热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 96-115.doi: 10.11978/2022133CSTR: 32234.14.2022133
南海北部陆缘不均匀伸展及脉动式构造升降史*
赵中贤1,2,3( ), 孙珍1,3(
), 孙珍1,3( ), 毛云华4, 张伙带2
), 毛云华4, 张伙带2
- 1.中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室, 南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 511458
2.自然资源部海底矿产资源重点实验室, 中国地质调查局广州海洋地质调查局, 广东 广州 510760
3.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
4.中国电建集团昆明勘测设计研究院有限公司, 云南 昆明 650051
-
收稿日期:2022-06-10修回日期:2022-08-15出版日期:2023-05-10发布日期:2022-09-07 -
作者简介:赵中贤(1985—), 男, 山东省菏泽市人, 研究员, 从事构造沉降与地球动力学研究。email: zxzhao@scsio.ac.cn
*感谢中国海洋石油公司提供的反射地震数据。感谢编辑部老师和两位匿名审稿专家提出的宝贵建议。
-
基金资助:中国科学院青年创新促进会资助项目; 自然资源部海底矿产资源重点实验室开放基金(KLMMR-2018-B-06); 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0205); 国家重点研发计划(2021YFC3100604); 国家自然科学基金面上基金(42076077)
Heterogeneous extension and pulsed tectonic subsidence in the northern South China Sea margin*
ZHAO Zhongxian1,2,3( ), SUN Zhen1,3(
), SUN Zhen1,3( ), MAO Yunhua4, ZHANG Huodai2
), MAO Yunhua4, ZHANG Huodai2
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 511458, China
2. Key Laboratory of Marine Mineral Resources, Ministry of Natural Resources, Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, Guangzhou 510760, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
4. Kunming Engineering Corporation Limited, Kunming 650051, China
-
Received:2022-06-10Revised:2022-08-15Online:2023-05-10Published:2022-09-07 -
Supported by:Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS; Key Laboratory of Marine Mineral Resources, Ministry of Natural Resources(KLMMR-2018-B-06); Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0205); National Key Research and Development Program of China(2021YFC3100604); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42076077)
摘要:
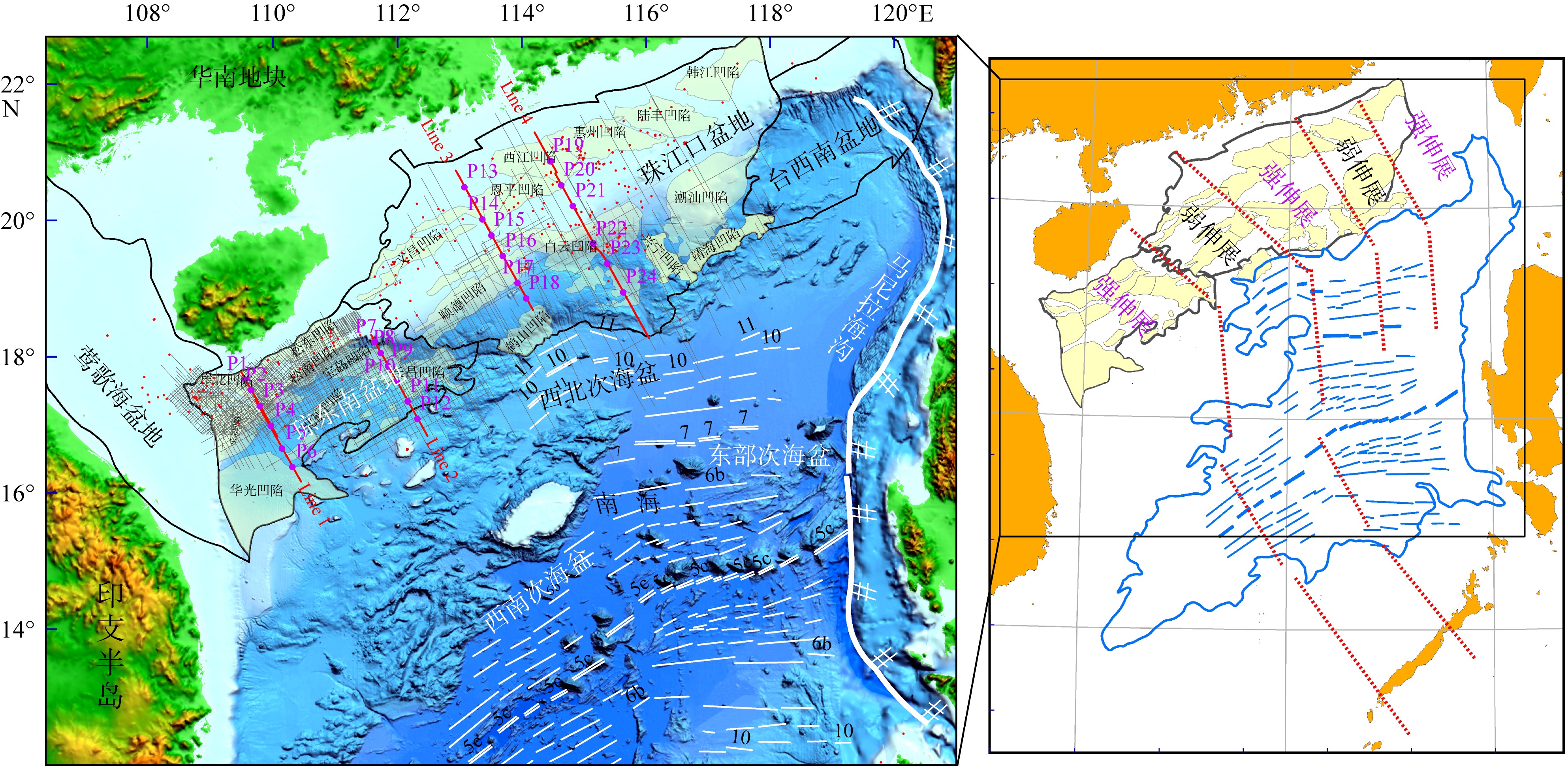
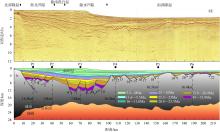
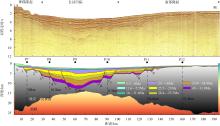
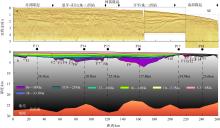
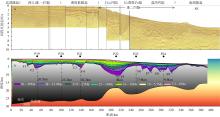
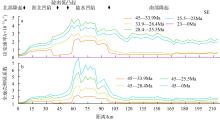
