热带海洋学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 177-188.doi: 10.11978/2021074CSTR: 32234.14.2021074
线纹海马肠道菌群结构与功能对迟钝爱德华氏菌(Edwardsiella tarda)感染的响应特征研究
张乐乐1( ), 邹强2, 田雅楠1, 吕春晖1, 郑诗怡1, 姜广峻1, 高龙坤1, 侯玉平3, 王凯1(
), 邹强2, 田雅楠1, 吕春晖1, 郑诗怡1, 姜广峻1, 高龙坤1, 侯玉平3, 王凯1( )
)
- 1. 鲁东大学农学院, 山东 烟台 264025
2. 烟台市科技创新促进中心, 山东 烟台 264003
3. 鲁东大学生命科学学院, 山东 烟台 264025
-
收稿日期:2021-06-11修回日期:2021-07-22出版日期:2022-03-10发布日期:2021-07-26 -
通讯作者:王凯 -
作者简介:张乐乐(1998—), 女, 山东省聊城市人, 硕士研究生, 主要从事海洋动物病害研究。email:2508408930@qq.com -
基金资助:山东省高等学校优秀青年创新团队科技计划项目(2020KJF007);烟台市科技创新发展计划项目(2020LJRC120);烟台市科技创新发展计划项目(2019CXJJ040);山东省高校科技计划项目(J18KA146);LAMB联合资助开放基金课题(LMB20200103);威海市科技发展计划项目(2017GNS10)
Dysbiosis of both structure and function of intestinal microbiota in lined seahorses (Hippocampus erectus) as response to Edwardsiella tarda infection
ZHANG Lele1( ), ZOU Qiang2, TIAN Yanan1, LÜ Chunhui1, ZHENG Shiyi1, JIANG Guangjun1, GAO Longkun1, HOU Yuping3, WANG Kai1(
), ZOU Qiang2, TIAN Yanan1, LÜ Chunhui1, ZHENG Shiyi1, JIANG Guangjun1, GAO Longkun1, HOU Yuping3, WANG Kai1( )
