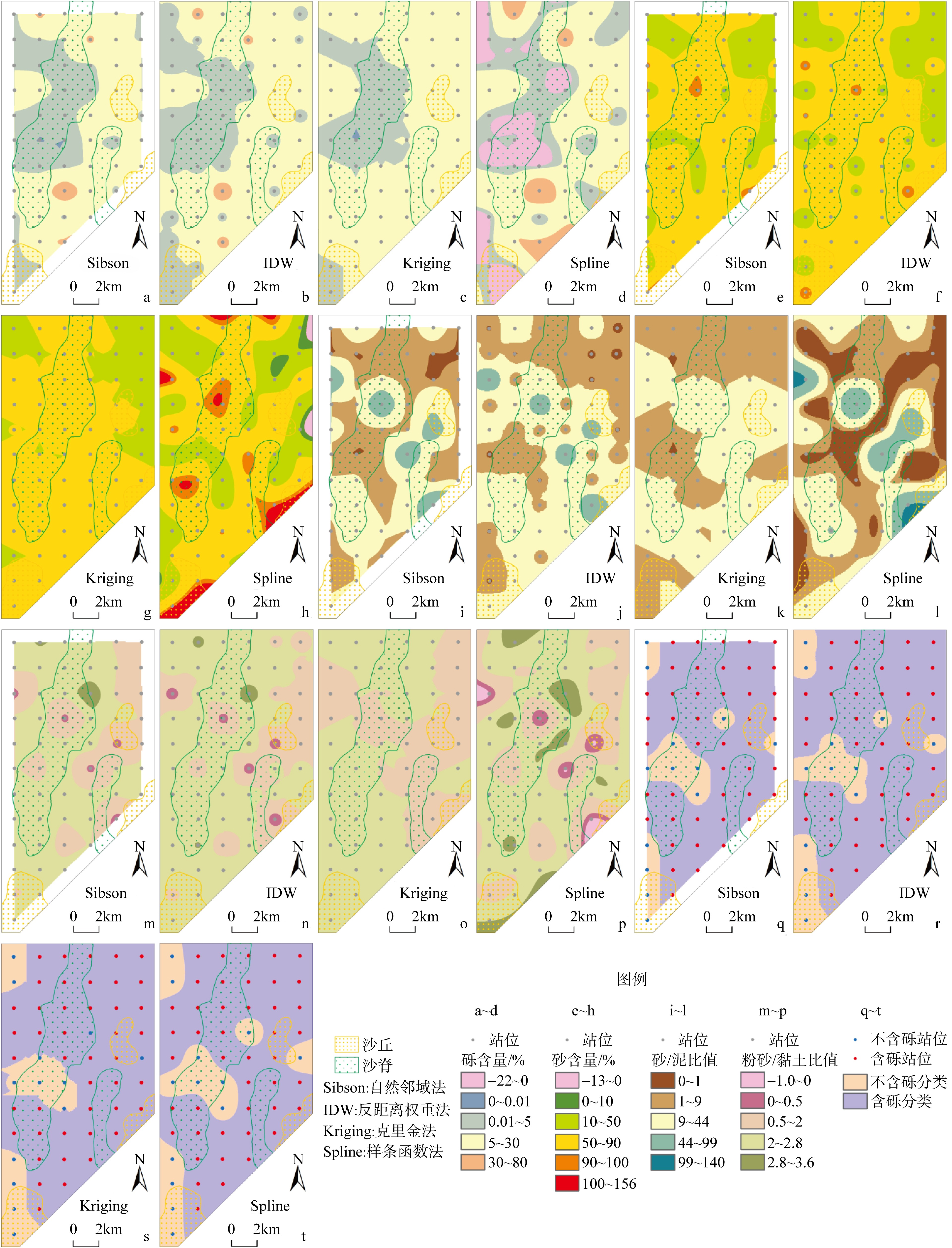
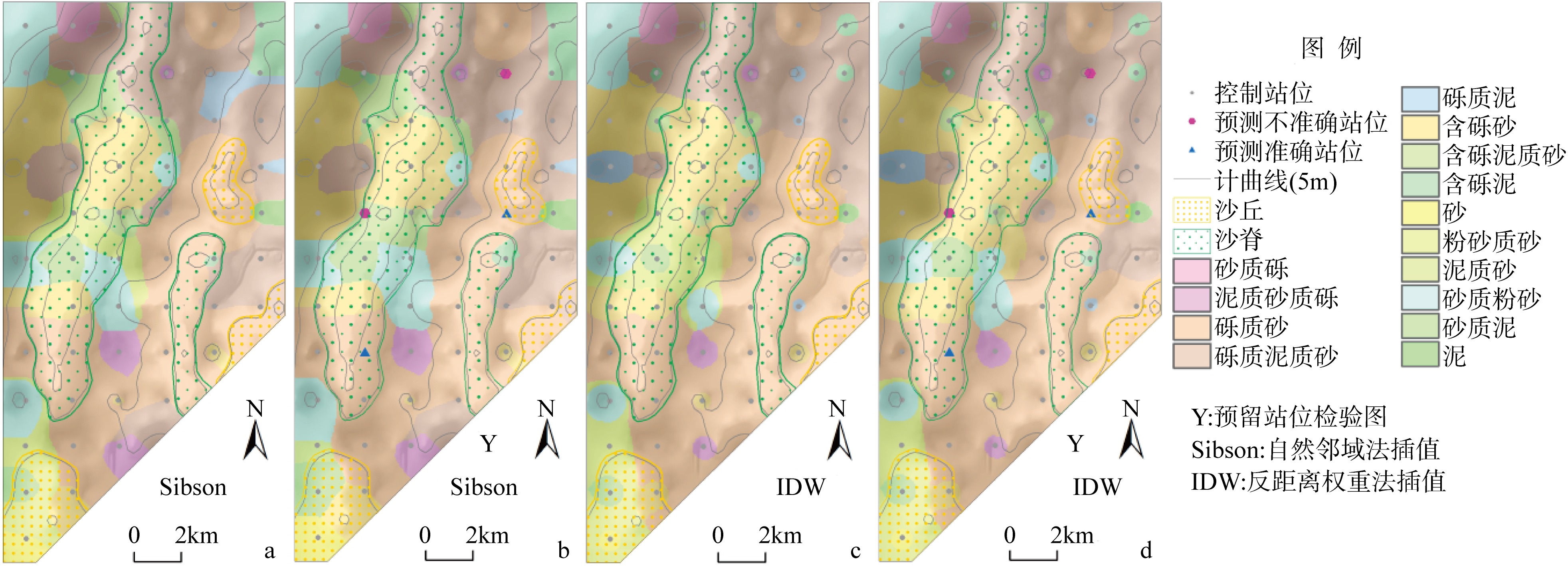
| [1] |
曹兵, 马越, 王长海, 2011. 海洋表层沉积物类型分布图绘制方法研究[J]. 海洋通报, 30(6): 615-618.
|
|
CAO BING, MA YUE, WANG CHANGHAI, 2011. Drawing method study on the distribution graph of surface sediment types at seabed[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 30(6):615-618 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
冯永财, 郝连成, 胡延斌, 等, 2024. 渤海湾曹妃甸海域沉积物粒度分布特征及运移趋势分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 40(11): 57-69.
|
|
FENG YONGCAI, HAO LIANCHENG, HU YANBIN, et al, 2024. Characterization of grain size distribution of sediments and transport trend analysis in Caofeidian sea area, Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 40(11): 57-69 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
郝连成, 远继东, 郑立龙, 等, 2022. 湛江湾海域表层沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 38(8): 1-10.
