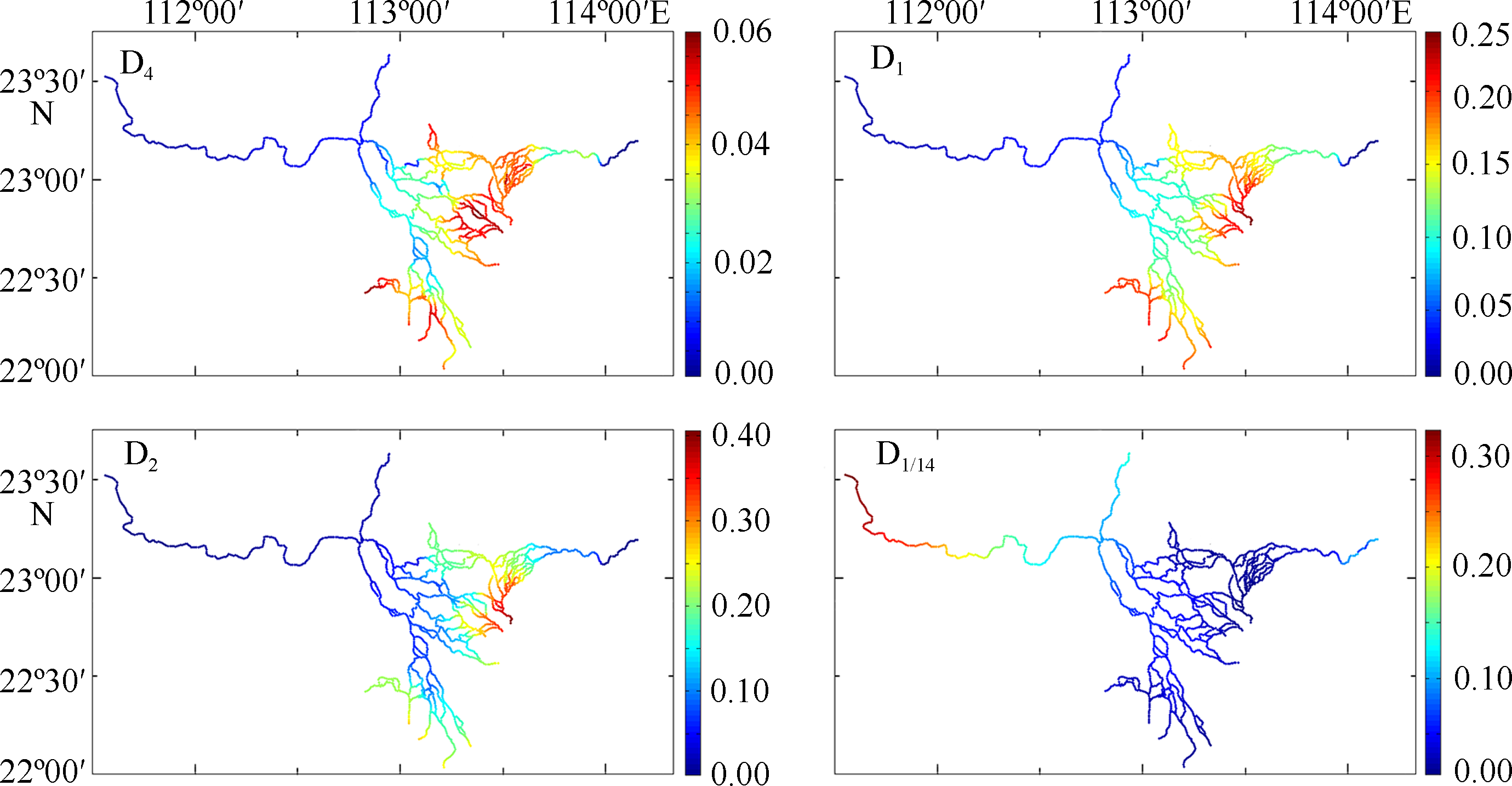
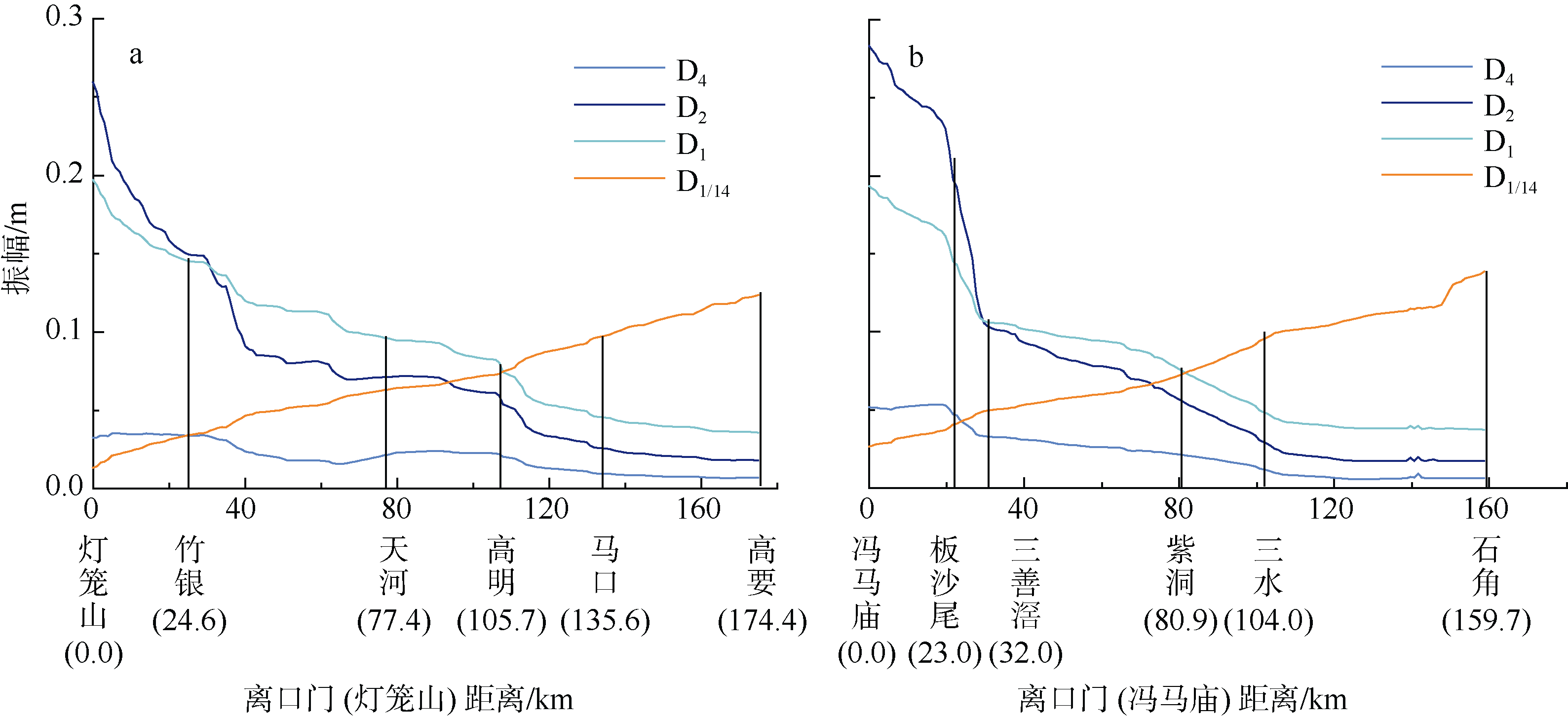
| [1] |
官明开, 蒋齐嘉, 徐龑文, 等, 2016. 基于一维盐度模型的珠江河网咸潮上溯距离分析[J]. 水运工程, (11): 66-71.
