热带海洋学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 90-102.doi: 10.11978/2020019CSTR: 32234.14.2020019
琼东南盆地陆架区晚中新世以来断层活动性研究
胡守祥1,2,3( ), 姚衍桃1,2, 李健1,2,3, 李爽1,2,3, 汪灵1,2,3, 詹文欢1,2,3, 李伟1,2,3(
), 姚衍桃1,2, 李健1,2,3, 李爽1,2,3, 汪灵1,2,3, 詹文欢1,2,3, 李伟1,2,3( ), 冯英辞1,2
), 冯英辞1,2
- 1.中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 510301
3.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2020-02-23修回日期:2020-04-10出版日期:2021-03-10发布日期:2020-04-16 -
通讯作者:李伟 -
作者简介:胡守祥(1993—), 男, 河南省南阳市人, 博士研究生, 主要从事海洋新构造与深海沉积研究。email:hushouxiang16@mails.ucas.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家科技基础资源调查专项(2017FY201406);国家自然科学基金(41876067);中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室资助项目(OMG18-11)
Study on fault activities since the Late Miocene in the continental shelf of Qiongdongnan Basin
HU Shouxiang1,2,3( ), YAO Yantao1,2, LI Jian1,2,3, LI Shuang1,2,3, WANG Ling1,2,3, ZHAN Wenhuan1,2,3, LI Wei1,2,3(
), YAO Yantao1,2, LI Jian1,2,3, LI Shuang1,2,3, WANG Ling1,2,3, ZHAN Wenhuan1,2,3, LI Wei1,2,3( ), FENG Yingci1,2
), FENG Yingci1,2
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2020-02-23Revised:2020-04-10Online:2021-03-10Published:2020-04-16 -
Contact:LI Wei -
