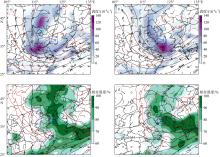
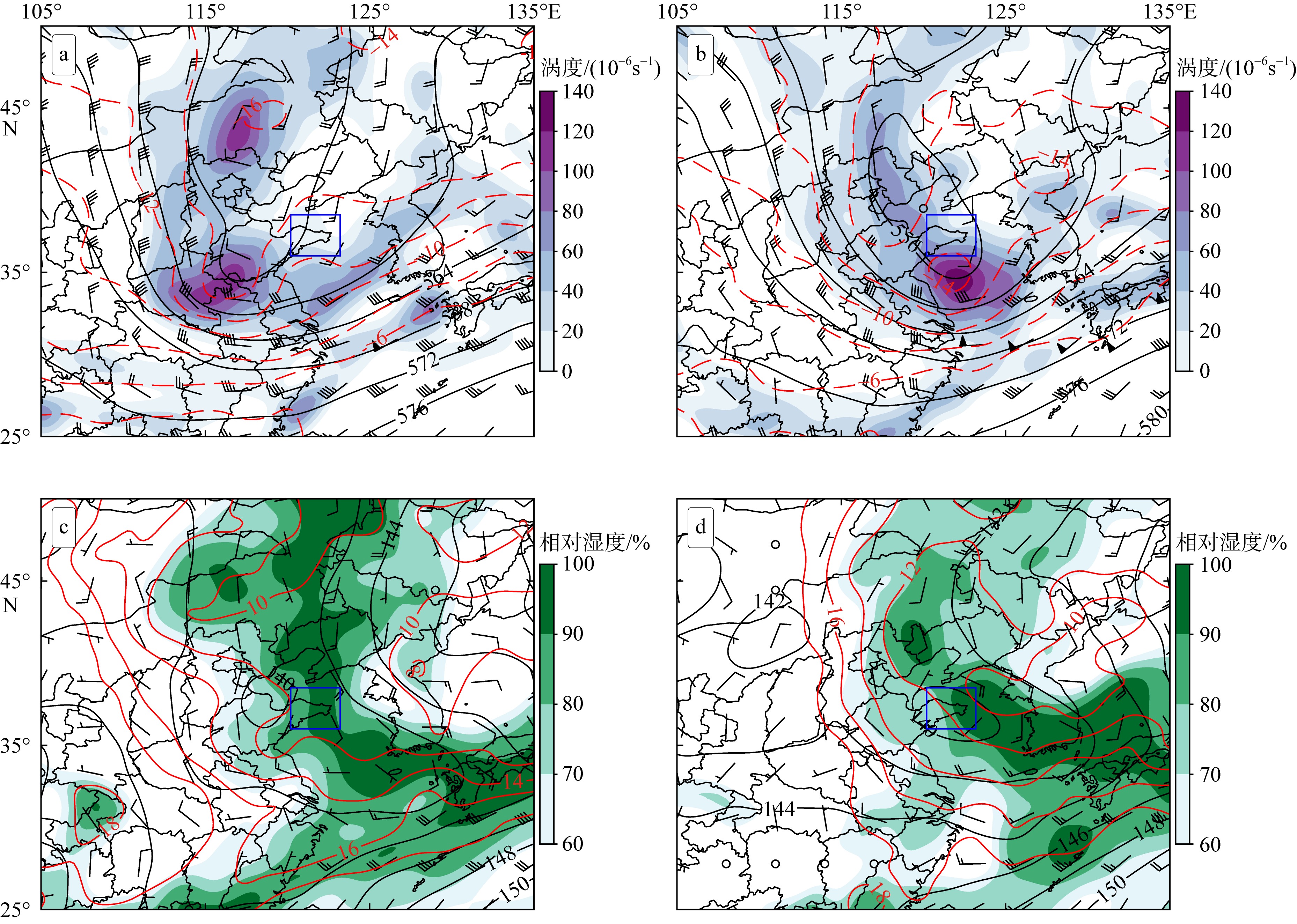
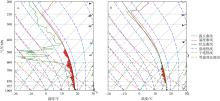
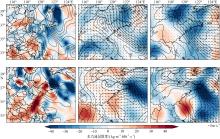
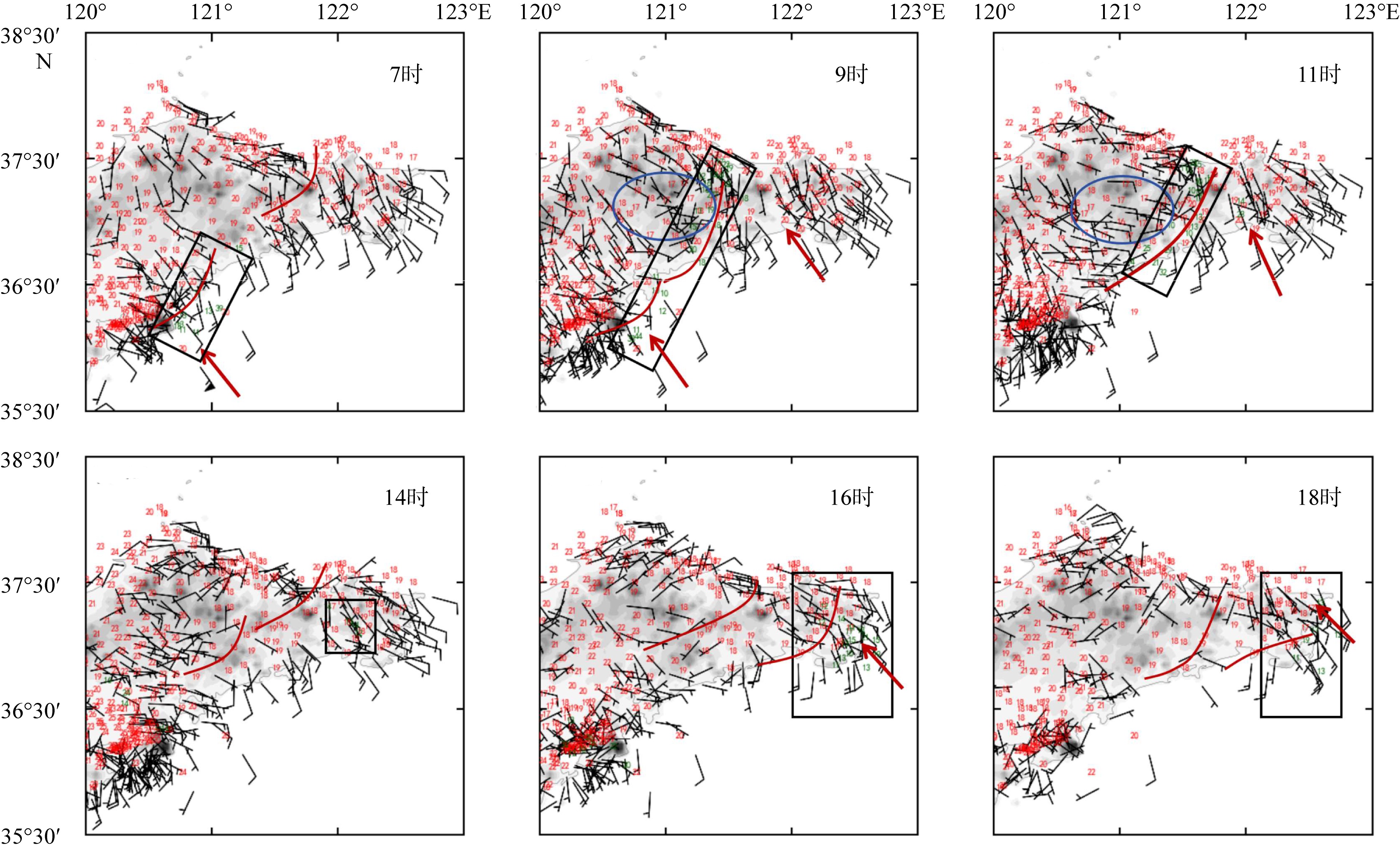
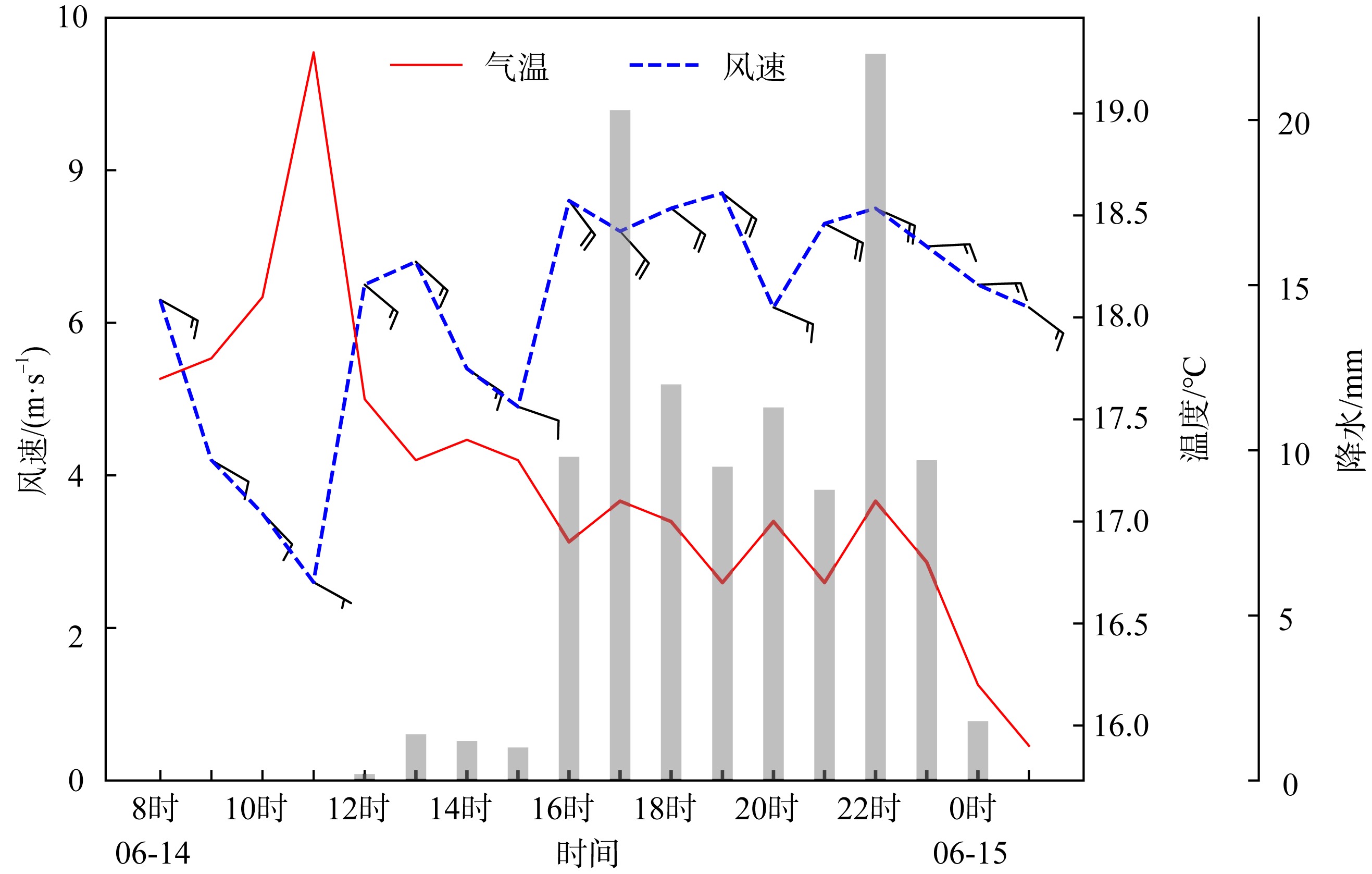
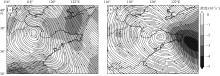
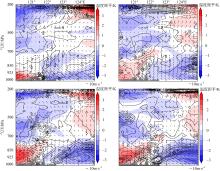
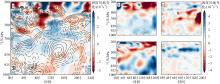
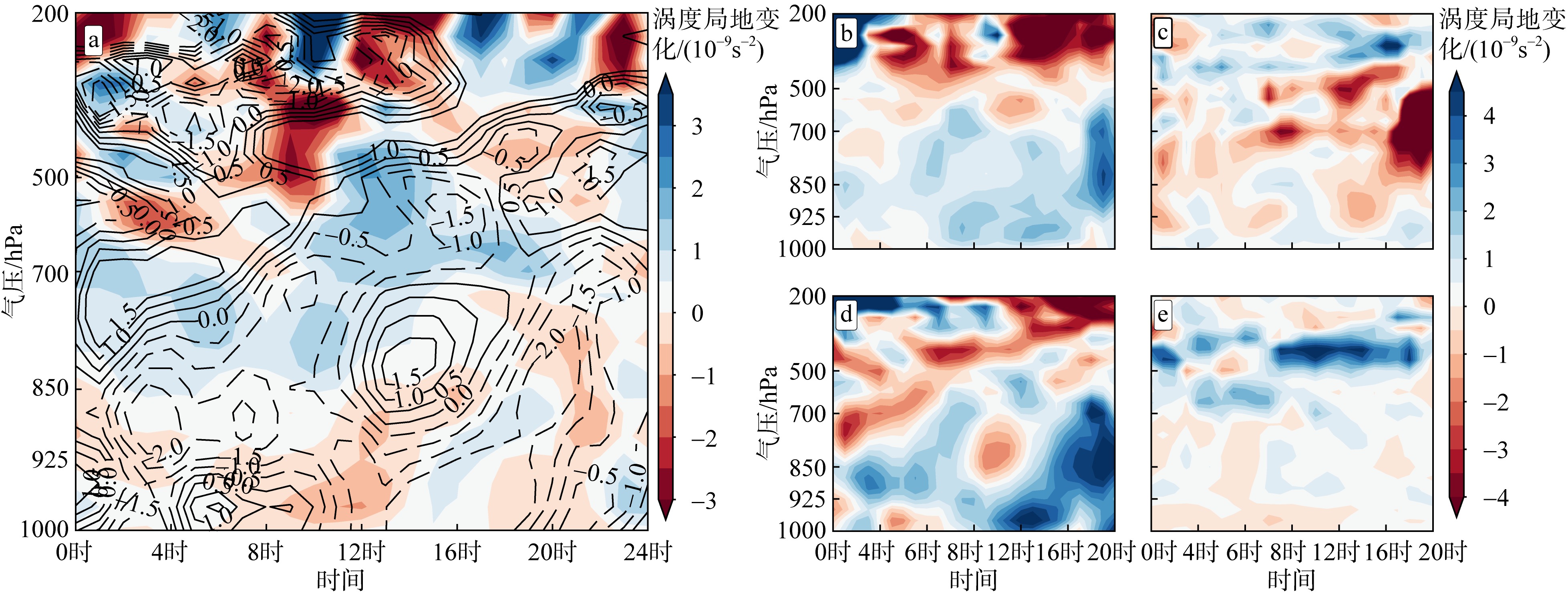
| [1] |
陈涛, 陈博宇, 于超, 等, 2020. 华南前汛期锋面对流系统和暖区对流系统的多尺度特征和集合预报敏感性对比分析[J]. 气象, 46(9): 1129-1142.
|
|
CHEN TAO, CHEN BOYU, YU CHAO, et al, 2020. Analysis of multiscale features and ensemble forecast