|
|
HAO LIANCHENG, YUAN JIDONG, ZHENG LILONG, et al, 2022. Grain-size characteristics of surface sediment and sedimentary environment in Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 38(8): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
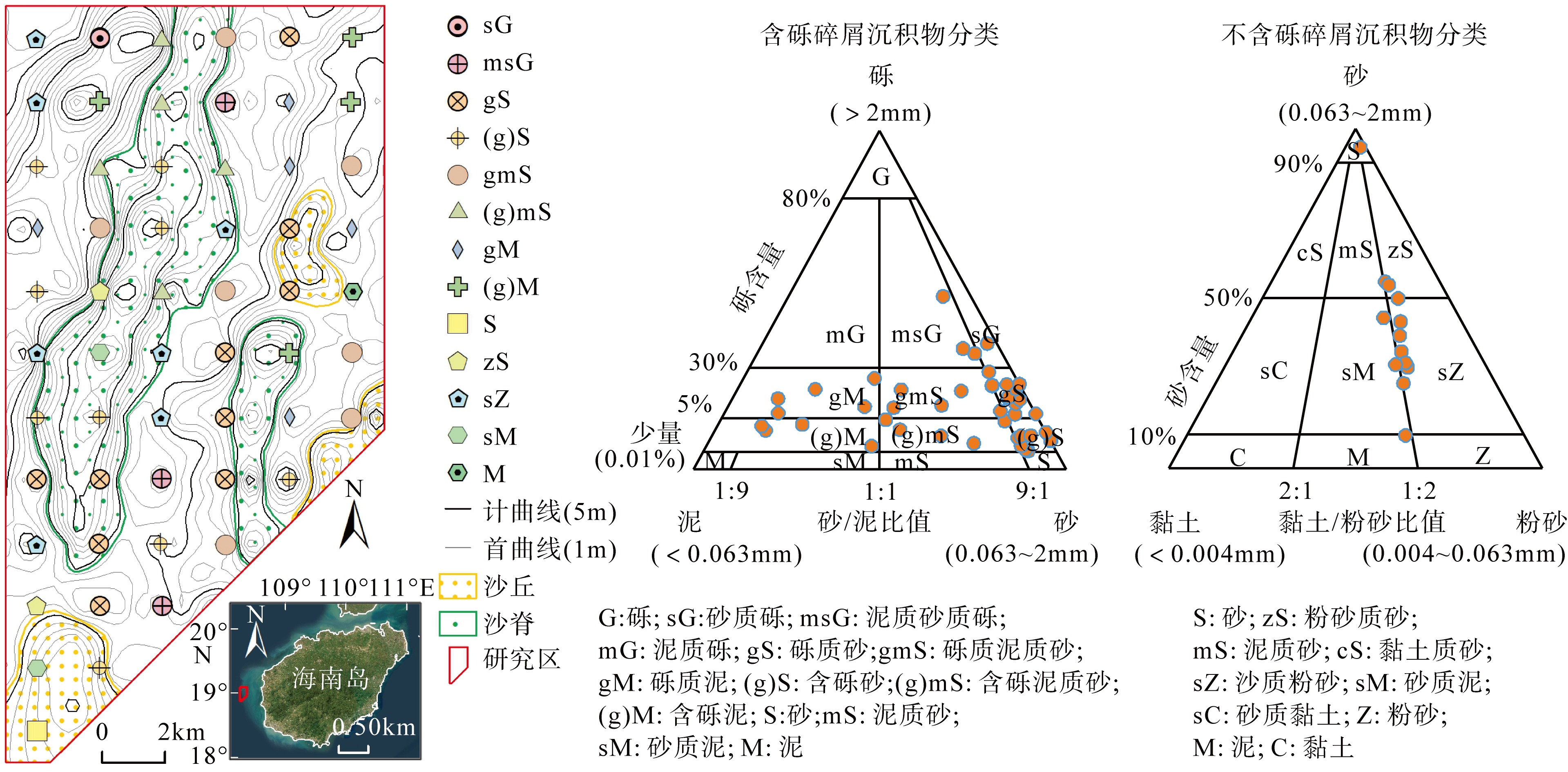
何起祥, 李绍全, 刘健, 2002. 海洋碎屑沉积物的分类[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 22(1): 115-121.
