热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 156-167.doi: 10.11978/2023004CSTR: 32234.14.2023004
• 海洋环境科学 • 上一篇
海南岛北部海湾表层海水重金属分布特征、主控因素及污染评价
曾维特1,2( ), 张东强1,3(
), 张东强1,3( ), 刘兵1,4, 杨永鹏1,3, 张航飞5, 吴多誉1, 王晓林1,3
), 刘兵1,4, 杨永鹏1,3, 张航飞5, 吴多誉1, 王晓林1,3
- 1.海南省海洋地质资源与环境重点实验室, 海南 海口 570206
2.海南省海洋地质调查院, 海南 海口 570206
3.海南省地质调查院, 海南 海口 570206
4.海南省海洋地质调查局, 海南 海口 570206
5.四川省地质矿产勘查开发局二零七地质队, 四川 乐山 614000
-
收稿日期:2023-01-04修回日期:2023-04-06出版日期:2023-11-10发布日期:2023-04-14 -
作者简介:曾维特(1986—), 男, 海南省澄迈县人, 高级工程师, 博士, 主要研究方向为海洋地质、海岸带环境地质。email: zengweite@126.com
-
基金资助:海南省科学技术协会青年科技英才创新计划项目(QCXM202008); 海南省自然科学基金青年基金项目(421QN369); 海南省海洋地质资源与环境重点实验室课题(ZZ[2020]2019256-01)
Distribution, main controlling factors and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface seawater of the Northern Bay of Hainan Island, south China
ZENG Weite1,2( ), ZHANG Dongqiang1,3(
), ZHANG Dongqiang1,3( ), LIU Bing1,4, YANG Yongpeng1,3, ZHANG Hangfei5, WU Duoyu1, WANG Xiaolin1,3