sensitivity for MCSs in front-zone and warm sector during pre-summer rainy season in South China[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 46(9): 1129-1142 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
邓承之, 张焱, 李强, 等, 2023. 四川盆地一次暖性西南低涡大暴雨的中尺度分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 42(1): 24-36.
|
|
DENG CHENGZHI, ZHANG YAN, LI QIANG, et al, 2023. Mesoscale analysis on one warm Southwest Vortex rainstorm in the Sichuan basin[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 42(1): 24-36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
冯晋勤, 刘铭, 蔡菁, 2018. 闽西山区“7·22”极端降水过程中尺度对流特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 29(6): 748-758.
|
|
FENG JINQIN, LIU MING, CAI JING, 2018. Meso-scale convective characteristics of “7·22” extreme rain in the west mountainous area of Fujian[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 29(6): 748-758 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
高晓梅, 白莉娜, 郭蓉, 等, 2023. 台风“利奇马”北上锋生导致山东省创纪录暴雨天气学成因分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2023, 39(2): 145-158.
|
|
GAO XIAOMEI, BAI LINA, GUO RONG, et al, 2023. Synoptic analysis of the extreme rainfall in Shandong Province caused by the frontogenesis of typhoon Lekima during its northward movement[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 39(2): 145-158 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
龚琬丁, 周玉淑, 钟珊珊, 等, 2023. 山东地区一次夏季极端暴雨中尺度系统发展演变过程及机理分析[J]. 大气科学, 47(3): 786-804.
|
|
GONG WANDING, ZHOU YUSHU, ZHONG SHANSHAN, et al, 2023. Evolution process and mechanism analysis of the mesoscale system of an extreme summer rainstorm in Shandong Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 47(3): 786-804 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
何编, 孙照渤, 李忠贤, 2012. 一次华南持续性暴雨的动力诊断分析和数值模拟[J]. 大气科学学报, 35(4): 466-476.
