]. PLoS One, 8(9): e73748.
|
| [40] |
MACREADIE P I, TREVATHAN-TACKETT S M, SKILBECK C G, et al, 2015. Losses and recovery of organic carbon from a seagrass ecosystem following disturbance[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 282(1817): 20151537.
|
| [41] |
MOHAMMAD R, PAUL S, LAVERY, et al, 2016. Long-term carbon storage and its recent loss in an estuarine Posidonia australis meadow (Albany, Western Australia)[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 171: 58-65.
|
| [42] |
ONG J E, GONG W K, WONG C H, 2004. Allometry and partitioning of the mangrove, Rhizophora apiculata[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 188(1-3): 395-408.
|
| [43] |
PEDERSEN M Ø, SERRANO O, MATEO M Á, et al, 2011. Temperature effects on decomposition of a Posidonia oceanica mat[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 65(2): 169-182.
|
| [44] |
RICART A M, YORK P H, RASHEED M A, et al, 2015. Variability of sedimentary organic carbon in patchy seagrass landscapes[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100(1): 476-482.
doi: S0025-326X(15)30047-3
pmid: 26428624
|
| [45] |
SERRANO O, LAVERY P S, ROZAIMI M, et al, 2014. Influence of water depth on the carbon sequestration capacity of seagrasses[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 28(9): 950-961.
|
| [46] |
WANG GANG, GUAN DONGSHENG, PEART M R, et al, 2013. Ecosystem carbon stocks of mangrove forest in Yingluo Bay, Guangdong Province of South China[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 310: 539-546.
|
 ), 凌娟1,3,4,5, 岳维忠1, 王友绍1, 程皓1, 孙红岩2, 黄小芳1,3,5, 梁童茵1,6, 周卫国1,3, 董俊德1,3,4,5(
), 凌娟1,3,4,5, 岳维忠1, 王友绍1, 程皓1, 孙红岩2, 黄小芳1,3,5, 梁童茵1,6, 周卫国1,3, 董俊德1,3,4,5( )
)
 ), LING Juan1,3,4,5, YUE Weizhong1, WANG Youshao1, CHENG Hao1, SUN Hongyan2, HUANG Xiaofang1,3,5, LIANG Tongyin1,6, ZHOU Weiguo1,3, DONG Junde1,3,4,5(
), LING Juan1,3,4,5, YUE Weizhong1, WANG Youshao1, CHENG Hao1, SUN Hongyan2, HUANG Xiaofang1,3,5, LIANG Tongyin1,6, ZHOU Weiguo1,3, DONG Junde1,3,4,5( )
)