)
- 1. School of Agriculture, Ludong University, Yantai 264025, China
2. Yantai Science and Technology Innovation Promotion Center, Yantai 264003, China
3. School of Life Science, Ludong University, Yantai 264025, China
-
Received:2021-06-11Revised:2021-07-22Online:2022-03-10Published:2021-07-26 -
Contact:WANG Kai -
Supported by:Program for Outstanding Youth of Colleges and Universities(2020KJF007);Yantai Foundation for Development of Science and Technology(2020LJRC120);Yantai Foundation for Development of Science and Technology(2019CXJJ040);Shandong Province Science and Technology Research Program for Colleges and Universities(J18KA146);LMM;LMB, LMM and LAMB Co-funded Open Funds of the South China Sea Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(LMB20200103);Weihai Foundation for Development of Science and Technology(2017GNS10)
摘要:
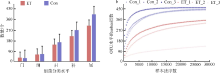
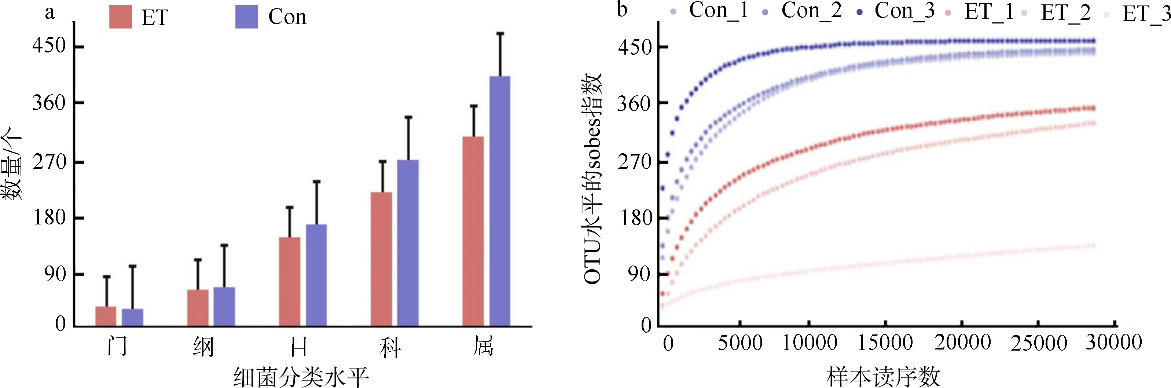
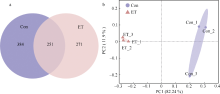
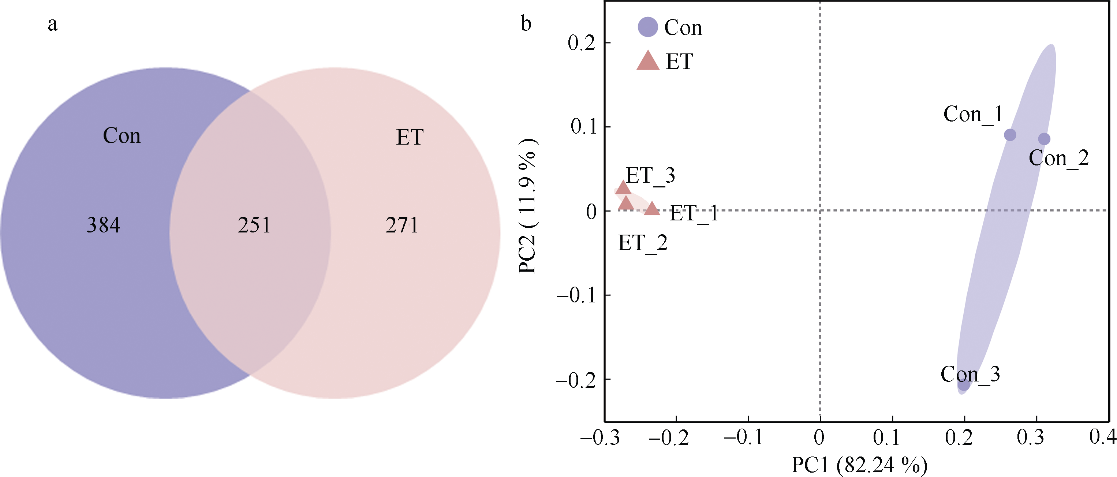
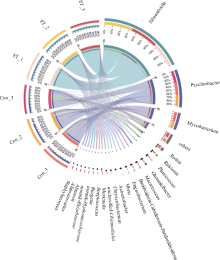