Supported by:Special Foundation for National Science and Technology Basic Research Program of China(2017FY201406);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41876067);Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, Chinese Academy of Sciences(OMG18-11)
摘要:
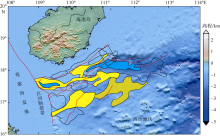
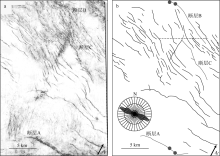
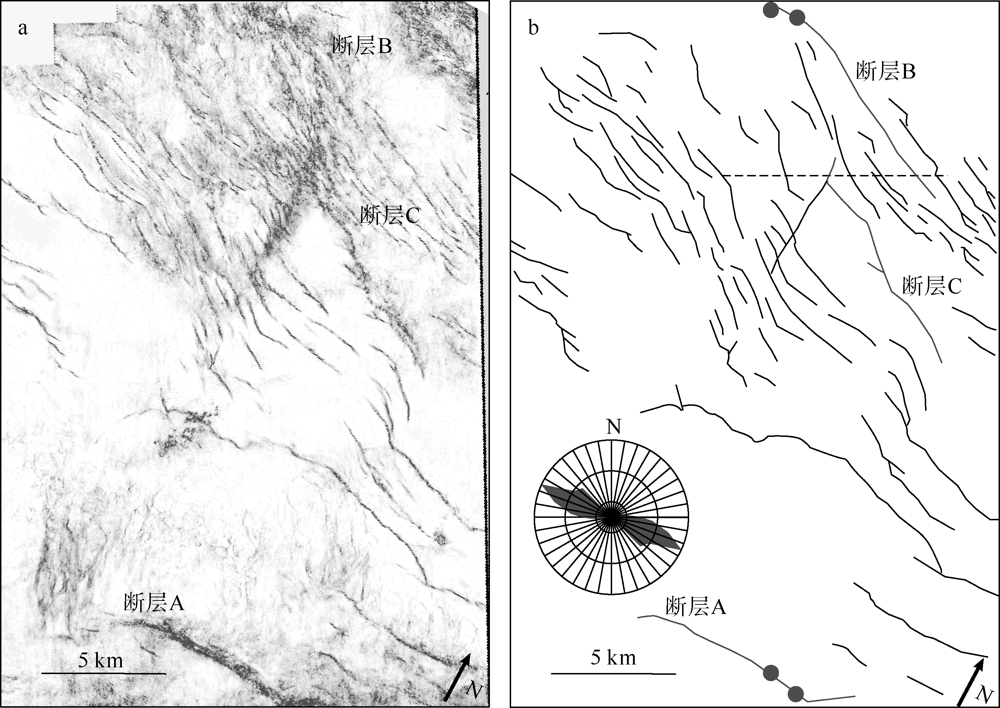
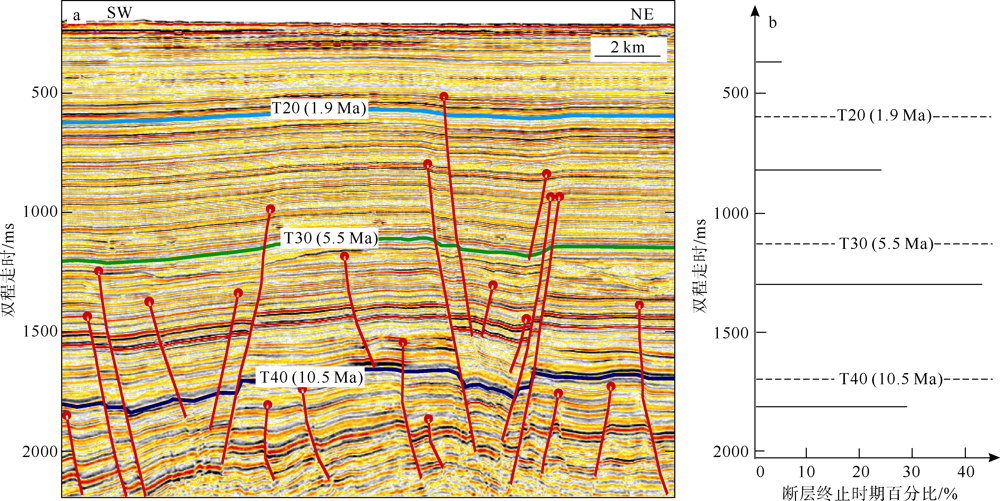
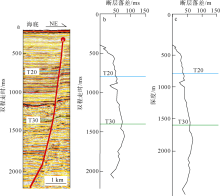
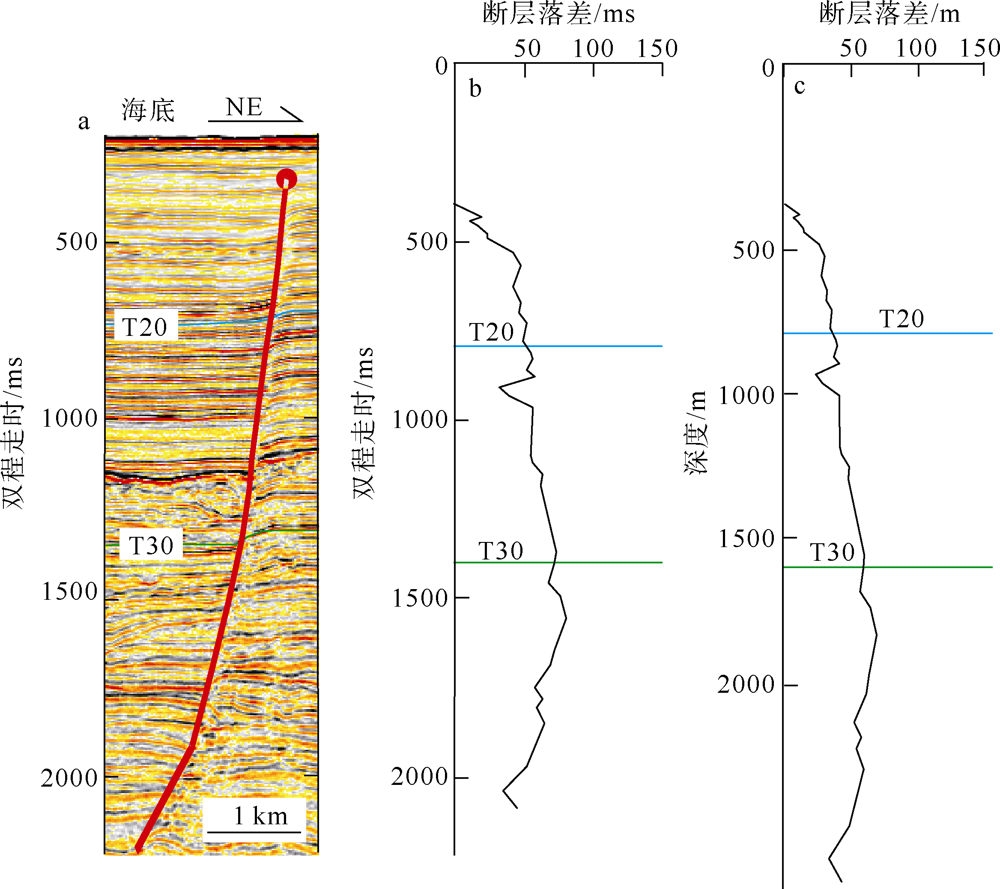
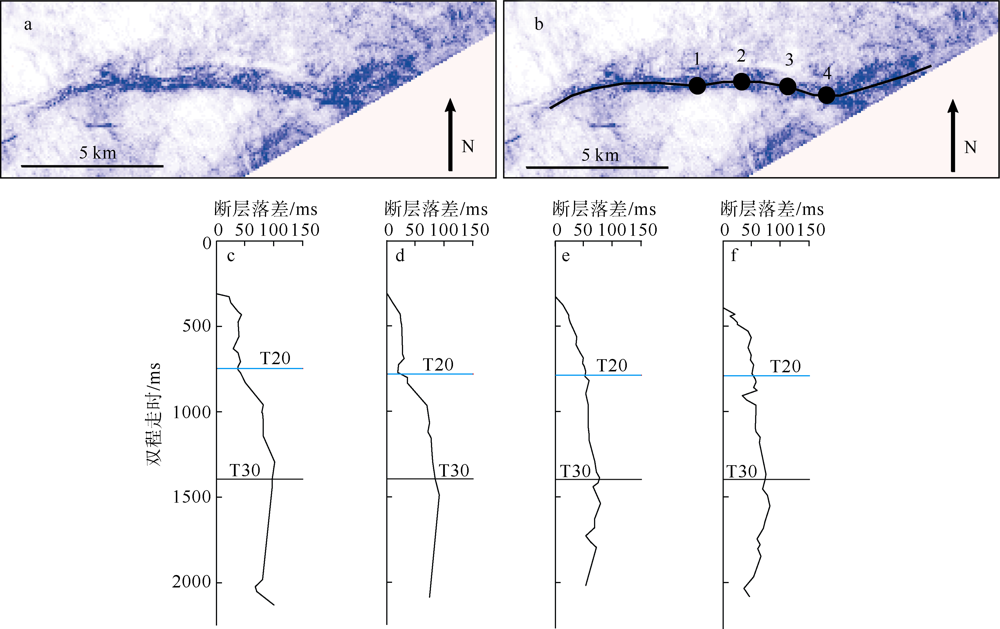
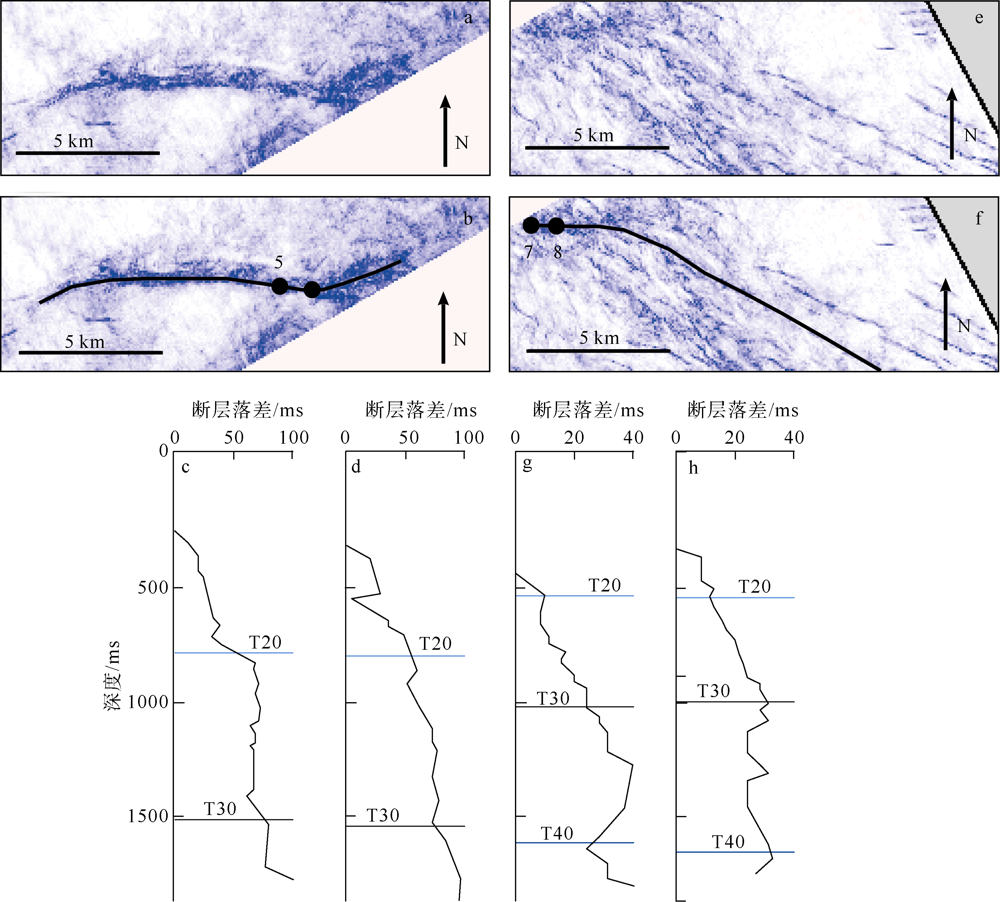
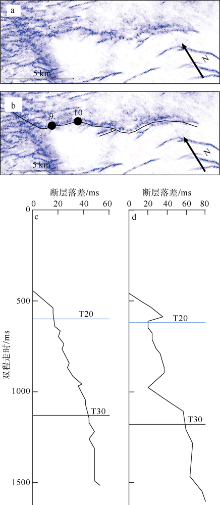
