热带海洋学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (3): 61-72.doi: 10.11978/2016088CSTR: 32234.14.2016088
珠海横琴岛芒洲湿地红树林人工恢复期大型底栖动物群落结构研究
- 华南师范大学生命科学学院, 广东省高等学校生态与环境科学重点实验室, 广东 广州 510631
-
收稿日期:2016-09-25修回日期:2016-12-29出版日期:2017-05-20发布日期:2017-06-01 -
作者简介:作者简介:罗章凤(1989—), 女, 羌族, 四川省汶川县人, 硕士, 从事水生动物生态研究。E-mail:
251223123@qq.com -
基金资助:广东省科技计划项目(2009B030600006);国家科技支撑计划项目(2009BADB280401-02);珠海市科技计划项目(PC20081050)
A study on the community structure of macrobenthos during the period of artificial mangrove restoration in Mangzhou wetland of Hengqin Island, Zhuhai
Zhangfeng LUO( ), Zhanqiang FANG(
), Zhanqiang FANG( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Ecology and Environmental Science in Guangdong Higher Education, College of Life Science, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
-
Received:2016-09-25Revised:2016-12-29Online:2017-05-20Published:2017-06-01 -
Supported by:Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (2009B030600006);National Science and Technology Support Program Sub-topics (2009BADB280401-02);Science and Technology Project of Zhuhai City (PC20081050)
摘要:
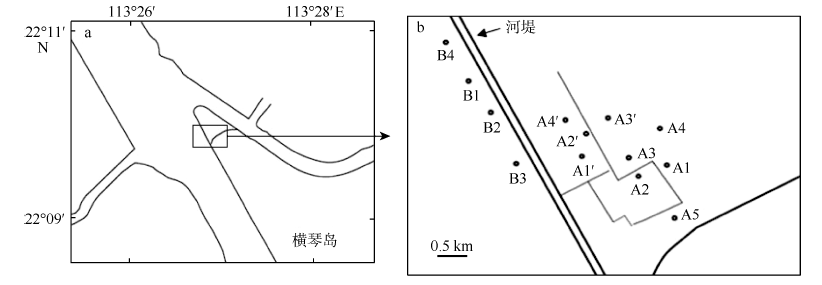
