热带海洋学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 94-105.doi: 10.11978/2019048CSTR: 32234.14.2019048
天然气水合物稳定带内流体压裂计算的程序耦合方法
刘金龙1,2,3,4, 王淑红1,2,3, AsiriObeysekara5, XIANGJiansheng5,6, PabloSalinas5, ChristopherPain5, JonnyRutqvist7, 颜文1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1. 中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室(南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
2. 中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 510301
3. 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
4. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2019-05-13修回日期:2019-05-18出版日期:2020-01-20发布日期:2020-01-09 -
通讯作者:颜文 -
作者简介:刘金龙(1987—), 男, 山东省德州市人, 博士研究生, 主要从事海洋天然气水合物研究。E-mail: liujinlong@scsio.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41176052);国家自然科学基金项目(41576035);国家自然科学基金项目(41276050);南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory Guangzhou);广东省自然科学基金面上项目(Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province);中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院创新发展基金项目(the Innovation Development Fund of South China Sea Eco-Environmental Engineering Innovation Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences);the U.S. Department of Energy(the U.S. Department of Energy)
Codes coupling method for simulating hydraulic fracturing within the gas hydrate stability zone
LIU Jinlong1,2,3,4, WANG Shuhong1,2,3, Asiri Obeysekara5, XIANG Jiansheng5,6, Pablo Salinas5, Christopher Pain5, Jonny Rutqvist7, YAN Wen1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China
2. Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2019-05-13Revised:2019-05-18Online:2020-01-20Published:2020-01-09 -
Contact:Wen YAN -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41176052);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41576035);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41276050)
摘要:
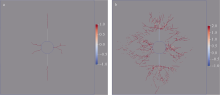
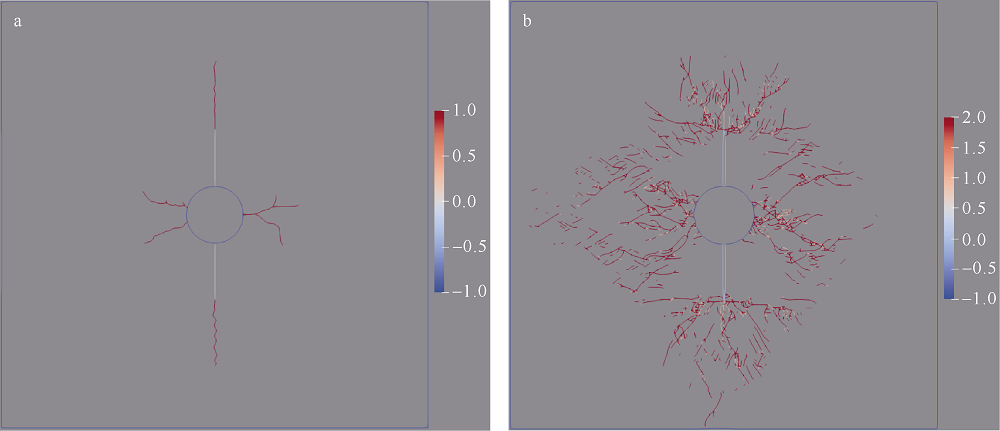
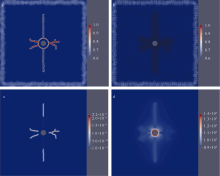
海洋天然气水合物稳定带气烟囱结构中存在被水合物充填的裂隙, 表明在自然条件下沉积物中曾发生过流体压裂以及相关的流体流动和水合物形成。在水合物稳定带内实施人为的流体压裂工程, 并联合其他方法(如降压或注热)进行水合物开采, 有望提高开采效率。水合物稳定带内, 无论是自然条件下发生的流体压裂过程, 还是人为实施的流体压裂工程, 都存在水合物反应和沉积物裂隙变形之间的耦合响应。当前, 已有不少数值程序对水合物反应与沉积物弹塑性变形的耦合过程进行了定量研究, 但尚没有数值程序能够计算水合物反应和离散裂隙变形之间的耦合过程。文章将TOUGH+Hydrate程序、IC-FERST和Solidity两者的耦合程序进行了进一步耦合, 为水合物稳定带内的流体压裂计算提供了一种耦合计算方法, 同时通过一个算例初步验证了该耦合计算方法的可行性。验证结果表明, 该耦合计算方法经进一步改进后有望应用于定量研究水合物稳定带内的裂隙变形和水合物反应过程。
中图分类号:
- P736
引用本文
刘金龙, 王淑红, AsiriObeysekara, XIANGJiansheng, PabloSalinas, ChristopherPain, JonnyRutqvist, 颜文. 天然气水合物稳定带内流体压裂计算的程序耦合方法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(1): 94-105.
