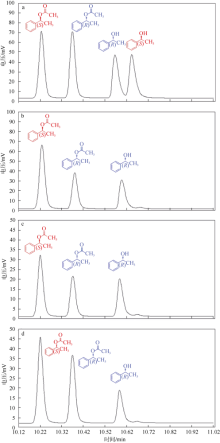
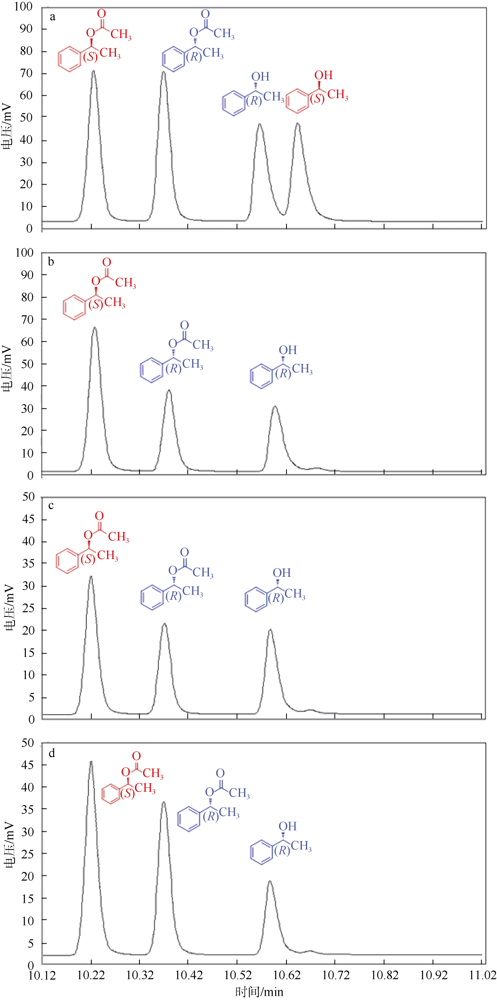
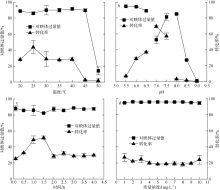
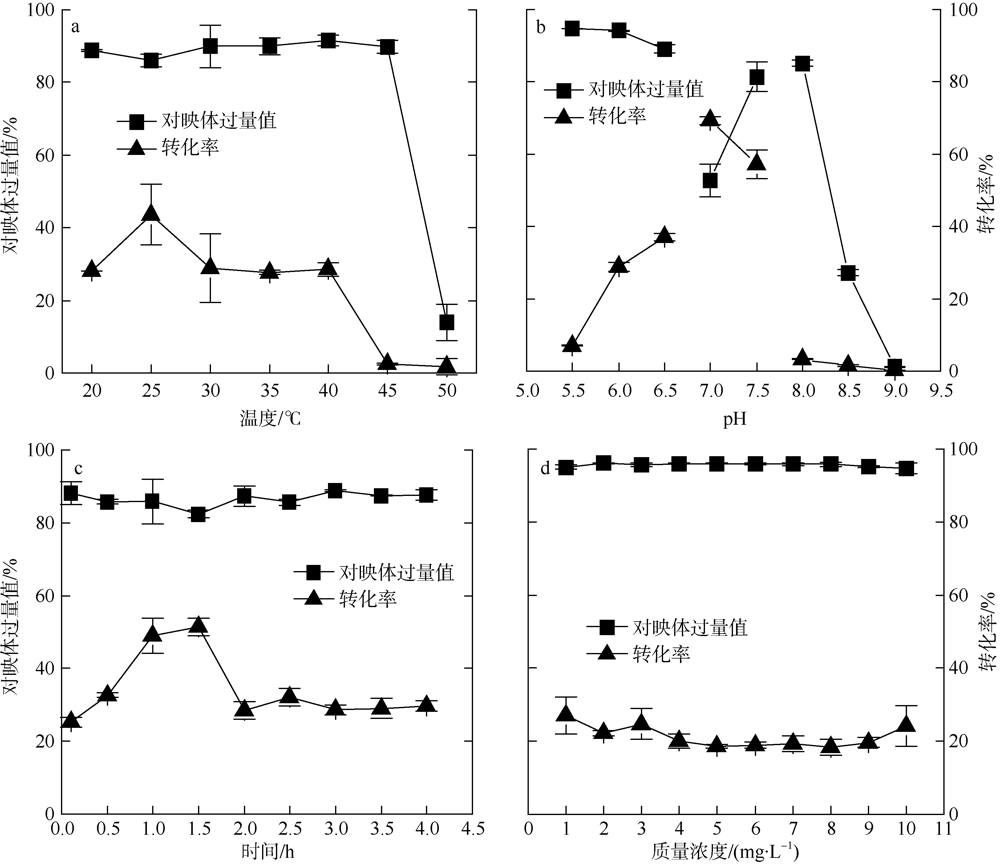
| [1] |
曹莹莹, 邓盾, 夏方亮, 等, 2016. 南海深海微生物酯酶EST12-7在制备(R)-2-氯丙酸乙酯中的应用研究[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 36(12):59-65.