|
|
HE BIAN, SUN ZHAOBO, LI ZHONGXIAN, 2012. Dynamic diagnosis and numerical simulation of a persistent torrential rain case in South China[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 35(4): 466-476 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
侯淑梅, 孙兴池, 范苏丹, 等, 2014. 切变线冷区和暖区暴雨落区分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 37(3): 333-343.
|
|
HOU SHUMEI, SUN XINGCHI, FAN SUDAN, et al, 2014. Analysis on cold and warm sector heavy rain area of shear line[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 37(3): 333-343 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
黄莉, 詹莹玉, 孙莹, 等, 2011. “黑格比”后期异常强降水形成机理分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(6): 57-63.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.06.057
|
|
HUANG LI, ZHAN YINGYU, SUN YING, et al, 2011. Analysis of the heavy rain caused by Typhoon Hagupit[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30(6): 57-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
李卓, 黎伟标, 张奡褀, 2022. 台风登陆前华南地区降水日变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(2): 26-37.
doi: 10.11978/2021045
|
|
LI ZHUO, LI WEIBIAO, ZHANG AOQI, 2022. Analysis of diurnal variation characteristics of precipitation over South China before typhoon landfall[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(2): 26-37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2021045
|
| [10] |
林慧敏, 闵锦忠, 朱利剑, 等, 2023. 太行山地形在“7·19”华北持续性低涡暴雨中的作用[J]. 气象科学, 43(1): 46-58.
|
|
LIN HUIMIN, MIN JINZHONG, ZHU LIJIAN, et al, 2023. The role of Taihang Mountain topography in “7·19” persistent low vortex rainstorm in North China[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 43(1): 46-58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
林晓霞, 冯业荣, 张诚忠, 等, 2017. 华南一次暴雨过程热力和动力特征的诊断分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 33(6): 975-984.
|
|
LIN XIAOXIA, FENG YERONG, ZHANG CHENGZHONG, et al, 2017. Diagnostic analysis of thermal and dynamic characteristics of a rainstorm process in southern China[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 33(6): 975-984 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
蒙伟光, 张艳霞, 袁金南, 等, 2014. 华南沿海2011年7月15—18日持续暴雨过程中的季风槽与中尺度对流系统相互作用[J]. 气象学报, 72(3): 508-525.
|
|
MENG WEIGUANG, ZHANG YANXIA, YUAN JINNAN, et al, 2014. Monsoon trough and MCSs interactions during the persistent torrential rainfall event of 15-18 July 2011 along the South China coast[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 72(3): 508-525 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
覃皓, 王志毅, 石怡宁, 等, 2023. 广西沿海一次冬季暖区暴雨的多尺度能量诊断[J]. 暴雨灾害, 42(3): 283-292.
|
|
QIN HAO, WANG ZHIYI, SHI YINING, et al, 2023. Multiscale diagnosis of the energy budget for a warm-sector rainstorm event in winter in the coastal area of Guangxi[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 42(3): 283-292 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
沈新勇, 张弛, 高焕妍, 等, 2020. 三类高空冷涡的划分及其动态合成分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 39(1): 1-9.
|
|
SHEN XINYONG, ZHANG CHI, GAO HUANYAN, et al, 2020. Classification and dynamic composite analysis of three kinds of high altitude cold vortex[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 39(1): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
王宁, 张立凤, 彭军, 等, 2014. 局部地形对北京“7. 21”特大暴雨影响的数值研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 33(1): 10-18.
|
|
WANG NING, ZHANG LIFENG, PENG JUN, et al, 2014. Numerical study of the effects of local terrain on “7. 21” extreme torrential rain in Beijing[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 33(1): 10-18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
尉英华, 陈宏, 何群英, 等, 2019. 渤海西岸偏东风对天津局地大暴雨的影响分析[J]. 气象, 45(1): 61-72.
|
|
WEI YINGHUA, CHEN HONG, HE QUNYING, et al, 2019. Influence of easterly winds from west coast of Bohai Sea on local heavy rainfall in Tianjin[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 45(1): 61-72 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
吴乃庚, 温之平, 邓文剑, 等, 2020. 华南前汛期暖区暴雨研究新进展[J]. 气象科学, 40(5): 605-616.
