热带海洋学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 1-16.doi: 10.11978/2021121CSTR: 32234.14.2021121
• 海洋水文学 • 下一篇
基于生成对抗网络模型的热带和亚热带海洋中尺度涡预报研究
- 1.热带海洋环境国家重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2021-09-07修回日期:2021-12-27出版日期:2022-09-10发布日期:2021-12-28 -
通讯作者:经志友 -
作者简介:刘爽(1996—), 女, 黑龙江省七台河市人, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋过程与大数据研究。email: liushuang_57@126.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(92058201);国家自然科学基金(41776040);国家自然科学基金(41949907);国家自然科学基金(42149907);中国科学院基础前沿科学研究计划原始创新项目(ZDBS-LY-DQC011);广州市科学研究计划(201904010420)
Predicting the mesoscale eddy in the tropical and subtropical ocean based on generative adversarial network model
LIU Shuang1,2( ), JING Zhiyou1(
), JING Zhiyou1( ), ZHAN Haigang1
), ZHAN Haigang1
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-09-07Revised:2021-12-27Online:2022-09-10Published:2021-12-28 -
Contact:JING Zhiyou -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(92058201);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41776040);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41949907);National Natural Science Foundation of China(42149907);Original Innovation Project of Basic Frontier Scientific Research Program of CAS(ZDBS-LY-DQC011);Guangzhou Science and Technology Project(201904010420)
摘要:
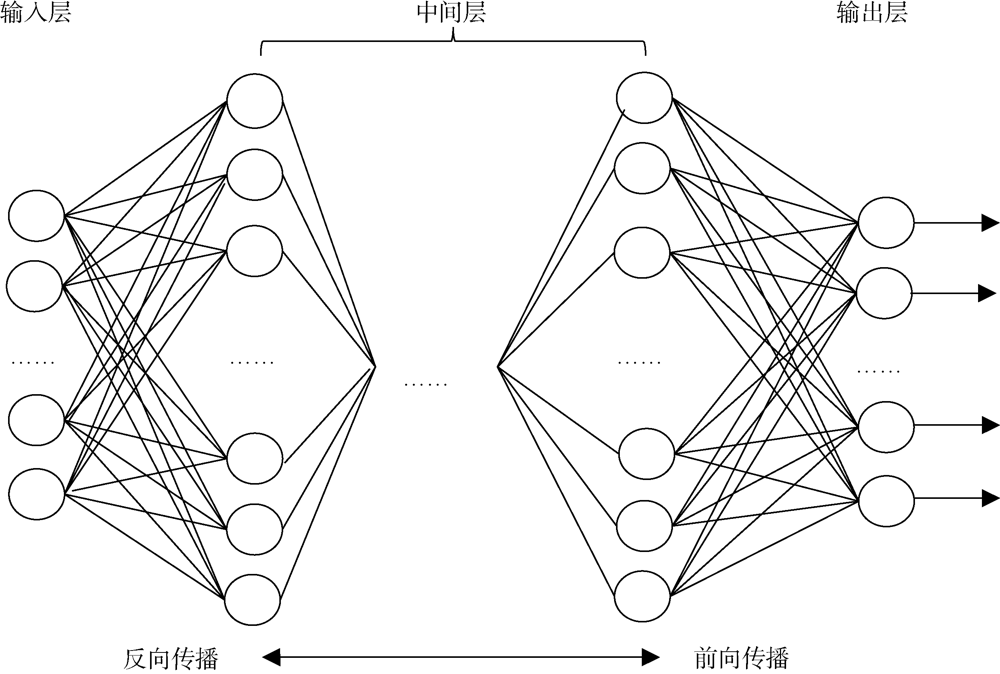
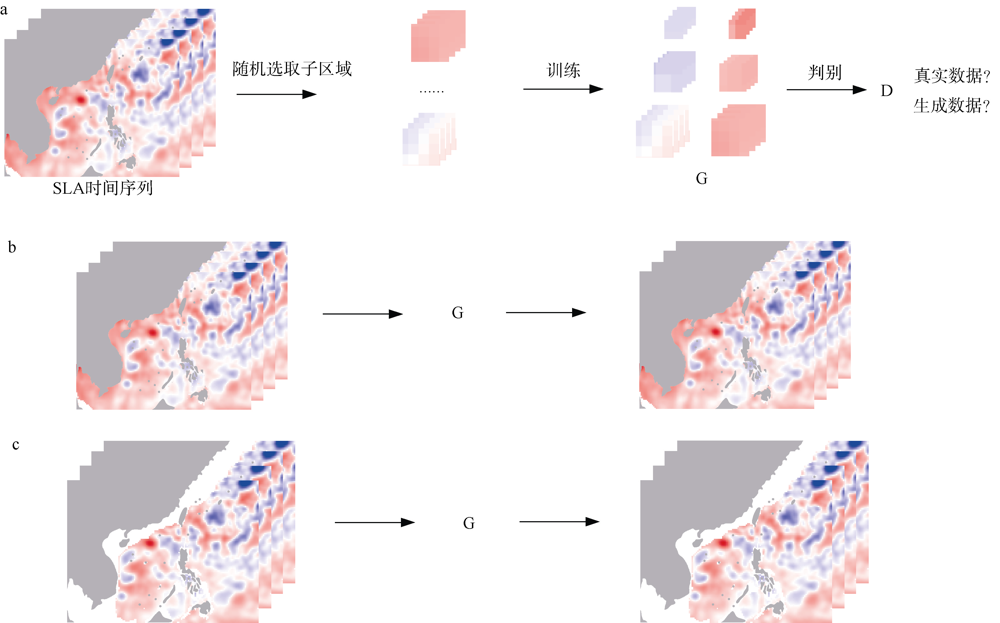
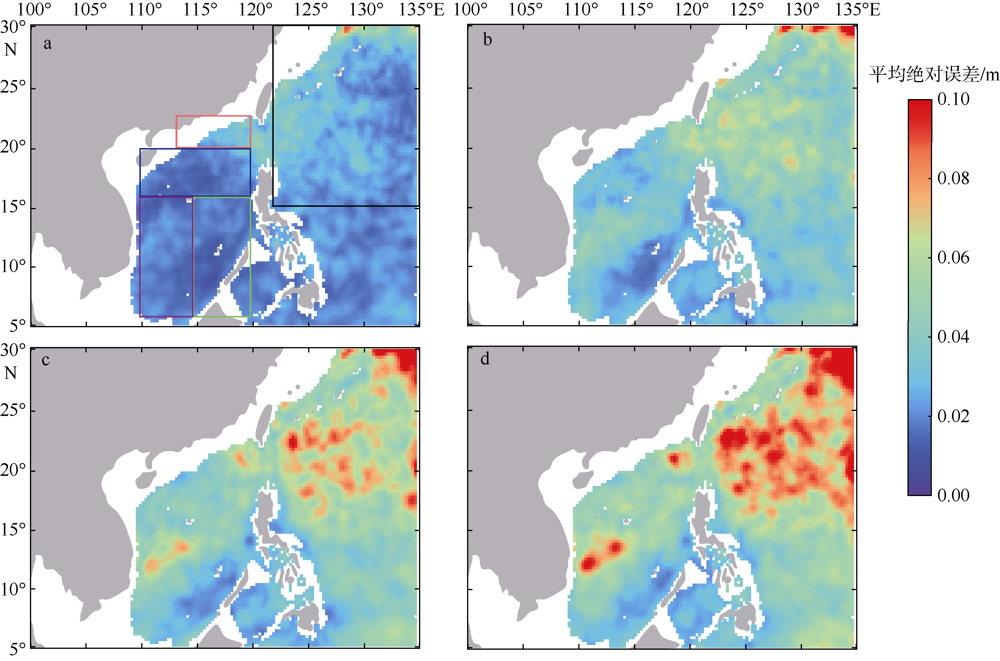
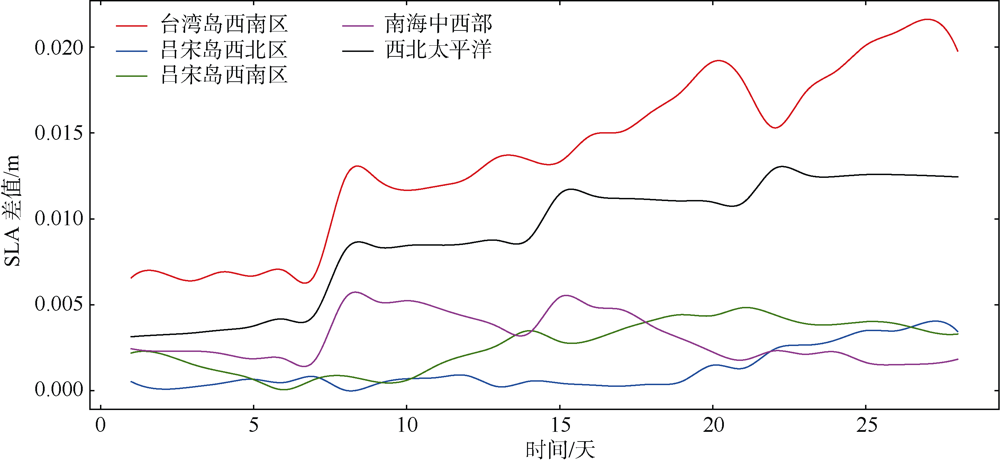
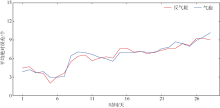