), LIU Bing1,4, YANG Yongpeng1,3, ZHANG Hangfei5, WU Duoyu1, WANG Xiaolin1,3
- 1. Hainan Key Laboratory of Marine Geological Resources and Environment, Haikou 570206, China
2. Marine Geological Survey of Hainan Province, Haikou 570206, China
3. Hainan Geological Survey, Haikou 570206, China
4. Hainan Marine Geological Survey, Haikou 570206, China
5. No. 207 Geological Team, Sichuan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Leshan 614000, China
-
Received:2023-01-04Revised:2023-04-06Online:2023-11-10Published:2023-04-14 -
Supported by:Young Talents' Science and Technology Innovation Project of Hainan Association for Science and Technology(QCXM202008); Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China(421QN369); Independent project of Key Laboratory of Marine Geology Resources and Environment of Hainan Province(ZZ[2020]2019256-01)
摘要:
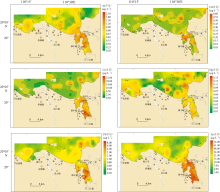
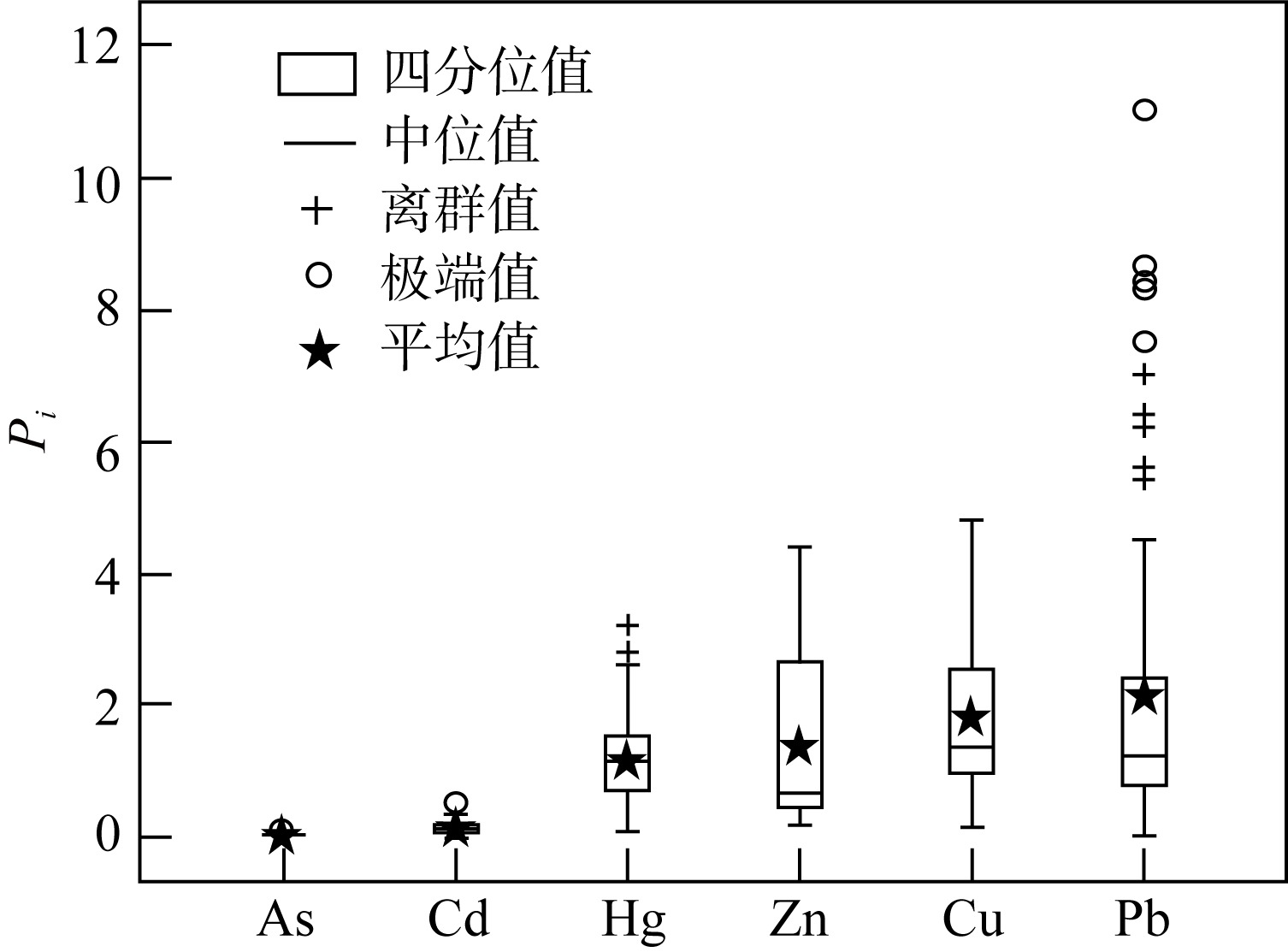
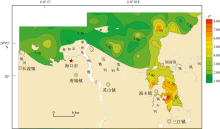
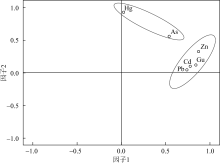
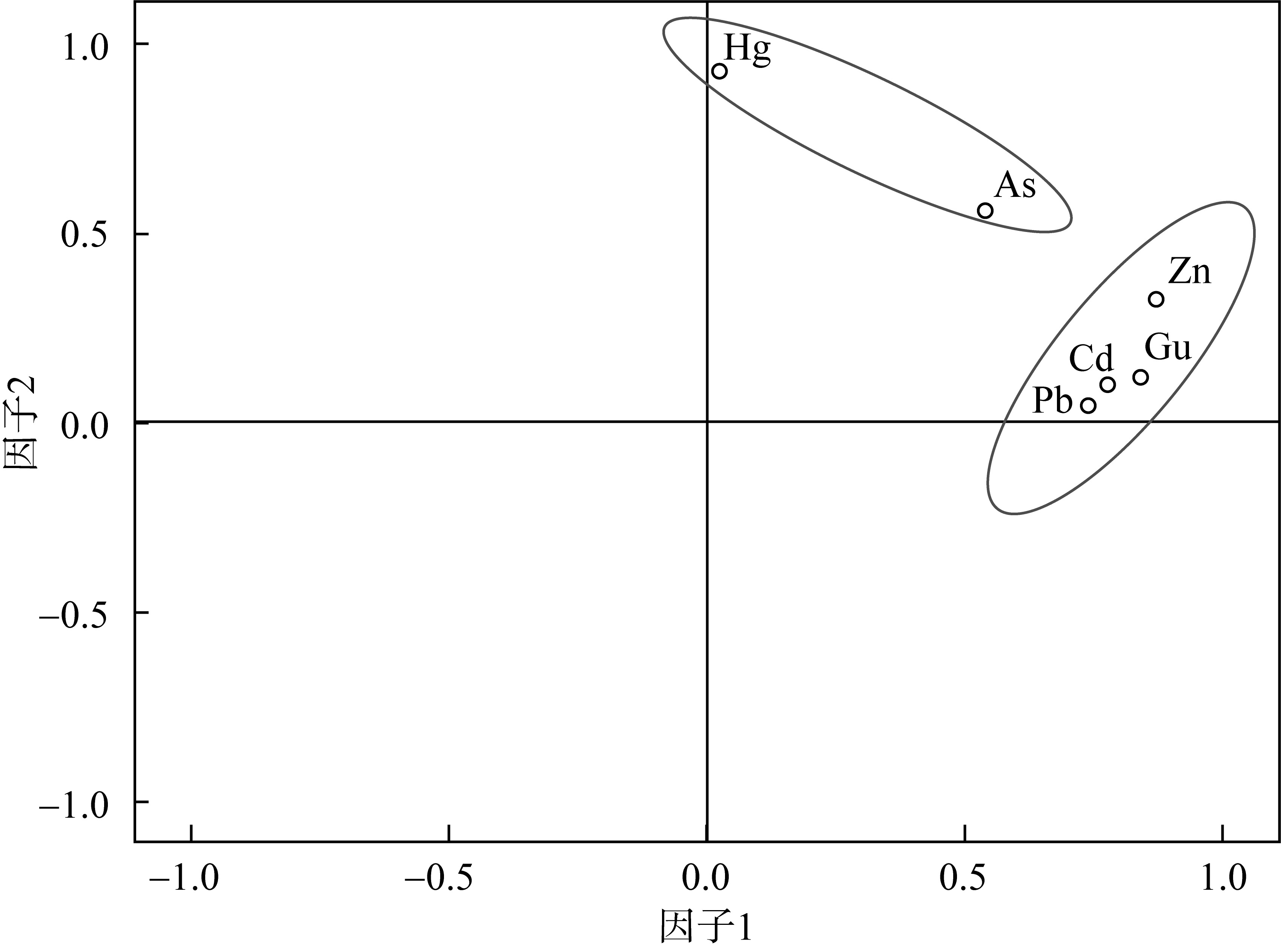
对海南岛北部海湾研究区表层海水进行调查取样及地球化学分析测试, 查明表层海水中重金属(溶解态)As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Pb和Zn含量及其空间分布。基于相关性分析和因子分析明确海水中溶解态重金属来源并研究控制其分布的主要因子, 基于单因子污染指数和权重修正内梅罗污染指数评价研究区海域海水重金属污染情况。结果表明, 表层海水中As、Cd、Cu、Hg、Pb和Zn平均含量分别为0.58、0.14、8.68、0.057、2.07和26.24μg·L-1, Cr含量低于检测限。重金属含量高值区主要分布于东寨港、铺前湾湾顶及东侧沿岸、迈雅河与道孟河河口处。南渡江入海口、如意岛周边海域和海口湾近岸海域, 表层海水清洁度高, 评价为无污染。海口港外围、迈雅河与道孟河入海口、铺前湾湾顶及东侧沿岸、木兰湾西侧, 污染程度低—中等。东寨港内部污染程度中等—严重, 其中演丰河入海口污染程度最为严重。重金属污染严重程度从大到小为Pb、Cu、Zn、Hg、Cd、As, 应将Pb、Cu和Zn同时作为今后该海域环境重点监测对象。近岸海水中重金属主要来自陆源输入, 其次为船舶污染, 同时还包括大气输入、农业和水产养殖业等污染源。高盐度低pH可促使重金属从水体悬浮颗粒中解吸释放, 此外水动力条件也是重金属分布差异性主控因素之一。
引用本文
曾维特, 张东强, 刘兵, 杨永鹏, 张航飞, 吴多誉, 王晓林. 海南岛北部海湾表层海水重金属分布特征、主控因素及污染评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 156-167.