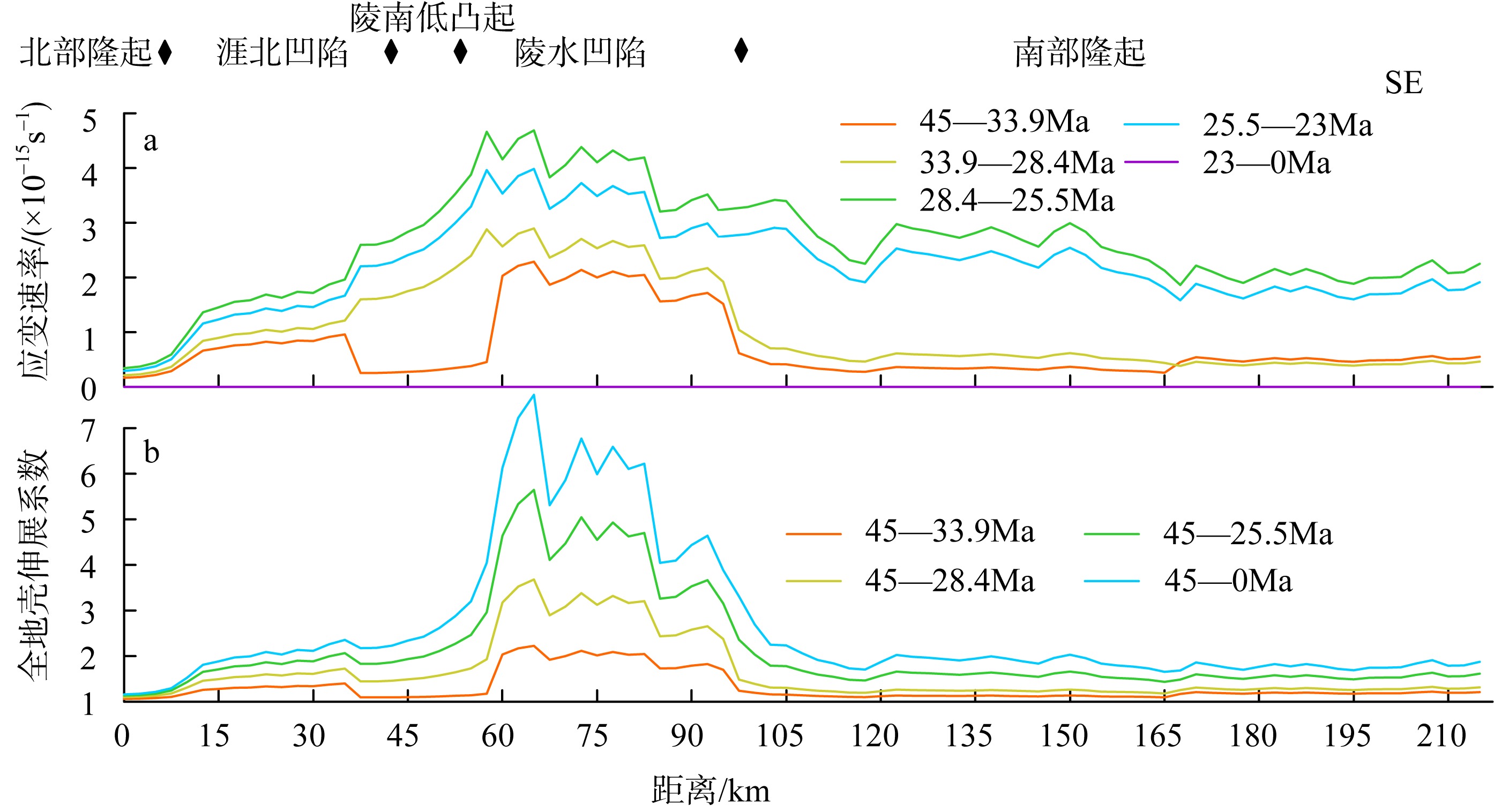
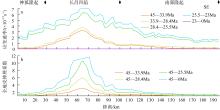
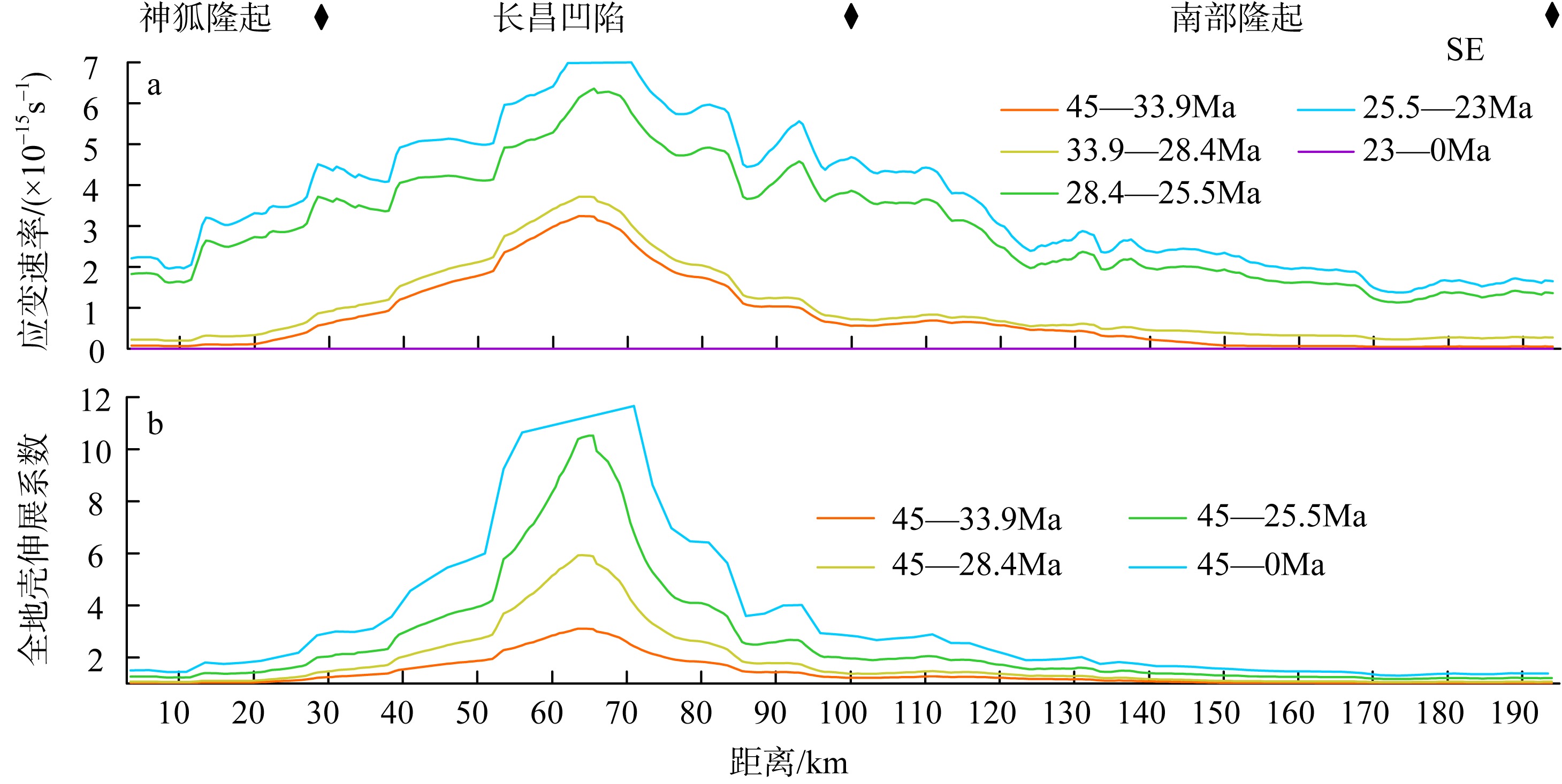
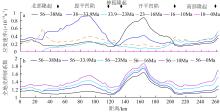
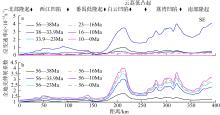
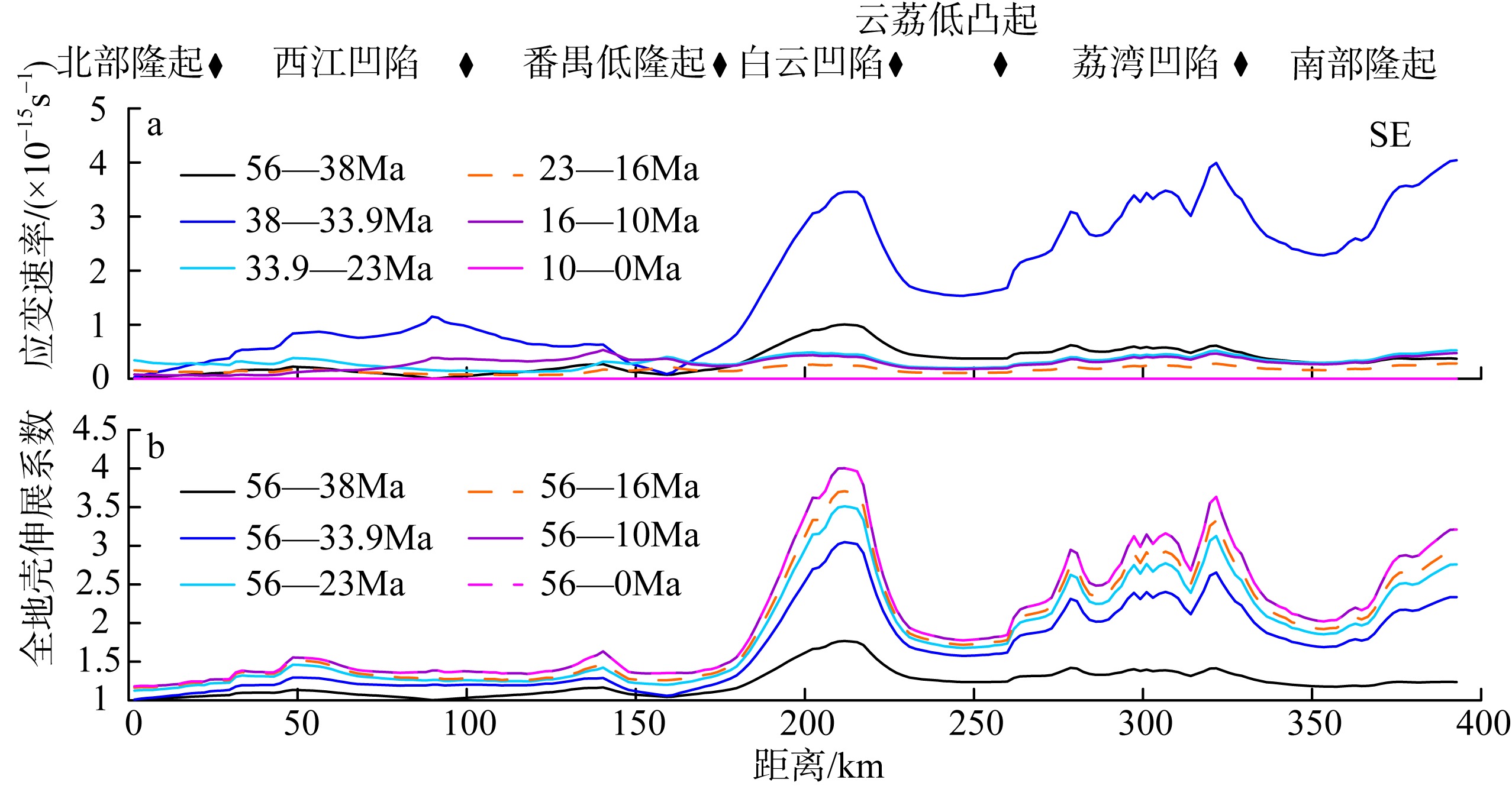
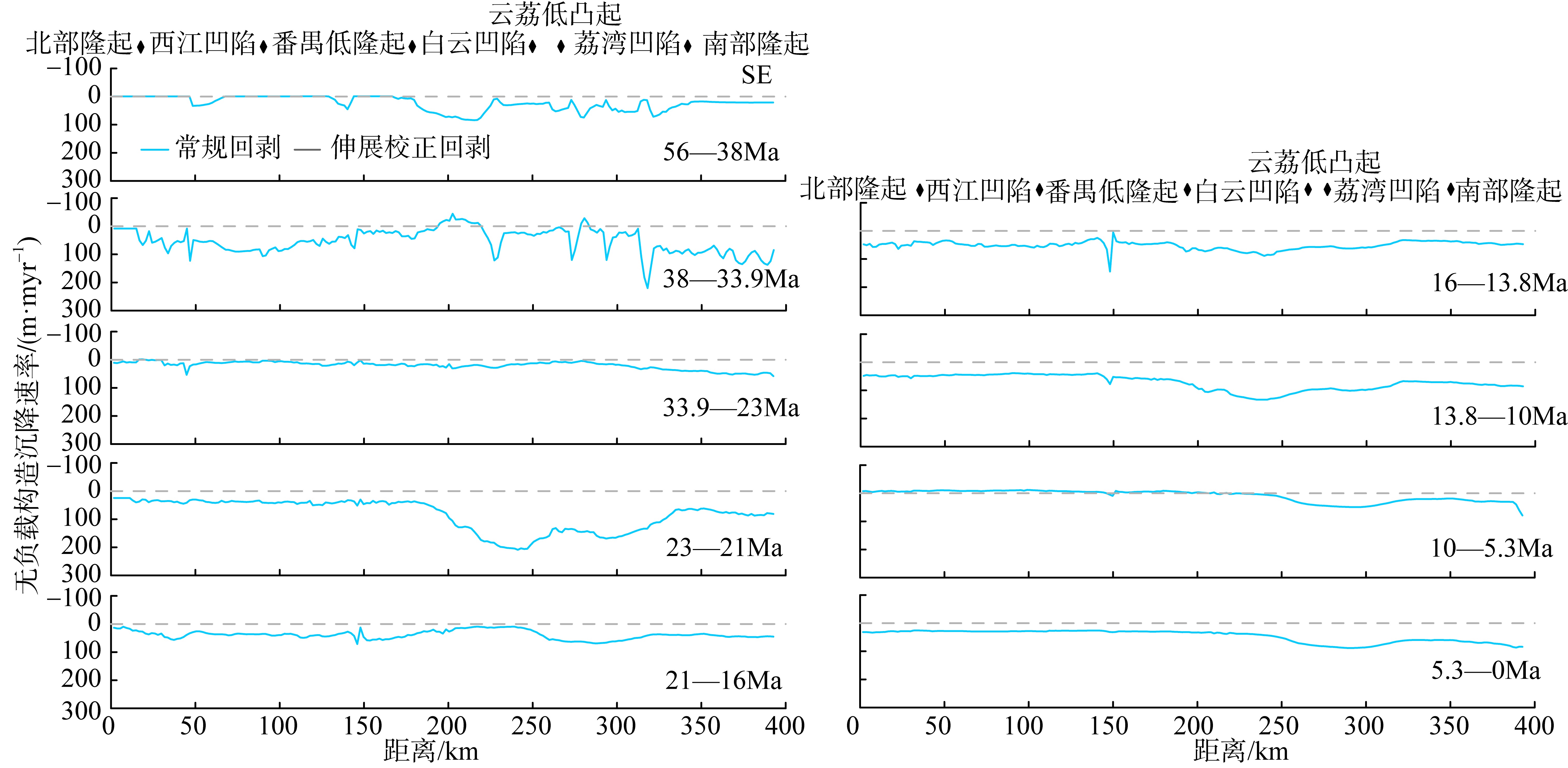
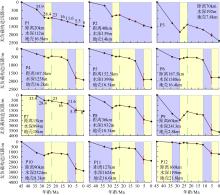
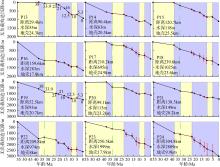
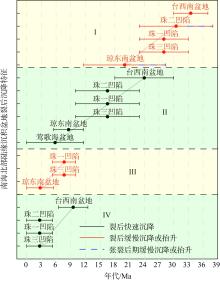
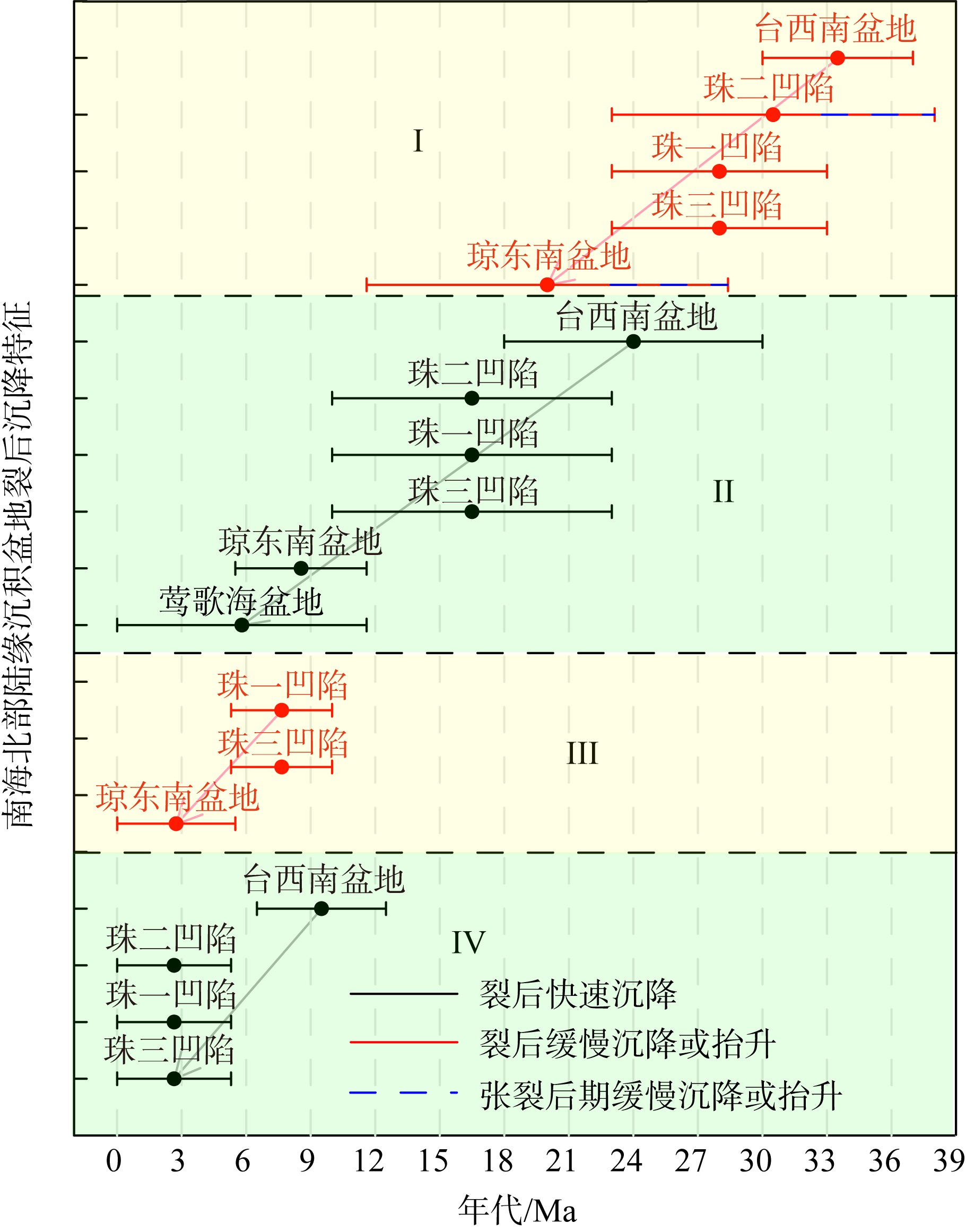
南海北部陆缘在区域板块构造和深部地幔流影响下, 发育了复杂的构造、岩浆和基底升降过程。本文采用最新提出的伸展校正回剥技术和4条长地震剖面, 对南海北部陆缘新生代伸展变形和从张裂到裂后的构造升降过程开展详细研究。结果表明南海北部陆缘伸展减薄差别大, 强伸展与弱伸展不仅具有南北分带特点, 还具有东西交替出现的分块特征。琼东南盆地、珠江口盆地中部、台西南盆地伸展减薄大, 部分地壳被减薄至10km以下; 而珠江口西部和东部伸展减薄小, 地壳厚度大都在20km以上。强伸展与弱伸展陆缘总应变不同, 但应变速率均具有张裂早期慢、晚期快的二阶段特征。强伸展陆缘最大应变速率在4×10-15~7×10-15s-1之间, 地壳最大伸展系数为4~10; 弱伸展陆缘最大应变速率小于1×10-15s-1, 最大伸展系数小于1.9。南海北部陆缘构造升降具有脉动式、快慢交替的特征。张裂期构造沉降快, 裂后构造升降表现为4幕先慢后快及东早西晚的特点。陆缘西部琼东南盆地脉动式升降主要与深部地幔上升流引起的动力地形有关。陆缘东部珠江口和台西南盆地脉动式构造升降则可能受南海打开过程及吕宋岛弧与南海陆缘碰撞的影响。
引用本文
赵中贤, 孙珍, 毛云华, 张伙带. 南海北部陆缘不均匀伸展及脉动式构造升降史*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 96-115.
ZHAO Zhongxian, SUN Zhen, MAO Yunhua, ZHANG Huodai. Heterogeneous extension and pulsed tectonic subsidence in the northern South China Sea margin*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 96-115.
表1
测线1断层活动速率"
| 断层 | 活动速率/(m·Myr-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45—33.9Ma | 33.9—28.4Ma | 28.4—25.5Ma | 25.5—23Ma | 23—0Ma | |
| F1 | 120.8 | 283.5 | 236.2 | 232.0 | - |
| F4 | 9.8 | 16.2 | 58.0 | 29.6 | - |
| F5 | 70.7 | 82.4 | 57.7 | 46.2 | - |
| F6 | 125.9 | 85.5 | 201.2 | 26.7 | - |
| F7 | 43.1 | 62.0 | 271.5 | - | - |
| F8 | 35.9 | 83.6 | 88.7 | - | - |
| F9 | 122.1 | 99.5 | 205.4 | - | - |
| F10 | 178.3 | 339.8 | 370.4 | 200.5 | - |
| F14 | - | 121.7 | 109.9 | 181.0 | - |
| F15 | - | 60.4 | 26.4 | 55.1 | - |
| F16 | - | - | - | 78.3 | - |
| F17 | - | - | - | 54.9 | - |
| F18 | - | 43.6 | 67.6 | 317.6 | - |
| F19 | 31.5 | 55.5 | - | 231.5 | - |
| F20 | 22.2 | 29.2 | - | 140.6 | - |
| 平均 | 71.1 | 90.0 | 145.7 | 123.8 | 0 |
表2
测线2断层活动速率"