|
|
HE QIXIANG, LI SHAOQUN, LIU JIAN, 2002. Classification of marine clastic sediments[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 22(1): 115-121 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
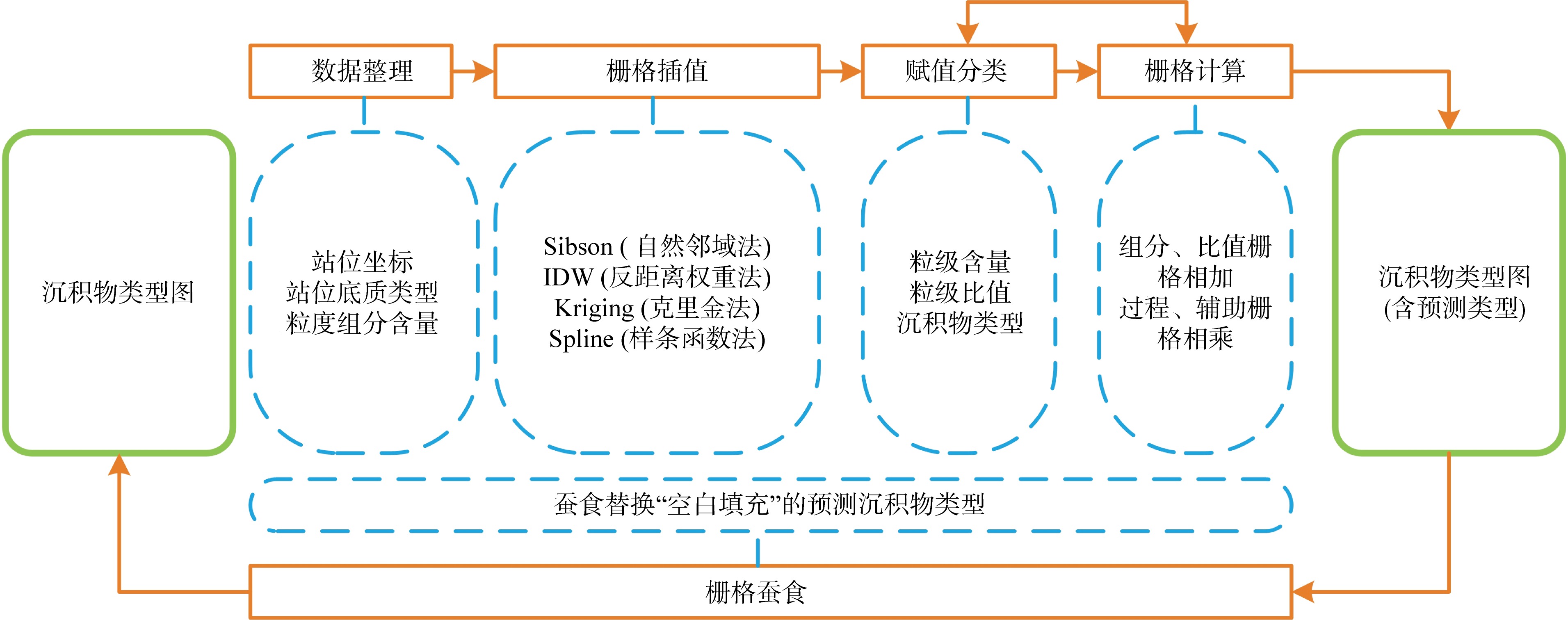
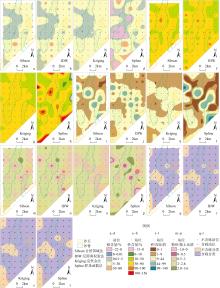
孔祥淮, 徐庆建, 徐刚, 等, 2014. 海底沉积物类型判别及其平面分布图绘制[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 30(5): 9-14.
