| [1] |
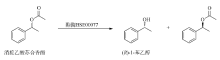
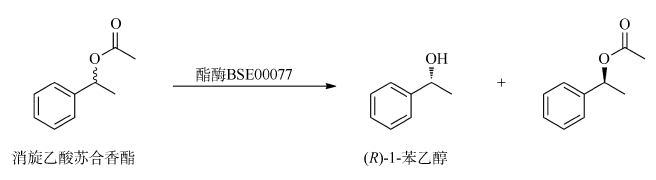
范卫东, 范永仙, 陈小龙, 2012. 用Candida lipolytica脂肪酶手性转酯拆分农药中间体rac-1-苯乙醇[J]. 浙江农业科学, (12): 1689-1692.
|
| [2] |
严祥辉, 薛屏, 2009. 用壳聚糖修饰的MCM-48固定化脂肪酶拆分(R, S)-1-苯乙醇[J]. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版), 30(1): 50-54.
|
|
YAN XIANHUI, XUE PING, 2009. Chiral resolution of (R, S)-1-phenylethanol catalyzed by lipase immobilized on MCM-48 coated chitosan[J]. Journal of Ningxia University (Natural Science Edition), 30(1): 50-54 (in Chinses).
|
| [3] |
BLASCO M A, GRÖGER H, 2014. Enzymatic resolution of racemates with a ‘remote’ stereogenic center as an efficient tool in drug, flavor and vitamin synthesis[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 22(20): 5539-5546.
|
| [4] |
BORNSCHEUER U T, 2014. Enzymes in lipid modification: past achievements and current trends[J]. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 116(10): 1322-1331.
|
| [5] |
CAMBOU B, KLIBANOV A M, 1984. Preparative production of optically active esters and alcohols using esterase-catalyzed stereospecific transesterification in organic media[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 106(9): 2687-2692.
|
| [6] |
CHANG LEI, OUYANG LIMING, XU YI, et al, 2010. Highly enantioselective hydrolysis of phenyl-1,2-ethanediol cyclic carbonates by newly isolated Bacillus sp. ECU0015[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 66(1/2): 95-100.
|
| [7] |
CHEN C S, FUJIMOTO Y, GIRDAUKAS G, et al, 1982. Quantitative analyses of biochemical kinetic resolutions of enantiomers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 104(25): 7294-7299.
|
| [8] |
FAN YONGXIAN, XIE ZHANGMING, ZHANG HUAWEI, et al, 2011. Kinetic resolution of both 1-phenylethanol enantiomers produced by hydrolysis of 1-phenylethyl acetate with Candida antarctica lipase B in different solvent systems[J]. Kinetics and Catalysis, 52(5): 686-690.
|
| [9] |
FERNÁNDEZ-ÁLVARO E, KOURIST R, WINTER J, et al, 2010. Enantioselective kinetic resolution of phenylalkyl carboxylic acids using metagenome-derived esterases[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 3(1): 59-64.
|
| [10] |
FILLAT A, ROMEA P, PASTOR F I J, et al, 2015. Kinetic resolution of esters from secondary and tertiary benzylic propargylic alcohols by an improved esterase-variant from Bacillus sp. BP-7[J]. Catalysis Today, 255: 16-20.
|
| [11] |
GIRI A, DHINGRA V, GIRI C C, et al, 2001. Biotransformations using plant cells, organ cultures and enzyme systems: current trends and future prospects[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 19(3): 175-199.
|
| [12] |
KITAGUCHI H, FITZPATRICK P A, HUBER J E, et al, 1989. Enzymic resolution of racemic amines: crucial role of the solvent[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 111(8): 3094-3095.
|
| [13] |
LAANE C, BOEREN S, VOS K, et al, 1987. Rules for optimization of biocatalysis in organic solvents[J]. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 30(1): 81-87.
|
| [14] |
NOJIRI M, TAOKA N, YASOHARA Y, 2014. Characterization of an enantioselective amidase from Cupriavidus sp. KNK-J915 (FERM BP-10739) useful for enzymatic resolution of racemic 3-piperidinecarboxamide[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 109: 136-142.
|
| [15] |
PANDA T, GOWRISHANKAR B S, 2005. Production and applications of esterases[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67(2): 160-169.
|
| [16] |
SALAMEH M, WIEGEL J, 2007. Lipases from extremophiles and potential for industrial applications[J]. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 61: 253-283.
|
| [17] |
SMITH M E, BANERJEE S, SHI YONGLIANG, et al, 2012. Investigation of the cosolvent effect on six isoenzymes of PLE in the enantioselective hydrolysis of selected α,α-disubstituted malonate esters[J]. Chemcatchem, 4(4): 472-475.
|
| [18] |
TANG XIAOLING, LIU JI, WANG BO, et al, 2011. Cloning, screening and characterization of enantioselective ester hydrolases from Escherichia coli K-12[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 27(1): 129-136.
|
| [19] |
THÖRN C, GUSTAFSSON H, OLSSON L, 2011. Immobilization of feruloyl esterases in mesoporous materials leads to improved transesterification yield[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 72(1/2): 57-64.
|
| [20] |
TIAN XIN, ZHENG GAOWEI, LI CHUNXIU, et al, 2011. Enantioselective production of (S)-1-phenyl-1,2-ethanediol from dicarboxyesters by recombinant Bacillus subtilis esterase[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 73(1/2/3/4): 80-84.
|
| [21] |
WEBER N, GORWA-GRAUSLUND M, CARLQUIST M, 2014. Engineered baker’s yeast as whole-cell biocatalyst for one-pot stereo-selective conversion of amines to alcohols[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 13(1): 118-127.
|
| [22] |
ZHENG JIANYONG, WANG YUQIANG, LUO WEIFENG, et al, 2015. Biocatalytic resolution of Boc-DL-alanine methyl ester by a newly isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WZZ002[J]. Catalysis Communications, 60: 134-137.
|
| [23] |
ZHENG RENCHAO, ZHENG YUGUO, LI AIPENG, et al, 2014. Enantioselective synthesis of (S)-3-cyano-5-methylhexanoic acid by a high DMSO concentration tolerable Arthrobacter sp. ZJB-09277[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 83: 97-103.
|
| [24] |
ZOU SHUPING, ZHENG YUGAO, DU ERHONG, et al, 2014. Enhancement of (S)-2,3-dichloro-1-propanol production by recombinant whole-cell biocatalyst in n-heptane-aqueous biphasic system[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 188: 42-47.
|
 ), 张云1,3, 孙爱君1,3, 胡云峰1,3,4(
), 张云1,3, 孙爱君1,3, 胡云峰1,3,4( )
)
 ), Yun ZHANG1,3, Aijun SUN1,3, Yunfeng HU1,3,4(
), Yun ZHANG1,3, Aijun SUN1,3, Yunfeng HU1,3,4( )
)