LIU Jinlong, WANG Shuhong, Asiri Obeysekara, XIANG Jiansheng, Pablo Salinas, Christopher Pain, Jonny Rutqvist, YAN Wen. Codes coupling method for simulating hydraulic fracturing within the gas hydrate stability zone[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(1): 94-105.
表1
模型物理参数"
| 参数名称 | 数值 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 沉积物颗粒的密度/($\text{kg}\cdot {{\text{m}}^{-\text{3}}}$) | 2650 | Garg et al, 2008 |
| 甲烷在孔隙水中的扩散系数/(${{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\cdot {{\text{s}}^{-\text{1}}}$) | $\text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-\text{9}}}$ | Garg et al, 2008 |
| 盐离子在孔隙水中的扩散系数/(${{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\cdot {{\text{s}}^{-\text{1}}}$) | $\text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-\text{9}}}$ | Garg et al, 2008 |
| 沉积物颗粒的半径/m | $\text{1}\text{.48}\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-\text{6}}}$ | Gràcia et al, 2005 |
| 沉积物压缩系数/$\text{P}{{\text{a}}^{-1}}$ | ${{10}^{-8}}$ | Rutqvist et al, 2009 |
| 热膨胀系数/${{\text{K}}^{-1}}$ | 0.0 |
表2
热导率、毛细管压力和相对渗透率方程及参数"
| 方程或参数名称 | 表达式或数值 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 沉积物热导率模型 | $\begin{align} & {{K}_{\Theta }}=\left( 1-{{\phi }_{0}} \right){{K}_{\text{dry}}}+ \\ & {{\phi }_{0}}\left( {{S}_{\text{a}}}{{K}_{\text{a}}}+{{S}_{\text{h}}}{{K}_{\text{h}}}+{{S}_{\text{g}}}{{K}_{\text{g}}} \right) \\ \end{align}$ | |
| 沉积物颗粒的热导率${{K}_{\text{dry}}}$/($\text{W}\cdot {{\text{m}}^{-\text{1}}}\cdot {{\text{K}}^{-\text{1}}}$) | 3.61 | |
| 因水合物存在而引起的渗透率降低模型 | ${{k}_{\text{rS}}}={{\left[ \frac{{{\phi }_{0}}\left( 1-{{S}_{\text{h}}} \right)-{{\phi }_{\text{c}}}}{{{\phi }_{0}}-{{\phi }_{\text{c}}}} \right]}^{{{n}_{\text{H}}}}}$ | |
| 基质沉积物中的临界孔隙度${{\phi }_{\text{c}}}$ | 0.01 | |
| 裂隙中的临界孔隙度${{\phi }_{\text{c}}}$ | 0.0 | |
| 基质沉积物中的渗透率降低指数${{n}_{\text{H}}}$ | 11.1 | |
| 裂隙中的渗透率降低指数${{n}_{\text{H}}}$ | 3.0 | |
| 存在水合物时的毛细管压力模型 | ${{P}_{\text{cap}}}=\sqrt{\frac{1-{{S}_{\text{h}}}}{{{k}_{\text{rS}}}}}{{P}_{\text{cap,00}}}$ | |
| 不存在水合物时的毛细管压力模型 (Van Genuchten模型) | ${{P}_{\text{cap,00}}}=-{{P}_{0}}{{\left[ {{\left( {{S}^{*}} \right)}^{-{1}/{\lambda }\;}}-1 \right]}^{1-\lambda }}$ ${{S}^{*}}={\left( {{S}_{\text{a}}}-{{S}_{\text{irA}}} \right)}/{\left( {{S}_{\text{mxA}}}-{{S}_{\text{irA}}} \right)}\;$ | |
| Van Genuchten指数$\lambda$ | 0.45 | |
| 基质沉积物中的毛细管入口压力${{P}_{0}}$/Pa | $2.3\times {{10}^{5}}$ | |
| 裂隙中的${{P}_{0}}$/Pa | 144 | |
| 基质沉积物中的残余孔隙水饱和度${{S}_{\text{irA}}}$ | 0.19 | |
| 裂隙中的${{S}_{\text{irA}}}$ | 0.09 | |
| 最大孔隙水饱和度${{S}_{\text{mxA}}}$ | 1.0 | |
| 基质沉积物中的最大毛细管压力${{P}_{\text{cap,mx}}}$/Pa | $6.5\times {{10}^{7}}$ | |
| 裂隙中的${{P}_{\text{cap,mx}}}$/Pa | $5.0\times {{10}^{7}}$ | |
