热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 21-33.doi: 10.11978/2023093CSTR: 32234.14.2023093
基于高通量测序技术的深圳湾真核浮游植物群落结构研究
黄圆1,2( ), 岑竞仪1,2, 梁芊艳1, 吕颂辉1,2, 王建艳3(
), 岑竞仪1,2, 梁芊艳1, 吕颂辉1,2, 王建艳3( )
)
- 1.暨南大学生命科学技术学院赤潮与海洋生物学研究中心, 广东 广州 510632
2.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(珠海), 广东 珠海 519082
3.国家自然博物馆生命科学部, 北京 100050
-
收稿日期:2023-07-03修回日期:2023-08-17出版日期:2024-03-10发布日期:2024-03-26 -
作者简介:黄圆(1999—), 女, 广东省河源市人, 硕士研究生, 从事藻类分类学研究。email: 18813211378@163.com
-
基金资助:北京市自然科学基金项目(8232026); 国家自然科学基金项目(41906112); 基础资源调查专项(2018FY100200)
Study on the community structure of eukaryotic phytoplankton in the Shenzhen Bay based on high-throughput sequencing technology
HUANG Yuan1,2( ), CEN Jingyi1,2, LIANG Qianyan1, LYU Songhui1,2, WANG Jianyan3(
), CEN Jingyi1,2, LIANG Qianyan1, LYU Songhui1,2, WANG Jianyan3( )
)
- 1. Research Center of Harmful Algae and Marine Biology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory, Zhuhai 519082, China
3. Department of Life Sciences, National Natural History Museum of China, Beijing 100050, China
-
Received:2023-07-03Revised:2023-08-17Online:2024-03-10Published:2024-03-26 -