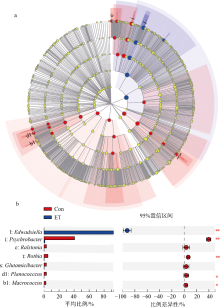
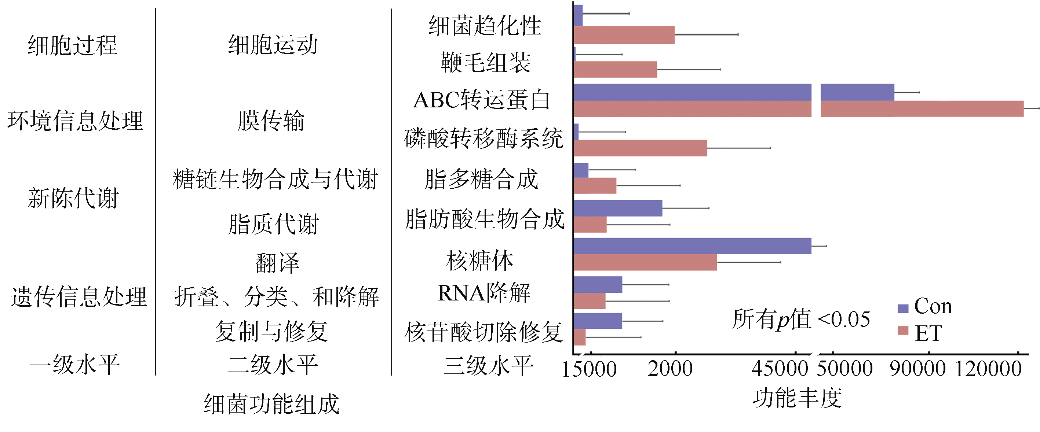
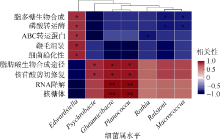
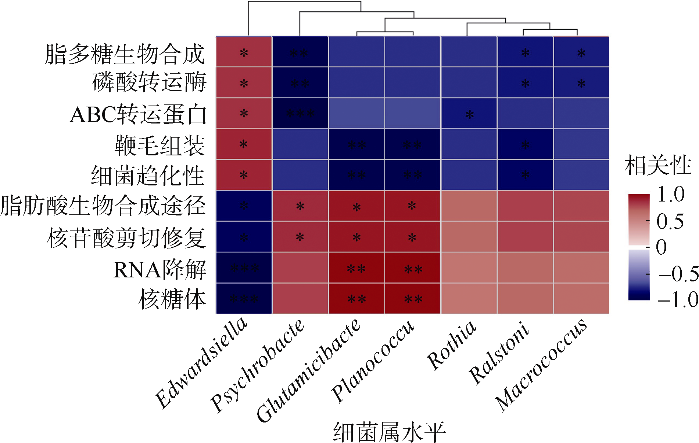
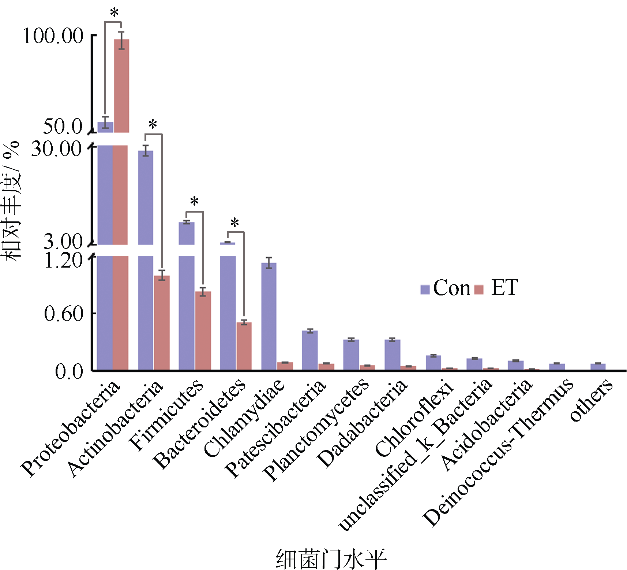
细菌性肠炎对海马养殖业影响巨大, 但病原对海马肠道菌群的具体影响尚不清楚。文章利用已分离的病原细菌 Edwardsiella tarda YT1和海马细菌性肠炎模型, 结合16S rDNA高通量测序技术, 探究病原细菌侵染对海马肠道菌群的影响。结果发现, E. tarda侵染改变了海马肠道菌群的结构组成、多样性和丰度, 并显著降低了其多样性(p<0.05); 显著增加了海马肠道变形菌门(Proteobacteria)的相对丰度(p<0.05), 减少了放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)的相对丰度(p<0.05); 导致致病菌爱德华氏菌属(Edwardsiella)在属水平的相对丰度极显著增加(p<0.01), 而肠道固有菌群嗜冷杆菌属(Psychrobacter)和罗氏菌属(Rothia)极显著减少(p<0.01), 以及球菌属(Macrococcus)与动球菌属(Planococcus)显著减少(p<0.05)。研究结果表明, E. tarda能通过改变海马肠道固有优势菌群的相对丰度导致菌群失调。菌群功能变化及其相关性分析表明, E. tarda可能通过显著提高细菌趋化性、鞭毛组装、ABC转运蛋白、磷酸转运酶系统以及脂多糖生物合成途径的活性(p<0.05), 抑制肠道核心菌群如嗜冷杆菌属、动球菌属和谷氨酸杆菌属的丰度及其核糖体、RNA降解、核苷酸剪切修复与脂肪酸生物合成途径的活性(p<0.05), 导致肠道菌群功能失调, 并诱发肠炎。
中图分类号:
- P735.51
引用本文
张乐乐, 邹强, 田雅楠, 吕春晖, 郑诗怡, 姜广峻, 高龙坤, 侯玉平, 王凯. 线纹海马肠道菌群结构与功能对迟钝爱德华氏菌(Edwardsiella tarda)感染的响应特征研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 177-188.
