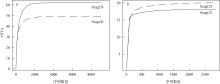
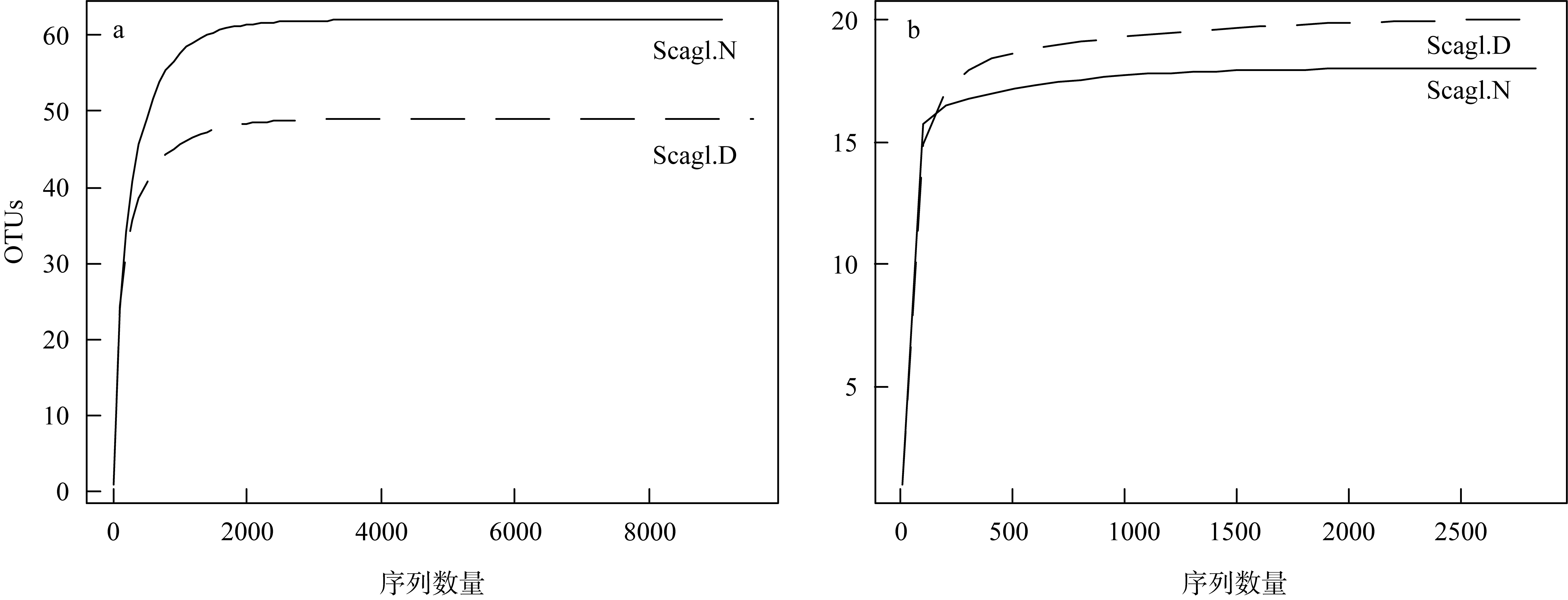
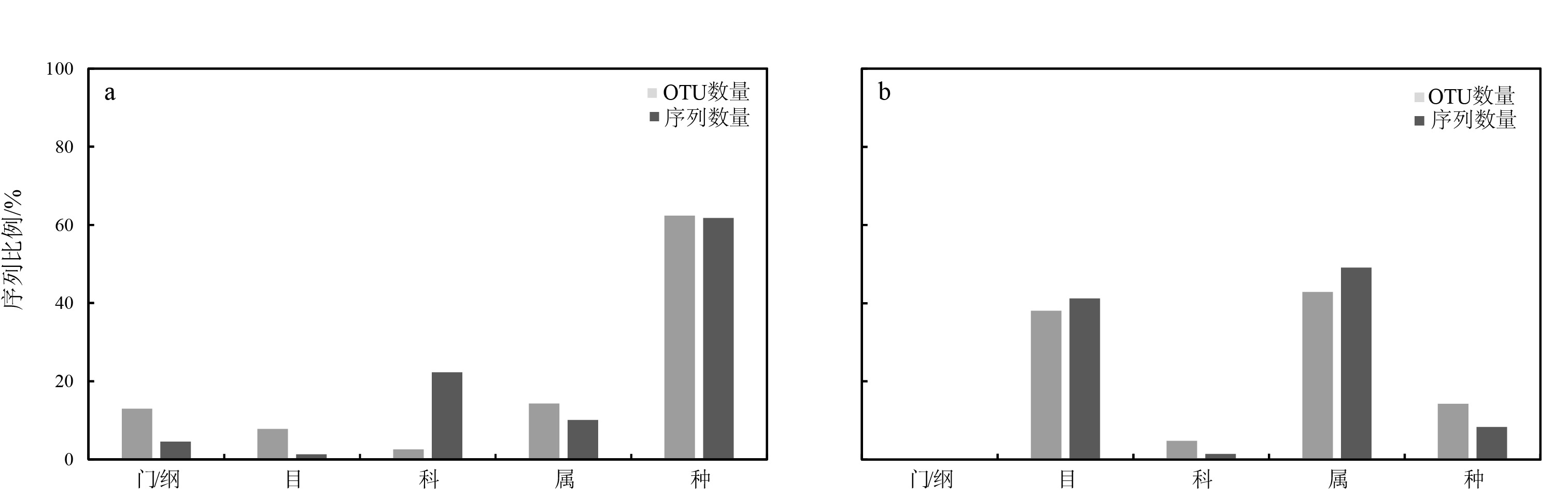
| [1] |
林先智, 胡思敏, 刘胜, 等, 2018. 传统测序与高通量测序在稚鱼食性分析中的比较[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(9): 3093-3101.
|
|
LIN XIANZHI, HU SIMIN, LIU SHENG, et al, 2018. Comparison between traditional sequencing and high-throughput sequencing on the dietary analysis of juvenile fish[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(9): 3093-3101 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201809.005
|
| [2] |
张琛, 胡思敏, 林先智, 等, 2022. 南沙珊瑚礁区波纹钩鳞鲀(Balistapus undulatus)食性和营养级分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(1): 7-14.
doi: 10.11978/2021008
|
|
ZHANG CHEN, HU SIMIN, LIN XIANZHI, et al, 2022. Diet and trophic level analysis of triggerfish (Balistapus undulatuse) in coral reefs of Nansha[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(1): 7-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2021008
|
| [3] |
周天成, 胡思敏, 林先智, 等, 2020. 基于18S rDNA条形码技术的珊瑚礁区塔形马蹄螺(Tectus pyramis)食性分析[J]. 海洋科学, 44(2): 99-107.
|
|
