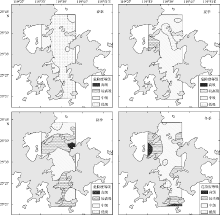
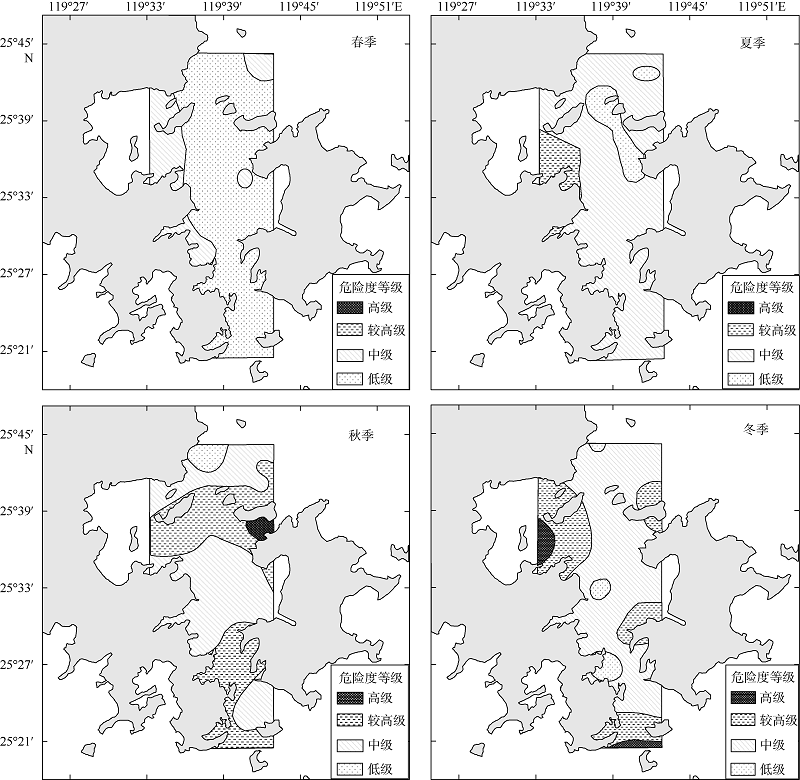
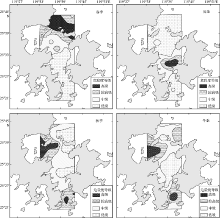
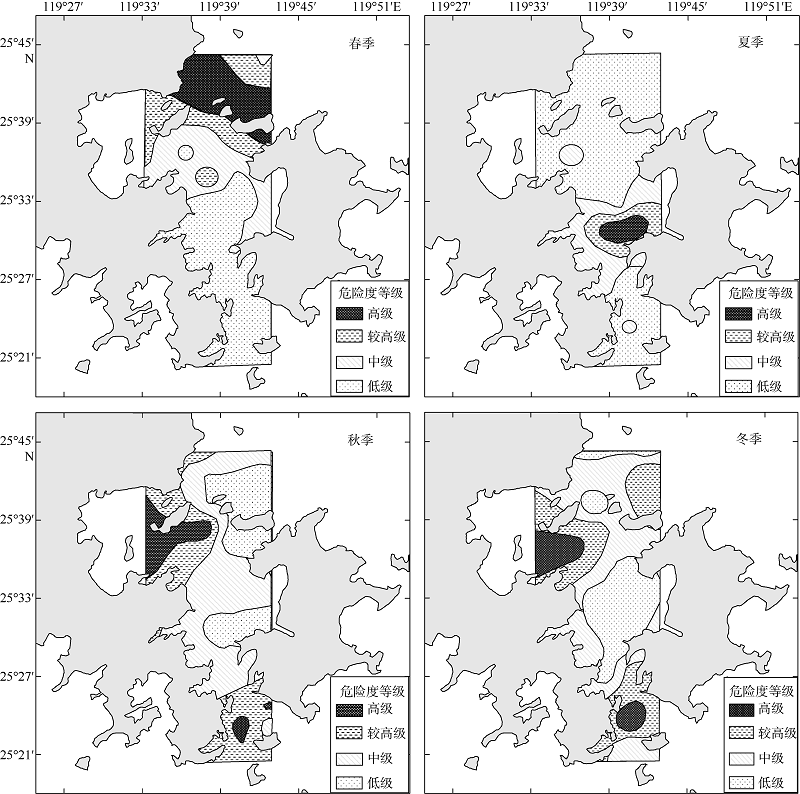
| [1] |
柴勋, 赵冬至, 韩震, 等, 2011. 赤潮灾害风险评估系统的初步设计[J]. 海洋环境科学, 30(2): 259-263.
