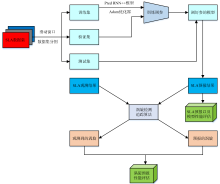
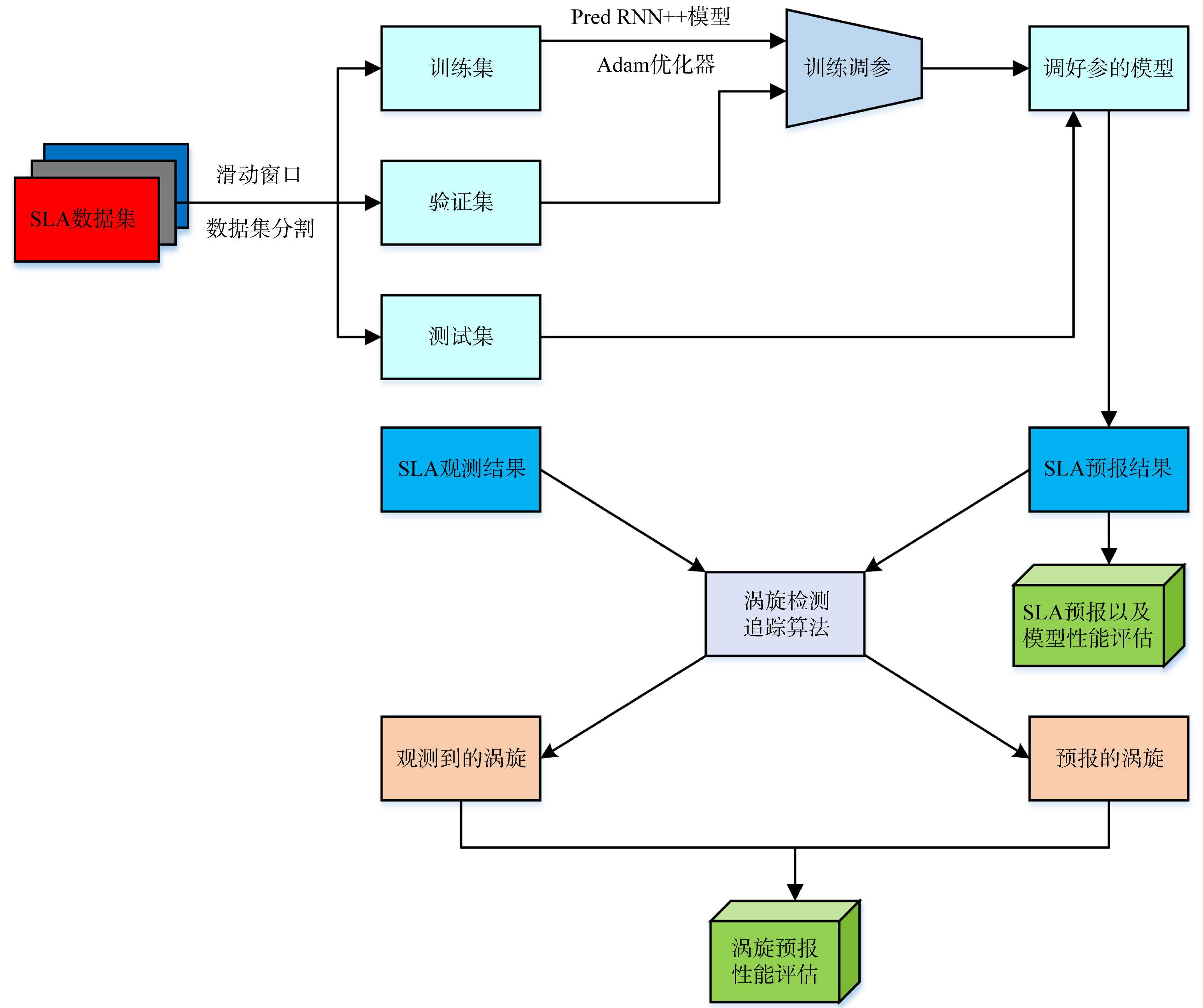
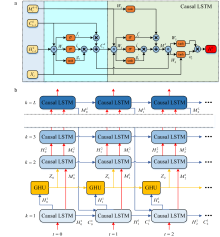
