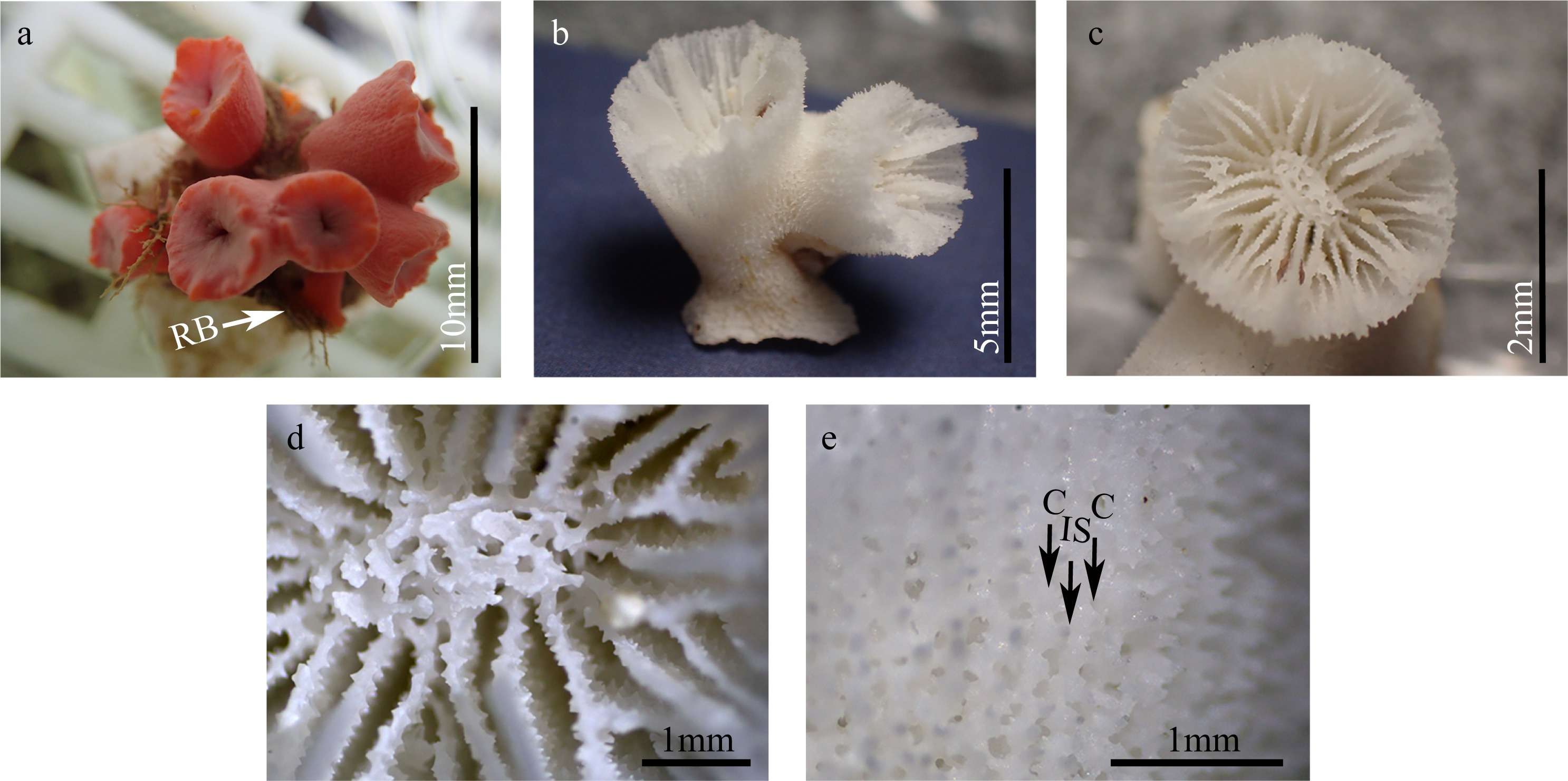
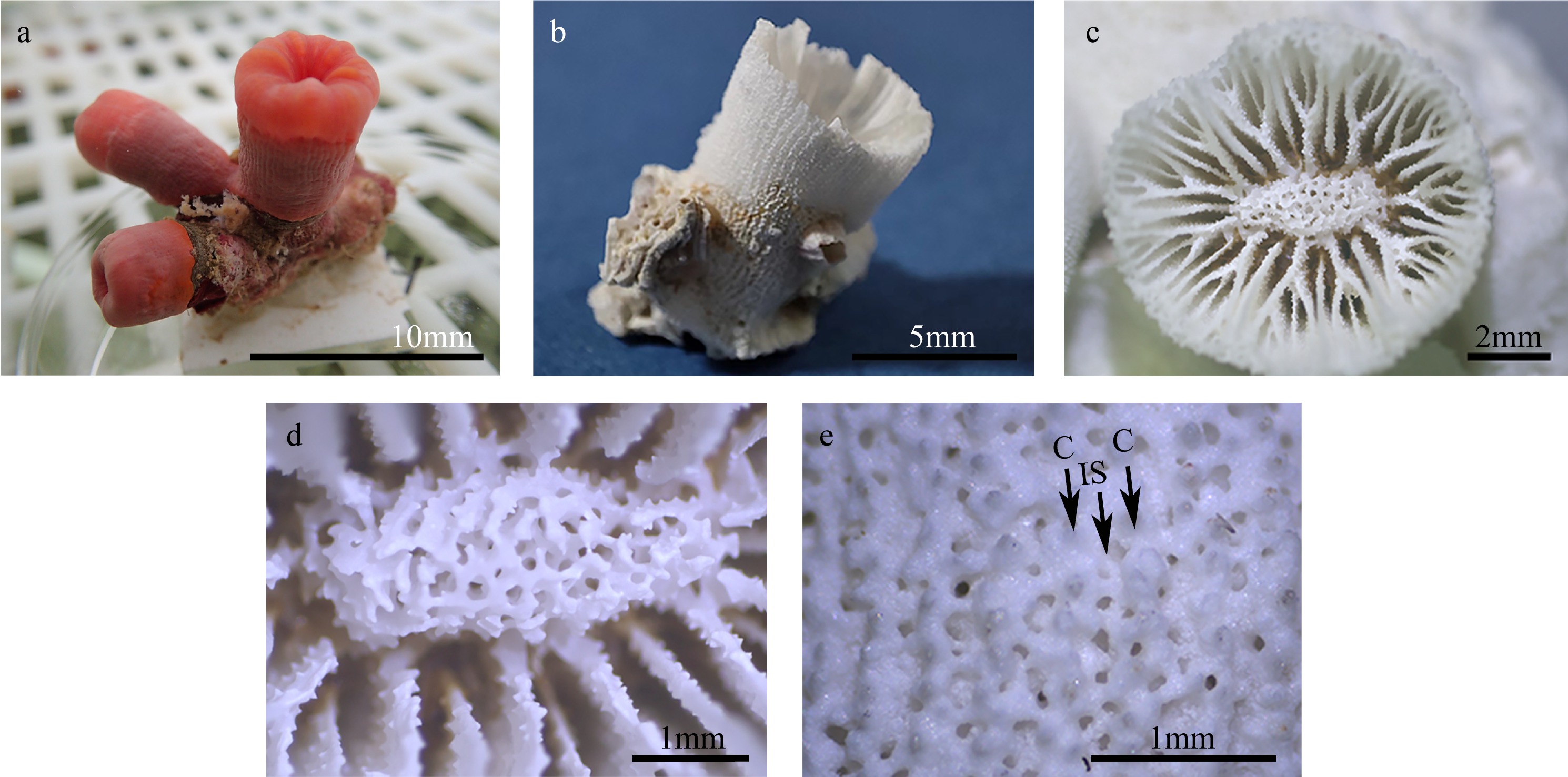
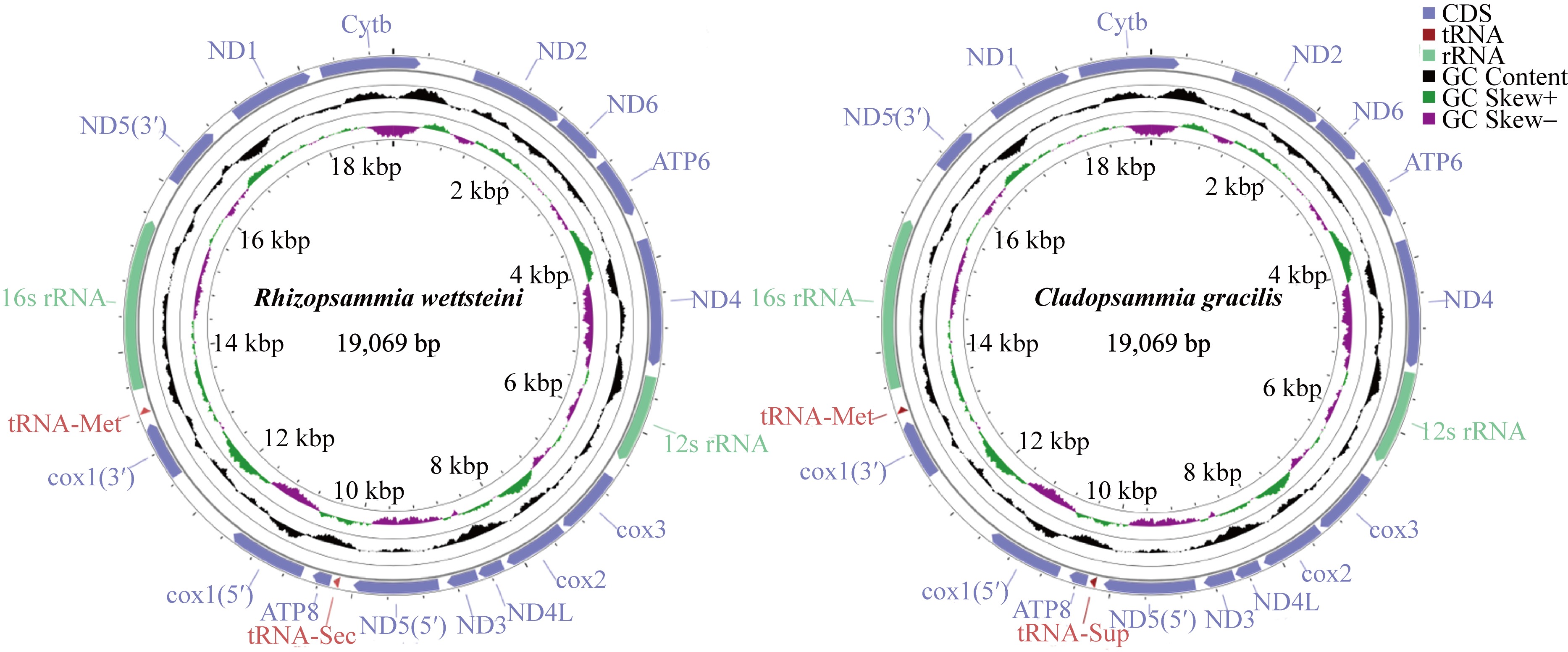
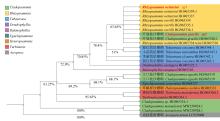
| [1] |
戴昌凤, 洪圣雯, 2009. 台湾珊瑚图鉴[M]. 台北: 猫头鹰出版社: 1-256 (in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
戴昌凤, 郑有容, 2020. 台湾珊瑚全图鉴(上): 石珊瑚[M]. 台北: 猫头鹰出版社: 1-557 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
倪智, 刘佳英, 宋倩倩, 等, 2017. 厦门白哈礁海域石珊瑚的分类鉴定[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 36(4): 550-557.
|
|