Supported by:Beijing Natural Science Foundation(8232026); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41906112); National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Programme(2018FY100200)
摘要:
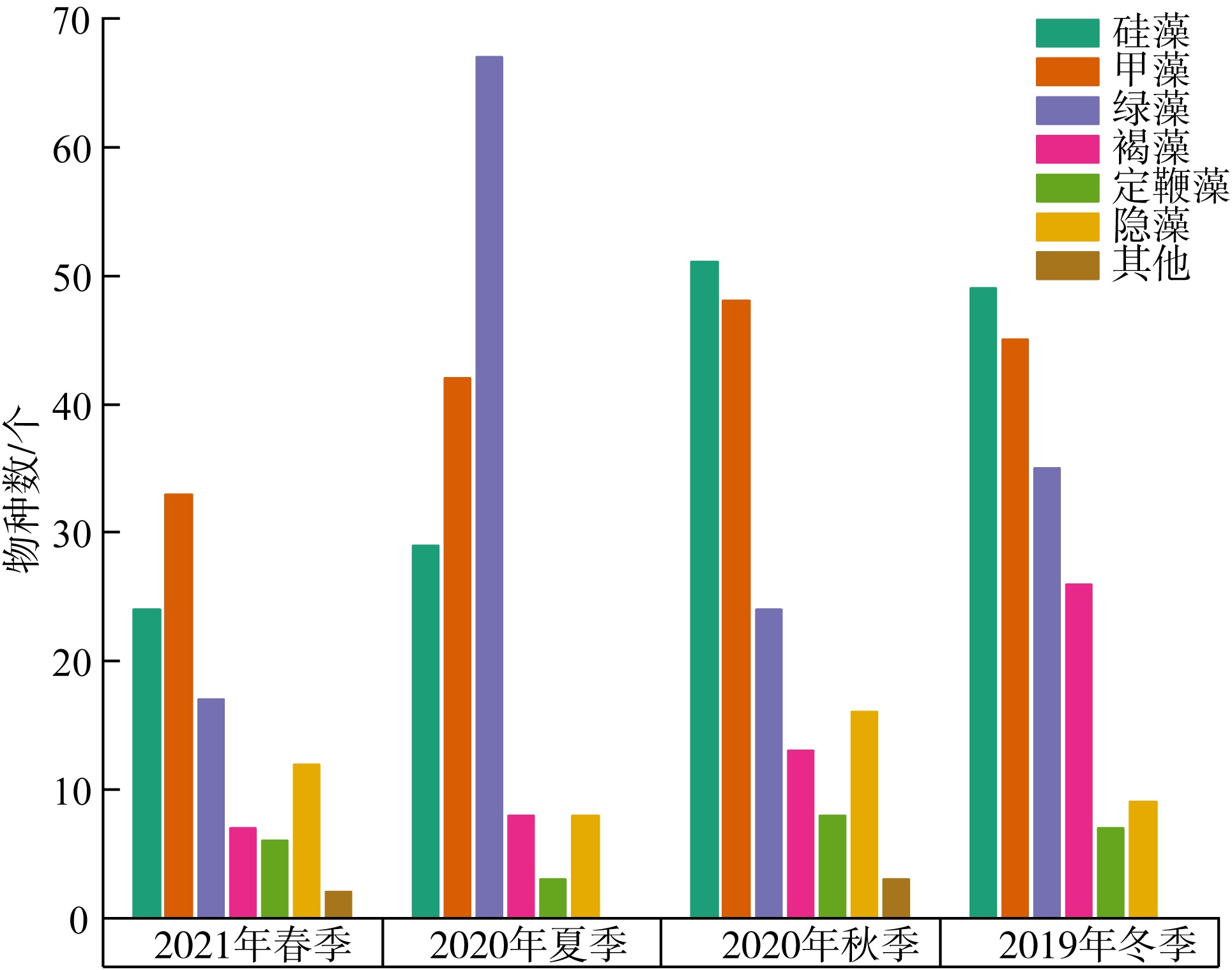
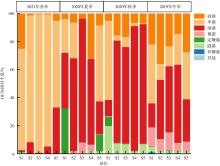
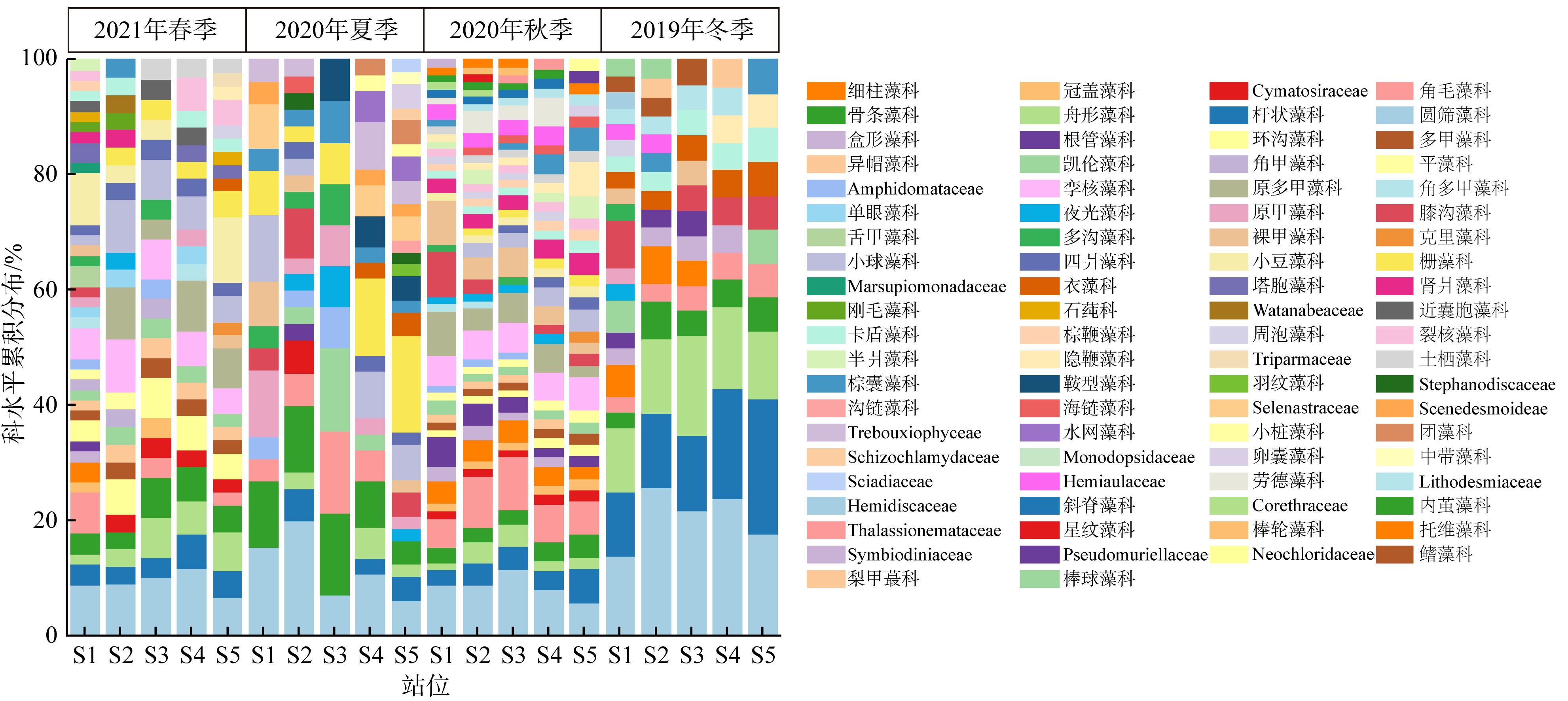
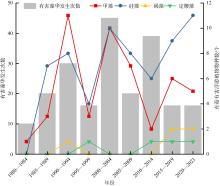
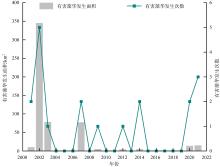
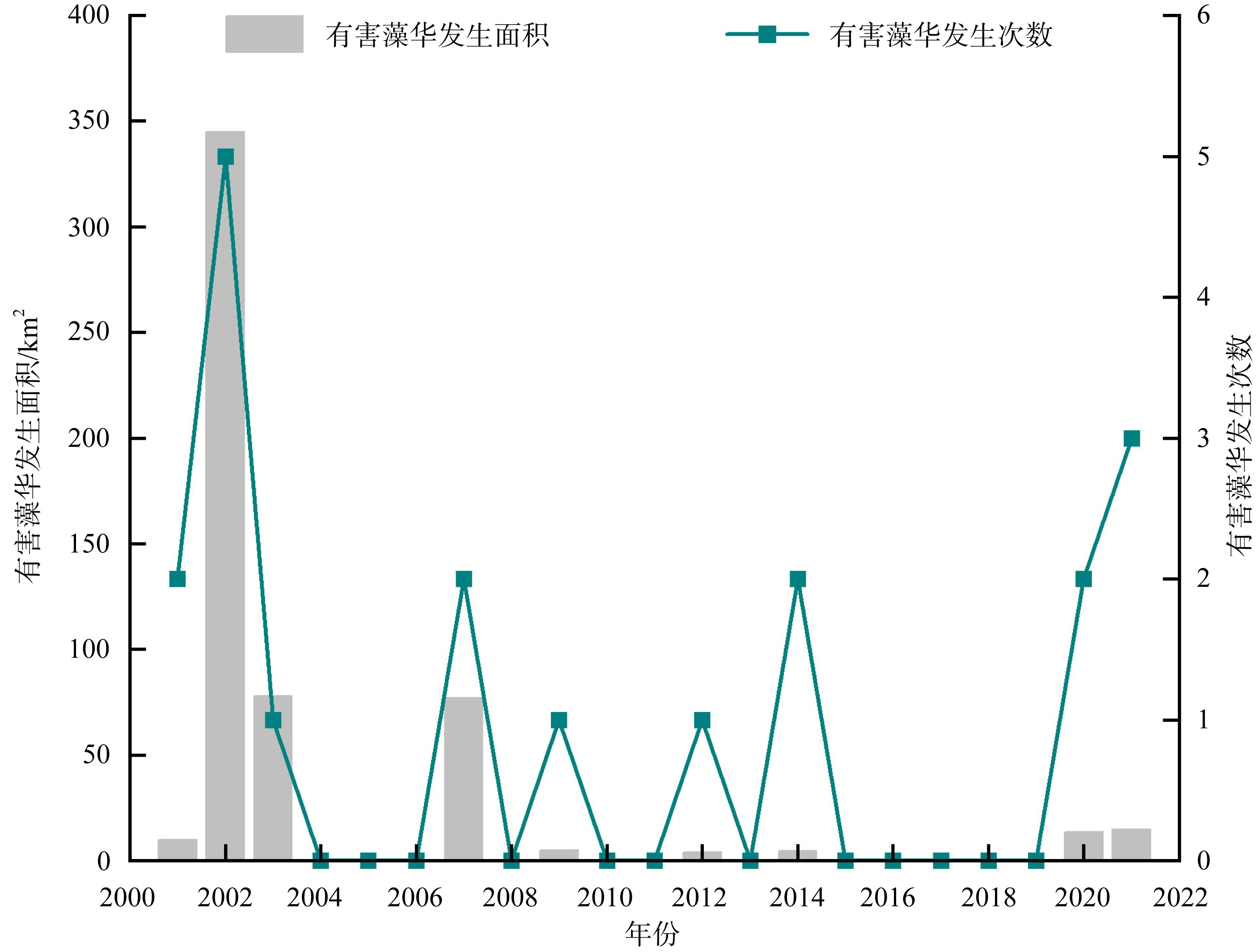
以18S rDNA V4区为目标基因, 采用Illumina Miseq高通量测序技术, 对深圳湾2019年冬季—2021年春季4个季节海水中浮游植物群落结构进行研究, 并整理该海域有害藻华生物的历史纪录数据, 以探讨深圳湾有毒有害浮游植物的群落组成及演替规律。高通量测序结果显示, 深圳湾海域真核浮游植物含硅藻、甲藻、绿藻、褐藻、定鞭藻、隐藻和红藻7个类群, 共82科269种。其中以微微型浮游植物为主要类群, 春季和秋季以微拟球藻(Nannochloris sp.)为优势种, 夏季以球等鞭金藻(Isochrysis galbana)为优势种, 冬季以极小海链藻(Thalassiosira minima)为优势种。冬季浮游植物多样性指数为全年最高。此次调查共检测出有毒有害浮游植物32种, 其中甲藻15种、硅藻13种、褐藻3种、定鞭藻1种。与历史资料相比, 深圳湾海域的有毒有害浮游植物呈微型化和多样性逐渐增加的趋势, 呈现由甲藻或硅藻为主的有毒有害单类群群落演替到以甲藻和硅藻为主的有毒有害双类群群落的趋势。
引用本文
黄圆, 岑竞仪, 梁芊艳, 吕颂辉, 王建艳. 基于高通量测序技术的深圳湾真核浮游植物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 21-33.
HUANG Yuan, CEN Jingyi, LIANG Qianyan, LYU Songhui, WANG Jianyan. Study on the community structure of eukaryotic phytoplankton in the Shenzhen Bay based on high-throughput sequencing technology[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 21-33.