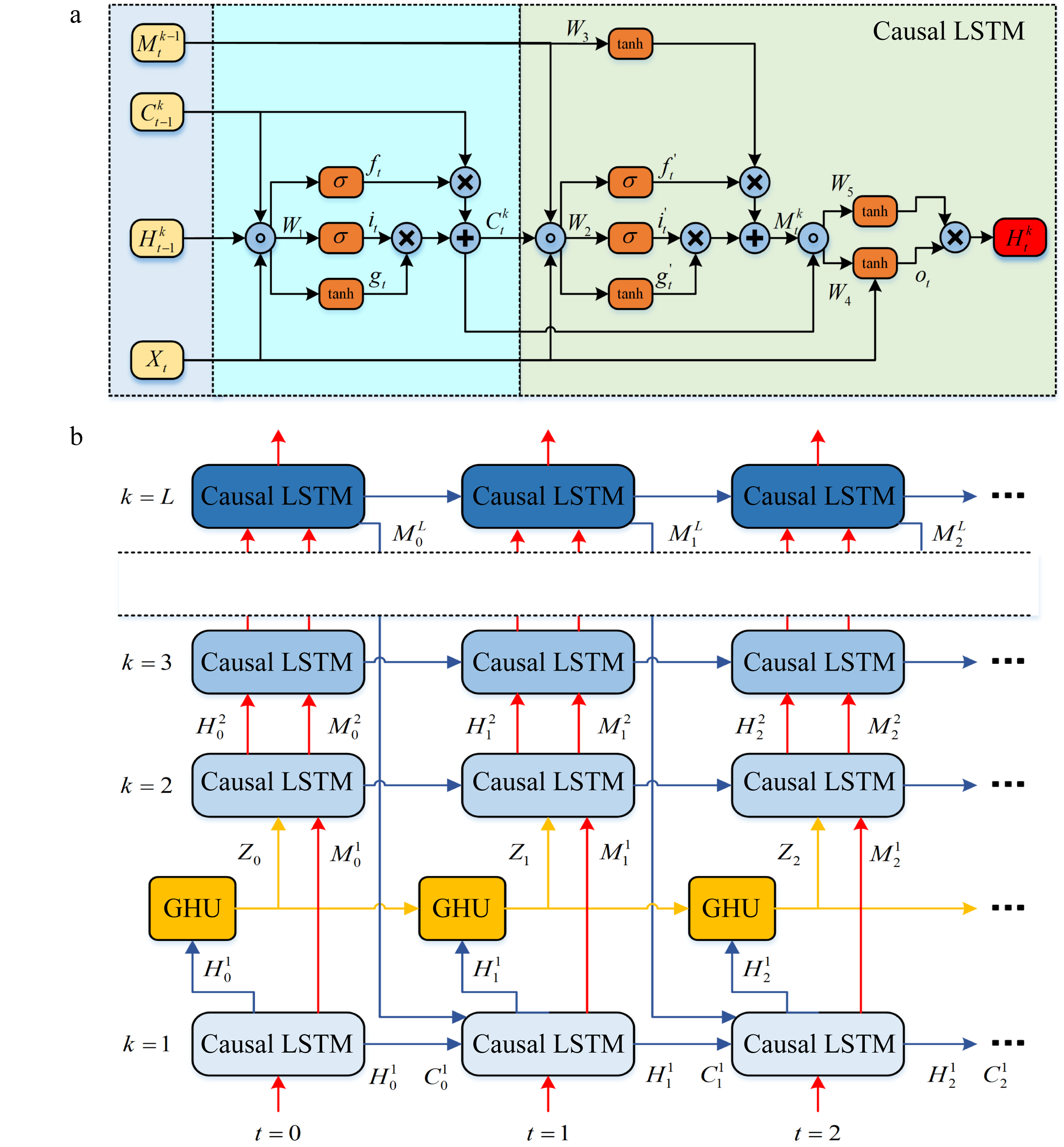
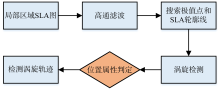
| [1] |
韩玉康, 周林, 吴炎成, 2016. 基于HYCOM的南海中尺度涡数值模拟[J]. 海洋通报, 35(3): 299-316.