|
|
KONG XIANGHUAI, XU QINGJIAN, XU GANG, et al, 2014. Identification of marine clastic sediments and mapping of spatial distribution pattern[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 30(5): 9-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
李春轩, 罗毅, 包安明, 等, 2012. 基于对数比转换的成分数据空间插值研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 45(4): 648-655.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2012.04.005
|
|
LI CHUNXUAN, LUO YI, BAO ANMING, et al, 2012. Study on spatial interpolation of compositional data based on log-ratio transformation[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 45(4): 648-655 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
刘付程, 彭俊, 2015. 基于对数比转换方法的沉积物粒级组分空间预测与底质类型制图[J]. 海洋科学, 39(6): 122-128.
|
|
LIU FUCHENG, PENG JUN, 2015. A logratio transformation based Kriging method for spatial prediction of sediment grain size compositions and sediment type mapping[J]. Marine Sciences, 39(6): 122-128 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
刘付程, 彭俊, 张瑞, 等, 2011. 一种近海底质类型图生成的非参数方法[J]. 海洋通报, 30(5): 551-556.
|
|
LIU FUCHENG, PENG JUN, ZHANG RUI, et al, 2011. A non-parametric method to generate type and distribution of coastal surface sediment map based on indicator Kriging[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 30(5): 551-556 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
梅西, 李学杰, 密蓓蓓, 等, 2020. 中国海域表层沉积物分布规律及沉积分异模式[J]. 中国地质, 47(5): 1447-1462.
|
|
MEI XI, LI XUEJIE, MI BEIBEI, et al, 2020. Distribution regularity and sedimentary differentiation patterns of China seas surface sediments[J]. Geology in China, 47(5): 1447-1462 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
缪卫东, 李世杰, 冯金顺, 等, 2016. 长江三角洲NB5孔第四纪地层划分及环境变化信息[J]. 中国地质, 43(6): 2022-2035.
|
|
MIAO WEIDONG, LI SHIJIE, FEN JINSHUN, et al, 2016. Stratigraphic division of NB5 core in the Yangtze delta area and its environmental change information[J]. Geology in China, 43(6):2022-2035 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
覃茂刚, 龙根元, 李海云, 等, 2023. 基于K-means聚类层次分析模型的中沙环礁地质环境稳定性定量分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(2): 113-123.
|
|
QIN MAOGANG, LONG GENYUAN, LI HAIYUN, et al, 2023. Quantitative analysis of geological environment stability of the Zhongsha Atoll based on K-means clustering AHP model[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 42(2): 113-123 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
孙思佳, 刘付程, 周艺, 等, 2023. 沉积物粒度组分空间预测的地理加权回归残余Kriging方法[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 45(6): 34-42.
doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2023.06.005
|
|
SUN SIJIA, LIU FUCHENG, ZHOU YI, et al, 2023. Geographically weighted regression residual Kriging method applicable for the spatial prediction of sediment grain size compositions[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 45(6):34-42 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
喜扬洋, 王日明, 冯炳斌, 等, 2022. 北海银滩响应台风作用的动力地貌过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(4): 97-104.
doi: 10.11978/2021097
|
|
XI YANGYANG, WANG RIMING, FENG BINGBIN, et al, 2022. Morphodynamic processes of the Yintan Beach in response to typhoon[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(4): 97-104 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2021097
|
| [14] |
许冬, 葛倩, 韩喜彬, 等, 2022. 海洋沉积源-汇过程的驱动因素: 以北部湾为例[J]. 海洋学研究, 40(3): 17-32.
|
|
XU DONG, GE QIAN, HAN XIBIN, et al, 2022. Driving force of marine sedimentary source to sink: A case study from Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 40(3): 17-32 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969-j.issn.1001-909X.2022.03.003
|
| [15] |
杨康, 张永战, 2007. 基于栅格叠合的沉积物底质图生成方法[J]. 第四纪研究, 27(5): 889-895.
|
|
YANG KANG, ZHANG YONGZHAN, 2007. A method to generate types and distribution of surface sediment map based on raster overlay function of GIS[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 27(5): 889-895 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
殷志强, 秦小光, 李玉梅, 等, 2008. 源区距离对黄土粒度多组分分布特征的影响[J]. 中国地质, 35(5): 1037-1044.