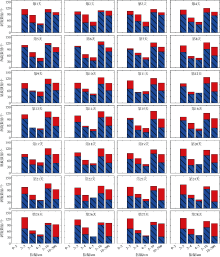
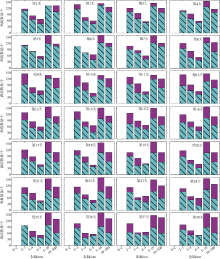
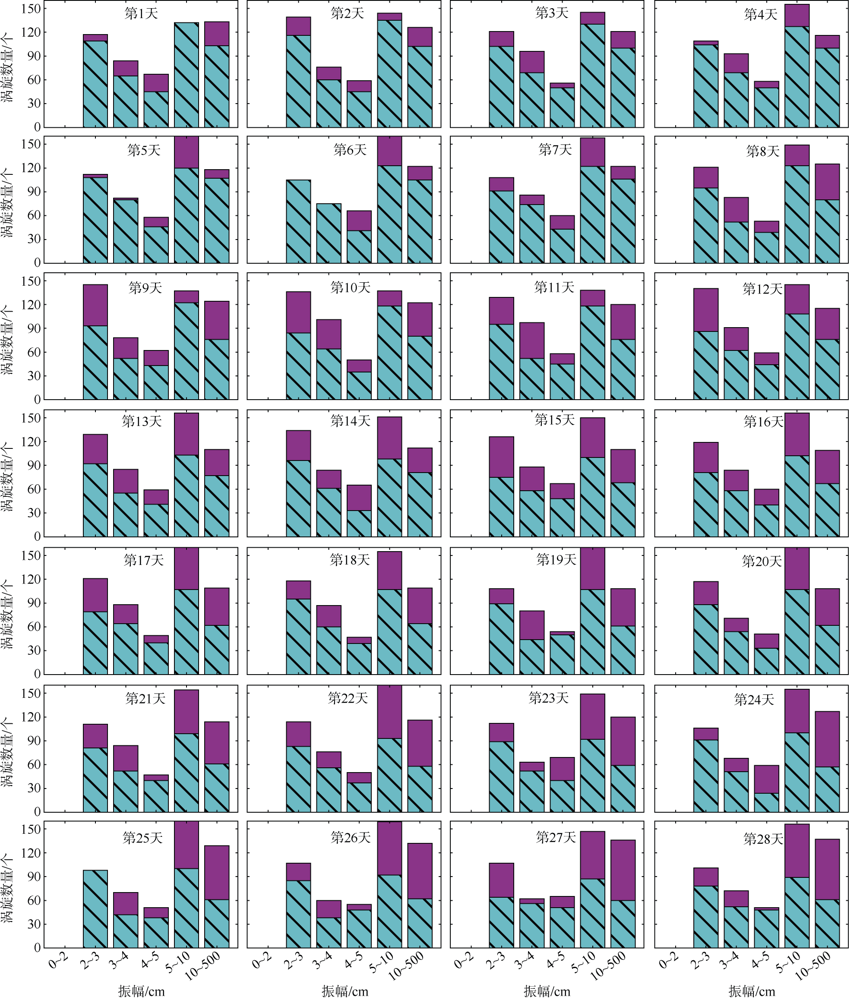
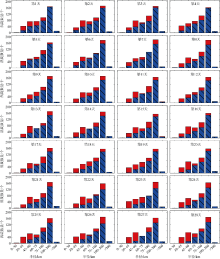
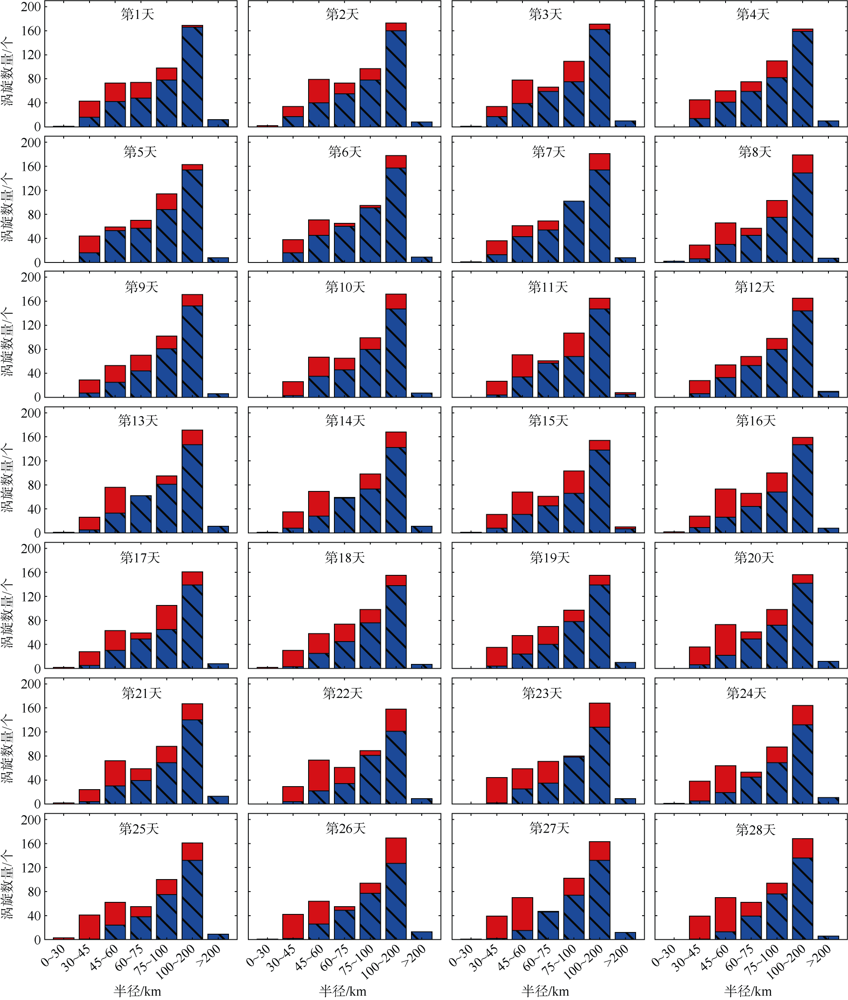
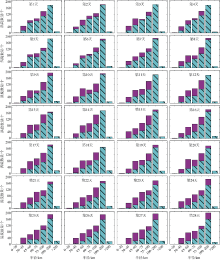
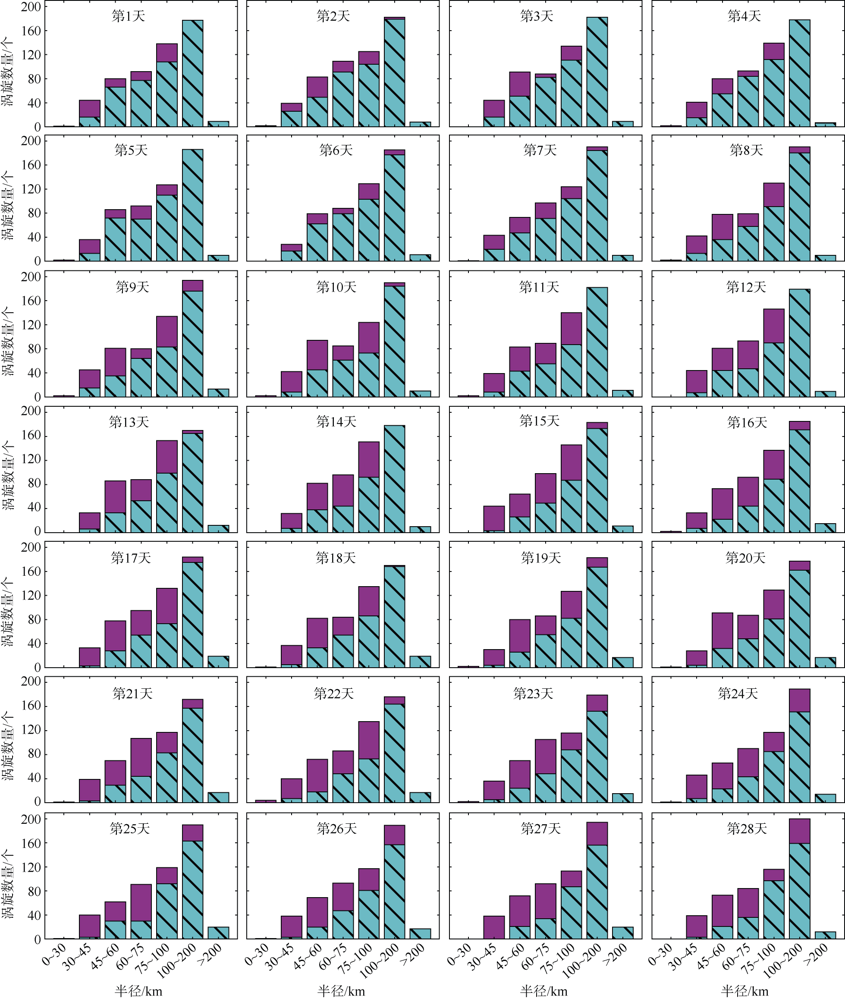
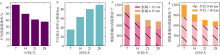
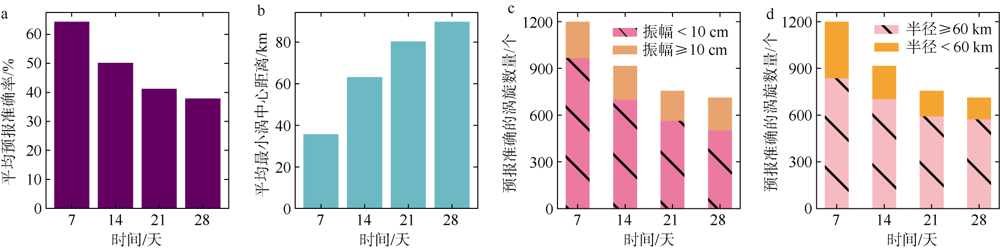
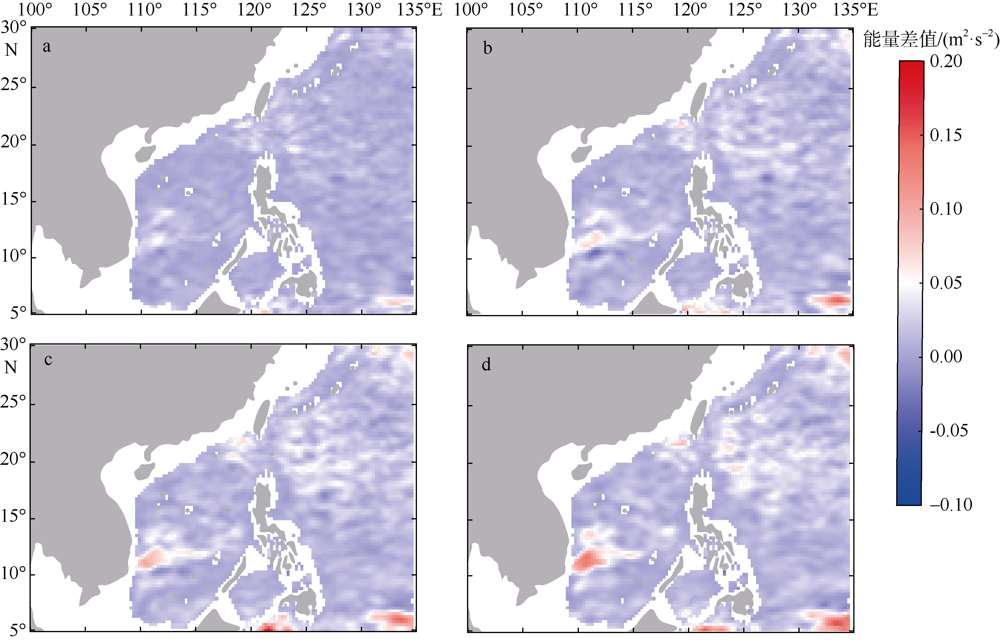
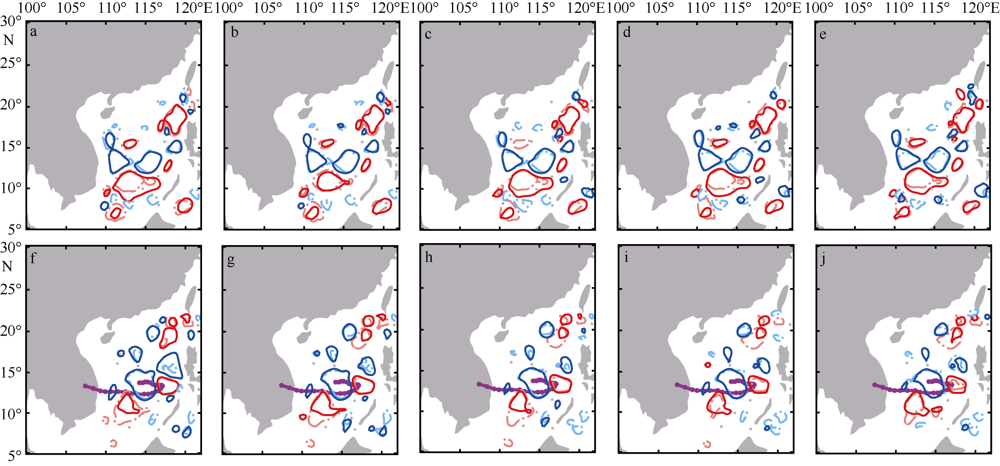
中尺度涡蕴含海洋超过90%的动能, 显著影响海洋物质能量循环。对中尺度涡的预报是目前物理海洋学研究的热点和难点。文章基于卫星高度计观测的近30年海表面高度异常数据(sea level anomaly, SLA), 采用基于博弈思想的生成对抗网络方法(generative adversarial networks, GAN), 构建了中尺度涡预报模型, 进行了28天预报, 并采用独立样本分析了预报涡旋的空间分布、时间分布、能量强度等特征参数, 探讨影响预报结果准确性和时效性的主要因素。结果表明, 半径为100~200km的涡旋在15天左右的预报时长仍能保持较好的准确性及时效性, 误差在20%以内。该区域的平均涡动能约为0.875m2·s-2, 其预报的均方根误差(root mean square error, RMSE)普遍介于0.02~0.04m2·s-2。且涡旋预报结果受异常天气影响较小, 在正常天气条件和台风娜基莉条件下具有相似的预报能力。这些结果对进一步理解并应用生成对抗网络这一新方法预报海洋中尺度涡提供了参考。
中图分类号:
- P731.27
引用本文
刘爽, 经志友, 詹海刚. 基于生成对抗网络模型的热带和亚热带海洋中尺度涡预报研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 1-16.