|
|
CHAI XUN, ZHAO DONGZHI, HAN ZHEN, et al, 2011. Design of risk assessment system for HAB[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 30(2):259-263 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
陈峰, 巫朝鑫, 赵伟, 等, 2013. 谈海坛海峡的安全通航[J]. 航海技术, (3):4-6 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
程立海, 唐宏, 周廷刚, 等, 2011. 自然灾害强度的评估方法及应用——基于综合灾情指数的研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 20(1):46-50.
|
|
CHENG LIHAI, TANG HONG, ZHOU YANGANG, et al, 2011. Evaluation method of natural disaster intensity and its application: a research based on comprehensive disaster condition index[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 20(1):46-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
丁赞, 沈铭, 2019. 基于层次分析法和变异系数法的黄冈市地质环境承载力研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 33(S1):70-74, 91.
|
|
DING ZAN, SHEN MING, 2019. Study on the bearing capacity of geological environment in Huanggang City based on analytic hierarchy process and variation coefficient method[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 33(S1):70-74, 91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
杜凯, 陈前火, 张立香, 等, 2018. 平潭海坛海峡海洋环境现状调查及保护对策研究[J]. 福建轻纺, (3):30-35 (in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
郭皓, 2004. 中国近海赤潮生物图谱[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1-107.
|
|
GUO HAO, 2004. Illustrations of planktons responsible for the blooms in Chinese coastal waters[M]. Beijing: Maritime Press, 1-107(in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
黄良敏, 李军, 张雅芝, 等, 2010. 闽江口及附近海域渔业资源现存量评析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(5):142-148.
|
|
HUANG LIANGMIN, LI JUN, ZHANG YAZHI, et al, 2010. Current fishery resource assessment in the Minjiang River Estuary and its neighboring waters[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 29(5):142-148 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
黎鑫, 洪梅, 王博, 等, 2012. 南海-印度洋海域海洋安全灾害评估与风险区划[J]. 热带海洋学报, 31(6):121-127.
|
|
LI XIN, HONG MEI, WANG BO, et al, 2012. Disaster assessment and risk zoning concerning the South China Sea and Indian Ocean safety[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 31(6):121-127 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
李绪兴, 2006. 赤潮及其对渔业的影响[J]. 水产科学, 25(1):45-47.
|
|
LI XUXING, 2006. Influences of Red tide on fisheries[J]. Fisheries Science, 25(1):45-47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
刘聚涛, 高俊峰, 赵家虎, 等, 2010. 太湖蓝藻水华灾害程度评价方法[J]. 中国环境科学, 30(6):829-832.
|
|
LIU JUTAO, GAO JUNFENG, ZHAO JIAHU, et al, 2010. Method of cyanobacteria bloom hazard degree evaluation in Taihu Lake[J]. China Environmental Science, 30(6):829-832 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
吕小梅, 方少华, 张跃平, 等, 2008. 福建海坛海峡潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构及次级生产力[J]. 动物学报, 54(3):428-435.
|
|
LV XAOMEI, FANG SHAIHUA, ZHANG YUEPING, et al, 2008. Community structure and secondary production of macrobenthos in the intertidal zone of Haitan Strait, Fujian Province[J]. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 54(3):428-435. (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
王立盟, 孟浩, 2018. 基于熵值和变异系数组合赋权法的生态文明评价体系构建及实证分析[J]. 高技术通讯, 28(4):372-381.
|
|
WANG LIMENG, MENG HAO, 2018. Design and empirical research on the ecological civilization construction evaluation system based on entropy method and coefficient of variation[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 28(4):372-381 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
王婷, 宋亮, 赵文, 2005. 赤潮及其对渔业经济的影响[J]. 中国渔业经济, (6):41-44.
|
|
WANG TING, SONG LIANG, ZHAO WEN, 2005. Red tide and its effects on fishing economy[J]. Chinese Fisheries Economics, (6):41-44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
王臻, 李荣茂, 2018. 海坛海峡水环境状况及驱动因素分析[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 43(4):30-33.