ZHANG Lele, ZOU Qiang, TIAN Yanan, LÜ Chunhui, ZHENG Shiyi, JIANG Guangjun, GAO Longkun, HOU Yuping, WANG Kai. Dysbiosis of both structure and function of intestinal microbiota in lined seahorses (Hippocampus erectus) as response to Edwardsiella tarda infection[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 177-188.
| [1] | 邓钢, 吕军仪, 林强, 2005. 大海马育苗池水华发生期间细菌动态及相关理化参数[J]. 中国水产科学, 12(4): 477-482. |
| DENG GANG, LÜ JUNYI, LIN QIANG, 2005. Effects of water-bloom on environmental factors in breeding water for juvenile seahorse, Hippocamppus kuda Bleeker[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 12(4): 477-482. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 李焕宇, 付婷婷, 张云, 等, 2017. 5种方法提取真菌基因组DNA作为PCR模板效果的比较[J]. 中国农学通报, 33(16): 28-35. |
| LI HUANYU, FU TINGTING, ZHANG YUN, et al, 2017. Effect comparison of five methods to extract fungal genomic DNA as PCR templates[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 33(16): 28-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 刘国信, 茹贺军, 2006. 海马的人工养殖技术[J]. 水产科技情报, 33(6): 254-256. |
| LIU GUOXIN, RU HEJUN, 2006. Artificial culture technique of horse fish[J]. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 33(6): 254-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 吕军仪, 吴金英, 杨大伟, 等, 2001. 大海马在人工养殖条件下的生长速率[J]. 中国水产科学, 8(1): 59-63. |
| LÜ JUNYI, WU JINYING, YANG DAWEI, et al, 2001. Growth rate of Hippocampus kuda under intensive culture[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 8(1): 59-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] |
BALCÁZAR J L, GALLO-BUENO A, PLANAS M, et al, 2010. Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio splendidus from captive-bred seahorses with disease symptoms[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 97(2): 207-210.
doi: 10.1007/s10482-009-9398-4 |
| [6] |
BOKULICH N A, SUBRAMANIAN S, FAITH J J, et al, 2013. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing[J]. Nature Methods, 10(1): 57-59.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2276 |
| [7] |
BUSCHKE N, SCHRÖDER H, WITTMANN C, 2011. Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for production of 1,5-diaminopentane from hemicellulose[J]. Biotechnology Journal, 6(3): 306-317.
doi: 10.1002/biot.v6.3 |
| [8] |
CAIPANG C M A, BRINCHMANN M F, KIRON V, 2010. Antagonistic activity of bacterial isolates from intestinal microbiota of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua, and an investigation of their immunomodulatory capabilities[J]. Aquaculture Research, 41(2): 249-256.