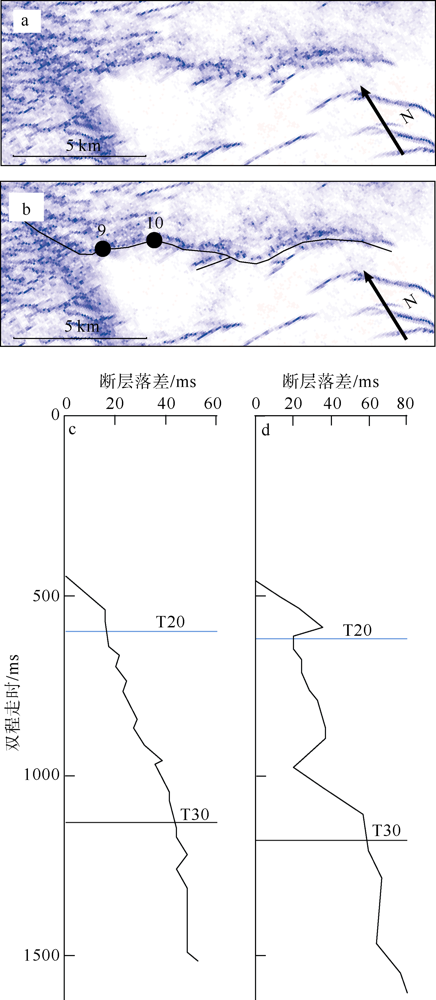
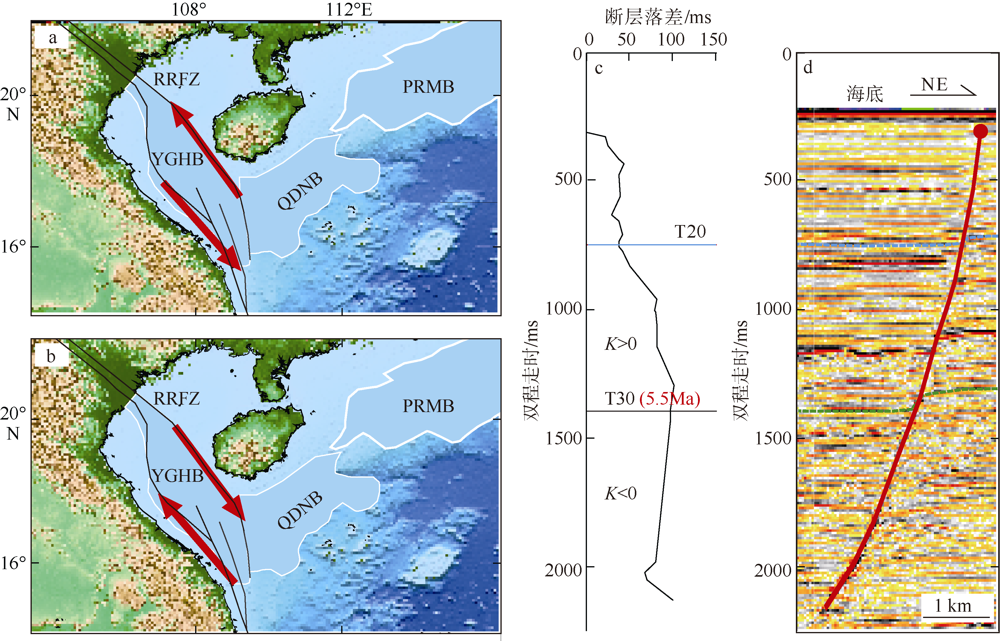
对琼东南盆地陆架区晚中新世以来的断层活动性进行研究, 有助于理解南海西北部晚中新世以来的构造演化, 也对该区钻井平台的安全性评估、海洋工程勘查以及区域稳定性评价等有重要意义。研究区断层走向主要为NWW向, 多数断层在晚中新世时期停止活动。通过对断层几何形态的统计分析以及使用高分辨率断层落差图法(T-Z图示法)对断层活动性进行量化分析, 结果显示: 断层活动性在晚中新世末期(5.5Ma)发生转变; 研究区南部的断层落差值大于北部; 南部断层停止活动的时间较北部断层稍晚。这些研究成果表明, 晚中新世末期研究区断层受构造应力变化的影响, 在生长发育过程中断层活动性质发生了改变, 由逆断层转为正断层。红河断裂带对琼东南盆地的构造演化起着重要的控制作用, 文章推测研究区断层活动性变化是由红河断裂带的构造反转所导致, 因为红河断裂带在5.5Ma时发生了走滑运动的反转, 与研究区的断层活动性变化在时间和性质上相耦合。
中图分类号:
- P736.1
引用本文
胡守祥, 姚衍桃, 李健, 李爽, 汪灵, 詹文欢, 李伟, 冯英辞. 琼东南盆地陆架区晚中新世以来断层活动性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(2): 90-102.