LIU Shuang, JING Zhiyou, ZHAN Haigang. Predicting the mesoscale eddy in the tropical and subtropical ocean based on generative adversarial network model[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 1-16.
| [1] | 白杨, 李威, 邵祺, 2020. 基于经验正交函数和机器学习的南海海面高度异常预测[J]. 海洋通报, 39(6): 678-688. |
| BAI YANG, LI WEI, SHAO QI, 2020. A prediction model of sea surface height anomaly based on empirical orthogonal function and machine learning[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 39(6): 678-688. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 陈敏, 侯一筠, 赵保仁, 2003. 冬季东中国海环流中的中尺度涡旋数值模拟[J]. 海洋科学, 27(1): 53-60. |
| CHEN MIN, HOU YIJUN, ZHAO BAOREN, 2003. Numerical simulation of the MESO-scale eddy in the East China Sea in winter[J]. Marine Sciences, 27(1): 53-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 崔凤娟, 2015. 南海中尺度涡的识别及统计特征分析[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学. |
| CUI FENGJUAN, 2015. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: identification and statistical characteristics analysis[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 江璟瑜, 徐丹亚, 韩宁生, 等, 2021. 基于LSTM的海表面高度异常预测方法[J]. 舰船电子工程, 41(2): 97-99. |
| JIANG JINGYU, XU DANYA, HAN NINGSHENG, et al, 2021. Sea surface height anomaly prediction method based on LSTM[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 41(2): 97-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 李佳讯, 张韧, 陈奕德, 等, 2011. 海洋中尺度涡建模及其在水声传播影响研究中的应用[J]. 海洋通报, 30(1): 37-46. |
| LI JIAXUN, ZHANG REN, CHEN YIDE, et al, 2011. Ocean mesoscale eddy modeling and its application in studying the effect on underwater acoustic propagation[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 30(1): 37-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] |
王桂华, 苏纪兰, 齐义泉, 2005. 南海中尺度涡研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 20(8): 882-886.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2005.08.0882 |
| WANG GUIHUA, SU JILAN, QI YIQUAN, 2005. Advances in studying mesoscale eddies in South China Sea[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 20(8): 882-886. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] |
吴新荣, 韩桂军, 张学峰, 等, 2012. 人工神经网络在南海近海面气温反演中的应用研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 31(2): 7-14.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.02.002 |
| WU XINRONG, HAN GUIJUN, ZHANG XUEFENG, et al, 2012. Retrieving near-surface air temperature in the South China Sea using artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 31(2): 7-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 肖汶斌, 刘巍, 程兴华, 等, 2018. 海洋中尺度涡水声场特性分析[C]// 2018年全国声学大会论文集:B水声物理. 北京: 中国声学学会: 12-13. |
| XIAO WENBIN, LIU WEI, CHENG XINGHUA, et al, 2018. Acoustical propagation characteristics of an ocean mesoscale eddy[C]// Proceedings of National Conference ACOUSTICS 2018:B underwater acoustic physics. Beijing: Acoustical Society of China: 12-13. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 张盟, 杨玉婷, 孙鑫, 等, 2020. 基于深度卷积网络的海洋涡旋检测模型[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 52(5): 708-713. |
| ZHANG MENG, YANG YUTING, SUN XIN, et al, 2020. Ocean eddy detection model based on deep convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 52(5): 708-713. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 郑全安, 谢玲玲, 郑志文, 等, 2017. 南海中尺度涡研究进展[J]. 海洋科学进展, 35(2): 131-158. |
| ZHENG QUAN’AN, XIE LINGLING, ZHENG ZHIWEN, et al, 2017. Progress in research of mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 35(2): 131-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] |
周水华, 洪晓, 梁昌霞, 等, 2020. 基于人工神经网络的台风浪高快速计算方法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(4): 25-33.
doi: 10.11978/2019089 |
|
ZHOU SHUIHUA, HONG XIAO, LIANG CHANGXIA, et al, 2020. A method of tropical cyclone wave height calculation based on Artificial Neural Network[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(4): 25-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11978/2019089 |
|
| [12] |
APARNA S G, D’SOUZA S, ARJUN N B, 2018. Prediction of daily sea surface temperature using artificial neural networks[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39(12): 4214-4231.