|
|
YIN ZHIQIANG, QIN XIAOGUANG, LI YUMEI, et al, 2008. Influence of the dust source distance on the multimodal grain-size distribution characteristics of loess[J]. Geology in China, 35(5): 1037-1044 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
COHEN J, 1960. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales[J]. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20(1): 37-46.
doi: 10.1177/001316446002000104
|
| [18] |
FOLK R L, ANDREWS P B, LEWIS D W, 1970. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 13(4): 937-968.
doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
|
| [19] |
FRANKE R, 1982. Smooth interpolation of scattered data by local thin plate splines[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 8(4): 273-281.
doi: 10.1016/0898-1221(82)90009-8
|
| [20] |
GAO MAOSHENG, GUO FEI, HUANG XUEYONG, et al, 2019. Sediment distribution and provenance since Late Pleistocene in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China[J]. China Geology, 2(1): 16-25.
doi: 10.31035/cg2018062
|
| [21] |
GAO S, COLLINS M B, LANCKNEUS J, et al, 1994. Grain size trends associated with net sediment transport patterns: An example from the Belgian continental shelf[J]. Marine Geology, 121(3-4): 171-185.
doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(94)90029-9
|
| [22] |
JOURNEL A G, 1983. Nonparametric estimation of spatial distributions[J]. Journal of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, 15(3): 445-468.
doi: 10.1007/BF01031292
|
| [23] |
LE N D, ZIDEK J V, 2006. Statistical analysis of environmental space-time processes[M]. New York: Springer.
|
| [24] |
MCLAREN P, BOWLES D, 1985. The effects of sediment transport on grain-size distributions[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 55(4): 457-470.
|
| [25] |
MITÁŠ L, MITÁŠOVÁ H, 1988. General variational approach to the interpolation problem[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 16(12): 983-992.
doi: 10.1016/0898-1221(88)90255-6
|
| [26] |
ODEH I O A, TODD A J, TRIANTAFILIS J, 2003. Spatial prediction of soil particle-size fractions as compositional data[J]. Soil Science, 168(7): 501-515.
|
| [27] |
PEJRUP M, 1988. The triangular diagram used for classification of estuarine sediments: a new approach[M]//DE B, VAND G, NIO. Tide-Influenced Sedimentary Environments and Facies. Oxford: Pergamon Press: 289-300.
|
| [28] |
PHILIP G M, WATSON D F, 1982. A precise method for determining contoured surfaces[J]. The APPEA Journal, 22(1): 205-212.
|
| [29] |
SHEPARD F P, 1954. Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 24(3): 151-158.
|
| [30] |
SHU GAO, COLLINS M, 2001. The use of grain size trends in marine sediment dynamics: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 19(3): 265-271.
doi: 10.1007/BF02850664
|
| [31] |
SIBSON R, 1981. A brief description of natural neighbor interpolation[C]// BARNETT V. Interpreting Multivariate Data. New York: John Wiley & Sons: 21-36.
|
| [32] |
WATSON D, MERRIAM D F, 1992. Contouring: a guide to the analysis and display of spatial data[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
|
| [33] |
WATSON D, PHILIP G M, 1985. A refinement of inverse distance weighted interpolation[J]. Geo-processing, 2(4): 315-327.
|
 ), 覃茂刚1,2(
), 覃茂刚1,2( ), 陈旸1,2, 陈波1,2, 王雪木1,2, 刘艳锐1,3, 宋家伟1,2, 孙龙飞1,2
), 陈旸1,2, 陈波1,2, 王雪木1,2, 刘艳锐1,3, 宋家伟1,2, 孙龙飞1,2
 ), QIN Maogang1,2(
), QIN Maogang1,2( ), CHEN Yang1,2, CHEN Bo1,2, WANG Xuemu1,2, LIU Yanrui1,3, SONG Jiawei1,2, SUN Longfei1,2
), CHEN Yang1,2, CHEN Bo1,2, WANG Xuemu1,2, LIU Yanrui1,3, SONG Jiawei1,2, SUN Longfei1,2