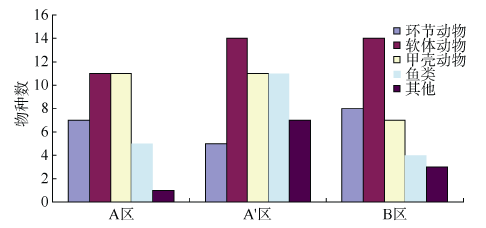
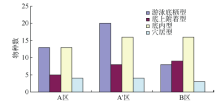
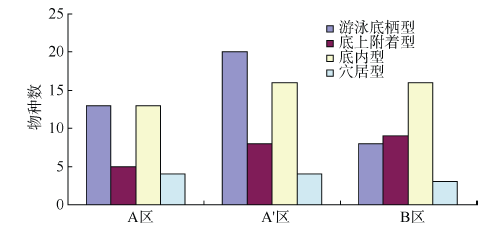
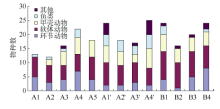
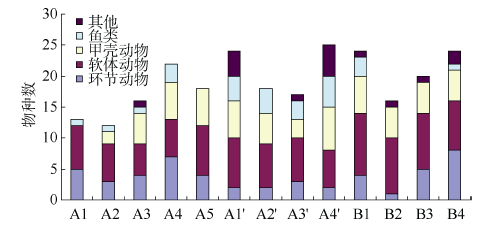
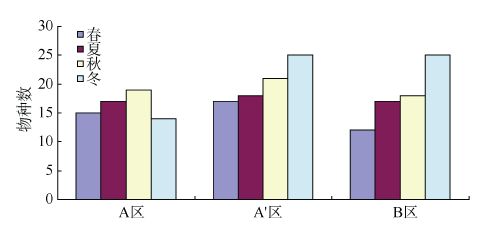
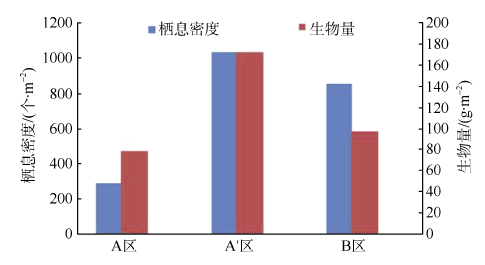
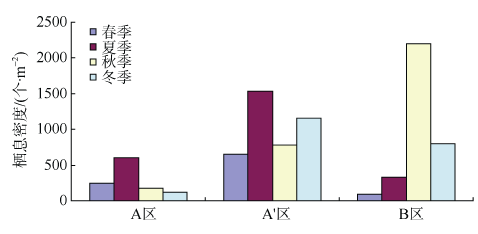
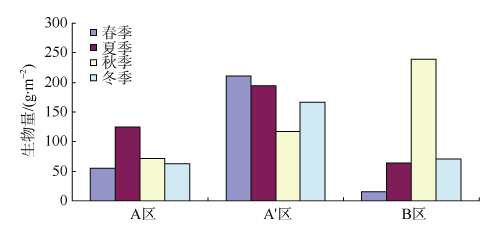
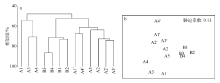
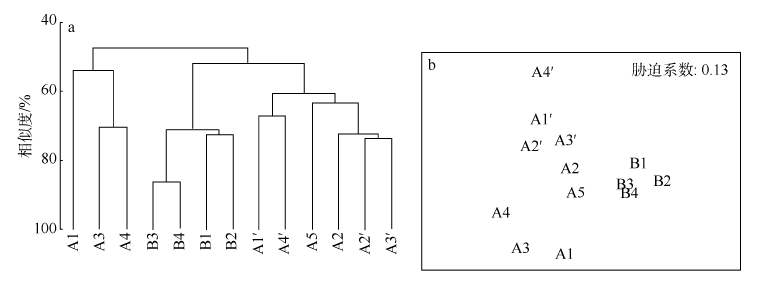
探讨珠海横琴岛芒洲红树林湿地不同人为干扰及不同植被类型下大型底栖动物的群落结构和多样性。共采获大型底栖动物66种, 包括软体动物20种, 甲壳动物15种, 鱼类14种, 环节动物9种及其他8种(主要为昆虫幼虫)。结果显示, 大型底栖动物生活型主要由底内型和底上附着型为主, 穴居型蟹类最少。采样点优势种及优势度都集中在少数几个r-对策者, 例如瘤蜷、乌苏里圆田螺、麦克碟尾虫、脊尾白虾和谭氏泥蟹。各区域栖息密度和生物量最大的均为软体动物。底栖动物类型主要以体型较小, 生活周期短的r-对策者为主, 而缺乏大型的有较长寿命的k-对策者, 显示群落在演替初期常出现的现象。Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H°)、Pielou均匀度指数(J°)、Margalef丰富度指数(d)以及Simpson多样性指数(C)在区域间和季节间的差异均不显著(P>0.05)。磨刀门河道天然次生林(B区)物种集中性最高(C=0.4896), 多样性最低(H°=1.288), 物种丰富度(d=4.301)及均匀度(J°=0.3583)也最低; 人工恢复区(A和A°区)物种多样性及丰富度、均匀度均大于河道天然林区, 表明红树林植被在发育初期有益于滩涂生态系统的生境复杂性以及底栖动物的多样性。同时大型底栖动物的多样性、均匀度及丰富度等均较低, 表明整个系统处于生物演替的初级阶段。
引用本文
罗章凤, 方展强. 珠海横琴岛芒洲湿地红树林人工恢复期大型底栖动物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(3): 61-72.