|
|
CAO YINGYING, DENG DUN, XIA FANGLIANG, et al, 2016. Utilization of a marine microbial esterase in the enantio-selective preparation of (R)-ethyl 2-chloropropionate[J]. China Biotechnology, 36(12):59-65 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
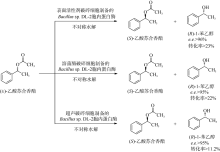
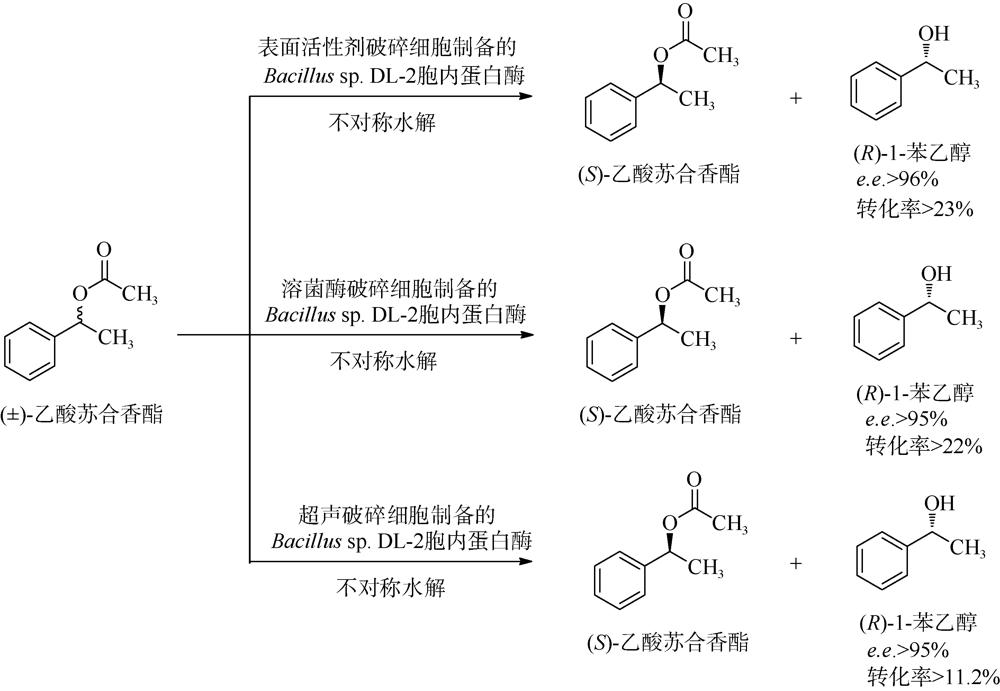
董璐, 张继福, 张云, 等. 2020. 环氧树脂固定化的Bacillus sp. DL-2胞外蛋白酶在拆分(±)-乙酸苏合香酯中的应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 40(4):49-58.
|
|
DONG LU, ZHANG JIFU, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2020. Immobilization of extracellaluar proteases of Bacillus sp. DL-2 using epoxy resin to asymmetrically hydrolyze (±)-1-phenylethyl acetate[J]. China Biotechnology, 40(4):49-58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
公颜慧, 马三梅, 张云, 等, 2016. 新颖微生物低温酯酶EstP8的酶学性质研究与在手性催化中的应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 36(10):35-44.
|
|
GONG YANHUI, MA SANMEI, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2016. Functional characterization of a novel microbial psychrophilic lipase and its utilization in stereo-selective biocatalysis[J]. China Biotechnology, 36(10):35-44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
公颜慧, 马三梅, 王永飞, 等, 2018. 新颖深海微生物酯酶EstC11的酶学性质及其在手性拆分乙酸苏合香酯中的应用[J]. 微生物学通报, 45(8):1632-1640.
|
|
GONG YANHUI, MA SANMEI, WANG YONGFEI, et al, 2018. Characterization of a novel deep-sea microbial esterase EstC11 for enantioselective resolution of (±)-1-phenylethl acetate[J]. Microbiology China, 45(8):1632-1640 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
黄锦龙, 张云, 孙爱君, 等, 2017. 一种新颖深海微生物羧酸酯酶制备(R)-苯乙醇的研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(3):55-60.