|
|
GUAN MINGKAI, JIANG QIJIA, XU YANWEN, et al, 2016. Saltwater intrusion lengths in the Pearl River networks based on one-dimension salinity model[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, (11): 66-71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
康玲, 杨正祥, 姜铁兵, 2009. 基于Morlet小波的丹江口水库入库流量周期性分析[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 31(11): 149-152.
|
|
KANG LING, YANG ZHENGXIANG, JIANG TIEBING, 2009. The periodical analysis of the Danjiangkou reservoir inflow based on the Morlet wavelet[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 31(11): 149-152 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
纳跃跃, 于剑, 2013. 一种用于谱聚类图像分割的像素相似度计算方法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 49(2): 159-168.
|
|
NA YUEYUE, YU JIAN, 2013. A new pixel affinity for spectral image segmentation[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 49(2): 159-168 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
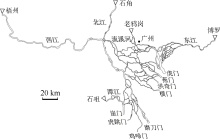
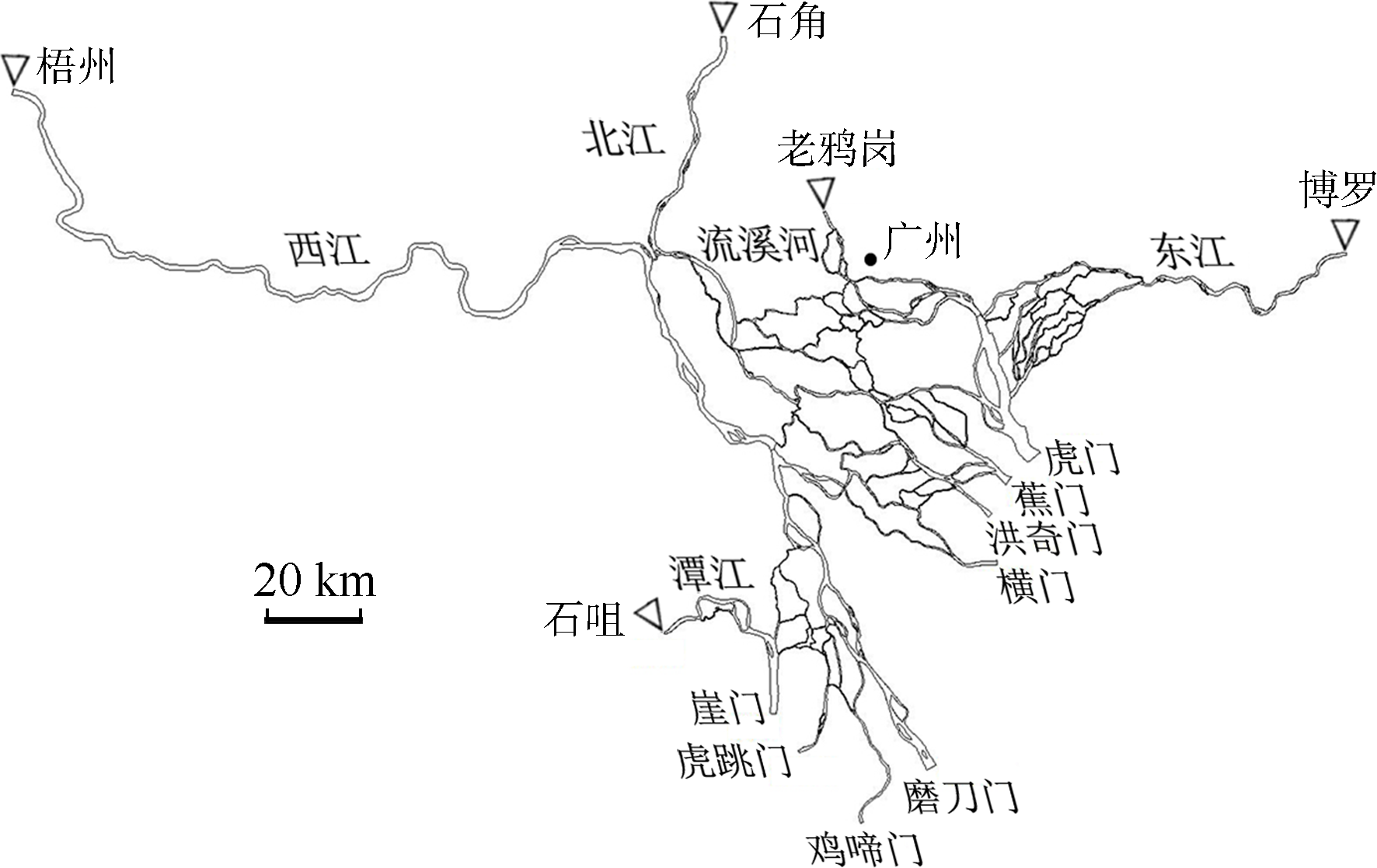
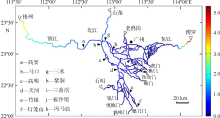
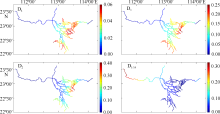
珠江水利科学研究院, 水利部珠江河口海岸工程技术研究中心,2013. 珠江河口治理开发研究[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
BUSCHMAN F A, HOITINK A J F, VAN DER VEGT M, et al, 2009. Subtidal water level variation controlled by river flow and tides[J]. Water Resources Research, 45(10): W10420.
|
| [6] |
FLINCHEM E P, JAY D A, 2000. An introduction to wavelet transform tidal analysis methods[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 51(2): 177-200.
|
| [7] |
GODIN G, 1999. The propagation of tides up rivers with special considerations on the upper saint Lawrence River[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 48(3): 307-324.
|
| [8] |
GUO LEICHENG, VAN DER WEGEN M, JAY D A, et al, 2015. River-tide dynamics: exploration of nonstationary and nonlinear tidal behavior in the Yangtze River estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 120(5): 3499-3521.
