| [1] |
邸有鹏, 王全勇, 孙乐川, 2019. 海南岛邦塘湾海岸侵蚀演变及原因分析[J]. 工程与建设, 33(2): 155-156, 172.
|
|
DI YOUPENG, WANG QUANYONG, SUN LECHUAN, 2019. Evolution and cause analysis of coastal erosion in Bangtang Bay, Hainan island[J]. Engineering and Construction, 33(2): 155-156, 172 (in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
樊祺诚, 孙谦, 李霓, 等, 2004. 琼北火山活动分期与全新世岩浆演化[J]. 岩石学报, 20(3): 533-544.
|
|
FAN QICHENG, SUN QIAN, LI NI, et al, 2004. Periods of volcanic activity and magma evolution of Holocene in North Hainan Island[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3): 533-544 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
冯兴如, 李近元, 尹宝树, 等, 2018. 海南东方近岸海域海浪观测特征研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(3): 1-8.
doi: 10.11978/2017102
|
|
FENG XINGRU, LI JINYUAN, YIN BAOSHU, et al, 2018. Characteristics of ocean waves in coastal area of Dongfang, Hainan Island based on observations[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(3): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2017102
|
| [4] |
符启基, 沈金羽, 林才, 2012. 海南省笔架岭火山口及峨蔓湾地质遗迹景观开发初探[J]. 资源环境与工程, 26(6): 641-644.
|
|
FU QIJI, SHEN JINYU, LIN CAI, 2012. Discussion on development of geological relic landscape of Bijialing Crater and Mindanao Man Bay in Hainan Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 26(6): 641-644 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
韩孝辉, 吕剑泉, 陈文, 2018. 海南岛峨蔓火山海岸地质遗迹评价[J]. 华东地质, 39(2): 151-160.
|
|
HAN XIAOHUI, LYU JIANQUAN, CHEN WEN, 2018. Geological relics assessment on E’man volcanic coast in the Hainan Island[J]. East China Geology, 39(2): 151-160 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
黄心裕, 唐军, 王晓宇, 2022. 基于Prophet算法的海南近海波浪长时段时序分析与预测[J]. 海洋学报, 44(4): 114-121.
|
|
HUANG XINYU, TANG JUN, WAGN XIAOYU, 2022. Long term time series analysis and prediction of waves at Hainan offshore zone based on Prophet algorithm[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 44(4): 114-121 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
季荣耀, 罗宪林, 陆永军, 等, 2007. 海南岛海岸侵蚀特征及主因分析[C]// 第十三届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社: 374-377 (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
李丽, 武兴, 郭雅, 2019. 海南岛西北部海岸线时空变化分析[J]. 中国地质调查, 6(2): 87-93.
|
|
WU XING, GUO YA, 2019. Temporal and spatial variation analysis of the coastline of northwestern Hainan Island[J]. Geological Survey of China, 6(2): 87-93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
石海莹, 2013. 海南岛沿岸海洋灾害特征及防御对策[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 30(12): 70-75 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
石海莹, 吕宇波, 冯朝材, 2018. 海南岛典型岸段侵蚀现状及特征分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 37(3): 383-388.
|
|
SHI HAIYING, LYU YUBO, FENG ZHAOCAI, 2018. Analysis on the erosion status and characteristics of typical coasts in Hainan Island[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 37(3): 383-388 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
侍茂崇, 高劲松, 陈波, 等, 2011. 洋浦港附近冬季潮、余流特征分析[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (2): 1-6.
|
|
SHI MAOCHONG, GAO JINSONG, CHEN BO, et al, 2011. Analysis of the tidal current and the residual current near the YangPu port in winter[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (2): 1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
王颖, 周旅复, 1990. 海南岛西北部火山海岸的研究[J]. 地理学报, 45(3): 321-330.
doi: 10.11821/xb199003008
|
|
WANG YING, ZHOU LYUFU, 1990. The volcanic coast in the area of Northwest Thainan Island[J]. Acta Geolraphica Sinica, 45(3): 321-330 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
文世勇, 王紫竹, 王涛, 等, 2020. 基于遥感技术的海南省海岸侵蚀现状与趋势评估[J]. 灾害学, 35(1): 138-143.
|
|
WEN SHIYONG, WANG ZIZHU, WANG TAO, et al, 2020. Status and trend assessment of coastal erosion at Hainan Province based on remote sensing technology[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 35(1): 138-143 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
徐笑梅, 高抒, 周亮, 等, 2019. 海南岛东北部海岸极端波浪事件沉积记录[J]. 海洋学报, 41(6): 48-63.