HU Shouxiang, YAO Yantao, LI Jian, LI Shuang, WANG Ling, ZHAN Wenhuan, LI Wei, FENG Yingci. Study on fault activities since the Late Miocene in the continental shelf of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(2): 90-102.
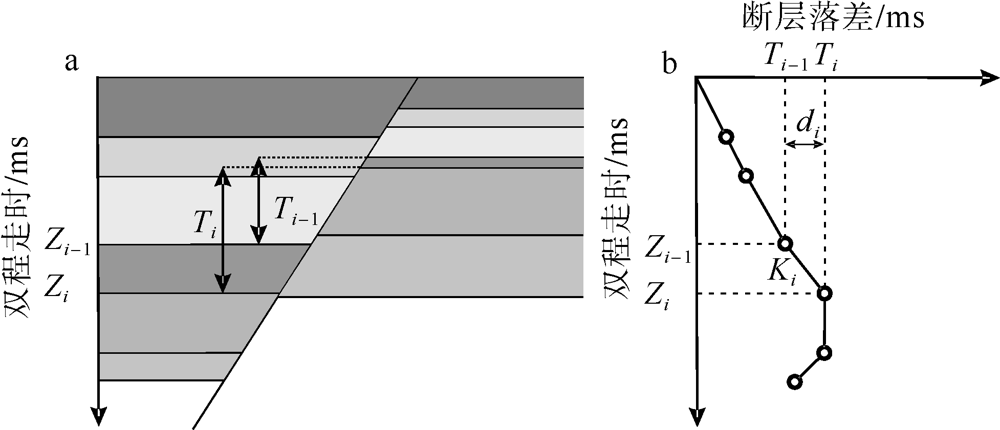
表1
断层T-Z图量化参数总结"
| 地层 | 参数 | 断层A | 断层C | 断层B | 平均 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T20—海底 | 变异系数 | 0.53 | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.65 |
| 断层落差/ms | 28.39 | 14.26 | 6.61 | 16.42 | |
| T-Z图折线斜率 | 0.05 | 0.09 | / | 0.05 | |
| T30—T20 | 变异系数 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.24 |
| 断层落差/ms | 63.10 | 29.85 | 17.82 | 36.92 | |
| T-Z图折线斜率 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| T40—T30 | 变异系数 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.13 |
| 断层落差/ms | 73.43 | 58.33 | 28.76 | 53.51 | |
| T-Z图折线斜率 | -0.04 | 0.03 | 0.001 | -0.003 |
| [1] | 蔡佳, 2009. 琼东南盆地古近系古地貌恢复及其对层序样式和沉积特征的控制[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学: 1-216. |
| CAI JIA, 2009. Paleo-morphologic restoration of paleogene in Qiongdongnan Basin and its control on sequence architecture and sedimentary characteristics[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences: 1-216 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 何丽娟, 熊亮萍, 汪集旸, 等, 2000. 莺歌海盆地构造热演化模拟研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 30(4):415-419. |
| HE LIJUAN, XIONG LIANGPING, WANG JIYANG, et al, 2001. Tectono-thermal modeling of the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 44(1):7-13 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 何云龙, 2012. 琼东南盆地陆坡区重力流沉积特征及其成因机制[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学: 1-148. |
| HE YUNLONG, 2012. The characteristics and mechanism of sediment gravity flow in slope area in Qiongdongnan Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences: 1-148 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 李居云, 2015. 琼东南盆地北部坳陷带构造演化及其对煤系烃源岩的控制[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学: 1-98. |
| LI JUYUN, 2015. Tectonic evolution and its control on coal source rocks in northern depression belt of Qiongdongnan Basin[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology: 1-98 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 李绪宣, 朱光辉, 2005. 琼东南盆地断裂系统及其油气输导特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 17(1):1-7. |
| LI XUXUAN, ZHU GUANGHUI, 2005. The fault system and its hydrocarbon carrier significance in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 17(1):1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 梁富康, 于兴河, 李先平, 等, 2011. 冀中坳陷深县凹陷的生长断层特点及其对沉积的控制作用[J]. 中国地质, 38(2):263-270. |
| LIANG FUKANG, YU XINGHE, LI XIANPING, et al, 2011. Growth faults in Shenxian depression and their control over the sedimentation[J]. Geology in China, 38(2):263-270 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 任金锋, 2016. 琼东南盆地陆架边缘斜坡地形的定量演化过程[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学: 1-184. |
| REN JINFENG, 2016. The quantitative evolution of shelf-margin clinoforms in the Qiongdongnan Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences: 1-184 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 孙珍, 钟志洪, 周蒂, 等, 2003. 红河断裂带的新生代变形机制及莺歌海盆地的实验证据[J]. 热带海洋学报, 22(2):1-9. |