| 断层 | 活动速率/(m·Myr-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45—33.9Ma | 33.9—28.4Ma | 28.4—25.5Ma | 25.5—23Ma | 23—0Ma | |
| F1 | - | 45.9 | 135.0 | 370.4 | - |
| F2 | - | 74.3 | - | 41.9 | - |
| F3 | 57.3 | 178.6 | - | - | - |
| F4 | 116.4 | 20.3 | - | - | - |
| F5 | 39.3 | 106.5 | 150.9 | - | - |
| F6 | 35.8 | 267.1 | 107.5 | - | - |
| F7 | 122.6 | 107.9 | 102.4 | 80.8 | - |
| F8 | 41 | 196.8 | - | 131.8 | - |
| F9 | 32.7 | 84.9 | - | 127.1 | - |
| 平均 | 63.6 | 120.3 | 124.0 | 150.4 | 0 |
表3
测线3断层活动速率"
| 断层 | 活动速率/(m·Myr-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56—38Ma | 38—33.9Ma | 33.9—23Ma | 23—16Ma | 16—0Ma | |
| F1 | 23.7 | 56.5 | - | - | - |
| F2 | 10.8 | 98.5 | 16.4 | 37.7 | - |
| F3 | - | 45.8 | - | - | - |
| F4 | 10.6 | 47.9 | - | - | - |
| F5 | 16.9 | 32.7 | 17 | - | - |
| F6 | 14.8 | 99.4 | - | - | - |
| F7 | - | 38.1 | - | - | - |
| F8 | 45 | 62 | 13.2 | - | - |
| F9 | 197 | 88.9 | - | - | - |
| F10 | - | - | - | 18.9 | - |
| F11 | 49.3 | 33 | 11.5 | 10.9 | - |
| F12 | 14.9 | - | - | 12.7 | - |
| F13 | 13.2 | - | - | - | - |
| F14 | 13.6 | - | 10.3 | - | - |
| F15 | - | 11 | - | - | - |
| 平均 | 37.3 | 55.8 | 13.7 | 20 | 0 |
表4
测线4断层活动速率"
| 断层 | 活动速率/(m·Myr-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56—38Ma | 38—33.9Ma | 33.9—23Ma | 23—16Ma | 16—10Ma | 10—0Ma | |
| F1 | - | 111.4 | 68.4 | 66.7 | 21.8 | - |
| F2 | 44 | 179.4 | 77.6 | - | 11.7 | - |
| F3 | - | 45.9 | - | - | 4.9 | - |
| F4 | 70 | 144.9 | 25.9 | 14 | 59.6 | - |
| F5 | 157.1 | 363.8 | 19.6 | - | 38.7 | - |
| F6 | 84.6 | 86.6 | 7.6 | - | - | - |
| F7 | 66.5 | 221 | 12.8 | - | - | - |
| F8 | 29.9 | 327.8 | - | - | - | - |
| F9 | 21.2 | 613.8 | - | - | - | - |
| 平均 | 67.6 | 232.7 | 30.3 | 40.4 | 27.3 | 0 |
| [1] |
陈汉宗, 吴湘杰, 周蒂, et al, 2005. 珠江口盆地中新生代主要断裂特征和动力背景分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 24(2): 52-61.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈梅, 施小斌, 刘凯, 等, 2017. 南海北缘珠三坳陷新生代构造沉降特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 37(6): 47-56.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