doi: 10.1111/are.2010.41.issue-2 |
| [9] |
CAPORASO J G, KUCZYNSKI J, STOMBAUGH J, et al, 2010. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data[J]. Nature Methods, 7(5): 335-336.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303 |
| [10] |
CLEMENTE J C, URSELL L K, PARFREY L W, et al, 2012. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view[J]. Cell, 148(6): 1258-1270.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.035 |
| [11] | COHEN F P A, VALENTI W C, PLANAS M, et al, 2017. Seahorse aquaculture, biology and conservation: knowledge gaps and research opportunities[J]. Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture, 25(1): 100-111. |
| [12] |
DENG YIQIN, ZHANG YAQIU, CHEN HAOXIANG, et al, 2020. Gut-liver immune response and gut microbiota profiling reveal the pathogenic mechanisms of Vibrio harveyi in pearl gentian grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ × E. fuscoguttatus♀)[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 11: 607754. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.607754.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.607754 |
| [13] |
EDGAR R C, 2010. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST[J]. Bioinformatics, 26(19): 2460-2461.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461 |
| [14] |
EDGAR R C, HAAS B J, CLEMENTE J C, et al, 2011. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection[J]. Bioinformatics, 27(16): 2194-2200.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381 |
| [15] | ERHARDT M, 2016. Strategies to block bacterial pathogenesis by interference with motility and chemotaxis[M]// STADLER M, DERSCH P. How to overcome the antibiotic crisis:facts, challenges, technologies and future perspectives. Cham: Springer: 185-205. |
| [16] | FRANK D N, AMAND A L S, FELDMAN R A, et al, 2007. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(34): 13780-13785. |
| [17] |
GAO TANTAN, DING MINGZHENG, YANG C H, et al, 2019. The phosphotransferase system gene ptsH plays an important role in MnSOD production, biofilm formation, swarming motility, and root colonization in Bacillus cereus 905[J]. Research in Microbiology, 170(2): 86-96.
doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2018.10.002 |
| [18] |
HAMMER B K, BASSLER B L, 2003. Quorum sensing controls biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 50(1): 101-104.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03688.x |
| [19] | HARIKRISHNAN R, BALASUNDARAM C, HEO M S, 2010. Scuticociliatosis and its recent prophylactic measures in aquaculture with special reference to South Korea: taxonomy, diversity and diagnosis of scuticociliatosis: part Ⅰ control strategies of scuticociliatosis: part Ⅱ[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 29(1): 15-31. |
| [20] |
HAYAKAWA T, MASUDA T, KUROSAWA D, et al, 2016. Dietary administration of probiotics to sows and/or their neonates improves the reproductive performance, incidence of post-weaning diarrhea and histopathological parameters in the intestine of weaned piglets[J]. Animal Science Journal, 87(12): 1501-1510.
doi: 10.1111/asj.2016.87.issue-12 |
| [21] |
KAMADA N, KIM Y G, SHAM H P, et al, 2012. Regulated virulence controls the ability of a pathogen to compete with the gut microbiota[J]. Science, 336(6086): 1325-1329.
doi: 10.1126/science.1222195 |
| [22] |
LEPAGE V, DUTTON C J, KUMMROW M, et al, 2012. Neoplasia of captive yellow sea horses (Hippocampus kuda) and weedy sea dragons (Phyllopteryx taeniolatus)[J]. Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine, 43(1): 50-58.
doi: 10.1638/2010-0236.1 |
| [23] |
LI FENG, WANG KAI, LUO WEI, et al, 2015. Comparison of the intestinal bacterial flora in healthy and intestinal-diseased seahorses Hippocampus trimaculatus, Hippocampus erectus, and Hippocampus spinosissimus[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 46(3): 263-272.
doi: 10.1111/jwas.2015.46.issue-3 |
| [24] |
LI HUILI, SUN BOGUANG, NING XIANHUI, et al, 2019. A comparative analysis of Edwardsiella tarda-induced transcriptome profiles in RAW264.7 cells reveals new insights into the strategy of bacterial immune evasion[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22): 5724. doi: 10.3390/ ijms20225724.
doi: 10.3390/ ijms20225724 |
| [25] |
LI TONGTONG, LONG MENG, JI CHENG, et al, 2016. Alterations of the gut microbiome of largemouth bronze gudgeon (Coreius guichenoti) suffering from furunculosis[J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1): 30606. doi: 10.1038/srep30606.
doi: 10.1038/srep30606 |
| [26] |
LIM G H, SINGHAL R, KACHROO A, et al, 2017. Fatty acid- and lipid-mediated signaling in plant defense[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 55: 505-536.