| SUN ZHEN, ZHONG ZHIHONG, ZHOU DI, et al, 2003. Deformation mechanism of red river fault zone during cenozoic and experimental evidences related to Yinggehai Basin formation[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 22(2):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 谢文彦, 张一伟, 孙珍, 等, 2007. 琼东南盆地断裂构造与成因机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 27(1):71-78. |
| XIE WENYAN, ZHANG YIWEI, SUN ZHEN, et al, 2007. Characteristics and formation mechanism of faults in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 27(1):71-78 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 谢玉洪, 童传新, 范彩伟, 等, 2015. 琼东南盆地断裂系统特征与演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 39(5):795-807. |
| XIE YUHONG, TONG CHUANXIN, FAN CAIWEI, et al, 2015. Characteristics and evolution of fault system in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 39(5):795-807 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 徐果明, 姚华建, 朱良保, 等, 2007. 中国西部及其邻域地壳上地幔横波速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(1):193-208. |
| XU GUOMING, YAO HUAJIAN, ZHU LIANGBAO, et al, 2007. Shear wave velocity structure of the crust and upper mantle in western China and its adjacent area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(1):193-208 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 徐子英, 孙珍, 2015. 琼东南盆地西南部反转构造发育机制物理模拟[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 31(8):47-52. |
| XU ZIYING, SUN ZHEN, 2015. Analogue modeling of reversed structural deformation in the southwestern Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 31(8):47-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 袁玉松, 杨树春, 胡圣标, 等, 2008. 琼东南盆地构造沉降史及其主控因素[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(2):376-383. |
| YUAN YUSONG, YANG SHUCHUN, HU SHENGBIAO, et al, 2008. Tectonic subsidence of Qiongdongnan Basin and its main control factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(2):376-383 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 张功成, 王璞珺, 吴景富, 等, 2015. 边缘海构造旋回: 南海演化的新模式[J]. 地学前缘, 22(3):27-37. |
| ZHANG GONGCHENG, WANG PUJUN, WU JINGFU, et al, 2015. Tectonic cycle of marginal oceanic basin: a new evolution model of the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(3):27-37 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
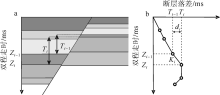
| [15] | 张焱林, 刘晓峰, 郭忻, 2010. 高分辨率断层落差图的基本原理及其应用[J]. 断块油气田, 17(2):181-184. |
| ZHANG YANLIN, LIU XIAOFENG, GUO XIN, 2010. Principles and application of high resolution fault throw plot[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 17(2):181-184 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 赵孟为, 1989. 断层生长指数探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 11(3):250-254. |
| ZHAO MENGWEI, 1989. Discussion on the growth index of fault[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 11(3):250-254 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [17] | 郑勇, 傅容珊, 熊熊, 2006. 中国大陆及周边地区现代岩石圈演化动力学模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(2):415-427. |
| ZHENG YONG, FU RONGSHAN, XIONG XIONG, 2006. Dynamic simulation of lithospheric evolution from the modern China mainland and its surrounding areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(2):415-427 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] |
ALLEN C R, GILLESPIE A R, YUAN HAN, et al, 1984. Red River and associated faults, Yunnan Province, China: quaternary geology, slip rates, and seismic hazard[J]. GSA Bulletin, 95(6):686-700.
doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1984)95<686:RRAAFY>2.0.CO;2 |
| [19] | BAUDON C, CARTWRIGHT J, 2008a. The kinematics of reactivation of normal faults using high resolution throw mapping[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 30(8):1072-1084. |
| [20] | BAUDON C, CARTWRIGHT J A, 2008b. 3D seismic characterisation of an array of blind normal faults in the Levant Basin, Eastern Mediterranean[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 30(6):746-760. |
| [21] | BEN-AVRAHAM Z, UYEDA S, 1973. The evolution of the China Basin and the mesozoic paleogeography of Borneo[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 18(2):365-376. |
| [22] | BERTOK C, MARTIRE L, PEROTTI E, et al, 2012. Kilometre-scale palaeoescarpments as evidence for Cretaceous synsedimentary tectonics in the External Briançonnais Domain (Ligurian Alps, Italy)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 251- 252: 58-75. |
| [23] | BRIAIS A, PATRIAT P, TAPPONNIER P, 1993. Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading stages in the south China Sea: implications for the Tertiary tectonics of Southeast Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 98(B4):6299-6328. |
| [24] | CARTWRIGHT J, BOUROULLEC R, JAMES D, et al, 1998. Polycyclic motion history of some Gulf Coast growth faults from high-resolution displacement analysis[J]. Geology, 26(9):819-822. |
| [25] | CLIFT P D, SUN ZHEN, 2006. The sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Yinggehai-Song Hong basin and the southern Hainan margin, South China Sea: implications for Tibetan uplift and monsoon intensification[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(B6):B06405. |
| [26] | HENSTRA G A, ROTEVATN A, GAWTHORPE R L, et al, 2015. Evolution of a major segmented normal fault during multiphase rifting: the origin of plan-view zigzag geometry[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 74: 45-63. |
| [27] | JACKSON C A L, ROTEVATN A, 2013. 3D seismic analysis of the structure and evolution of a salt-influenced normal fault zone: a test of competing fault growth models[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 54: 215-234. |
| [28] | JACKSON C A L, BELL R E, ROTEVATN A, et al, 2017. Techniques to determine the kinematics of synsedimentary normal faults and implications for fault growth models[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 439(1):187-217. |
| [29] | LEE T Y, LAWVER L A, 1994. Cenozoic plate reconstruction of the South China Sea region[J]. Tectonophysics, 235(1-2):149-180. |
| [30] | LEE T Y, LAWVER L A, 1995. Cenozoic plate reconstruction of Southeast Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 251(1-4):85-138. |
| [31] | LÜDMANN T, WONG H K, 1999. Neotectonic regime on the passive continental margin of the northern South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 311(1-4):113-138. |
| [32] |
MANSFIELD C S, CARTWRIGHT J A, 1996. High resolution fault displacement mapping from three-dimensional seismic data: evidence for dip linkage during fault growth[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 18(2-3):249-263.
doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(96)80048-4 |
| [33] |
MILLER K G, KOMINZ M A, BROWNING J V, et al, 2005. The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change[J]. Science, 310(5752):1293-1298.
doi: 10.1126/science.1116412 pmid: 16311326 |
| [34] | MURAOKA H, KAMATA H, 1983. Displacement distribution along minor fault traces[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 5(5):483-495. |
| [35] | REN JINFENG, WANG HUA, SUN MING, et al, 2014a. Sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary facies of Lower Oligocene Yacheng Formation in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea: implications for coal-bearing source rocks[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 25(5):871-883. |
| [36] | REN JIANYE, ZHANG DAOJUN, TONG DIANJUN, et al, 2014b. Characterising the nature, evolution and origin of detachment fault in central depression belt, Qiongdongnan Basin of South China Sea: evidence from seismic reflection data[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 33(12):118-126. |
| [37] | REPLUMAZ A, LACASSIN R, TAPPONNIER P, et al, 2001. Large river offsets and Plio‐Quaternary dextral slip rate on the Red River fault (Yunnan, China)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106(B1):819-836. |
| [38] | SUN ZHEN, ZHOU DI, ZHONG ZHIHONG, et al, 2003. Experimental evidence for the dynamics of the formation of the Yinggehai basin, NW South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 372(1-2):41-58. |