崔涛, 解习农, 任建业, 等, 2008. 莺歌海盆地异常裂后沉降的动力学机制[J]. 地球科学, 33(3): 349-356.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
郝天珧, 徐亚, 孙福利, 等, 2011. 南海共轭大陆边缘构造属性的综合地球物理研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(12): 3098-3116.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
焦养泉, 李思田, 解习农, 等, 1997. 多幕裂陷作用的表现形式——以珠江口盆地西部及其外围地区为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 19(3): 222-227.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
雷超, 任建业, 佟殿君, 2013. 南海北部洋陆转换带盆地发育动力学机制[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1287-1299.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
李昌年, 王方正, 钟称生, 2005. 广西北海涠洲岛(含斜阳岛)第四纪玄武质火山岩的地球化学性质及其源区特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 24(1): 1-11.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李三忠, 索艳慧, 李玺瑶, 等, 2018. 西太平洋中生代板块俯冲过程与东亚洋陆过渡带构造-岩浆响应[J]. 科学通报, 63(16): 1550-1593.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
林畅松, 张燕梅, 1999. 盆地的形成和充填过程模拟——以拉伸盆地为例[J]. 地学前缘, 6(B05): 139-146.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
刘明辉, 梅廉夫, 杨亚娟, 等, 2015. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷北部裂陷期与拗陷期沉降作用时空差异及主控因素[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 37(2): 31-43.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
刘少峰, 2009. 大陆边缘动力沉降及其深部构造作用控制[J]. 地质科学, 44(4): 1199-1212.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
马明, 漆家福, 张远泽, 等, 2019. 珠江口盆地新生代沉降特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质, 46(2): 269-289.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
毛云华, 赵中贤, 孙珍, 2020. 珠江口盆地西部陆缘伸展-减薄机制[J]. 地球科学, 45(5): 1622-1635.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
庞雄, 任建业, 郑金云, 等, 2018. 陆缘地壳强烈拆离薄化作用下的油气地质特征——以南海北部陆缘深水区白云凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 45(1): 27-39.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.01.03 |
|
|
|
| [15] |
任建业, 雷超, 2011. 莺歌海-琼东南盆地构造-地层格架及南海动力变形分区[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(12): 3303-3314.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