| 相对渗透率模型 (Modified Stone’s模型) | ${{k}_{\text{rA}}}={{\left[ {\left( {{S}_{\text{a}}}-{{S}_{\text{irA}}} \right)}/{\left( 1-{{S}_{\text{irA}}} \right)}\; \right]}^{n}}$ ${{k}_{\text{rG}}}={{\left[ {\left( {{S}_{\text{g}}}-{{S}_{\text{irG}}} \right)}/{\left( 1-{{S}_{\text{irA}}} \right)}\; \right]}^{n}}$ | |
| 基质沉积物中的残余孔隙水饱和度${{S}_{\text{irA}}}$ | 0.20 | |
| 裂隙中的${{S}_{\text{irA}}}$ | 0.10 | |
| 基质沉积物中的残余气体饱和度${{S}_{\text{irG}}}$ | 0.02 | |
| 裂隙中的${{S}_{\text{irG}}}$ | 0.01 | |
| 相对渗透率指数n | 3.57 |
表3
裂隙计算中使用的沉积物力学参数"
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 黏聚力/MPa | 1.06 |
| 内摩擦系数 | 0.76 |
| 联接摩擦系数 | 0.76 |
| 拉伸强度/MPa | 1.0 |
| 模型I的能量释放率/($\text{J}\cdot {{\text{m}}^{-\text{2}}}$) | 1.0 |
| 模型II的能量释放率/($\text{J}\cdot {{\text{m}}^{-\text{2}}}$) | 10.0 |
| 质量系数 | 300 |
| 第一拉梅常数λ | $2.31\times {{10}^{9}}$ |
| 第二拉梅常数μ | $1.538\times {{10}^{9}}$ |
| 弹性惩罚因子 | $4.0\times {{10}^{9}}$ |
| 接触惩罚因子 | $4.0\times {{10}^{8}}$ |
| 界面摩擦系数 | 0.76 |
| 最大拉伸强度/MPa | 1000 |
| 实验尺度的联接粗糙度系数 | 15 |
| 实验尺度的联接压缩强度/MPa | 120 |
| 联接样本长度/m | 0.2 |
| [1] | 卢静生, 李栋梁, 何勇 , 等, 2017. 天然气水合物开采过程中出砂研究现状[J]. 新能源进展, 5(5):394-402. |
| LU JINGSHENG, LI DONGLIANG, HE YONG , et al, 2017. Research status of sand production during the gas hydrate exploitation process[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy, 5(5):394-402 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] |
ASADOLLAHI P, INVERNIZZI M C A, ADDOTTO S , et al, 2010. Experimental validation of modified Barton’s model for rock fractures[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 43(5):597-613.
doi: 10.1007/s00603-010-0085-6 |
| [3] | DAIGLE H, BANGS N L, DUGAN B , 2011. Transient hydraulic fracturing and gas release in methane hydrate settings: A case study from southern Hydrate Ridge[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 12(12):1-15. |
| [4] | DAVIE M K, BUFFETT B A , 2001. A numerical model for the formation of gas hydrate below the seafloor[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 106(B1):497-514. |
| [5] | DAVIE M K, BUFFETT B A , 2003. A steady state model for marine hydrate formation: constraints on methane supply from pore water sulfate profiles[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B10):2495. |
| [6] |
DUGDALE D S , 1960. Yielding of steel sheets containing slits[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 8(2):100-104.
doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(60)90013-2 |
| [7] |
FARRELL P E, MADDISON J R , 2011. Conservative interpolation between volume meshes by local Galerkin projection[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 200(1-4):89-100.
doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2010.07.015 |
| [8] |
FARRELL P E, PIGGOTT M D, PAIN C C , et al, 2009. Conservative interpolation between unstructured meshes via supermesh construction[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 198(33-36):2632-2642.
doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2009.03.004 |
| [9] |
FENG YONGCHANG, CHEN LIN, SUZUKI A , et al, 2019. Enhancement of gas production from methane hydrate reservoirs by the combination of hydraulic fracturing and depressurization method[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 184:194-204.
doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.01.050 |
| [10] | GARG S K, PRITCHETT J W, KATOH A , et al, 2008. A mathematical model for the formation and dissociation of methane hydrates in the marine environment[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 113(B1):B01201. |
| [11] | GRÀCIA E, MARTÍNEZ-RUIZ F, PIÑERO E , et al, 2005. Data report: Grain-size and bulk and clay mineralogy of sediments from the summit and flanks of southern Hydrate Ridge, Sites 1244-1250, ODP Leg 204[M] //TRÉHU A M, BOHRMANN G, TORRES M E, et al. Proceedings of the ocean drilling program, scientific results volume 204. College Station, TX: Ocean Drilling Program: 1-19. |
| [12] |
GUO LIWEI, LATHAM J P, XIANG JIANSHENG , 2015. Numerical simulation of breakages of concrete armour units using a three-dimensional fracture model in the context of the combined finite-discrete element method[J]. Computers & Structures, 146:117-142.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226611 pmid: 31910214 |
| [13] |
GUPTA S, DEUSNER C, HAECKEL M , et al, 2017. Testing a thermo-chemo-hydro-geomechanical model for gas hydrate-bearing sediments using triaxial compression laboratory experiments[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 18(9):3419-3437.
doi: 10.1002/ggge.v18.9 |
| [14] |
GUPTA S, HELMIG R, WOHLMUTH B , 2015. Non-isothermal, multi-phase, multi-component flows through deformable methane hydrate reservoirs[J]. Computational Geosciences, 19(5):1063-1088.
doi: 10.1007/s10596-015-9520-9 |
| [15] |
GUPTA S, WOHLMUTH B, HELMIG R , 2016. Multi-rate time stepping schemes for hydro-geomechanical model for subsurface methane hydrate reservoirs[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 91:78-87.
doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.02.013 |
| [16] | HAUKWA C B , 1998. AMESH—a mesh creating program for the integral finite difference method: a user's manual[R]. Report LBNL-45284. Berkeley, California: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: 1-52. |
| [17] | ITO T, IGARASHI A, SUZUKI K, et al, 2008. Laboratory study of hydraulic fracturing behavior in unconsolidated sands for methane hydrate production [C]//Offshore technology conference. Houston, Texas, USA: Offshore Technology Conference: 1-8. |
| [18] | KIM J, YANG D, MORIDIS G J, et al, 2012. Numerical studies on two-way coupled fluid flow and geomechanics in hydrate deposits [C]//SPE reservoir simulation symposium. The Woodlands, Texas, USA: Society of Petroleum Engineers: 485-501. |
| [19] |
KIMOTO S, OKA F, FUSHITA T , 2010. A chemo-thermo- mechanically coupled analysis of ground deformation induced by gas hydrate dissociation[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 52(2):365-376.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2009.10.008 |
| [20] |
KLAR A, SOGA K, NG M Y A , 2010. Coupled deformation-flow analysis for methane hydrate extraction[J]. Géotechnique, 60(10):765-776.
doi: 10.1680/geot.9.P.079-3799 |
| [21] |
KONNO Y, JIN Y, YONEDA J , et al, 2016. Hydraulic fracturing in methane-hydrate-bearing sand[J]. RSC Advances, 6(77):73148-73155.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA15520K |
| [22] |
KOSSEL E, DEUSNER C, BIGALKE N , et al, 2018. The dependence of water permeability in quartz sand on gas hydrate saturation in the pore space[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(2):1235-1251.
doi: 10.1002/jgrb.v123.2 |
| [23] |
LATHAM J-P, XIANG JIANSHENG, BELAYNEH M , et al, 2013. Modelling stress-dependent permeability in fractured rock including effects of propagating and bending fractures[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 57:100-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.08.002 |
| [24] |
LEI QINGHUA, LATHAM J-P, XIANG JIANSHENG , et al, 2014. Effects of geomechanical changes on the validity of a discrete fracture network representation of a realistic two-dimensional fractured rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 70:507-523.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.06.001 |
| [25] |
LEI QINGHUA, LATHAM J-P, TSANG C-F , et al, 2015a. A new approach to upscaling fracture network models while preserving geostatistical and geomechanical characteristics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120(7):4784-4807.