ZENG Weite, ZHANG Dongqiang, LIU Bing, YANG Yongpeng, ZHANG Hangfei, WU Duoyu, WANG Xiaolin. Distribution, main controlling factors and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface seawater of the Northern Bay of Hainan Island, south China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 156-167.
表3
海水溶解态重金属含量测试结果统计"
| 统计量 | 重金属含量/(μg·L-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Cd | Cu | Hg | Pb | Zn | |
| 最小值 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.64 | 0.0040 | 0.20 | 3.44 |
| 最大值 | 2.12 | 0.60 | 24.00 | 0.1600 | 11.00 | 88.00 |
| 平均值 | 0.58 | 0.14 | 8.68 | 0.0573 | 2.07 | 26.24 |
| 标准差 | 0.36 | 0.13 | 5.57 | 0.0308 | 2.21 | 24.53 |
| 变异系数 | 0.62 | 0.93 | 0.64 | 0.54 | 1.07 | 0.93 |
| 南渡江(祁士华 等, | 0.26 | 0.005 | 0.51 | 0.001 | 1.03 | 2.00 |
| 海南岛近岸(国土资源部中国地质调查局, | 3.78 | 0.62 | 6.35 | 0.101 | 3.14 | 20.61 |
| 琼州海峡(刘翠梅 等, | — | 0.02 | 1.37 | 0.046 | 0.11 | 11.11 |
| 南海中部(李景喜 等, | 1.90 | 1.30 | 1.60 | — | 1.99 | 6.47 |
表5
重金属、盐度、pH和悬浮物相关系数"
| Zn | As | Cu | Pb | Cd | Hg | 盐度 | pH | 悬浮物 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 1.000 | ||||||||
| As | 0.675** | 1.000 | |||||||
| Cu | 0.778** | 0.414** | 1.000 | ||||||
| Pb | 0.560** | 0.256* | 0.549** | 1.000 | |||||
| Cd | 0.630** | 0.459** | 0.502** | 0.460** | 1.000 | ||||
| Hg | 0.272* | 0.312** | 0.176 | 0.196 | 0.130 | 1.000 | |||
| 盐度 | 0.338** | -0.014 | 0.318** | 0.379** | 0.300** | 0.144 | 1.000 | ||
| pH | -0.590** | 0.080 | -0.472** | -0.492** | -0.391** | -0.221* | -0.481** | 1.000 | |
| 悬浮物 | 0.531** | 0.439** | 0.450** | 0.433** | 0.341** | 0.253* | 0.301** | -0.501** | 1.000 |
| [1] |
邴海健, 吴艳宏, 刘恩峰, 等, 2010. 长江中下游不同湖泊沉积物中重金属污染物的累积及其潜在生态风险评价[J]. 湖泊科学, 22(5): 675-683.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈春华, 谷尚莉, 王道儒, 2003. 海口湾水质污染监测可比性问题的初步探讨[J]. 海洋环境科学, 22(4): 30-33.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
崔衍波, 冯永亮, 刘群群, 等, 2019. 东营市三个河口区域表层海水重金属的分布与生态风险评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 49(1): 93-101.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
国家环境保护局, 1998. GB-3097-1997 海水水质标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-21. GB-3097-1997, 1997.