|
|
XU XIAOMEI, GAO SHU, ZHOU LIANG, et al, 2019. Sedimentary records of extreme wave events on the northeastern Hainan Island coast, southern China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 41(6): 48-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
杨文健, 赵波, 于红梅, 等, 2022. 琼北峨蔓地区火山地质与喷发历史[J]. 地震地质, 44(4): 859-875.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.003
|
|
YANG WENJIAN, ZHAO BO, YU HONGMEI, et al, 2022. Study on volcanic geology and history of eruption in E’man area, northern Hainan Island[J]. Seismology and Geology, 44(4): 859-875 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
曾其爽, 1985. 海南岛西北部玄武岩海岸地貌研究[J]. 热带地貌, 6(2): 19-61.
|
|
ZENG QISHUANG, 1985. The study of the basaltic coast of the Northwest part of Hainan Island[J]. Tropical Geomorphology, 6(2): 19-61 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
赵勇伟, 李霓, 陈正全, 等, 2022. 海南峨蔓兵马角海岸火山地质特征与喷发灾害类型[J]. 地震地质, 44(2): 281-296.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.001
|
|
ZHAO YONGWEI, LI NI, CHEN ZHENGQUAN, et al, 2022. Geological characteristics and eruption hazards types of Bingmajiao: A coastal volcano in E’man, Hainan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 44(2): 281-296 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
庄克琳, 李广雪, 1999. 基岩海岸侵蚀数值研究进展[J]. 海洋地质动态, (11): 1-2 (in Chinese).
|
| [19] |
ANDRIANI G F, WALSH N, 2007. Rocky coast geomorphology and erosional processes: A case study along the Murgia coastline South of Bari, Apulia—SE Italy[J]. Geomorphology, 87(3): 224-238.
|
| [20] |
AYDIN A, BASU A, 2005. The Schmidt hammer in rock material characterization[J]. Engineering Geology, 81(1): 1-14.
|
| [21] |
BEETHAM E P, KENCH P S, 2011. Field observations of infragravity waves and their behaviour on rock shore platforms[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 36(14): 1872-1888.
|
| [22] |
BIRD E C F, 1993. The coast of Victoria: The shaping of scenery[M]. Victoria: Melbourne University Press.
|
| [23] |
DOI I, MATSUURA S, OSAWA H, et al, 2020. Effects of coastal erosion on landslide activity revealed by multi sensor observations[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 45(10): 2291-2299.
|
| [24] |
KENNEDY D M, 2015. Where is the seaward edge? A review and definition of shore platform morphology[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 147: 99-108.
|
| [25] |
KENNEDY D M, MILKINS J, 2015. The formation of beaches on shore platforms in microtidal environments[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 40(1): 34-46.
|
| [26] |
KOGURE T, 2022. Rocky coastal cliffs reinforced by vegetation roots and potential collapse risk caused by sea-level rise[J]. CATENA, 217: 106457.
|
| [27] |
KRASTEL S, SCHMINCKE H U, JACOBS C L, et al, 2001. Submarine landslides around the Canary Islands[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 106(B3): 3977-3997.
|
| [28] |
MASSELINK G, SCOTT T, POATE T, et al, 2016. The extreme 2013/2014 winter storms: hydrodynamic forcing and coastal response along the southwest coast of England[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 41(3): 378-391.
|
| [29] |
ODÉRIZ I, KNÖCHELMANN N, SILVA R, et al, 2020. Reinforcement of vegetated and unvegetated dunes by a rocky core: A viable alternative for dissipating waves and providing protection?[J]. Coastal Engineering, 158: 103675.
|
| [30] |
POATE T, MASSELINK G, AUSTIN M J, et al, 2018. The role of bed roughness in wave transformation across sloping rock shore platforms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 123(1): 97-123.
|
| [31] |
RAMALHO R S, WINCKLER G, MADEIRA J, et al, 2015. Hazard potential of volcanic flank collapses raised by new megatsunami evidence[J]. Science Advances, 1(9): e1500456.
|
| [32] |
STEPHENSON W J, DICKSON M E, TRENHAILE A S, 2022. Rock coasts, treatise on geomorphology[M]. 2nd ed. Oxford: Academic Press: 561-586.
|
| [33] |
SUNAMURA T, 1992. Geomorphology of rocky coasts[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
|
| [34] |
SUNAMURA T, TSUJIMOTO H, AOKI H, 2014. Chapter 12 The rock coast of Japan[J]. Geological Society, London, Memoirs, 40(1): 203-223.
|
| [35] |
TRENHAILE A S, 2000. Modeling the development of wave-cut shore platforms[J]. Marine Geology, 166(1-4): 163-178.
|
| [36] |
TRENHAILE A S, 2002. Rock coasts, with particular emphasis on shore platforms[J]. Geomorphology, 48(1-3): 7-22.
|
| [37] |
TRENHAILE A S, 2016. Rocky coasts ― their role as depositional environments[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 159: 1-13.
|
| [38] |
ZHAO ZHONGWEI, MITCHELL N C, QUARTAU R, et al, 2019. Submarine platform development by erosion of a Surtseyan cone at Capelinhos, Faial Island, Azores[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 44(15): 2982-3006.