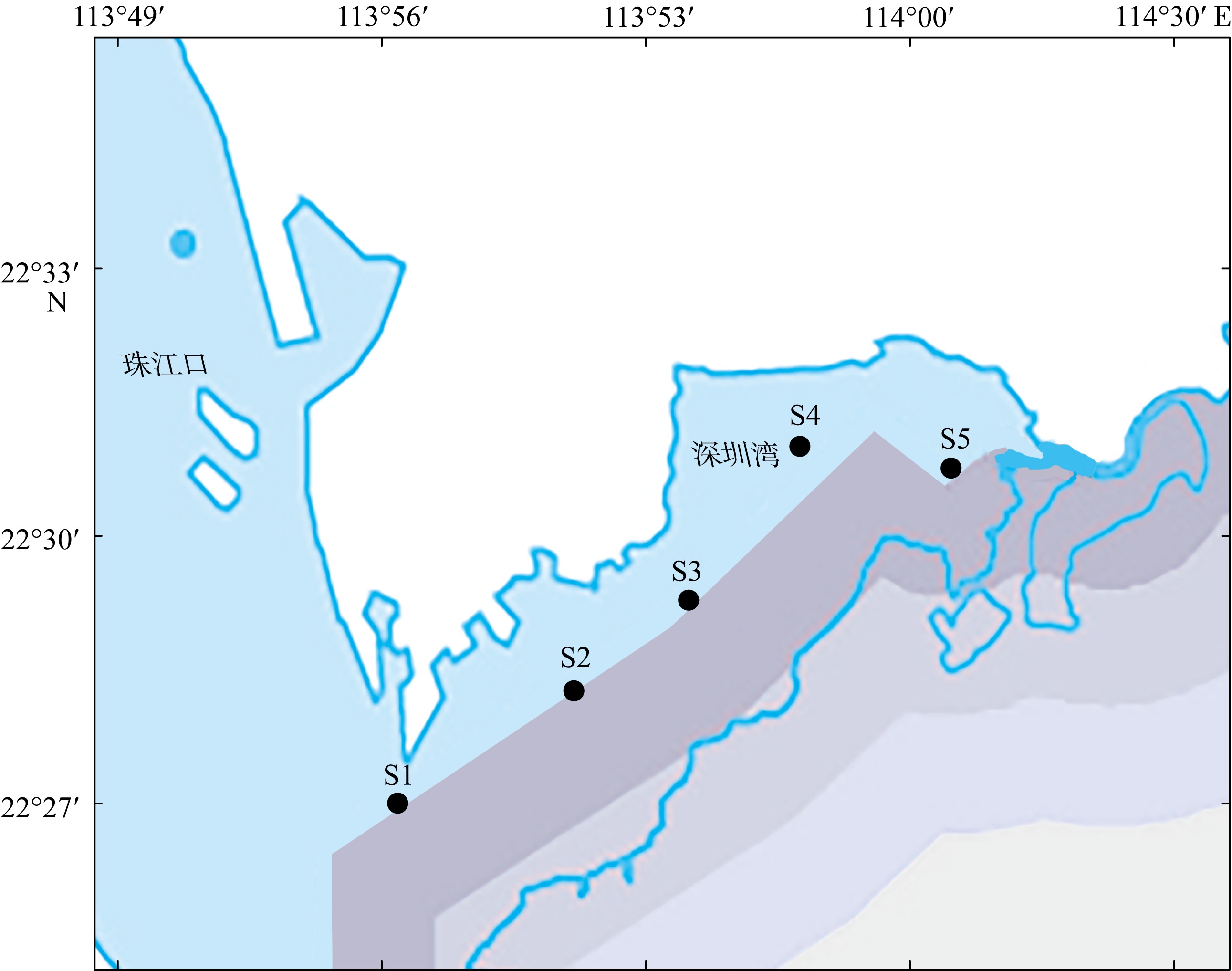
表3
深圳湾4个季节浮游植物优势种"
| 季节 | 物种 | 拉丁名 | 优势度 | 出现频率/% | 平均丰度/(×103个·m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021年春季 | 微拟球藻 | Nannochloris sp. | 0.54 | 100 | 43.12 |
| 小环藻 | Cyclotella choctawhatcheeana | 0.17 | 100 | 13.77 | |
| Picochlorum maculatum | Picochlorum maculatum | 0.08 | 80 | 8.13 | |
| 环沟藻 | Gyrodinium sp. | 0.08 | 100 | 6.40 | |
| 新月筒柱藻 | Cylindrotheca closterium | 0.02 | 80 | 2.41 | |
| 2020年夏季 | 球等鞭金藻 | Isochrysis galbana | 0.47 | 100 | 46.71 |
| 小球藻 | Chlorella sorokiniana | 0.07 | 60 | 11.78 | |
| 威氏海链藻 | Thalassiosira weissflogii | 0.08 | 80 | 10.34 | |
| 吉思纳海链藻 | Thalassiosira gessneri | 0.06 | 60 | 9.20 | |
| 双眉藻 | Sellaphora sp. | 0.04 | 60 | 5.91 | |
| 2020年秋季 | 微拟球藻 | Nannochloris sp. | 0.71 | 100 | 103.40 |
| 垂裂莱万藻 | Levanderina fissa | 0.02 | 100 | 2.94 | |
| 骨条藻 | Skeletonema sp. | 0.05 | 100 | 7.61 | |
| 异帽藻 | Heterocapsa sp. | 0.03 | 100 | 3.59 | |
| 海链藻 | Thalassiosira sp. | 0.04 | 100 | 5.63 | |
| 小环藻 | Cyclotella choctawhatcheeana | 0.02 | 100 | 3.10 | |
| 2019年冬季 | 赤潮异弯藻 | Heterosigma akashiwo | 0.26 | 100 | 7.75 |
| 舟形藻 | Navicula sp. | 0.04 | 100 | 1.18 | |
| 亚当斯骨条藻 | Skeletonema ardens | 0.06 | 100 | 1.93 | |
| 菱形藻 | Nitzschia sp. | 0.03 | 100 | 0.88 | |
| 新月筒柱藻 | Cylindrotheca closterium | 0.06 | 100 | 1.79 | |
| 极小海链藻 | Thalassiosira minima | 0.43 | 100 | 12.83 | |
| 梅尼小环藻 | Cyclotella meneghiniana | 0.03 | 80 | 0.93 |
表4
深圳湾浮游植物多样性指数"
| 季节 | 站位 | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 | Margalef丰富度指数 | Pielou均匀度指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021年春季 | S1 | 1.03 | 6.03 | 0.25 |
| S2 | 1.20 | 3.37 | 0.35 | |
| S3 | 1.88 | 3.58 | 0.57 | |
| S4 | 1.51 | 3.20 | 0.44 | |
| S5 | 1.11 | 3.83 | 0.30 | |
| 2020年夏季 | S1 | 1.41 | 1.89 | 0.48 |
| S2 | 1.51 | 3.46 | 0.44 | |
| S3 | 1.53 | 1.39 | 0.60 | |
| S4 | 1.25 | 1.94 | 0.41 | |
| S5 | 1.75 | 1.97 | 0.57 | |
| 2020年秋季 | S1 | 2.74 | 8.12 | 0.63 |
| S2 | 1.45 | 7.22 | 0.33 | |