任建业, 庞雄, 于鹏, 等, 2018. 南海北部陆缘深水-超深水盆地成因机制分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(12): 4901-4920.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
佟殿君, 任建业, 雷超, 等, 2009. 琼东南盆地深水区岩石圈伸展模式及其对裂后期沉降的控制[J]. 地球科学, 34(6): 963-974.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
王贤觉, 吴明清, 梁德华, 等, 1984. 南海玄武岩的某些地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, (4): 42-50.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
卫小冬, 阮爱国, 赵明辉, 2011. 穿越东沙隆起和潮汕坳陷的OBS广角地震剖面[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(12): 3325-3335.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
吴能友, 曾维军, 宋海斌, 等, 2003. 南海区域构造沉降特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 23(1): 55-65.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
吴时国, 孙启良, 吴拓宇, 等, 2009. 琼东南盆地深水区多边形断层的发现及其油气意义[J]. 石油学报, 30(1): 22-32.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200901005 |
|
doi: 10.7623/syxb200901005 |
|
| [22] |
徐义刚, 魏静娴, 邱华宁, 等, 2012. 用火山岩制约南海的形成演化:初步认识与研究设想[J]. 科学通报, 57(20): 1863-1878.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
鄢全树, 石学法, 2007. 海南地幔柱与南海形成演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 13(2): 311-322.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
鄢全树, 石学法, 王昆山, 等, 2008. 南海新生代碱性玄武岩主量、微量元素及Sr-Nd-Pb同位素研究[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 38(1): 56-71.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
杨军, 施小斌, 王振峰, 等, 2015. 琼东南盆地张裂期沉降亏损与裂后期快速沉降成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 35(1): 81-90.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
易海, 张莉, 林珍, 2012. 南海北部中生代构造格局与盆地发育特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 34(4): 388-394.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
袁玉松, 杨树春, 胡圣标, 等, 2008. 琼东南盆地构造沉降史及其主控因素[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(2): 376-383.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
张云帆, 孙珍, 周蒂, 等, 2007. 南海北部陆缘新生代地壳减薄特征及其动力学意义[J]. 中国科学, 37(12): 1609-1616.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