ZHOU TIANCHENG, HU SIMIN, LIN XIANZHI, et al, 2020. Study on the feeding habits of Tectus pyramis in the coral reef ecosystem based on 18S rDNA barcoding[J]. Marine Sciences, 44(2): 99-107. (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
ADAM T C, KELLEY M, RUTTENBERG B I, et al, 2015. Resource partitioning along multiple niche axes drives functional diversity in parrotfishes on Caribbean coral reefs[J]. Oecologia, 179(4): 1173-1185.
doi: 10.1007/s00442-015-3406-3
pmid: 26245147
|
| [5] |
AFEWORKI Y, BRUGGEMANN J H, VIDELER J J, 2011. Limited flexibility in resource use in a coral reef grazer foraging on seasonally changing algal communities[J]. Coral Reefs, 30(1): 109-122.
|
| [6] |
ALWANY M A, THALER E, STACHOWITSCH M, 2009. Parrotfish bioerosion on Egyptian Red Sea reefs[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 371(2): 170-176.
|
| [7] |
BELLWOOD D R, HUGHES T P, FOLKE C, et al, 2004. Confronting the coral reef crisis[J]. Nature, 429(6994): 827-833.
|
| [8] |
BONALDO R M, BELLWOOD D R, 2008. Size-dependent variation in the functional role of the parrotfish Scarus rivulatus on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 360: 237-244.