| S3 | 1.44 | 7.02 | 0.33 | |
| S4 | 0.85 | 5.42 | 0.21 | |
| S5 | 0.71 | 4.38 | 0.19 | |
| 2019年冬季 | S1 | 2.96 | 4.57 | 0.84 |
| S2 | 1.38 | 3.06 | 0.41 | |
| S3 | 1.29 | 2.29 | 0.42 | |
| S4 | 1.69 | 2.12 | 0.58 | |
| S5 | 1.93 | 1.66 | 0.71 |
表5
深圳湾4个季节有毒有害浮游植物名录"
| 序号 | 门类 | 种名 | 拉丁文名 | 危害 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甲藻门 | 近缘亚历山大藻 | Alexandrium affine | 有毒 | √ | √ | √ | |
| 2 | 广野亚历山大藻 | Alexandrium hiranoi | 有毒 | √ | ||||
| 3 | 链状亚历山大藻 | Alexandrium catenella | 有毒 | √ | ||||
| 4 | 奥斯亚历山大藻 | Alexandrium ostenfeldii | 有毒 | √ | √ | |||
| 5 | 安德森亚历山大藻 | Alexandrium andersonii | 有毒 | √ | ||||
| 6 | 塔玛亚历山大藻 | Alexandrium tamarense | 有毒 | √ | ||||
| 7 | 渐尖鳍藻 | Dinophysis acuminata | 有毒 | √ | ||||
| 8 | 具刺膝沟藻 | Gonyaulax spinifera | 有毒 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 9 | 垂裂莱万藻(原名条纹环沟藻) | Levanderina fissa | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 10 | 剧毒卡尔藻 | Karlodinium veneficum | 有毒 | √ | √ | |||
| 11 | 夜光藻 | Noctiluca scintillans | 有害 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 12 | 凹面原甲藻 | Prorocentrum concavum | 有毒 | √ | √ | |||
| 13 | 钝齿原甲藻(原名东海原甲藻) | Prorocentrum obtusidens | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 14 | 巴哈马麦甲藻 | Pyrodinium bahamense | 有毒 | √ | ||||
| 15 | 双胞多沟藻 | Polykrikos geminatum | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 16 | 硅藻门 | 薄壁几内亚藻 | Guinardia flaccida | 有害 | √ | |||
| 17 | 柔弱角毛藻 | Chaetoceros debilis | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 18 | 并基角毛藻 | Chaetoceros decipiens | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 19 | 平孢角毛藻 | Chaetoceros laevisporus | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 20 | 格氏圆筛藻 | Coscinodiscus granii | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 21 | 琼氏圆筛藻 | Coscinodiscus jonesianus | 有害 | √ | √ | |||
| 22 | 辐射圆筛藻 | Coscinodiscus radiatus | 有害 | √ | √ | |||
| 23 | 环纹娄氏藻 | Lauderia annulata | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 24 | 丹麦细柱藻 | Leptocylindrus danicus | 有害 | √ | √ | |||