doi: 10.1146/phyto.2017.55.issue-1 |
| [27] |
LIN QIANG, LIN JUNDA, ZHANG DONG, 2008. Breeding and juvenile culture of the lined seahorse, Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810[J]. Aquaculture, 277(3-4): 287-292.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.02.030 |
| [28] |
LIN QIANG, LIN JUNDA, HUANG LIANGMIN, 2010. Effects of light intensity, stocking density and temperature on the air-bubble disease, survivorship and growth of early juvenile seahorse Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810[J]. Aquaculture Research, 42(1): 91-98.
doi: 10.1111/are.2010.42.issue-1 |
| [29] |
LIU FENGYUN, FAN CHAO, ZHANG LIANGZHI, et al, 2020. Alterations of gut microbiome in Tibetan patients with coronary heart disease[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 10: 373. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00373.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00373 |
| [30] |
LOURIE S A, PRITCHARD J C, CASEY S, et al, 1999. The taxonomy of Vietnam’s exploited seahorses (family Syngnathidae)[J]. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 66(2): 231-256.
doi: 10.1111/bij.1999.66.issue-2 |
| [31] |
LOURIE S A, VINCENT A C J, 2004. A marine fish follows Wallace’s Line: the phylogeography of the three-spot seahorse (Hippocampus trimaculatus, Syngnathidae, Teleostei) in Southeast Asia[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 31(12): 1975-1985.
doi: 10.1111/jbi.2004.31.issue-12 |
| [32] |
LOZUPONE C A, STOMBAUGH J I, GORDON J I, et al, 2012. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota[J]. Nature, 489(7415): 220-230.
doi: 10.1038/nature11550 |
| [33] |
LOZUPONE C, HAMADY M, KNIGHT R, 2006. UniFrac - an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 7: 371. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-371.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-371. |
| [34] |
MAGOČ T, SALZBERG S L, 2011. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies[J]. Bioinformatics, 27(21): 2957-2963.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507 |
| [35] | MAKLED S O, HAMDAN A M, EL-SAYED A F M, et al, 2017. Evaluation of marine psychrophile, Psychrobacter namhaensis SO89, as a probiotic in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) diets[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 61: 194-200. |
| [36] |
MANIKANDAN P, SENTHILKUMAR P K, 2017. An overview of saltpan halophilic bacterium[J]. Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 3(4): 1000151. doi: 10.4172/2472-1212.1000151.
doi: 10.4172/2472-1212.1000151 |
| [37] | MATILLA M A, KRELL T, 2018. The effect of bacterial chemotaxis on host infection and pathogenicity[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 42(1): fux052. |
| [38] |
MIYATA S T, UNTERWEGER D, RUDKO S P, et al, 2013. Dual expression profile of type Ⅵ secretion system immunity genes protects pandemic Vibrio cholerae[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 9(12): e1003752.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003752 |
| [39] |
NOWARSKI R, JACKSON R, FLAVELL R A, 2017. The stromal intervention: regulation of immunity and inflammation at the epithelial-mesenchymal barrier[J]. Cell, 168(3): 362-375.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.040 |
| [40] |
PÉREZ-SÁNCHEZ A, BARRAJÓN-CATALÁN E, HERRANZ- LÓPEZ M, et al, 2018. Nutraceuticals for skin care: a comprehensive review of Human clinical studies[J]. Nutrients, 10(4): 403. doi: 10.3390/nu10040403.
doi: 10.3390/nu10040403 |
| [41] |
PETRYSZYN P W, WIELA-HOJEŃSKA A, 2018. The importance of the polymorphisms of the ABCB1 gene in disease susceptibility, behavior and response to treatment in inflammatory bowel disease: a literature review[J]. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 27(10): 1459-1463.
doi: 10.17219/acem/92936 |
| [42] | PURCHIARONI F, TORTORA A, GABRIELLI M, et al, 2013. The role of intestinal microbiota and the immune system[J]. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 17(3): 323-333. |
| [43] |
QIN G, WANG X, TAN S, et al, 2017. A bacterial infection by Vibrio harveyi causing heavy reduction of cultured lined seahorse Hippocampus erectus[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 40(4): 601-605.