doi: 10.1002/2014JB011736 |
| [26] |
LEI QINGHUA, LATHAM J-P, XIANG JIANSHENG , et al, 2015b. Polyaxial stress-induced variable aperture model for persistent 3D fracture networks[J]. Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 1:34-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.gete.2015.03.003 |
| [27] | LIU XIAOLI, FLEMINGS P B , 2007. Dynamic multiphase flow model of hydrate formation in marine sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B3):B03101. |
| [28] | LIU XIAOLI, FLEMINGS P B , 2011. Capillary effects on hydrate stability in marine sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978-2012), 116(B07102):1-24. |
| [29] |
LIU ZHICHAO, DAI SHENG, NING FULONG , et al, 2018. Strength estimation for hydrate-bearing sediments from direct shear tests of hydrate-bearing sand and silt[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(2):715-723.
doi: 10.1002/grl.v45.2 |
| [30] |
MATSUDA H, YAMAKAWA T, SUGAI Y , et al, 2016. Gas production from offshore methane hydrate layer and seabed subsidence by depressurization method[J]. Engineering, 8(6):353-364.
doi: 10.4236/eng.2016.86033 |
| [31] | MORIDIS G J, KOWALSKY M B, PRUESS K , 2008. TOUGH+HYDRATE v1.0 user's manual: a code for the simulation of system behavior in hydrate-bearing geologic media[R]. Berkeley, California: Earth Sciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: 1-279. |
| [32] | MUNJIZA A , 2004. The combined finite-discrete element method[M]. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd:1-333. |
| [33] |
MUNJIZA A, ANDREWS K R F, WHITE J K , 1999. Combined single and smeared crack model in combined finite-discrete element analysis[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 44(1):41-57.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0207 |
| [34] | OBEYSEKARA A , 2018. Numerical modelling of hydraulic fracturing in naturally fractured rock[D]. London: Imperial College London: 1-235. |
| [35] | OBEYSEKARA A, LEI QINGHUA, SALINAS P, et al, 2016. A fluid-solid coupled approach for numerical modeling of near-wellbore hydraulic fracturing and flow dynamics with adaptive mesh refinement [C]//Proceedings of the 50th U.S. rock mechanics/geomechanics symposium. Houston, Texas: American Rock Mechanics Association: 1-12. |
| [36] | OBEYSEKARA A, LEI QINGHUA, SALINAS P, et al, 2017. Modelling the evolution of a fracture network under excavation-induced unloading and seepage effects based on a fully coupled fluid-solid simulation [C]//Proceedings of the 51st U.S. rock mechanics/geomechanics symposium. San Francisco, California, USA: American Rock Mechanics Association: 1-12. |
| [37] | OLSSON R, BARTON N , 2001. An improved model for hydromechanical coupling during shearing of rock joints[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 38(3):317-329. |
| [38] | PARK K P, BAHK J J, KWON Y , et al, 2008. Korean national program expedition confirm rich gas hydrate deposits in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice: Methane Hydrate Newsletter, 2008: 6-9. |
| [39] |
PRUESS K, TSANG Y W , 1990. On two-phase relative permeability and capillary pressure of rough-walled rock fractures[J]. Water Resources Research, 26(9):1915-1926.
doi: 10.1029/WR026i009p01915 |
| [40] | REMPEL A W, BUFFETT B A , 1997. Formation and accumulation of gas hydrate in porous media[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 102(B5):10151-10164. |
| [41] |
REMPEL A W, BUFFETT B A , 1998. Mathematical models of gas hydrate accumulation[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 137(1):63-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.031 pmid: 22609679 |
| [42] |
RUTQVIST J, MORIDIS G J , 2009. Numerical studies on the geomechanical stability of hydrate-bearing sediments[J]. SPE Journal, 14(2):267-282.
doi: 10.2118/126129-PA |
| [43] |
SMITH A J, FLEMINGS P B, LIU XIAOLI , et al, 2014. The evolution of methane vents that pierce the hydrate stability zone in the world's oceans[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 119(8):6337-6356.
doi: 10.1002/jgrb.v119.8 |
| [44] |
STONE H L , 1970. Probability model for estimating three-phase relative permeability[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 22(2):214-218.