| 25 | 伦德海链藻 | Thalassiosira lundiana | 有害 | √ | √ | |||
| 26 | 极小海链藻 | Thalassiosira minima | 有害 | √ | √ | |||
| 27 | 威氏海链藻 | Thalassiosira weissflogii | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 28 | 萎软海链藻 | Thalassiosira mala | 有害 | √ | ||||
| 29 | 褐藻门 | 海洋卡盾藻 | Chattonella marina | 有害 | √ | |||
| 30 | 盐生卡盾藻 | Chattonella subsalsa | 有毒 | √ | √ | |||
| 31 | 赤潮异弯藻 | Heterosigma akashiwo | 有害 | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 32 | 定鞭藻门 | 球形棕囊藻 | Phaeocystis globosa | 有害 | √ | √ |
| [1] |
陈思, 2020. 基于层次分析法的深圳湾禁渔效果评价研究[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学:60-63.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈思, 陈海刚, 田斐, 等, 2021. 深圳湾浮游植物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态科学, 40(1): 9-16.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
广东省海洋与渔业局, 广东省海洋环境质量公报[EB/OL]. (2009, 2010). http://gdee.gd.gov.cn/hjzkgb/index_2.html (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
广东省海洋与渔业局, 广东省海洋环境状况公报[EB/OL]. (2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017). http://gdeegd.gov.cn/hjzkgb/index_2.html (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
广东省生态环境厅. 广东省生态环境状况公报[EB/OL]. (2018, 2019, 2020, 2021). http://gdee.gd.gov.cn/hjzkgb/index_2.html (in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
桓清柳, 庞仁松, 周秋伶, 等, 2016. 深圳近岸海域氮、磷营养盐变化趋势及其与赤潮发生的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 35(6): 908-914.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
冷科明, 江天久, 2004. 深圳海域近20年赤潮发生的特征分析[J]. 生态科学, 23(2): 166-170.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李港, 林妙丽, 陈诚, 等, 2021. 京杭运河苏北段秋冬季浮游植物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 水生态学杂志, 42(5): 119-126.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
刘华健, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 等, 2017. 珠江口浮游植物叶绿素a和初级生产力的季节变化及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(1): 81-91.