NI ZHI, LIU JIAYING, SONG QIANQIAN, et al, 2017. Classification and identification of the scleractinian corals in Baiha reef of Xiamen waters[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 36(4): 550-557 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
张喆, 俞晓磊, 梁宇娴, 等, 2022. 海水升温对非虫黄藻共生型珊瑚Cladopsammia sp. 的生理影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(5): 141-149.
doi: 10.11978/2021140
|
|
ZHANG ZHE, YU XIAOLEI, LIANG YUXIAN, et al, 2022. Effect of ocean warming on the physiology of azooxanthellate coral-Cladopsammia sp.[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(5): 141-149 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2021140
|
| [5] |
赵东波, 杨顺良, 姬厚德, 2022. 厦门同安湾海域猩红筒星珊瑚移植初步试验[J]. 渔业研究, 44(3): 275-283.
doi: 10.14012/j.cnki.fjsc.2022.03.0010
|
|
ZHAO DONGBO, YANG SHUNLIANG, JI HOUDE, 2022. Preliminary study on transplantation of Tubastraea coccinea in Tong’an Bay, Xiamen[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 44(3): 275-283 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
邹仁林, 2001. 中国动物志, 腔肠动物门, 珊瑚虫纲, 石珊瑚目, 造礁石珊瑚[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-289.