|
|
HUANG JINLONG, ZHANG YUN, SUN AIJUN, et al, 2017. Enantioselective production of (R)-1-phenylethanol by a novel marine microbial carboxylesterase[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(3):55-60 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
黄锦龙, 张继福, 胡洁莹, 等, 2018. 深海来源微生物乙酰酯酶的酶学性质鉴定及拆分制备D-乳酸甲酯[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(4):38-44.
|
|
HUANG JINLONG, ZHANG JIFU, HU JIEYING, et al, 2018. Characterization of one deep-sea derived microbial acetyl esterase and its utilization in the preparation of D-methyl lactate through kinetic resolution[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(4):38-44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
李琦, 张兰威, 韩雪, 等, 2011. 破壁方法对嗜热链球菌SP1.1胞内乳糖代谢关键酶活性的影响及其条件优化[J]. 食品科学, 32(9):183-187.
|
|
LI QI, ZHANG LANWEI, HAN XUE, et al, 2011. Effect of different cell wall disruption methods on key enzyme activities involved in intracellular lactose metabolism in Streptococcus thermophilus SP1.1 and optimization of lysozyme digestion conditions[J]. Food Science, 32(9):183-187 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
李清, 2004. Rhodococcus equi 4-2胆固醇氧化酶的发酵、纯化及初步应用[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学.
|
|
LI QING, 2004. Production, purification and primary application of the cholesterol oxidase from Rhodococcus equi 4-2[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
刘树文, 2009. 合成香料技术手册[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社: 227-228, 396-397.
|
|
LIU SHUWEN, 2009. Technical handbook of synthetic perfume materials[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Light Industry Press: 227-228, 396-397(in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
吕国英, 张作法, 程鸯祺, 2016. 刺芹侧耳降解孔雀石绿的酶学研究[J]. 食药用菌, 24(1):48-50 (in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
孙永红, 2010. 臭曲霉产α-转移葡萄糖苷酶液体发酵条件及酶学性质研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学.
|
|
SUN YONGHONG, 2010. Fermentation conditions and characterization of α-transglucosidase from Aspergillus foetidus SH4[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2010 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
田红玉, 2011. 手性香料及其不对称合成[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社: 1-3, 34-35, 265.
|
|
TIAN HONGYU, 2011. Chiral flavors and fragrances and asymmetric synthesis[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press: 1-3, 34-35, 265 (in Chinese).
|
| [13] |
CAO YINGYING, DENG DUN, SUN AIJUN, et al, 2016. Functional characterization of a novel marine microbial esterase and its utilization in the enantioselective preparation of (R)-methyl 2-chloropropionate[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(2):210-227.
pmid: 27118550
|
| [14] |
CHANG Y K, CHU L, 2007. A simple method for cell disruption by immobilization of lysozyme on the extrudate-shaped NaY zeolite[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 35(1):37-47.
|
| [15] |
CHEN C S, FUJIMOTO Y, GIRDAUKAS G, et al, 1982. Quantitative analyses of biochemical kinetic resolutions of enantiomers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 104(25):7294-7299.
|
| [16] |
CHUA L S, SARMIDI M R, 2004. Immobilised lipase-catalysed resolution of (R, S)-1-phenylethanol in recirculated packed bed reactor[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 28(2-3):111-119.
|
| [17] |
DE LOS RÍOS A P, VAN RANTWIJK F, SHELDON R A, 2012. Effective resolution of 1-phenyl ethanol by Candida antarctica lipase B catalysed acylation with vinyl acetate in protic ionic liquids (PILs)[J]. Green Chemistry, 14(6):1584-1588.
|
| [18] |
DENG DUN, ZHANG YUN, SUN AIJUN, et al, 2016a. Enantio-selective preparation of (S)-1-phenylethanol by a novel marine GDSL lipase MT6 with reverse stereo-selectivity[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 37(11):1966-1974.
|
| [19] |
DENG DUN, ZHANG YUN, SUN AIJUN, et al, 2016b. Functional characterization of a novel Dactylosporangium esterase and its utilization in the asymmetric synjournal of (R)-methyl mandelate[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(2):228-247.
pmid: 27118549
|
| [20] |
DENG DUN, ZHANG YUN, SUN AIJUN, et al, 2016c. Functional characterization of a novel marine microbial GDSL lipase and its utilization in the resolution of (±)-1-phenylethanol[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 179(1):75-93.
pmid: 26754423
|
| [21] |
DENG DUN, ZHANG YUN, SUN AIJUN, et al, 2018. Functional characterization of a New Antarctic microbial esterase EST112-2 and its use in the preparation of chiral tertiary alcohol (S)-linalool[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 38(5):1185-1192.