Zhangfeng LUO, Zhanqiang FANG. A study on the community structure of macrobenthos during the period of artificial mangrove restoration in Mangzhou wetland of Hengqin Island, Zhuhai[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(3): 61-72.
表1
各样点大型底栖动物物种及功能群的组成与分布"
| 物种 | 采样站点 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A1' | A2' | A3' | A4' | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | |
| 青纵沟纽虫Lineus fuscovirids | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 疣吻沙蚕 Tylorrhynchus heterochaetus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 羽须鳃沙蚕Dendronereis pinnaticirrus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 单叶沙蚕Namalycastis abiuma | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 日本刺沙蚕Neanthes japonica | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 沙蚕 Nereis virens | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 双齿围沙蚕Pernereis aibuhitensis | + | + | |||||||||||
| 长吻沙蚕 Glycera chirori | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 孔雀缨鳃虫 Sabella pavonina | + | + | |||||||||||
| 小头虫 Capitella capitata | + | + | |||||||||||
| 瘤蜷 Tarebia granifera | + | ++ | + | + | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | |
| 塔蜷Thiara scabra scabra | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||
| 流纹蜷 Thiara riqueti | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 瘤拟黑螺 Melanoides tuberculatus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 乌苏里圆田螺Cipangopaludina ussuriensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | +++ | ||||
| 铜锈环棱螺Bellamya aeroginosa | + | ||||||||||||
| 紫游螺 Neritina[Dostia]violacea | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 斑马游螺 Neritina (Vittina) zebra | + | ||||||||||||
| 微黄镰玉螺 Lunatia gilva | + | + | |||||||||||
| 光滑狭口螺Stenothyra glabra | + | ||||||||||||
| 耳萝卜螺Radix auricularia | + | + | |||||||||||
| 赛氏女教士螺Pythia cecillei | + | ||||||||||||
| 彩虹明樱蛤 Moerella iridescens | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| 红树蚬 Geloina erosa | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 河蚬 Corbicula fluminea | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||
| 湖球蚬Sphaerium lacustre | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 缢蛏Sinonovacula constricta | + | ||||||||||||
| 日本杓蛤 Cuspidaria japonica | + | ||||||||||||
| 翡翠贻贝 Perna viridis | ++ | + | |||||||||||
| 隆起隔贻贝Septifer excisus | + | ||||||||||||
| 麦克碟尾虫 Discapseudes mackiei | ++ | + | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | |||
| 日本拟背水虱Paranthura japonica | + | + | |||||||||||
| 中华蜾蠃蜚 Corophium sinensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 蚤状钩虾 Gammarus pulex | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 脊尾白虾 Exopalaemon carinicauda | + | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | ||