|
|
State Environmental Protection Administration, 1998. Sea water quality standard[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-21 (in Chinese).
|
|
| [5] |
国土资源部中国地质调查局, 2011. 中华人民共和国多目标区域地球化学图集. 海南岛[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-84 (in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
贺志鹏, 宋金明, 张乃星, 等, 2008. 南黄海表层海水重金属的变化特征及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 29(5): 1153-1162.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
暨卫东, 2015. 近海重金属污染元素监测与评价方法[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-210 (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
季一诺, 赵志忠, 吴丹, 等, 2016. 海南东寨港红树林沉积物中重金属的分布及其生物有效性[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(2): 593-600.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李景喜, 李俊飞, 郑立, 等, 2013. 南海中南部水域海水中重金属的分布特征[J]. 中国环境监测, 29(3): 65-71.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李鹏山, 林国尧, 谢跟踪, 等, 2010. 海口湾近岸海域水质状况分析与评价[J]. 海南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 23(1): 108-114.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
李悦昭, 陈海洋, 孙文超, 2020. “河-湖”沉积物重金属环境特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 41(6): 2646-2652.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
李占海, 柯贤坤, 王倩, 等, 2003. 琼州海峡水沙输运特征研究[J]. 地理研究, 22(2): 151-159.
|
|
doi: 10.11821/yj2003020003 |
|
| [13] |
林红梅, 王伟力, 林彩, 等, 2020. 钦州湾及其邻近海域重金属的时空变化特征和影响因素[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 39(4): 490-500.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
刘翠梅, 温伟英, 何清溪, 2002. 琼州海峡海洋环境现状调查与评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 21(4): 24-28.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
刘华峰, 傅杨荣, 杨奕, 等, 2010. 琼州海峡表层沉积物重金属元素分布特征与生态风险评价[J]. 安全与环境工程, 17(4): 33-36.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
刘慧杰, 刘文君, 刘继平, 等, 2017. 南中国海表层海水重金属含量及其潜在生态风险分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(10): 3891-3898.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
刘建波, 刘洁, 陈春华, 等, 2012. 海口湾东部表层沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 安徽农业科学, 40(17): 9416-9418.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
刘艳丽, 张劲, 何会军, 2018. 黄、东海表层沉积物重金属赋存形态及风险评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 48(12): 71-78.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
罗万次, 苏搏, 刘熊, 等, 2014. 广西北仑河口红树林保护区表层海水溶解态重金属时空分布及其影响因素[J]. 海洋通报, 33(6): 668-675.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
祁士华, 傅杨荣, 刘华峰, 等, 2009. 海南岛生态地球化学调查海岸带生态系统地球化学评价报告[R]. 海南: 海南省地质调查院: 17-27 (in Chinese).