|
| [22] |
DONG LU, XU YONGKAI, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2019a. Enantioselective resolution of (±)-1-phenylethyl acetate by extracellular proteases from deep-sea bacterium Bacillus sp. DL-2[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 37(6):466-478.
|
| [23] |
DONG LU, XU YONGKAI, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2019b. Enantioselective resolution of (±)-1-phenylethyl acetate by using the whole cells of deep-sea bacterium Bacillus sp. DL-2[J]. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 35(5):792-798.
|
| [24] |
FAN YONGXIAN, XIE ZHANGMING, ZHANG HUAWEI, et al, 2011. Kinetic resolution of both 1-phenylethanol enantiomers produced by hydrolysis of 1-phenylethyl acetate with Candida antarctica lipase B in different solvent systems[J]. Kinetics and Catalysis, 52(5):686-690.
doi: 10.1134/S0023158411050065
|
| [25] |
GONG YANHUI, MA SANMEI, WANG YONGFEI, et al, 2018. Characterization of a novel deep-sea microbial esterase EstC10 and its use in the generation of (R)-methyl 2- chloropropionate[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 36(2):473-482.
|
| [26] |
HUANG JINLONG, XU YONGKAI, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2018. Utilization of one novel deep-sea microbial protease sin3406-1 in the preparation of ethyl (S)-3-hydroxybutyrate through kinetic resolution[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34(9):124.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-018-2513-9
pmid: 30083971
|
| [27] |
HUANG JINLONG, ZHANG YUN, HU YUNFENG, 2016. Functional characterization of a marine Bacillus esterase and its utilization in the stereo-selective production of D-methyl lactate[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(8):1467-1481.
pmid: 27364331
|
| [28] |
LIANG JIAYUAN, SUN AIJUN, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2016a. Functional characterization of a novel microbial esterase identified from the Indian Ocean and its use in the stereoselective preparation of (R)-methyl mandelate[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 34(6):1269-1277.
|
| [29] |
LIANG JIAYUAN, ZHANG YUN, SUN AIJUN, et al, 2016b. Enantioselective resolution of (±)-1-phenylethanol and (±)-1-phenylethyl acetate by a novel esterase from Bacillus sp. SCSIO 15121[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 178(3):558-575.
pmid: 26467742
|
| [30] |
NOYORI R, KITAMURA M, 1991. Enantioselective addition of organometallic reagents to carbonyl compounds: chirality transfer, multiplication, and amplification[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 30(1):49-69.
|
| [31] |
WANG YILONG, XU SHAN, LI RENQIANG, et al, 2019a. Characterization of one novel microbial esterase WDEst9 and its use to make L-methyl lactate[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 37(3):190-200.
|
| [32] |
WANG YILONG, XU YONGKAI, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2018a. Utilization of deep-sea microbial esterase PHE21 to generate chiral sec-butyl acetate through kinetic resolutions[J]. Chirality, 30(8):1027-1035.
doi: 10.1002/chir.v30.8
|
| [33] |
WANG YILONG, XU YONGKAI, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2018b. Functional characterization of salt-tolerant microbial esterase WDEst17 and its use in the generation of optically pure ethyl (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate[J]. Chirality, 30(6):769-776.
pmid: 29573466
|
| [34] |
WANG YILONG, XU YONGKAI, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2019b. Utilization of one novel microbial esterase WDEst9 in the kinetic resolution of (S)-methyl 2-chloropropionate and (S)-ethyl 2-chloropropionate[J]. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 35(5):830-836.
doi: 10.1007/s40242-019-9104-7
|
| [35] |
WANG YILONG, ZHANG YUN, HU YUNFENG, 2016a. Functional characterization of a robust marine microbial esterase and its utilization in the stereo-selective preparation of ethyl (S)-3-hydroxybutyrate[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(6):1196-1212.
pmid: 27299920
|
| [36] |
WANG YILONG, ZHANG YUN, SUN AIJUN, et al, 2016b. Characterization of a novel marine microbial esterase and its use to make D-methyl lactate[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 37(8):1396-1402.
|
| [37] |
WERKHOFF P, KRAMMER G, BRENNECKE S, et al, 2002. Methyl dihydrojasmonate and its stereoisomers: sensory properties and enantioselective analysis[J]. Food Reviews International, 18(2-3):103-122.
|
 ), 董璐1,4, 张继福3, 张云1,2, 胡云峰1,2(
), 董璐1,4, 张继福3, 张云1,2, 胡云峰1,2( )
)
 ), DONG Lu1,4, ZHANG Jifu3, ZHANG Yun1,2, HU Yunfeng1,2(
), DONG Lu1,4, ZHANG Jifu3, ZHANG Yun1,2, HU Yunfeng1,2( )
)