doi: 10.1111/jfd.2017.40.issue-4 |
| [44] |
QIN GENG, ZHANG YUAN, ZHANG BO, et al, 2018. Seahorse TLR5 gene responses to Vibrio vulnificus infection, which in combination with scuticociliates causes heavy reductions in seahorse aquaculture[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 41(12): 1933-1936.
doi: 10.1111/jfd.2018.41.issue-12 |
| [45] |
RIVERA-PÉREZ W A, YÉPES-PÉREZ A F, MARTÍNEZ-PABÓN M C, 2019. Molecular docking and in silico studies of the physicochemical properties of potential inhibitors for the phosphotransferase system of Streptococcus mutans[J]. Archives of Oral Biology, 98: 164-175.
doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.09.020 |
| [46] |
ROBERTSON S J, GOETHEL A, GIRARDIN S E, et al, 2018. Innate immune influences on the Gut microbiome: lessons from mouse models[J]. Trends in Immunology, 39(12): 992-1004.
doi: 10.1016/j.it.2018.10.004 |
| [47] |
ROESELERS G, MITTGE E K, STEPHENS W Z, et al, 2011. Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish[J]. The ISME Journal, 5(10): 1595-1608.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.38 |
| [48] |
SHAO PENG, YONG PENGZHENG, WANG XIAOYU, et al, 2019. Isolation, identification, and histopathological analysis of Vibrio tubiashii from lined seahorse Hippocampus erectus[J]. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 133(3): 195-205.
doi: 10.3354/dao03350 |
| [49] |
SHIN N R, WHON T W, BAE J W, 2015. Proteobacteria: microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 33(9): 496-503.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.06.011 |
| [50] |
SOHRABI-JAHROMI S, HOFMANN K B, BOLTENDAHL A, et al, 2019. Transcriptome maps of general eukaryotic RNA degradation factors[J]. eLife, 8: e47040.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.47040 |
| [51] |
TERNES M L F, GERHARDINGER L C, SCHIAVETTI A, 2016. Seahorses in focus: local ecological knowledge of seahorse- watching operators in a tropical estuary[J]. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 12(1): 52. doi: 10.1186/s13002-016-0125-8.
doi: 10.1186/s13002-016-0125-8 |
| [52] |
TRAN N T, ZHANG JING, XIONG FAN, et al, 2018. Altered gut microbiota associated with intestinal disease in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus)[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34(6): 71. doi: 10.1007/s11274-018-2447-2.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-018-2447-2 |
| [53] |
TYAGI A, SINGH B, BILLEKALLU THAMMEGOWDA N K, et al, 2019. Shotgun metagenomics offers novel insights into taxonomic compositions, metabolic pathways and antibiotic resistance genes in fish gut microbiome[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 201(3): 295-303.
doi: 10.1007/s00203-018-1615-y |
| [54] |
WAGHMODE S, SURYAVANSHI M, SHARMA D, et al, 2020. Planococcus Species - An imminent resource to explore biosurfactant and bioactive metabolites for industrial applications[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 8: 996. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00996.
doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00996 |
| [55] |
WANG JIANMEI, BAI JING, ZHENG FANGYUAN, et al, 2020a. Diversity of the gut microbiome in three grasshopper species using 16S rRNA and determination of cellulose digestibility[J]. PeerJ, 8: e10194.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.10194 |
| [56] |
WANG KAI, LI KUNMING, SHAO JUNFENG, et al, 2017. Yeast and corn flour supplement to enhance large-scale culture efficiency of marine copepod Tisbe furcata, a potential live food for fish larvae[J]. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture- Bamidgeh, 69: 8. doi: 10.469891/001c.2169.
doi: 10.469891/001c.2169 |
| [57] |
WANG RUNPING, PAN XIA, XU YONGJIAN, 2020b. Altered intestinal microbiota composition associated with enteritis in yellow seahorses Hippocampus kuda (Bleeker, 1852)[J]. Current Microbiology, 77(5): 730-737.