|
| [9] |
HOITINK A J F, JAY D A, 2016. Tidal river dynamics: implications for deltas[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 54(1): 240-272.
|
| [10] |
JAIN A K, VAILAYA A, 1996. Image retrieval using color and shape[J]. Pattern Recognition, 29(8): 1233-1244.
|
| [11] |
JAY D A, FLINCHEM E P, 1999. A comparison of methods for analysis of tidal records containing multi-scale non-tidal background energy[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 19(13): 1695-1732.
|
| [12] |
JAY D A, LEFFLER K, DIEFENDERFER H L, et al, 2015. Tidal-fluvial and estuarine processes in the Lower Columbia River: I. Along-channel water level variations, Pacific Ocean to Bonneville Dam[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 38(2): 415-433.
|
| [13] |
SASSI M G, HOITINK A J F, DE BRYE B, et al, 2012. Downstream hydraulic geometry of a tidally influenced river delta[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 117(F4): F04022.
|
| [14] |
SASSI M G, HOITINK A J F, 2013. River flow controls on tides and tide-mean water level profiles in a tidal freshwater river[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 118(9): 4139-4151.
|
| [15] |
SPEER P E, AUBREY D G, 1985. A study of non-linear tidal propagation in shallow inlet/estuarine systems Part II: theory[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 21(2): 207-224.
|
| [16] |
ZHANG WEI, YAN YIXIN, ZHENG JINHAI, et al, 2009. Temporal and spatial variability of annual extreme water level in the Pearl River Delta region, China[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 69(1-2): 35-47.
|
| [17] |
ZHANG WEI, FENG HAOCHUAN, ZHENG JINHAI, et al, 2013. Numerical Simulation and analysis of saltwater intrusion lengths in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 29(2): 372-382.
|
 ), 张蔚1,2(
), 张蔚1,2( ), 官明开3, 赵晟4, 程梁秋5
), 官明开3, 赵晟4, 程梁秋5
 ), Wei ZHANG1,2(
), Wei ZHANG1,2( ), Mingkai GUAN3, Sheng ZHAO4, Liangqiu CHENG5
), Mingkai GUAN3, Sheng ZHAO4, Liangqiu CHENG5