|
|
WANG ZHEN, LI RONGMAO, 2018. Analysis of water environment and driving factors in the Haitan Strait[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 43(4):30-33 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
文世勇, 2007. 赤潮灾害风险评估理论与方法研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学.
|
|
WEN SHIYONG, 2017. The study of risk assessment theory and method of harmful algal blooms hazard[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
文世勇, 2010. 基于营养盐的赤潮灾害风险评估技术与应用研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学.
|
|
WEN SHIYONG, 2010. Risk assessment technology and application of red tide disaster based on nutrient[D]. Dalian Maritime University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
谢宏英, 王金辉, 2018. 宁德沿海赤潮灾害风险状况研究[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 27(4):553-563.
|
|
XIE HONGYING, WANG JINHUI, 2018. Study on the risk of harmful algal blooms hazard along Ningde Coast[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 27(4):553-563 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
薛祥生, 宋伦, 付志璐, 2019. 秦皇岛近岸海域赤潮生态风险评价[J]. 水产科学, 38(5):695-701.
|
|
XUE XIANGSHENG, SONG LUN, FU ZHILU, 2019. Ecological risk assessment of red tide in coastal area of Qinhuangdao[J]. Fisheries Science, 38(5):695-701 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
严军, 王婷, 秦珏, 2020. 基于变异系数法的马鞍山江心洲生态敏感性定量研究[J]. 生态科学, 39(2):124-132.
|
|
YAN JUN, WANG TING, QIN JUE, 2020. Research on ecological sensitivity analysis of Ma’anshan Jiangxinzhou based on the method of variation coefficient[J]. Ecological Science, 39(2):124-132 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [20] |
叶又茵, 项鹏, 王雨, 等, 2017. 福建6个港湾浮游植物多样性及其与水系的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 25(3):285-293.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2016315
|
|
YE YOUYIN, XIANG PENG, WANG YU, et al, 2017. Phytoplankton diversity and its relationship with currents in the six bays of Fujian[J]. Biodiversity Science, 25(3):285-293 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.17520/biods.2016315
|
| [21] |
张晓霞, 许自舟, 程嘉熠, 等, 2015. 赤潮灾害风险评估方法研究——以辽宁近岸海域为例[J]. 水产科学, 34(11):708-713.
|
|
ZHANG XIAOXIA, XU ZIZHOU, CHENG JIAYI, et al, 2015. Assessment methods of red tide disaster risk: a case in Liaoning coast[J]. Fisheries Science, 34(11):708-713 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [22] |
ANDERSON C R, KUDELA R M, KAHRU M, et al, 2016. Initial skill assessment of the California Harmful Algae Risk Mapping (C-HARM) system[J]. Harmful Algae, 59:1-18.
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2016.08.006
|
| [23] |
BROWN A R, LILLEY M, SHUTLER J, et al, 2020. Assessing risks and mitigating impacts of harmful algal blooms on mariculture and marine fisheries[J]. Reviews in Aquaculture, 12(3):1663-1688.
|
| [24] |
EKSTROM J A, MOORE S K, KLINGER T, 2020. Examining harmful algal blooms through a disaster risk management lens: A case study of the 2015 U.S. West Coast domoic acid event[J]. Harmful Algae, 94:101740.
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101740
|
| [25] |
FLEMING L E, BROAD K, CLEMENT A, et al, 2006. Oceans and human health: emerging public health risks in the marine environment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 53(10-12):545-560.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.08.012
|
| [26] |
LIN GUOHONG, LI KEQIANG, LIANG SHENGKANG, et al, 2020. Compound eutrophication index: an integrated approach for assessing ecological risk and identifying the critical element controlling harmful algal blooms in coastal seas[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 150:110585.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110585
|
| [27] |
WANG BAODONG, XIN MING, WEI QINSHENG, et al, 2018. A historical overview of coastal eutrophication in the China Seas[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 136:394-400.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.09.044
|
 ), 黄秀清2(
), 黄秀清2( ), 刘建华2, 徐美娜2, 蒋芸芸2, 邱桔斐2
), 刘建华2, 徐美娜2, 蒋芸芸2, 邱桔斐2
 ), HUANG Xiuqing2(
), HUANG Xiuqing2( ), LIU Jianhua2, XU Meina2, JIANG Yunyun2, QIU Jufei2
), LIU Jianhua2, XU Meina2, JIANG Yunyun2, QIU Jufei2