| 日本沼虾 Macrobrachium mipponensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 鼓虾Alpheus sp. | + | + | |||||||||||
| 无齿相手蟹Sesarma dehaani | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 印痕相手蟹Sesarma impressa | + | ||||||||||||
| 凹背新尖额蟹 Neorhynchoplax introversus | + | ||||||||||||
| 豆形短眼蟹 Xenophthalmus pinnotheroides | + | ||||||||||||
| 橄榄拳蟹 Philyra olivacea | + | ||||||||||||
| 锯缘青蟹 Scylla serrata | + | ||||||||||||
| 谭氏泥蟹 Ilyrplax deschampsi | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | |||||||
| 弧边招潮蟹Uca arcuata | + | ||||||||||||
| 蜻蜓幼虫 Odonata larvae | + | ||||||||||||
| 蟌科幼虫 Coenagrionidae larvae | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 蝇科幼虫 Muscidae larvae | + | ||||||||||||
| 摇蚊幼虫 Chironomid larvae | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 四节蜉幼虫Baetis thermicus larvae | + | + | |||||||||||
| 小仰蝽Anisops sp. | + | ||||||||||||
| 划蝽Micronecta scholtzi | + | + | |||||||||||
| 食蚊鱼Gambusia affinis | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 宽鳍 | + | ||||||||||||
| 条纹刺鲃Puntius semifasciolatus | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鳙鱼 Hypophthalmichthys nobilis | + | + | |||||||||||
| 鲫鱼 Carassius auratus | + | ||||||||||||
| 大弹涂鱼Boleophthalmus pectinirostris | + | ||||||||||||
| 舌鰕虎鱼 Glossogobius giuris | + | + | |||||||||||
| 斑纹舌 | + | ||||||||||||
| 鲻 | + | ||||||||||||
| 红狼牙 | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 少鳞 | + | ||||||||||||
| 尼罗罗非鱼Oreochromis nilotica | + | + | |||||||||||
| 香鱼 Plecoglossus altivelis | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 梭鱼Liza haematocheilus | + | ||||||||||||
表2
各样点优势种及优势度"
| 优势种 | 生活型 | 优势度指数 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 恢复区 | 河道 | |||||||||||||
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A1' | A2' | A3' | A4' | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | ||
| 青纵沟纽虫 | GSB | 0.048 | ||||||||||||
| 疣吻沙蚕 | GSB | 0.176 | 0.040 | 0.030 | ||||||||||
| 羽须鳃沙蚕 | GSB | 0.190 | 0.020 | 0.070 | 0.067 | |||||||||
| 单叶沙蚕 | GSB | 0.048 | ||||||||||||
| 日本刺沙蚕 | GSB | 0.022 | ||||||||||||
| 瘤蜷 | GS | 0.211 | 0.601 | 0.047 | 0.034 | 0.283 | 0.868 | 0.183 | 0.126 | 0.171 | 0.051 | 0.034 | ||
| 塔蜷 | GS | 0.032 | 0.026 | |||||||||||
| 瘤拟黑螺 | GS | 0.023 | 0.021 | 0.025 | ||||||||||
| 乌苏里圆田螺 | GS | 0.025 | 0.191 | 0.362 | 0.422 | |||||||||
| 翡翠贻贝 | GSB | 0.118 | ||||||||||||
| 彩虹明樱蛤 | GSB | 0.028 | ||||||||||||
| 河蚬 | GSB | 0.021 | ||||||||||||
| 麦克蝶尾虫 | GS | 0.542 | 0.054 | 0.156 | 0.023 | 0.495 | 0.167 | |||||||
| 脊尾白虾 | GS | 0.063 | 0.020 | 0.679 | 0.127 | 0.127 | 0.028 | |||||||
| 摇蚊幼虫 | GSB | 0.023 | ||||||||||||
| 谭氏泥蟹 | GSB | 0.447 | 0.327 | 0.038 | 0.053 | |||||||||
表3
各区域不同季节的优势种及优势度"
| 优势种 | 湿地 | A区 | A'区 | 河道 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 | 疣吻沙蚕 | 0.0393 | |||
| 羽须鰓沙蚕 | 0.0506 | ||||
| 瘤蜷 | 0.5365 | 0.6216 | 0.7397 | 0.0562 | |