|
| [39] |
ZHAO ZHONGWEI, MITCHELL N C, STEPHENSON W J, 2022. Testing the Sunamura et al. (2014) equations for wave attenuation over shore platforms[J]. Geomorphology, 419: 108480.
|
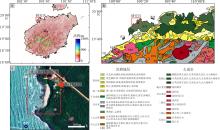
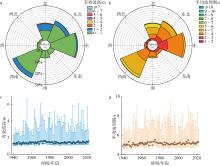
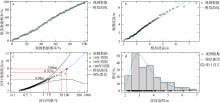
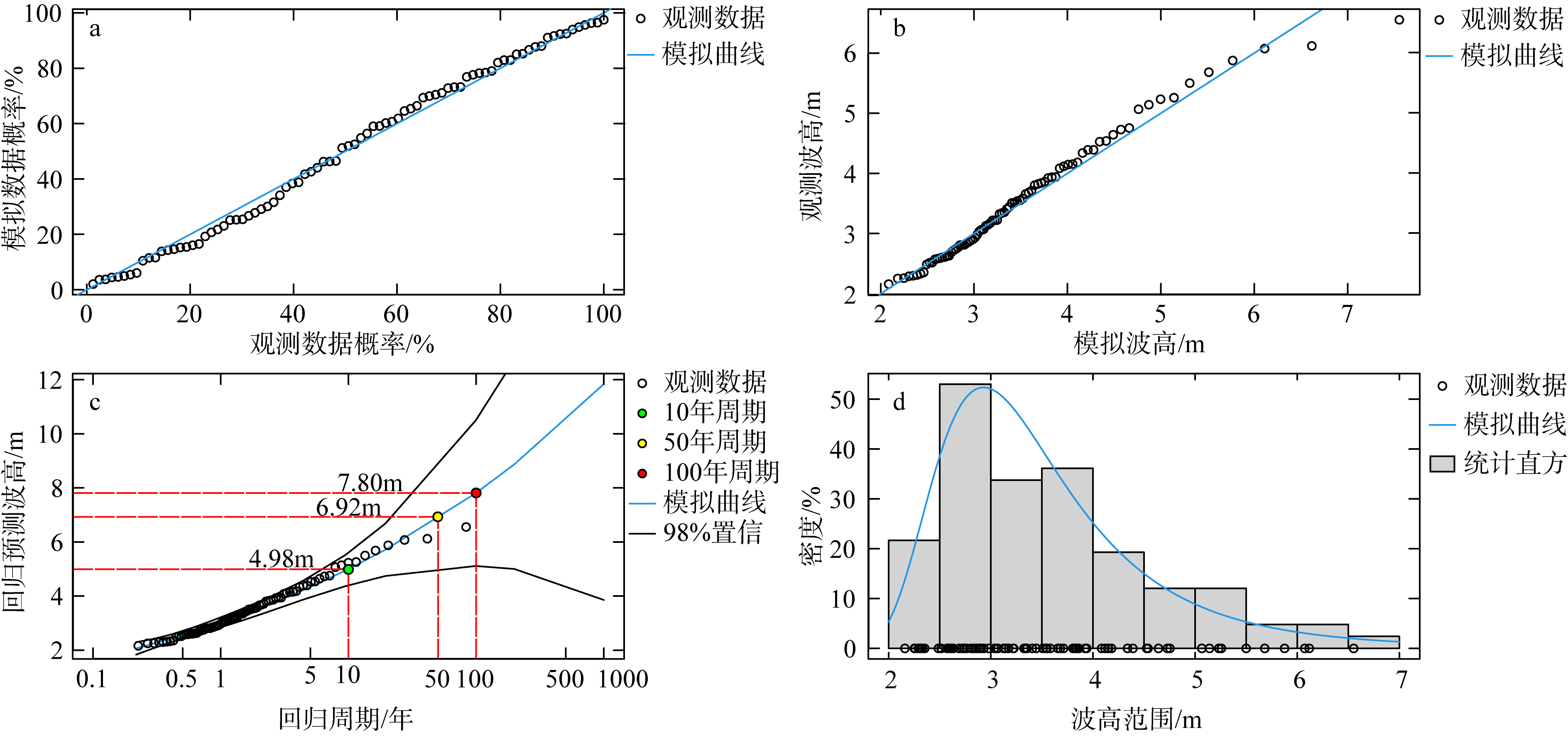
 ), 吴凌云1,3, 高伟健1,3, 李伟1,2,3(
), 吴凌云1,3, 高伟健1,3, 李伟1,2,3( )
)
 ), WU Lingyun1,3, GAO Weijian1,3, LI Wei1,2,3(
), WU Lingyun1,3, GAO Weijian1,3, LI Wei1,2,3( )
)