|
| [9] |
BONALDO R M, KRAJEWSKI J P, BELLWOOD D R, 2011. Relative impact of parrotfish grazing scars on massive Porites corals at Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 423: 223-233.
|
| [10] |
BONALDO R M, HOEY A S, BELLWOOD D R, 2014. The Ecosystem roles of parrotfishes on tropical reefs[M]// HUGHESR N, HUGHESD J, SMITHI P, Oceanography and marine biology: An annual review. Boca Raton: CRC Press: 81-132.
|
| [11] |
BRUGGEMANN J H, KUYPER M W M, BREEMAN A M, 1994a. Comparative-analysis of foraging and habitat use by the sympatric Caribbean parrotfish Scarus vetula and Sparisoma viride (Scaridae)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 112: 51-66.
|
| [12] |
BRUGGEMANN J H, VAN OPPEN M J H, BREEMAN A M, 1994b. Foraging by the stoplight-parrotfish Sparisoma-viride. I. food selection in different, socially determined habitats[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 106: 41-55.
|
| [13] |
BRUGGEMANN J H, VAN KESSEL A M, VAN ROOIJ J M, et al, 1996. Bioerosion and sediment ingestion by the Caribbean parrotfish Scarus vetula and Sparisoma viride: Implications of fish size, feeding mode and habitat use[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 134(1-3): 59-71.
|
| [14] |
BURKEPILE D E, HAY M E, 2008. Herbivore species richness and feeding complementarity affect community structure and function on a coral reef[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(42): 16201-16206.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801946105
pmid: 18845686
|
| [15] |
CHOAT J H, CLEMENTS K D, ROBBINS W D, 2002. The trophic status of herbivorous fishes on coral reefs - I: Dietary analyses[J]. Marine Biology, 140(3): 613-623.
|
| [16] |
CLEMENTS K D, GERMAN D P, PICHE J, et al, 2017. Integrating ecological roles and trophic diversification on coral reefs: multiple lines of evidence identify parrotfishes as microphages[J]. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 120(4): 729-751.
|
| [17] |
CNUDDE C, MOENS T, WERBROUCK E, et al, 2015. Trophodynamics of estuarine intertidal harpacticoid copepods based on stable isotope composition and fatty acid profiles[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 524: 225-239.
|
| [18] |
COMEROS-RAYNAL M T, CHOAT J H, POLIDORO B A, et al, 2012. The likelihood of extinction of iconic and dominant herbivores and detritivores of coral reefs: The Parrotfishes and Surgeonfishes[J]. PLoS One, 7(7): e39825.
|
| [19] |
CROSSMAN D J, CHOAT J H, CLEMENTS K D, 2005. Nutritional ecology of nominally herbivorous fishes on coral reefs[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 296: 129-142.
|
| [20] |
GORDON S E, GOATLEY C H R, BELLWOOD D R, 2016. Low-quality sediments deter grazing by the parrotfish Scarus rivulatus on inner-shelf reefs[J]. Coral Reefs, 35(1): 285-291.
|
| [21] |
HANMER J, WHITE J W, PAWLIK J R, 2017. Application of diet theory reveals context-dependent foraging preferences in an herbivorous coral reef fish[J]. Oecologia, 184(1): 127-137.
doi: 10.1007/s00442-017-3855-y
pmid: 28337605
|
| [22] |
HATCHER B G, 1988. Coral reef primary productivity: a beggar’s banquet[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 3(5): 106-111.
|
| [23] |
HOEY A S, BELLWOOD D R, 2008. Cross-shelf variation in the role of parrotfishes on the Great Barrier Reef[J]. Coral Reefs, 27(1): 37-47.
|
| [24] |
HUANG H, ZHOU G W, YANG J H, et al, 2013. Diversity of free-living and symbiotic Symbiodinium in the coral reefs of Sanya, South China Sea[J]. Marine Biology Research, 9(2): 117-128.