| 河蚬 | 0.0506 | ||||
| 中华蜾蠃蜚 | 0.0281 | ||||
| 麦克蝶尾虫 | 0.0518 | ||||
| 脊尾白虾 | 0.0776 | ||||
| 谭氏泥蟹 | 0.2753 | ||||
| 夏季 | 青纵纵沟纽虫 | 0.0918 | |||
| 羽须鰓沙蚕 | 0.0253 | ||||
| 单叶沙蚕 | 0.0201 | ||||
| 瘤蜷 | 0.4928 | 0.5342 | 0.6448 | ||
| 塔蜷 | 0.0463 | ||||
| 瘤拟黑螺 | 0.0440 | 0.0540 | 0.0806 | ||
| 彩虹明樱蛤 | 0.0209 | ||||
| 翡翠贻贝 | 0.0295 | ||||
| 麦克蝶尾虫 | 0.1356 | 0.0845 | 0.1503 | 0.2463 | |
| 脊尾白虾 | 0.0800 | ||||
| 谭氏泥蟹 | 0.0649 | ||||
| 秋季 | 疣吻沙蚕 | 0.0248 | 0.3261 | ||
| 羽须鳃沙蚕 | 0.1468 | 0.0674 | |||
| 瘤蜷 | 0.1355 | 0.0954 | 0.1207 | 0.0311 | |
| 乌苏里圆田螺 | 0.3929 | 0.8128 | |||
| 麦克蝶尾虫 | 0.0550 | ||||
| 脊尾白虾 | 0.0333 | 0.0917 | |||
| 谭氏泥蟹 | 0.0224 | 0.1056 | |||
| 鳙鱼 | 0.0440 | ||||
| 冬季 | 疣吻沙蚕 | 0.0393 | |||
| 羽须鳃沙蚕 | 0.0929 | ||||
| 沙蚕 | 0.0465 | ||||
| 瘤蜷 | 0.0219 | ||||
| 乌苏里圆田螺 | 0.0598 | 0.5132 | |||
| 河蚬 | 0.0155 | ||||
| 麦克蝶尾虫 | 0.1471 | 0.1784 | |||
| 脊尾白虾 | 0.2066 | 0.5208 | |||
| 谭氏泥蟹 | 0.0272 | 0.1855 | |||
| 平背蚔 | 0.0284 | ||||
| 四季平均值 | 疣吻沙蚕 | 0.0276 | |||
| 羽须鳃沙蚕 | 0.0344 | ||||
| 瘤蜷 | 0.2037 | 0.2346 | 0.2646 | 0.0263 | |
| 乌苏里圆田螺 | 0.0813 | 0.3416 | |||
| 麦克蝶尾虫 | 0.0533 | 0.0491 | 0.0915 | ||
| 脊尾白虾 | 0.0552 | 0.1843 | |||
| 谭氏泥蟹 | 0.1089 |
表4
各样点及区域的生物多样性指数表"
| 各样点及区域 | d | C | J' | H' |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 2.421 | 0.1705 | 0.7798 | 2.0000 |
| A2 | 1.690 | 0.6497 | 0.3537 | 0.8790 |
| A3 | 2.711 | 0.3245 | 0.6174 | 1.7120 |
| A4 | 3.840 | 0.2519 | 0.6613 | 2.0440 |
| A5 | 3.466 | 0.2123 | 0.6922 | 2.0010 |
| A区 | 4.676 | 0.2494 | 0.5795 | 2.0600 |
| A1' | 3.172 | 0.7569 | 0.2103 | 0.6685 |
| A2' | 2.399 | 0.5211 | 0.3398 | 0.9821 |
| A3' | 2.534 | 0.3385 | 0.4907 | 1.3900 |
| A4' | 3.489 | 0.2609 | 0.5241 | 1.6870 |
| A’区 | 5.645 | 0.3293 | 0.3818 | 1.4780 |
| B1 | 4.206 | 0.2328 | 0.6681 | 2.1230 |
| B2 | 2.437 | 0.2697 | 0.6030 | 1.6720 |
| B3 | 2.679 | 0.5484 | 0.3431 | 1.0280 |
| B4 | 3.142 | 0.7200 | 0.2234 | 0.7099 |
| B区 | 4.301 | 0.4896 | 0.3593 | 1.2880 |
| [1] | 安传光, 赵云龙, 林凌, 等, 2008. 崇明岛潮间带夏季大型底栖动物多样性[J]. 生态学报, 28(2): 577-586. |
| AN CHUANGUANG, ZHAO YUNLONG, LIN LING, et al, 2008. The biodiversity of marobenthos of intertidal zone on Chongming Island in summer[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(2): 577-586 (in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 杜飞雁, 王雪辉, 李纯厚, 等, 2008. 大亚湾大型底栖动物物种多样性现状[J]. 南方水产, 4(6): 33-41. |
| DU FEIYAN, WANG XUEHUI, LI CHUNHOU, et al, 2008. Study on species diversity of macrobenthos in Daya Bay, South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 4(6): 33-41 (in Chinese). | |
| [3] | 高爱根, 陈全震, 曾江宁, 等, 2005. 西门岛红树林区大型底栖动物的群落结构[J]. 海洋学研究, 23(2): 33-40. |
| GAO AIGEN, CHEN QUANZHEN, ZENG JIANGNING, et al, 2005. Macrofauna community in the mangrove area of Ximen Island, Zhejiang[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 23(2): 33-40 (in Chinese). | |