|
|
HAN YUKANG, ZHOU LIN, WU YANCHENG, 2016. Numerical simulation of the mesoscale eddy in the South China Sea based on HYCOM[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 35(3): 299-316 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
李佳讯, 张韧, 陈奕德, 等, 2011. 海洋中尺度涡建模及其在水声传播影响研究中的应用[J]. 海洋通报, 30(1): 37-46.
|
|
LI JIAXUN, ZHANG REN, CHEN YIDE, et al, 2011. Ocean mesoscale eddy modeling and its application in studying the effect on underwater acoustic propagation[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 30(1): 37-46 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
CHELTON D B, SCHLAX M G, SAMELSON R M, 2011. Global observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 91(2): 167-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2011.01.002
|
| [4] |
CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, CHU XIAOQING, 2011. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: mean properties, spatiotemporal variability, and impact on thermohaline structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(C6): C06018.
|
| [5] |
CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, ZHANG QILONG, et al, 2010. The eddy pair off eastern Vietnam: interannual variability and impact on thermohaline structure[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 30(7): 715-723.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.11.013
|
| [6] |
CHOW C H, LIU QINYU, 2012. Eddy effects on sea surface temperature and sea surface wind in the continental slope region of the northern South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(2): L02601.
|
| [7] |
DAS M, GHOSH S K, 2020. Data-Driven approaches for spatio-temporal analysis: a survey of the state-of-the-arts[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 35(3): 665-696.
doi: 10.1007/s11390-020-9349-0
|
| [8] |
DIPPNER J W, NGUYEN K V, HEIN H, et al, 2007. Monsoon-induced upwelling off the Vietnamese coast[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 57(1): 46-62.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-006-0091-0
|
| [9] |
DONG CHANGMING, MCWILLIAMS J C, LIU YU, et al, 2014. Global heat and salt transports by eddy movement[J]. Nature Communications, 5(1): 3294.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms4294
|
| [10] |
KUO N-J, ZHENG QUANNAN, HO C-R, 2000. Satellite observation of upwelling along the Western Coast of the South China Sea[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 74(3): 463-470.
doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00138-3
|
| [11] |
LI JIAXUN, WANG GUIHUA, XUE HUIJIE, et al, 2019. A simple predictive model for the eddy propagation trajectory in the northern South China Sea[J]. Ocean Science, 15(2): 401-412.
doi: 10.5194/os-15-401-2019
|
| [12] |
LI JIAXUN, WANG GUIHUA, ZHAI XIAOMING, 2017. Observed cold filaments associated with mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(1): 762-770.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v122.1
|
| [13] |
LI YUANLONG, HAN WEIQING, WILKIN J L, et al, 2014. Interannual variability of the surface summertime eastward jet in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(10): 7205-7228.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v119.10
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
MA CHUNYONG, LI SIQING, WANG ANNI, et al, 2019. Altimeter observation-based eddy nowcasting using an improved Conv-LSTM network[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(7): 783.
doi: 10.3390/rs11070783
|
| [16] |
MARTÍNEZ-MORENO J, HOGG A M, ENGLAND M H, et al, 2021. Global changes in oceanic mesoscale currents over the satellite altimetry record[J]. Nature Climate Change, 11(5): 397-403.
doi: 10.1038/s41558-021-01006-9
|
| [17] |
QIU CHUNHUA, YI ZHENHUI, SU DANYI, et al, 2022. Cross-Slope heat and salt transport induced by slope intrusion eddy’s horizontal asymmetry in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 127(9): e2022JC018406.