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2018.1454623 |
| [13] |
CHELTON D B, DESZOEKE R A, SCHLAX M G, et al, 1998. Geographical variability of the first baroclinic Rossby radius of deformation[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 28(3): 433-460.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1998)028<0433:GVOTFB>2.0.CO;2 |
| [14] | CHELTON D B, SCHLAX M G, SAMELSON R M, et al, 2007. Global observations of large oceanic eddies[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(15): L15606. |
| [15] |
CHELTON D B, SCHLAX M G, SAMELSON R M, 2011. Global observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 91(2): 167-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2011.01.002 |
| [16] | CHEN GENGXIN, HOU YIJUN, CHU XIAOQING, 2011. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: mean properties, spatiotemporal variability, and impact on thermohaline structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C6): C06018. |
| [17] |
DONG CHANGMING, MCWILLIAMS J C, LIU YU, et al, 2014. Global heat and salt transports by eddy movement[J]. Nature Communications, 5: 3294.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms4294 pmid: 24534770 |
| [18] |
DU YANLING, SONG WEI, HE QI, et al, 2019. Deep learning with multi-scale feature fusion in remote sensing for automatic oceanic eddy detection[J]. Information Fusion, 49: 89-99.
doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.006 |
| [19] |
DUO ZIJUN, WANG WENKE, WANG HUIZAN, 2019. Oceanic mesoscale eddy detection method based on deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(16): 1921.
doi: 10.3390/rs11161921 |
| [20] | DYELAX, 2021. Adversarial video generation[CP/OL]. https://github.com/dyelax/Adversarial_Video_Generation. |
| [21] | FRANZ K, ROSCHER R, MILIOTO A, et al, 2018. Ocean eddy identification and tracking using neural networks[C]// IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Valencia: IEEE: 6887-6890. |
| [22] | GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, COURVILLE A, 2016. Deep learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press. |
| [23] | GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al, 2014. Generative adversarial nets[C]// Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal: MIT Press: 2672-2680. |
| [24] |
HAM Y G, KIM J H, LUO JINGJIA, 2019. Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts[J]. Nature, 573(7775): 568-572.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1559-7 |
| [25] | KINGMA D P, BA L J, 2014. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]// International Conference on Learning Representation. Ithaca. |
| [26] | KURIAN J, COLAS F, CAPET X, et al, 2011. Eddy properties in the California current system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C8): C08027. |
| [27] |
LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G, 2015. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 521(7553): 436-444.
doi: 10.1038/nature14539 |
| [28] |
LEE S, YOU D, 2019. Data-driven prediction of unsteady flow over a circular cylinder using deep learning[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 879: 217-254.
doi: 10.1017/jfm.2019.700 |
| [29] | LGUENSAT R, SUN MIAO, FABLET R, et al, 2018. EddyNet: a deep neural network for pixel-wise classification of oceanic eddies[C]// IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Valencia: IEEE: 1764-1767. |
| [30] |
LI JIAXUN, WANG GUIHUA, XUE HUIJIE, et al, 2019. A simple predictive model for the eddy propagation trajectory in the northern South China Sea[J]. Ocean Science, 15(2): 401-412.
doi: 10.5194/os-15-401-2019 |
| [31] |
LIMA E, SUN XIN, DONG JUNYU, et al, 2017. Learning and transferring convolutional neural network knowledge to ocean front recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 14(3): 354-358.
doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2643000 |
| [32] |
LU WENFANG, SU HUA, YANG XIN, et al, 2019. Subsurface temperature estimation from remote sensing data using a clustering-neural network method[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 229: 213-222.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.04.009 |
| [33] |
LU XIAOQIN, YU HUI, YING MING, et al, 2021. Western North Pacific tropical cyclone database created by the China Meteorological Administration[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 38(4): 690-699.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0211-7 |
| [34] |
MA CHUNYONG, LI SIQING, WANG ANNI, et al, 2019. Altimeter observation-based eddy nowcasting using an improved Conv-LSTM network[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(7): 783.
doi: 10.3390/rs11070783 |
| [35] |
MASON E, PASCUAL A, MCWILLIAMS J C, 2014. A new sea surface height-based code for oceanic mesoscale eddy tracking[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 31(5): 1181-1188.
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-14-00019.1 |
| [36] | MASON E, 2020. The code used to compute the Mesoscale Eddy Trajectories Atlas from version 3.0 onwards, was developed in collaboration between IMEDEA (E. Mason) and CLS, is freely available under GNU General Public License[EB/OL]. https://github.com/AntSimi/py-eddy-tracker. |
| [37] | MATHIEU M, COUPRIE C, LECUN Y, 2015. Deep multi-scale video prediction beyond mean square error[C]// 4th International Conference on Learning Representation. San Juan. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05440. |
| [38] | PENVEN P, ECHEVIN V, PASAPERA J, et al, 2005. Average circulation, seasonal cycle, and mesoscale dynamics of the Peru Current System: a modeling approach[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 110(C10): C10021. |
| [39] | RASP S, DUEBEN P D, SCHER S, et al, 2020. WeatherBench: a benchmark data set for data-driven weather forecasting[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 12(11): e2020MS002203. |
| [40] |
ROBINSON A R, CARTON J A, MOOERS C N K, et al, 1984. A real-time dynamical forecast of ocean synoptic/mesoscale eddies[J]. Nature, 309(5971): 781-783.