doi: 10.11978/2016033 |
|
|
|
| [10] |
邱阳凌, 林育青, 刘俊杰, 等, 2018. 淮河干流及主要支流夏季浮游植物群落生物多样性评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(4): 1665-1672.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
孙金水, 戴纪翠, 倪晋仁, 等, 2010a. 深圳湾海域浮游植物的生态特征[J]. 环境科学, (1): 63-68.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
孙金水,
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王朝晖, 齐雨藻, 尹伊伟, 等, 2001. 1998年春深圳湾环节环沟藻赤潮及其发生原因的探讨[J]. 海洋科学, 25(5): 47-50.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
吴振斌, 贺锋, 付贵萍, 等, 2002. 深圳湾浮游生物和底栖动物现状调查研究[J]. 海洋科学, 26(8): 58-64.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
向晨晖, 刘甲星, 柯志新, 等, 2021. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构和种类组成对淡澳河河口水加富的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(2): 49-60.
doi: 10.11978/2020040 |
|
|
|
| [16] |
袁超, 徐宗军, 张学雷, 2015. 2010—2011年深圳湾浮游植物季节变化及其与环境因子关系[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (1): 112-120.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
张冬鹏, 黎晓涛, 黄远峰, 等, 2001. 深圳沿海浮游植物组成及赤潮发生趋势分析[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), 22(5): 122-126.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
张才学, 周凯, 孙省利, 等, 2010. 深圳湾浮游动物的群落结构及季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(11): 2686-2692.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906(2010)11-2686-07 |
|
|
|
| [19] |
赵东至, 2010. 中国典型海域赤潮灾害发生规律[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社:269- 273.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
朱广伟, 施坤, 李未, 等, 2020. 太湖蓝藻水华的年度情势预测方法探讨[J]. 湖泊科学, 32(5): 1421-1431.
|
|
doi: 10.18307/2020.0504 |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.2000.45.3.0591 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146823 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1261605 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604 pmid: 23955772 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1139/facets-2020-0025 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.3390/rs13173469 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiw229 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101772 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1086/704827 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.3354/ame01144 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1007/s10750-008-9388-y |
| [36] |
doi: S1874-7787(17)30144-7 pmid: 28625778 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.1978.23.6.1256 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/s12601-019-0007-9 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1002/ece3.v9.17 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1003017726533 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07 pmid: 17586664 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140993 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111010 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2022.102297 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106510 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2016.11.005 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130489 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135760 |
| [1] | 林先智, 周岩岩, 林皓晔, 胡思敏, 黄晖, 张黎, 刘胜. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁区黑斑鹦嘴鱼(Scarus globiceps)食性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 100-108. |
| [2] | 贾男, 周天成, 胡思敏, 张琛, 黄晖, 刘胜. 南沙群岛海域珊瑚礁区三种寄居蟹的摄食差异比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 109-121. |
| [3] | 张琛, 胡思敏, 林先智, 周天成, 黄晖, 刘胜. 南沙珊瑚礁区波纹钩鳞鲀(Balistapus undulatus)食性和营养级分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 7-14. |
| [4] | 王欢欢, 谭斯尹, 王慧, 杜虹, 侯涛, 陈贤建, 黎俊珺, 黄莹. ATS藻板与自然礁石上藻群生物多样性的比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(1): 43-48. |
| [5] | 吴鹏, 连忠廉, 姜重臣, 邓伟, 熊小飞, 时小军, 张敬怀, 娄全胜, 方宏达. 高通量测序分析涠洲油气田开发区的微生物群落结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(5): 48-54. |
| [6] | 周凯, 章洁香, 张瑜斌, 卢东伟, 丁玉静, 孙省利. 深圳湾浮游细菌生物量的时空分布及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(3): 65-71. |
|
||