| [1] |
戴晨, 夏非, 张永战, 等, 2015. 南黄海辐射沙脊群海域历史地震的浅地层记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 35(5): 77-85.
|
|
DAI CHEN, XIA FEI, ZHANG YONGZHAN, 2015. Shallow seismic stratigraphic records of earthquakes in the radial sand ridge field of South Yellow Sea. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 35(5): 77-85 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
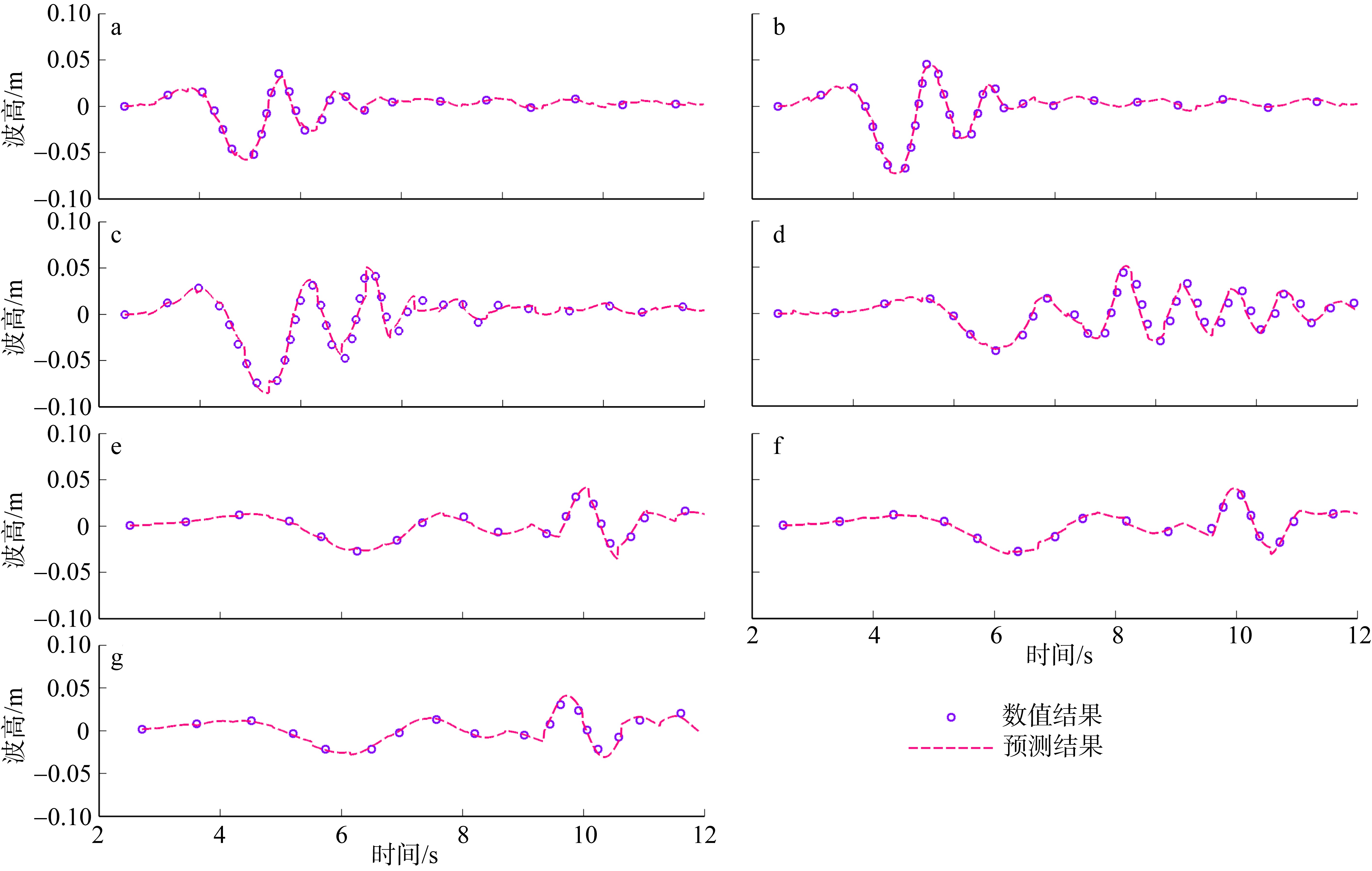
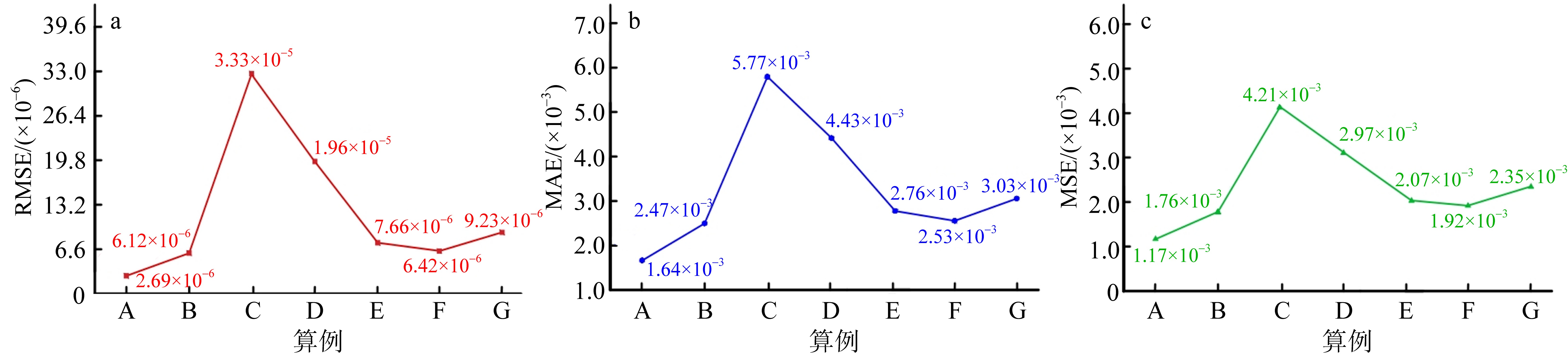
高榕泽, 屈科, 任兴月, 等, 2024. 卷积神经网络方法在岛礁类海啸波水动力特性演变的应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(4): 68-75.
|
|
GAO RONGZE, QU KE, REN XINGYUE, et al, 2024. Application of convolutional neural network methods in the evolution of hydrodynamic characteristics of tsunamis like-wave over fringing reef[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 43(4): 68-75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
胡光海, 2010. 东海陆坡海底滑坡识别及致滑因素影响研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
HU GUANGHAI, 2010. Identification of submarine landslides along the continental slope of the East China Sea and analysis of factors causing submarine landslides[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
贾永刚, 单红仙, 2000. 黄河口海底斜坡不稳定性调查研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 11(1): 1-5.
|
|
JIA YONGGANG, SHAN HONGXIAN, 2000. Investigation and study of slope unstability of subaqueous delta of modern Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 11(1): 1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
贾永刚, 王振豪, 刘晓磊, 等, 2017. 海底滑坡现场调查及原位观测方法研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 47(10): 61-72.
|
|
JIA YONGGANG, WANG ZHENHAO, LIU XIAOLEI, et al, 2017. The research progress of field investigation and in-situ observation methods for submarine landslide[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 47(10): 61-72 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
刘保华, 李西双, 赵月霞, 等, 2005. 冲绳海槽西部陆坡碎屑沉积物的搬运方式: 滑塌和重力流[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 36(1): 1-9.