| [39] | TAPPONNIER P, PELTZER G, LE DAIN A Y, et al, 1982. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: new insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J]. Geology, 10(12):611-616. |
| [40] | TAPPONNIER P, LACASSIN R, LELOUP P H, et al, 1990. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt: tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China[J]. Nature, 343(6257):431-437. |
| [41] | TAYLOR S K, NICOL A, WALSH J J, 2008. Displacement loss on growth faults due to sediment compaction[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 30(3):394-405. |
| [42] | THORSEN C E, 1963. Age of growth faulting in Southeast Louisiana[J]. GCAGS Transactions, 13: 103-110. |
| [43] | TRIBOVILLARD N, SANSJOFRE P, ADER M, et al, 2012. Early diagenetic carbonate bed formation at the sediment-water interface triggered by synsedimentary faults[J]. Chemical Geology, 300-301: 1-13. |
| [44] |
WANG DAWEI, WU SHIGUO, QIN ZHILIANG, et al, 2013. Seismic characteristics of the Huaguang mass transport deposits in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: implications for regional tectonic activity[J]. Marine Geology, 346: 165-182.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.09.003 |
| [45] | WANG DAWEI, WU SHIGUO, LI CHUNFENG, et al, 2016. Submarine slide evidence for late Miocene strike-slip reversal of the Red River Fault[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 59(11):2231-2239. |
| [46] | WANG PEILING, LO C H, LEE T Y, et al, 1998. Thermo- chronological evidence for the movement of the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone: a perspective from Vietnam[J]. Geology, 26(10):887-890. |
| [47] | WEI JIANGONG, LIANG JINQIANG, LU JINGAN, et al, 2019. Characteristics and dynamics of gas hydrate systems in the northwestern South China Sea - Results of the fifth gas hydrate drilling expedition[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 110: 287-298. |
| [48] | XIA ZHONGYU, WAN ZHIFENG, WANG XIANQING, et al, 2016. The tectonic differences between the east and the west in the deep-water area of the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(1):86-95. |
| [49] | YAN PIN, ZHOU DI, LIU ZHAOSHU, 2001. A crustal structure profile across the northern continental margin of the South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 338(1):1-21. |
| [50] | ZE TAO, ALVES T M, 2016. The role of gravitational collapse in controlling the evolution of crestal fault systems (Espírito Santo Basin, SE Brazil)[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 92: 79-98. |
| [51] | ZE TAO, ALVES T M, 2017. The role of gravitational collapse in controlling the evolution of crestal fault systems (Espírito Santo Basin, SE Brazil) - Reply[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 98: 12-14. |
| [52] | ZHANG CUIMEI, WANG ZHENFENG, SUN ZHIPENG, et al, 2013. Structural differences between the western and eastern Qiongdongnan Basin: evidence of Indochina block extrusion and South China Sea seafloor spreading[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 34(3):309-323. |
| [53] | ZHAO ZHONGXIAN, SUN ZHEN, WANG ZHENFENG, et al, 2015. The high resolution sedimentary filling in Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 361: 11-24. |
| [54] | ZHAO ZHONGXIAN, SUN ZHEN, LIU JIANBAO, et al, 2018. The continental extension discrepancy and anomalous subsidence pattern in the western Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 501: 180-191. |
| [55] | ZHU MANGZHENG, GRAHAM S, MCHARGUE T, 2009. The Red River Fault zone in the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 476(3-4):397-417. |
| [1] | 宋瑞有, 马光克, 何小胡, 万阳, 贺礼文. 琼东南盆地崖北凹陷构造沉积特征及油气勘探潜力[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 93-105. |
| [2] | 赵中贤, 孙珍, 毛云华, 张伙带. 南海北部陆缘不均匀伸展及脉动式构造升降史*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 96-115. |
| [3] | 孙云梅, 李金平. 红河断裂带不同构造区段的现今滑动速率与应变积累状况[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(4): 89-96. |
| [4] | 孙甜甜, 邬黛黛, 潘梦迪, 杨飞, 吴能友, 陈雪刚, 刘丽华. 南海北部琼东南盆地浅表层沉积物的地球化学特征及对沉积环境的指示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(4): 70-80. |
| [5] | 鲁宝亮, 王万银, 张功成, 王璞珺. 红河断裂带海域延伸位置的地球物理证据及其与南海扩张的关系*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(5): 64-74. |
| [6] | 何勇,苏正,吴能友,. 非烃类气体对琼东南盆地深水区水合物稳定带厚度的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 62-69. |
| [7] | 徐子英, 孙珍, 周蒂, 张云帆, 孙龙涛, 赵中贤. 软弱地质体对反转构造变形制约作用的物理模拟及其应用*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(3): 144-154. |
| [8] | 李亚敏,施小斌,徐辉龙,刘兵 . 琼东南盆地古近纪基底断裂的活动特征分析 * [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(6): 74-83. |
| [9] | 刘兵,吴世敏,龙根元,郭翔艳,曾广东 . 重力水平梯度矢量法在琼东南盆地基底断裂划分上的应用 * [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(5): 74-80. |
|
||