|
| [18] |
REICHSTEIN M, CAMPS-VALLS G, STEVENS B, et al, 2019. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science[J]. Nature, 566(7743): 195-204.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0912-1
|
| [19] |
ROBINSON A R, CARTON J A, MOOERS C N K, et al, 1984. A real-time dynamical forecast of ocean synoptic/mesoscale eddies[J]. Nature, 309(5971): 781-783.
doi: 10.1038/309781a0
|
| [20] |
SHAW P-T, 1999. The seasonal variation of the intrusion of the Philippine Sea water into the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 96(C1): 821-827.
|
| [21] |
SHI XIBNGJIAN, GAO ZHIHAN, LAUSEN L, et al, 2017. Deep learning for precipitation nowcasting: a benchmark and a new model[J]: 5622-5632. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03458
|
| [22] |
SHI XINGJIAN, CHEN ZHUORONG, WANG HAO, et al, 2015. Convolutional LSTM Network: a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[J/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.04214v2
|
| [23] |
THOPPIL P G, FROLOV S, ROWLEY C D, et al, 2021. Ensemble forecasting greatly expands the prediction horizon for ocean mesoscale variability[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2(1): 89.
|
| [24] |
WANG GUIHUA, CHEN DAKE, SU JILIAN, 2006. Generation and life cycle of the dipole in the South China Sea summer circulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C6): C06002.
|
| [25] |
WANG LIPING, KOBLINSKY C J, HOWDEN S, 2000. Mesoscale variability in the South China Sea from the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry data[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 47(4): 681-708.
doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(99)00068-0
|
| [26] |
WANG XIN, WANG HUIZAN, LIU DONGHAN, et al, 2020. The prediction of oceanic mesoscale eddy properties and propagation trajectories based on machine learning[J]. Water, 12(9): 2521.
doi: 10.3390/w12092521
|
| [27] |
WANG YUNBO, GAO ZHIFENG, LONG MINGSHENG, et al, 2018. PredRNN++: towards a resolution of the Deep-in-Time dlemma in spatiotemporal predictive learning[J/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.06300
|
| [28] |
WANG YUNBO, LONG MINGSHENG, WANG JIANMIN, et al, 2017. PredRNN: Recurrent Neural Networks for predictive learning using spatiotemporal LSTMs[C]// GUYON I, LUXBURG U V, BENGIO S, et al. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30. Long Beach: Curran Associates, Inc.:879-888.
|
| [29] |
XIA QIONG, HE YIJUN, DONG CHANGMING, et al, 2018. Prediction of the South China Sea Dipole using SSA-MEM[J]. Atmosphere-Ocean, 56(4): 240-253.
doi: 10.1080/07055900.2017.1406331
|
| [30] |
XIAO CHANGJIANG, CHEN NENGCHENG, HU CHULI, et al, 2019a. A spatiotemporal deep learning model for sea surface temperature field prediction using time-series satellite data[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 120: 104502.
|
| [31] |
XIAO CHANGJIANG, CHEN NENGCHENG, HU CHULI, et al, 2019b. Short and mid-term sea surface temperature prediction using time-series satellite data and LSTM-AdaBoost combination approach[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 233: 111358.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111358
|
| [32] |
ZENG XIANMING, LI YIZHEN, HE RUOYING, 2015. Predictability of the Loop Current Variation and Eddy Shedding Process in the Gulf of Mexico using an Artificial Neural Network approach[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 32(5): 1098-1111.
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-14-00176.1
|
| [33] |
ZHANG QIN, WANG HUI, DONG JUNYU, et al, 2017. Prediction of sea surface temperature using long short-term memory[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 14(10): 1745-1749.
doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2733548
|
| [34] |
ZHANG ZHENGGUANG, QIU BO, 2020. Surface chlorophyll enhancement in mesoscale eddies by submesoscale spiral bands[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 47(14): e2020GL088820.
|
| [35] |
ZHANG ZHENGGUANG, WANG WEI, QIU BO, 2014. Oceanic mass transport by mesoscale eddies[J]. Science, 345(6194): 322-324.
doi: 10.1126/science.1252418
pmid: 25035491
|
 ), LIN Yanjiang, LIU Ran, DU Rong
), LIN Yanjiang, LIU Ran, DU Rong