|
| [25] |
HUGHES T P, RODRIGUES M J, BELLWOOD D R, et al, 2007. Phase shifts, herbivory, and the resilience of coral reefs to climate change[J]. Current Biology, 17(4): 360-365.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.12.049
pmid: 17291763
|
| [26] |
KOHLER S T, KOHLER C C, 1992. Dead bleached coral provides new surfaces for dinoflagellates implicated in ciguatera fish poisonings[J]. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 35(4): 413-416.
|
| [27] |
KRAMER M J, BELLWOOD O, BELLWOOD D R, 2013. The trophic importance of algal turfs for coral reef fishes: the crustacean link[J]. Coral Reefs, 32(2): 575-583.
|
| [28] |
LIN X Z, HU S M, LIU S, et al, 2018. Unexpected prey of juvenile spotted scat (Scatophagus argus) near a wharf: The prevalence of fouling organisms in stomach contents[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 8(16): 8547-8554.
|
| [29] |
MUMBY P J, 2006. The impact of exploiting grazers (scaridae) on the dynamics of Caribbean coral reefs[J]. Ecological Applications, 16(2): 747-769.
pmid: 16711060
|
| [30] |
MUMBY P J, 2009. Herbivory versus corallivory: are parrotfish good or bad for Caribbean coral reefs?[J]. Coral Reefs, 28(3): 683-690.
|
| [31] |
MUSCATINE L, MCCLOSKEY L R, MARIAN R E, 1981. Estimating the daily contribution of carbon from zooxanthellae to coral animal respiration[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 26(4): 601-611.
|
| [32] |
NANAMI A, 2016. Parrotfish grazing ability: interspecific differences in relation to jaw-lever mechanics and relative weight of adductor mandibulae on an Okinawan coral reef[J]. PeerJ, 4(9):e2425.
|
| [33] |
NICHOLSON G M, CLEMENTS K D, 2020. Resolving resource partitioning in parrotfishes (Scarini) using microhistology of feeding substrata[J]. Coral Reefs, 39(5): 1313-1327.
|
| [34] |
PICHÉ J, IVERSON S J, PARRISH F A, et al, 2010. Characterization of forage fish and invertebrates in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands using fatty acid signatures: species and ecological groups[J]. Marine Ecology Progress, 41: 81-15.
|
| [35] |
POMPANON F, DEAGLE B E, SYMONDSON W O C, et al, 2012. Who is eating what: diet assessment using next generation sequencing[J]. Molecular Ecology, 21(8): 1931-1950.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05403.x
pmid: 22171763
|
| [36] |
PURCELL S W, BELLWOOD D R, 2001. Spatial patterns of epilithic algal and detrital resources on a windward coral reef[J]. Coral Reefs, 20(2): 117-125.
|
| [37] |
SAKKA A, LEGENDRE L, GOSSELIN M, et al, 2000. Structure of the oligotrophic planktonic food web under low grazing of heterotrophic bacteria: Takapoto Atoll, French Polynesia[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 197: 1-17.
|
| [38] |
STOECK T, BASS D, NEBEL M, et al, 2010. Multiple marker parallel tag environmental DNA sequencing reveals a highly complex eukaryotic community in marine anoxic water[J]. Molecular Ecology, 19(S1): 21-31.
|
| [39] |
TEBBETT S B, BELLWOOD D R, 2019. Algal turf sediments on coral reefs: what's known and what's next[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 149: 110542.
|
| [40] |
WILLIAMS I D, POLUNIN N V C, HENDRICK V J, 2001. Limits to grazing by herbivorous fishes and the impact of low coral cover on macroalgal abundance on a coral reef in Belize[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 222: 187-196.
|
| [41] |
WILSON S K, BELLWOOD D R, CHOAT J H, et al, 2003. Detritus in the epilithic algal matrix and its use by coral reef fishes[M]// GIBSONR N, ATKINSONR J A, Oceanography and marine biology:an annual review. London: Taylor & Francis: 279-309.
|
| [42] |
YANG D, NAM S, HWANG S J, et al, 2016. Fatty acid biomarkers to verify cyanobacteria feeding abilities of herbivorous consumers[J]. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 31(1): 77-91.
|