|
|
LIU BAOHUA, LI XISHUANG, ZHAO YUEXIA, et al, 2005. Debris transport on the western continental slope of the Okinawa trough: slumping and gravity flowing[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 36(1): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
马云, 2014. 南海北部陆坡区海底滑坡特征及触发机制研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
MA YUN, 2014. Study of submarine landslides and trigger mechanism along the continental slope of the Northern South China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
杨作升, 陈卫民, 陈彰榕, 等, 1994. 黄河口水下滑坡体系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 25(6): 573-581.
|
|
YANG ZUOSHENG, CHEN WEIMIN, CHEN ZHANGRONG, et al, 1994. Subaqueous landslide system in the Huanghe River (Yellow River) delta[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 25(6): 573-581 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
BRADFORD S F, AFFILIATIONS A, 2011. Nonhydrostatic model for surf zone simulation[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 137(4): 163-174.
|
| [10] |
ENET F, GRILLI S T, 2007. Experimental study of tsunami generation by three-dimensional rigid underwater landslides[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 133(6): 442-454.
|
| [11] |
GEE M J R, UY H S, WARREN J, et al, 2007. The Brunei slide: a giant submarine landslide on the North West Borneo Margin revealed by 3D seismic data[J]. Marine Geology, 246(1): 9-23.
|
| [12] |
GRAVES A, 2012. Long short-term memory[M]//GRAVES A, Supervised sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer: 37-45.
|
| [13] |
HSU S K, KUO J, LO C L, et al, 2008. Turbidity currents, submarine landslides and the 2006 Pingtung earthquake off SW Taiwan[J]. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 19(6): 767-772.
|
| [14] |
JIANG MINGJING, SUN CHAO, CROSTA G B, et al, 2015. A study of submarine steep slope failures triggered by thermal dissociation of methane hydrates using a coupled CFD-DEM approach[J]. Engineering Geology, 190: 1-16.
|
| [15] |
KINGMA D P, BA J, 2014. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412. 6980.
|
| [16] |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E, 2012. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]// Proceedings of the 26th international conference on neural information processing systems. Lake Tahoe: 1097-1105.
|
| [17] |
MA GANGFENG, SHI FENGYAN, KIRBY J T, 2012. Shock-capturing non-hydrostatic model for fully dispersive surface wave processes[J]. Ocean Modelling, 43-44: 22-35.
|
| [18] |
MA GANGFENG, KIRBY J T, SHI FENGYAN, 2013. Numerical simulation of tsunami waves generated by deformable submarine landslides[J]. Ocean Modelling, 69: 146-165.
|
| [19] |
MAKINOSHIMA F, OISHI Y, YAMAZAKI T, et al, 2021. Early forecasting of tsunami inundation from tsunami and geodetic observation data with convolutional neural networks[J]. Nat Commun, 12: 2253.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22348-0
pmid: 33859177
|
| [20] |
MURPHY K, SCHÖLKOPF B, SRIVASTAVA N, et al, 2014. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15(1): 1929-1958.
|
| [21] |
NAMEKAR S, YAMAZAKI Y, CHEUNG K F, 2009. Neural network for tsunami and runup forecast[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 36: L08604.
|
| [22] |
NIAN T, GUO X, ZHENG D, et al, 2019. Susceptibility assessment of regional submarine landslides triggered by seismic actions[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 93: 101964.
|
| [23] |
RASYIF T M, KATO S, SYAMSIDIK, et al, 2019. Numerical simulation of morphological changes due to the 2004 tsunami wave around Banda Aceh, Indonesia[J]. Geosciences, 9(3): 125.
|
| [24] |
ZHAO T, UTILI S, CROSTA G B, 2016. Rockslide and impulse wave modelling in the Vajont reservoir by DEM-CFD analyses[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 49(6): 2437-2456.
|
 ), 屈科1,2,3(
), 屈科1,2,3( ), 王旭1, 高榕泽1, 门佳1
), 王旭1, 高榕泽1, 门佳1
 ), QU Ke1,2,3(
), QU Ke1,2,3( ), WANG Xu1, GAO Rongze1, MEN Jia1
), WANG Xu1, GAO Rongze1, MEN Jia1