赵中贤, 孙珍, 谢辉, 等, 2011. 白云深水区新生代沉降及岩石圈伸展变形[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(12): 3336-3343.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
赵中贤, 周蒂, 廖杰, 2009. 珠江口盆地第三纪古地理及沉积演化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 28(6): 52-60.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.06.052 |
|
|
|
| [31] |
赵中贤, 周蒂, 廖杰, 等, 2010. 珠江口盆地陆架区岩石圈伸展模拟及裂后沉降分析[J]. 地质学报, 84(8): 1135-1145.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
邹和平, 李平鲁, 饶春涛, 1995. 珠江口盆地新生代火山岩地球化学特征及其动力学意义[J]. 地球化学, 24: 33-45.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1038/nature18319 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1038/313775a0 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(86)90146-9 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.03.032 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.147.3.0495 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2019.115932 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1029/97JB03295 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.11.003 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.11.003 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.11.020 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1002/ggge.v17.6 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2005.10.006 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.06.017 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.07.024 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.3.369 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1038/nature09988 |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90168-5 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz084 |
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(86)90053-X |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0198-1 |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.07.022 |
| [58] |
doi: 10.1002/jgrb.v119.3 |
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5063-9 |
| [62] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103647 |
| [63] |
doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5329-2 |
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2117.2003.00215.x |
| [66] |
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0735:CSAUOC>2.3.CO;2 |
| [67] |
doi: 10.1038/26212 |
| [68] |
doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90071-7 |
| [69] |
doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00035-6 |
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30003-X |
| [72] |
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<1079:IITNOT>2.3.CO;2 |
| [73] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2005.03.014 |
| [74] |
doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00222-0 |
| [75] |
doi: 10.1029/JB085iB07p03711 |
| [76] |
doi: 10.1080/00206814.2012.677136 |
| [77] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2005.07.004 |
| [78] |
doi: 10.1111/bre.2017.29.issue-3 |
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4835-2 |
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz116 |
| [83] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.02.018 |
| [84] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.09.002 |
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
doi: 10.1093/petrology/egr061 |
| [90] |
doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<963:QFDTOF>2.0.CO;2 |
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105140 |
| [94] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.03.004 |
| [95] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.08.005 |
| [96] |
doi: 10.1007/s11001-019-09378-6 |
| [97] |
doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00062-2 |
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.09.013 |
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
doi: 10.1007/s12583-011-0180-y |
| [102] |
doi: 10.1080/00206814.2019.1577189 |
| [103] |
doi: 10.1007/s12583-016-0708-2 |
| [104] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2021.101246 |
| [105] |
doi: 10.1080/00206814.2018.1531357 |
| [106] |