|
| [21] |
沈盎绿, 马继臻, 平仙隐, 等, 2009. 褶牡蛎对重金属的生物富集动力学特性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 28(4): 783-788.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
王百顺, 刘阿成, 陈忠阳, 2003. 1984—2000年长江口海域水质重金属浓度分布变化[J]. 海洋通报, 22(2): 32-38.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
王毅, 2018. 钦州近岸海域及其入海口重金属的分布、来源及污染风险评价[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 1-64.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
王宇彤, 2021. 沉积物中重金属迁移释放规律研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学: 1-57.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
魏俊峰, 吴大清, 彭金莲, 等, 2003. 污染沉积物中重金属的释放及其动力学[J]. 生态环境, 2: 127-130.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
翁焕新,
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
邢孔敏, 陈石泉, 蔡泽富, 等, 2018. 海南东寨港表层沉积物重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 海洋科学进展, 36(3): 478-488.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
曾维特, 杨永鹏, 张东强, 等, 2018. 海南岛北部海湾沉积物重金属来源、分布主控因素及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 39(3): 1085-1094.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
张恩仁, 张经, 2003. 长江河口悬浮物对几种金属吸附的pH效应[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 34(3): 267-273.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
张家友, 吴国爱, 傅杨荣, 等, 2012. 海口湾重金属富集与评价[J]. 国土资源科技管理, 29(5): 43-48.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
张兆永, 吉力力·阿不都外力, 姜逢清, 2015. 艾比湖表层沉积物重金属的来源、污染和潜在生态风险研究[J]. 环境科学, 36(2): 490-496.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
朱赖民, 高志友, 尹观, 等, 2007. 南海表层沉积物的稀土和微量元素的丰度及其空间变化[J]. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2963-2980.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2012.38.331 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11157-5 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.055 pmid: 22406241 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4959-8 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1007/s00203-019-01650-y pmid: 30888453 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3398-z |
| [39] |
doi: S0045-6535(17)30149-2 pmid: 28193587 |
| [40] |
doi: S0045-6535(18)30491-0 pmid: 29554504 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1007/s11368-017-1833-y |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113494 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.04.024 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10356-4 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2002)032<0103:TROQSI>2.0.CO;2 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146383 |
| [1] | 奚琛, 林宗轩, 萨如拉, 邓玺, 刘强, 倪亮, 罗来才, 马腾, 谢智杰, 陈思若, 陈松泽. 基于双浮标连续监测资料分析大亚湾西南部海域水体环境变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [2] | 吴雪萍, 叶红霞, 姚又菊, 刘浩翔, 李瑞华, 童潼. 3个地区可口革囊星虫营养成分及重金属含量的分析与评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 92-107. |
| [3] | 董汉英, 苏娟, 周声圳, 梁少霞, 陈观宇, 王凡. 南海西沙海域冬季海水重金属质量浓度水平及来源分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 169-177. |
| [4] | 谢勇, 王友绍. 重金属胁迫下四种红树植物幼苗生理响应特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 28-34. |
| [5] | 李傲, 冯洋, 王云涛, 薛惠洁. 基于OC-CCI数据的南海高叶绿素a浓度水域面积的时空变化研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 77-89. |
| [6] | 徐东海, 王利杰, 姚永坚, 孙珍, 邱宁. 礼乐盆地碳酸盐岩时空分布特征及构造意义[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(6): 49-62. |
| [7] | 庄晓珊, 桓清柳, 彭莹, 王节亮, 庞仁松, 周凯. 深圳东部近岸海域溶解氧的时空分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(5): 98-105. |
| [8] | 张际标, 杨波, 陈涛, 陈春亮. 深圳西部海域河流入海口沉积物酸可挥发性硫、同步提取重金属分布特征与生物毒性评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(6): 89-101. |
| [9] | 吴鹏, 连忠廉, 姜重臣, 邓伟, 熊小飞, 时小军, 张敬怀, 娄全胜, 方宏达. 高通量测序分析涠洲油气田开发区的微生物群落结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(5): 48-54. |
| [10] | 唐博, 龙江平, 金路, 许冬, 李团结. 珠江口和北部湾附近海域沉积物重金属生态风险比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(3): 75-81. |
| [11] | 甘华阳, 林进清, 梁开, 利锋, 段志鹏. 雷州半岛滨海湿地表层沉积物中重金属含量分布与生态风险评价*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(3): 79-87. |
| [12] | 王文洁, 徐建. 印-太暖池区全新世Mg/Ca温度转换中的盐度因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(2): 94-100. |
| [13] | 李磊, 王云龙, 沈盎绿, 蒋玫, 黄厚见, 沈新强. 沉积物暴露条件下文蛤Meretrix meretrix 对重金属Cu、Pb的富集动力学研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(1): 70-75. |
| [14] | 丘耀文,余克服. 海南红树林湿地沉积物中重金属的累积[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(2): 102-108. |
| [15] | 黄国勇,王友绍,孙翠慈,宋晖,吴梅林,董俊德. 秋茄叶对复合重金属的胁迫反应及其积累能力研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(6): 104-109. |
|
||