doi: 10.1038/309781a0 |
| [41] |
RÜTTGERS M, LEE S, JEON S, et al, 2019. Prediction of a typhoon track using a generative adversarial network and satellite images[J]. Scientific Reports, 9(1): 6057.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42339-y pmid: 30988405 |
| [42] | SHAO QI, LI WEI, HAN GUIJUN, et al, 2021. A deep learning model for forecasting sea surface height anomalies and temperatures in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 126(7): e2021JC017515. |
| [43] |
SHRIVER J F, HURLBURT H E, SMEDSTAD O M, et al, 2007. 1/32 degrees real-time global ocean prediction and value-added over 1/16 degrees resolution[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 65(1-4): 3-26.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2005.11.021 |
| [44] |
SUN MIAO, TIAN FENGLIN, LIU YINGJIE, et al, 2017. An improved automatic algorithm for global eddy tracking using satellite altimeter data[J]. Remote Sensing, 9(3): 206.
doi: 10.3390/rs9030206 |
| [45] |
WANG GUIHUA, SU JILAN, CHU P C, 2003. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea observed with altimeter data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(21): 2121.
doi: 10.1029/2003GL018532 |
| [46] |
WANG XIN, WANG HUIZAN, LIU DONGHAN, et al, 2020. The prediction of oceanic mesoscale eddy properties and propagation trajectories based on machine learning[J]. Water, 12(9): 2521.
doi: 10.3390/w12092521 |
| [47] | XIAO CHANGJIANG, CHEN NENGCHENG, HU CHULI, et al, 2019. A spatiotemporal deep learning model for sea surface temperature field prediction using time-series satellite data[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 120: 104502. |
| [48] |
XU GUANGJUN, YANG WENXIAN, et al, 2019. Oceanic eddy identification using an AI scheme[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(11): 1349.
doi: 10.3390/rs11111349 |
| [49] |
YANG HAIYUAN, WU LIXIN, LIU HAILONG, et al, 2013. Eddy energy sources and sinks in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118(9): 4716-4726.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20343 |
| [50] |
YANG YUTING, DONG JUNYU, SUN XIN, et al, 2018. A CFCC-LSTM model for sea surface temperature prediction[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 15(2): 207-211.
doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2780843 |
| [51] |
YING MING, ZHANG WEI, YU HUI, et al, 2014. An overview of the China Meteorological Administration tropical cyclone database[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 31(2): 287-301.
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-12-00119.1 |
| [52] |
ZHANG ZHENGGUANG, WANG WEI, QIU BO, 2014. Oceanic mass transport by mesoscale eddies[J]. Science, 345(6194): 322-324.
doi: 10.1126/science.1252418 pmid: 25035491 |
| [53] |
ZHANG ZHIWEI, TIAN JIWEI, QIU BO, et al, 2016. Observed 3D structure, generation, and dissipation of oceanic mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 6: 24349.
doi: 10.1038/srep24349 pmid: 27074710 |
| [54] |
ZHANG ZHIWEI, ZHAO WEI, QIU BO, et al, 2017. Anticyclonic eddy sheddings from kuroshio loop and the accompanying cyclonic eddy in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 47(6): 1243-1259.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-16-0185.1 |
| [1] | 杨潇霄, 曹海锦, 经志友. 南海上层海洋次中尺度过程空间差异和季节变化特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 10-24. |
| [2] | 罗士浩, 经志友, 闫桐, 郑瑞玺, 曹海锦, 齐义泉. 黑潮延伸体海域次中尺度过程的季节变化研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(1): 1-11. |
| [3] | 乐洲, 黄科, Venkata Subrahmanyam Mantravadi. 2000—2015年夏秋季孟加拉湾湾口区涡流相互作用能量学特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 11-14. |
| [4] | 李洁, 经志友, 张偲. 季风环流影响下的南海海洋细菌多样性特征初探[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(6): 1-15. |
| [5] | 黄旭媚, 王卫强, 刘海龙. 基于多套数据的印度洋深层经向翻转环流的动力特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(4): 11-20. |
| [6] | 向荣, 方文东, 鲁远征, 黄孝荣, 周生启. 2014年9月南海西部冷涡及东向急流三维结构观测[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(6): 1-10. |
| [7] | 王健, 杜岩, 郑少军, 刘凯. 2004~2011年印度尼西亚贯穿流在望加锡海峡中的年际变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(6): 9-16. |
| [8] | 宣莉莉, 邱云, 许金电, 曾明章. 热带东印度洋表层环流季节变化特征研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(1): 26-35. |
|
||