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2018.08.048 |
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
doi: 10.1111/bre.2018.30.issue-S1 |
| [109] |
doi: 10.1007/s11001-013-9188-2 |
| [110] |
doi: 10.1007/s11001-014-9238-4 |
| [111] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.01.002 |
| [112] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2018.02.002 |
| [1] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 袁丽, 徐晓璐. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编3. 数据共享服务及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [2] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 何云开, 袁丽, 徐晓璐. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编1. 资料整编技术及应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [3] | 徐超, 龙丽娟, 李莎, 徐晓璐, 袁丽. 南海及其附属岛礁海洋科学考察历史资料系统整编2. 数据治理技术与应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [4] | 宋瑞有, 马光克, 何小胡, 万阳, 贺礼文. 琼东南盆地崖北凹陷构造沉积特征及油气勘探潜力[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 93-105. |
| [5] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [6] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [7] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [8] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [9] | 邱燕, 鞠东, 黄文凯, 王英民, 聂鑫. 南海中央海盆海底初始扩张时间的重新认定[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 154-165. |
| [10] | 赵明辉, 袁野, 张佳政, 张翠梅, 高金尉, 王强, 孙珍, 程锦辉. 南海北部被动陆缘洋陆转换带张裂-破裂研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [11] | 黄谕, 王琳, 麦志茂, 李洁, 张偲. 南海热带岛礁生物土壤结皮中细菌的分离及其固砂特性初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [12] | 王辰燕, 史敬文, 颜安南, 康亚茹, 王煜轩, 覃素丽, 韩民伟, 张瑞杰, 余克服. 有机磷酸酯在南海长棘海星中的生物富集特征及来源解析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
| [13] | 李牛, 邸鹏飞, 冯东, 陈多福. 冷泉渗漏对海洋沉积物氧化还原环境地球化学识别的影响——以南海东北部F站位活动冷泉为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
| [14] | 张智晟, 谢玲玲, 李君益, 李强. 边缘海与开阔海中尺度涡生命周期演化规律对比分析: 以南海和黑潮延伸体为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 63-76. |
| [15] | 杨磊, 温金辉, 王强, 罗希, 黄华明, 何云开, 陈举. 热带气旋影响吕宋海峡输运的研究进展与展望*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 40-51. |
|
||