|
|
WU NAIGENG, WEN ZHIPING, DENG WENJIAN, et al, 2020. Advances in warm-sector heavy rainfall during the first rainy season in South China[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 40(5): 605-616 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
叶朗明, 吴乃庚, 张华龙, 等, 2019. 海陆风和地形对一次弱天气背景下暖区特大暴雨的影响分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 38(6): 597-605.
|
|
YE LANGMING, WU NAIGENG, ZHANG HUALONG, et al, 2019. Analysis of the influence of sea-land breeze and topography on the extraordinary heavy rain in warm sector under a weak weather background[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 38(6): 597-605 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
郑丽娜, 孙兴池, 孟伟, 2015. 夏季两次低槽冷锋型暴雨成因对比分析[J]. 气象科技, 43(6): 1133-1141.
|
|
ZHENG LINA, SUN XINGCHI, MENG WEI, 2015. Contrastive analysis of causes of two low-trough cold-front rainfall processes in summer[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 43(6): 1133-1141 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [20] |
郑丽娜, 孙兴池, 2016. 气旋类山东暴雨过程天气学特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 10(4): 74-80.
|
|
ZHENG LINA, SUN XINGCHI, 2016. Analysis on synoptic characteristic of rainstorm processes in Shandong Province caused by cyclone[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 10(4): 74-80 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [21] |
郑铮, 潘灵杰, 钱燕珍, 等, 2021. 台风“利奇马”造成浙江沿海极端强降水的演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 269-278.
|
|
ZHENG ZHENG, PAN LINGJIE, QIAN YANZHEN, et al, 2021. Evolution characteristics of extreme heavy precipitation in coast of Zhejiang Province caused by typhoon Lekima[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 39(2): 269-278 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [22] |
AL-RAWAS G A, VALEO C, 2009. Characteristics of rainstorm temporal distributions in arid mountainous and coastal regions[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 376(1-2): 318-326.
|
| [23] |
CHEN SHENG, LI WEIBIAO, DU YAODONG, et al, 2015. Urbanization effect on precipitation over the Pearl River Delta based on CMORPH data[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 6(1): 16-22.
|
| [24] |
DING YIHUI, LIU YANJU, 2001. Onset and the evolution of the summer monsoon over the South China Sea during SCSMEX field experiment in 1998[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan. Ser. II, 79(1B): 255-276.
|
| [25] |
DU YU, CHEN GUIXING, 2019. Heavy rainfall associated with double low-level jets over Southern China. Part Ⅱ: convection initiation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 147(2): 543-565.
|
| [26] |
HOSKINS B J, BRETHERTON F P, 1972. Atmospheric frontogenesis models: mathematical formulation and solution[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 29(1): 11-37.
|
| [27] |
HU CHENXI, FUNG K Y, TAM C Y, et al, 2021. Urbanization impacts on Pearl River Delta extreme rainfall sensitivity to land cover change versus anthropogenic heat[J]. Earth and Space Science, 8(3): e2020EA001536.
|
| [28] |
LIU RUIXIN, SUN JIANHUA, WEI JIE, et al, 2016. Classification of persistent heavy rainfall events over South China and associated moisture source analysis[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 30(5): 678-693.
|
| [29] |
LUO YALI, GONG YU, ZHANG DALIN, 2014. Initiation and organizational modes of an extreme-rain-producing mesoscale convective system along a Mei-Yu Front in East China[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 142(1): 203-221.
|
| [30] |
SUN JIANHUA, ZHANG YUANCHUN, LIU RUIXIN, et al, 2019. A review of research on warm-sector heavy rainfall in China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 36(12): 1299-1307.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-019-9021-1
|
| [31] |
WU MENGWEN, LUO YALI, 2016. Mesoscale observational analysis of lifting mechanism of a warm-sector convective system producing the maximal daily precipitation in China mainland during pre-summer rainy season of 2015[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 30(5): 719-736.
|
| [32] |
YE LANGMING, LIU XIANTONG, PU YILIANG, et al, 2022. Contrasts in the evolution and microphysical features of two convective systems during a heavy rainfall event along the coast of South China[J]. Atmosphere, 13(10): 1549.
|
 ), 梅婵娟2,3(
), 梅婵娟2,3( ), 张灿3, 万夫敬4, 辛文鹏3
), 张灿3, 万夫敬4, 辛文鹏3
 ), MEI Chanjuan2,3(
), MEI Chanjuan2,3( ), ZHANG Can3, WAN Fujing4, XIN Wenpeng3
), ZHANG Can3, WAN Fujing4, XIN Wenpeng3