doi: 10.1007/s00284-019-01859-6 |
| [58] |
WANG X, ZHANG Y, QIN G, et al, 2016. A novel pathogenic bacteria (Vibrio fortis) causing enteritis in cultured seahorses, Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 39(6): 765-769.
doi: 10.1111/jfd.12411 |
| [59] | WANG XIAOMENG, WANG FANG, CHEN GUOZHONG, et al, 2020c. Edwardsiella tarda induces enteritis in farmed seahorses (Hippocampus erectus): an experimental model and its evaluation[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 98: 391-400. |
| [60] |
WILLIAMS S M, CHEN YUTING, ANDERMANN T M, et al, 2007. Helicobacter pylori chemotaxis modulates inflammation and bacterium-gastric epithelium interactions in infected mice[J]. Infection and Immunity, 75(8): 3747-3757.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00082-07 |
| [61] |
WU H J, WU E, 2012a. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity[J]. Gut Microbes, 3(1): 4-14.
doi: 10.4161/gmic.19320 |
| [62] |
WU SHANGONG, WANG GUITANG, ANGERT E R, et al, 2012b. Composition, diversity, and origin of the bacterial community in grass carp intestine[J]. PLoS One, 7(2): e30440.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030440 |
| [63] |
XIONG JINBO, WANG KAI, WU JINFENG, et al, 2015. Changes in intestinal bacterial communities are closely associated with shrimp disease severity[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99(16): 6911-6919.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6632-z |
| [64] | XIONG JINBO, NIE LI, CHEN JIONG, 2019. Current understanding on the roles of gut microbiota in fish disease and immunity[J]. Zoological Research, 40(2): 70-76. |
| [65] |
XU JIAN, BJURSELL M K, HIMROD J, et al, 2003. A genomic view of the human-Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron symbiosis[J]. Science, 299(5615): 2074-2076.
doi: 10.1126/science.1080029 |
| [66] |
YANG HONGLING, SUN YUNZHANG, MA RULONG, et al, 2011. Probiotic Psychrobacter sp. improved the autochthonous microbial diversity along the gastrointestinal tract of grouper Epinephelus coioides[J]. Journal of Aquaculture Research & Development, doi: 10.4172/2155-9546.S1-001.
doi: 10.4172/2155-9546.S1-001 |
| [67] | YANG HUITING, ZOU SONGSONG, ZHAI LIJUAN, et al, 2017. Pathogen invasion changes the intestinal microbiota composition and induces innate immune responses in the zebrafish intestine[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 71: 35-42. |
| [68] |
YU GUIJING, WANG XIAOLAN, DOU YAFENG, et al, 2016. Riemerella anatipestifer M949_1360 gene functions on the lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and bacterial virulence[J]. PLoS One, 11(8): e0160708.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160708 |
| [69] |
ZHANG JIACHAO, GUO ZHUANG, XUE ZHENGSHENG, et al, 2015. A phylo-functional core of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across lifestyles, geography and ethnicities[J]. The ISME Journal, 9(9): 1979-1990.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.11 |
| [70] |
ZHANG QILIN, LI HONGWEI, WU WEI, et al, 2019. The response of microbiota community to Streptococcus agalactiae infection in zebrafish intestine[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10: 2848. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02848.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02848 |
| [71] |
ZHOU BOLUN, YUAN YUTONG, ZHANG SHANSHAN, et al, 2020. Intestinal flora and disease mutually shape the regional immune system in the intestinal tract[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 11: 575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00575.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00575 |
| [72] |
ZHOU XIANG, LIAO WENJUAN, LIAO JUNMING, et al, 2015. Ribosomal proteins: functions beyond the ribosome[J]. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, 7(2): 92-104.
doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjv014 |
| [1] | 陈灵珍, 秦耿, 王信, 刘雅莉, 肖旺红, 林强. 线纹海马(Hippocampus erectus)性腺特异性结构与生殖细胞发育特征研究 *[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6): 93-102. |
| [2] | 张媛, 秦耿, 张博, 林强. 线纹海马Hippocampus erectus的tlr21基因结构及其对CpG-ODN的应答特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(1): 67-75. |
|
||