| [4] | 何斌源, 范航清, 王瑁, 等, 2007. 中国红树林湿地物种多样性及其形成[J]. 生态学报, 27(11): 4859-4870. |
| HE BINYUAN, FAN HANGQING, WANG MAO, et al, 2007. Species diversity in mangrove wetlands of China and its causation analyses[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(11): 4859-4870 (in Chinese). | |
| [5] | 胡知渊, 鲍毅新, 葛宝明, 等, 2006. 围垦滩涂潮沟秋季大型底栖动物群落和生态位分析[J]. 动物学报, 52(4): 800-809. |
| HU ZHIYUAN, BAO YIXIN, GE BAOMING, et al, 2006. Macrobenthic community and niche analysis of creeks during autumn in diked tidal flat[J]. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 52(4): 800-809 (in Chinese). | |
| [6] | 胡知渊, 李欢欢, 鲍毅新, 等, 2008. 灵昆岛围垦区内外滩涂大型底栖动物生物多样性[J]. 生态学报, 28(4): 1498-1507. |
| HU ZHIYUAN, LI HUANHUAN, BAO YIXIN, et al, 2008. Biodiversity comparison of icrobenthic communities at tidal flat of Lingkun Island[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(4): 1498-1507 (in Chinese). | |
| [7] | 黄少峰, 刘玉, 李策, 等, 2011. 珠江口滩涂围垦对大型底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 17(4): 499-503. |
| HUANG SHAOFENG, LIU YU, LI CE, et al, 2011. Influence of reclamation on macrobenthic community in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 17(4): 499-503 (in Chinese). | |
| [8] | 赖廷和, 何斌源, 1998. 广西红树林区大型底栖动物种类多样性研究[J]. 广西科学, 5(3): 166-172. |
| LAI TINGHE, HE BINYUAN, 1998. Studies on the macrobenthos species diversity for Guangxi mangrove areas[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 5(3): 166-172 (in Chinese). | |
| [9] | 厉红梅, 李适宇, 蔡立哲, 2003. 深圳湾潮间带底栖动物群落与环境因子的关系[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5): 93-96. |
| LI HONGMEI, LI SHIYU, CAI LIZHE, 2003. Relationship between benthic community and environmental factors in Shenzhen Bay[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 42(5): 93-96 (in Chinese). | |
| [10] | 马坤, 2011. 海南东寨港红树林湿地大型底栖动物多样性的研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学. |
| MA KUN, 2001. Studies on the diversity of Macrobenthos in the mangrove wetland of Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan[D]. Haikou: Hainan University (in Chinese). | |
| [11] | 唐以杰, 方展强, 钟燕婷, 等, 2012. 不同生态恢复阶段无瓣海桑人工林湿地中大型底栖动物群落的演替[J]. 生态学报, 32(10): 3160-3169. |
| TANG YIJIE, FANG ZHANQIANG, ZHONG YANTING, et al, 2012. Succession of macrofauna communities in wetlands of Sonneratia apetala artificial mangroves during different ecological restoration stages[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(10): 3160-3169 (in Chinese). | |
| [12] | 唐以杰, 安东, 方展强, 等, 2015a. 珠海夹洲岛无瓣海桑与秋茄群落对重金属吸附能力的比较研究[J]. 生态科学, 34(3): 13-19. |
| TANG YIJIE, AN DONG, FANG ZHANQIANG, et al, 2015a. Comparative study of the heavy metal adsorption capacities of Sonneratia apetala and Kandelia candel communities on Jiazhou Island, Zhuhai, China[J]. Ecological Science, 34(3): 13-19 (in Chinese). | |
| [13] | 唐以杰, 方展强, 何清, 等, 2015b. 无瓣海桑与乡土红树植物混交对林地大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 生态学报, 35(22): 7355-7366. |