doi: 10.2118/2116-PA |
| [45] |
STRANNE C, O'REGAN M, JAKOBSSON M , 2017. Modeling fracture propagation and seafloor gas release during seafloor warming-induced hydrate dissociation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(16):8510-8519.
doi: 10.1002/2017GL074349 |
| [46] | TRÉHU A M, BOHRMANN G, RACK F R , et al, 2003. Proceedings of the ocean drilling program, initial reports, volume 204[R]. Station, Tex: Ocean Drilling Program. |
| [47] |
VAN GENUCHTEN M T , 1980. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 44(5):892-898.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2006.05.001 pmid: 16797103 |
| [48] |
VIRÉ A, XIANG JIANSHENG, MILTHALER F , et al, 2012. Modelling of fluid-solid interactions using an adaptive mesh fluid model coupled with a combined finite-discrete element model[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 62(10-12):1487-1501.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-012-0575-z |
| [49] |
VIRÉ A, XIANG JIANSHENG, PAIN C C , 2015. An immersed- shell method for modelling fluid-structure interactions[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 373(2035):20140085.
doi: 10.1098/rsta.2014.0085 pmid: 25583857 |
| [50] |
XIANG JIANSHENG, MUNJIZA A, LATHAM J-P , 2009. Finite strain, finite rotation quadratic tetrahedral element for the combined finite-discrete element method[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 79(8):946-978.
doi: 10.1002/nme.v79:8 |
| [51] | XU WENYUE, RUPPEL C , 1999. Predicting the occurrence, distribution, and evolution of methane gas hydrate in porous marine sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 104(B3):5081-5095. |
| [52] |
YANG PAN, XIANG JIANSHENG, CHEN M , et al, 2017. The immersed-body gas-solid interaction model for blast analysis in fractured solid media[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 91:119-132.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.10.006 |
| [1] | 李子正, 丘学林, 邢磊. 基于OBS和MCS数据的水合物地层速度特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 25-34. |
| [2] | 宋瑞有, 于俊峰, 晁彩霞, 宋鹏, 潘光超. 裂隙识别技术及其在油气和水合物勘探中的应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(1): 120-129. |
| [3] | 黄怡, 王淑红, 颜文, 程俊. 南海北部东沙海域天然气水合物分解事件及其与海底滑塌的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(4): 61-69. |
| [4] | 钟广见, 张如伟, 易海, 冯常茂, 赵忠泉. 南海北部陆坡深水区浅层天然气藏特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(3): 80-85. |
| [5] | 王吉亮, 吴时国, 姚永坚, 李波. 印度东部大陆边缘天然气水合物储层地球物理研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(6): 90-99. |
| [6] | 郝小柱, 赵庆献, 裴彦良. 用于天然气水合物勘探的大能量等离子体震源[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(1): 35-40. |
| [7] | 张宪政, 肖宏跃. 深部地热和天然气水合物组合利用可行性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(2): 85-89. |
| [8] | 刘金龙, 王淑红, 颜文. 海洋天然气水合物与深水油气共生关系探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(2): 39-51. |
| [9] | 许红, 蔡瑛, 孙和清, 闫桂京, 魏凯, 赵新伟, 朱玉瑞, 施剑,,董刚, 李清. 东海陆坡天然气水合物成藏地质条件和BSR反射及成藏类型特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(4): 22-29. |
| [10] | 李承峰,胡高伟,刘昌岭,业渝光,郑荣儿 . X射线计算机断层扫描在天然气水合物研究中的应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 93-99. |
| [11] | 王春娟,杜德文,刘永刚,朱志伟,闫仕娟,杨刚. 基于证据权模型的墨西哥湾天然气水合物矿产资源GIS评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 88-92. |
| [12] | 苏正,何勇,吴能友,. 南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物热激发开采潜力的数值模拟分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 74-82. |
| [13] | 何勇,苏正,吴能友,. 非烃类气体对琼东南盆地深水区水合物稳定带厚度的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 62-69. |
| [14] | 陈泓君,黄磊,彭学超,吴峧岐,李文成,王英民. 南海西北陆坡天然气水合物调查区滑坡带特征及成因探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 18-25. |
| [15] | 刘昌岭,业渝光,孟庆国,贺行良,陈强,胡高伟. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物样品的基本特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(5): 1-5. |
|
||