| TANG YIJIE, FANG ZHANQIANG, HE QING, et al, 2015b. Effects of mixed plantations of Sonneratia apetala and indigenous mangrove species on understory macrofauna[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(22): 7355-7366 (in Chinese). | |
| [14] | 王卉, 钟山, 方展强, 2013. 珠海鹤洲水道沿岸红树林湿地大型底栖动物群落特征. 生态学报, 33(21): 6913-6924. |
| WANG HUI, ZHONG SHAN, FANG ZHANQIANG, 2013. Characteristics of macrobenthic communities in mangrove wetlands along the waterways of North Hezhou, Zhuhai, South China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(21): 6913-6924 (in Chinese). | |
| [15] | 徐姗楠, 陈作志, 黄小平, 等, 2010. 底栖动物对红树林生态系统的影响及生态学意义[J]. 生态学杂志, 29(4): 812-820. |
| XU SHANNAN, CHEN ZUOZHI, HUANG XIAOPING, et al, 2010. Influence of benthic fauna on mangrove ecosystem and its ecological significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(4): 812-820 (in Chinese). | |
| [16] | 叶勇, 翁劲, 卢昌义, 等, 2006. 红树林生物多样性恢复[J]. 生态学报, 26(4): 1243-1250. |
| YE YONG, WENG JING, LU CHANGYI, et al, 2006. Mangrove biodiversity restoration[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(4): 1243-1250 (in Chinese). | |
| [17] | 袁兴中, 陆健健, 2001. 围垦对长江口南岸底栖动物群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 21(10): 1642-1647. |
| YUAN XINGZHONG, LU JIANJIAN, 2001. Influence of diking on the benthic macro-invertebrate community structure and diversity in the south bank of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 21(10): 1642-1647 (in Chinese). | |
| [18] | 张乔民, 隋淑珍, 2001. 中国红树林湿地资源及其保护[J]. 自然资源学报, 16(1): 28-36. |
| ZHANG QIAOMIN, SUI SHUZHEN, 2001. The mangrove wetland resources and their conservation in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 16(1): 28-36 (in Chinese). | |
| [19] | 钟山, 王卉, 方展强, 等, 2016. 珠海横琴红树林区不同季节大型底栖动物群落结构与分布[J]. 生态科学, 35(4): 38-46. |
| ZHONG SHAN, WANG HUI, FANG ZHANQIANG, et al, 2016. Comparison of the structure and distribution of macrobenthic communities in different seasons from mangrove regions in Hengqin Island, Zhuhai[J]. Ecological Science, 35(4): 38-46 (in Chinese). | |
| [20] | 钟燕婷, 张再旺, 唐以杰, 等, 2011. 淇澳岛两种红树林区大型底栖动物群落比较[J]. 生态科学, 30(5): 493-499. |
| ZHONG YANTING, ZHANG ZAIWANG, TANG YIJIE, et al, 2011. Comparison of the macrobenthic community in two mangrove regions in Qi’ao Island[J]. Ecological Science, 30(5): 493-499 (in Chinese). | |
| [21] | 周红, 张志南, 2003. 大型多元统计软件PRIMER的方法原理及其在底栖群落生态学中的应用[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 33(1): 58-64. |
| ZHOU HONG, ZHANG ZHINAN, 2003. Rationale of the multivariate statistical software PRIMER and its application in benthic community ecology[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 33(1): 58-64 (in Chinese). | |
| [22] | 朱晓君, 陆健健, 2003. 长江口九段沙潮间带底栖动物的功能群[J]. 动物学研究, 24(5): 355-361. |
| ZHU XIAOJUN LU JIANJIAN, 2003. Functional groups of zoobenthos in the intertidal zone of Jiuduansha, the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Zoological Research, 24(5): 355-361 (in Chinese). | |
| [23] | CAPEHART A A, HACKNEY C T, 1989. The potential role of roots and rhizomes in structuring salt-marsh benthic communities[J]. Estuaries, 12(2): 119-122. |
| [24] | MACINTOSH D J, ASHTON E C, HAVANON S, 2002. Mangrove rehabilitation and intertidal biodiversity: a study in the Ranong mangrove ecosystem, Thailand[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 55(3): 331-345. |
| [25] | STEPHENSON T A, STEPHENSON A, 1949. The universal features of zonation between tide-marks on rocky coasts[J]. Journal of Ecology, 37(2): 289-305. |
| [26] | TANG YIJIE, FANG ZHANQIANG, CHEN KANG, et al, 2012. Ecological influence of exotic plants of Sonneratia apetala on understory macrofauna[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(5): 115-125. |
| [27] | TANG YIJIE, FANG ZHANQIANG, ZHANG ZAIWANG, et al, 2014. Ecological indicators showing the succession of macrofauna communities in Sonneratia apetala artificial mangrove wetlands on Qi’ao Island at Zhuhai, South China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 33(8): 62-72. |
| [1] | 饶义勇, 赵美榕, 旷泽行, 黄洪辉, 谭萼辉. 浮筏式牡蛎养殖对大型底栖动物群落功能结构的影响——以大鹏澳为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 69-83. |
| [2] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [3] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [4] | 胡思敏, 周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 李涛, 黄晖. 悬浮物对三亚珊瑚礁区浮游动物群落结构及其摄食的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [5] | 罗勇, 黄林韬, 杨剑辉, 练健生, 刘骋跃, 江雷, 梁宇娴, 陈伦举, 雷新明, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海南临高红牌—马袅沿岸海域造礁石珊瑚群落结构及其环境影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [6] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [7] | 孙婷婷, 郝雯瑾, 徐鹏臻, 叶丽靖, 董志军. 海水酸化对海月水母螅状体共附生微生物的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 111-119. |
| [8] | 张兰兰, 程夏雯, 向荣, 邱卓雅, 常虎. 2019年春季孟加拉湾中部放射虫群落结构垂向变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [9] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [10] | 陈靖夫, 钟瑜, 王磊, 郭雨沛, 邱大俊. 环境DNA分析大亚湾夜光藻藻华对真核浮游生物群落的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [11] | 马文刚, 夏景全, 魏一凡, 尹洪洋, 覃乐政, 刘相波, 胡雪晴, 许强, 李秀保, 王爱民. 三亚蜈支洲岛海洋牧场近岛区底表大型底栖动物群落结构及评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [12] | 朱文涛, 夏景全, 刘相波, 尹洪洋, 朱铭, 任瑜潇, 谢敏睿, 黄建中, 李秀保. 丛生盔形珊瑚光合生理及共生真菌群落分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 132-141. |
| [13] | 张立明, 谭烨辉, 李佳俊, 黄小平, 刘甲星. 大亚湾夏季浮游植物群落结构及对淡澳河输入的响应特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [14] | 廖彤晨, 尹健强, 李开枝, 谭烨辉. 南海西北部夏冬季浮游介形类的分布及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 77-87. |
| [15] | 任玉正, 柯志新, 谭烨辉, 李开枝. 广东省南澳岛东部海域浮游动物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 65-76. |
|
||