|
|
ZOU RENLIN, 2001. Fauna Sinica · Coelenterata · Anthozoa · Scler- actinia · Hermatypic Coral[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-289 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
ARRIGONI R, KITANO Y F, STOLARSKI J, et al, 2014. A phylogeny reconstruction of the Dendrophylliidae (Cnidaria, Scleractinia) based on molecular and micromorphological criteria, and its ecological implications[J]. Zoologica Scripta, 43(6): 661-688.
|
| [8] |
BARON-SZABO R C, CAIRNS S D, 2019. Treatise Online no. 119: Part F, Revised, Volume 2, Chapter 14: Systematic descriptions of the Scleractinia family Dendrophylliidae[J]. Treatise Online, 119: 1-33.
|
| [9] |
CAIRNS S D, 1999. Cnidaria Anthozoa: Deep-water azooxanthellate Scleractinia from Vanuatu, and Wallis and Futuna Islands[M]// CROSNIER A. Résultats des campagnes MUSORSTOM, Vol 20. Paris: Mémoires du Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle, 180: 31-167.
|
| [10] |
CAIRNS S D, 2000. A revision of the shallow-water azooxanthellate Scleractinia of the Western Atlantic[J]. Studies on the Natural History of the Caribbean Region, 75(1): 1-192.
|
| [11] |
CAIRNS S D, 2001. A generic revision and phylogenetic analysis of the dendrophylliidae (Cnidaria: Scleractinia)[M]. Washington, D.C. : Smithsonian Instiution Press:1-48.
|
| [12] |
CAIRNS S D, 2007. Deep-water corals: an overview with special reference to diversity and distribution of deep-water scleractinian corals[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 81(3): 311-322.
|
| [13] |
CAIRNS S D, KITAHARA M V, 2012. An illustrated key to the genera and subgenera of the Recent azooxanthellate Scleractinia (Cnidaria, Anthozoa), with an attached glossary[J]. ZooKeys, (227): 1-47.
doi: 10.3897/zookeys.227.3612
pmid: 23166463
|
| [14] |
CAPEL K C C, MIGOTTO A E, ZILBERBERG C, et al, 2016. Complete mitochondrial genome sequences of Atlantic representatives of the invasive Pacific coral species Tubastraea coccinea and T. tagusensis (Scleractinia, Dendrophylliidae): implications for species identification[J]. Gene, 590(2): 270-277.
|
| [15] |
CHEN C, DAI Changfeng, PLATHONG S, et al, 2008. The complete mitochondrial genomes of needle corals, Seriatopora spp. (Scleractinia: Pocilloporidae): an idiosyncratic atp8, duplicated trnW gene, and hypervariable regions used to determine species phylogenies and recently diverged populations[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 46(1): 19-33.
|
| [16] |
CHOI E, SONG J I, 2016. A new record of Dendrophyllia compressa (Anthozoa: Hexacorallia: Scleractinia: Dendrophylliidae) from Korea[J]. Animal Systematics, Evolution and Diversity, 32(1): 38-43.
|
| [17] |
FORSMAN Z H, BARSHIS D J, HUNTER C L, et al, 2009. Shape-shifting corals: molecular markers show morphology is evolutionarily plastic in Porites[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 9: 45.
|
| [18] |
FUKAMI H, CHEN C A, BUDD A F, et al, 2008. Mitochondrial and nuclear genes suggest that stony corals are monophyletic but most families of stony corals are not (Order Scleractinia, Class Anthozoa, Phylum Cnidaria)[J]. PLoS One, 3(9): e3222.
|
| [19] |
HAMMERMAN N M, WILLIAMS S M, VEGLIA A J, et al, 2021. Cladopsammia manuelensis sensu Cairns, 2000 (Order: Scleractinia): a new distribution record for Hispaniola and Puerto Rico[J]. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 62: 1-10.
|
| [20] |
KITAHARA M V, CAIRNS S D, STOLARSKI J, et al, 2010. A comprehensive phylogenetic analysis of the Scleractinia (Cnidaria, Anthozoa) based on mitochondrial CO1 sequence data[J]. PLoS One, 5(7): e11490.
|
| [21] |
KITAHARA M V, LIN MEIFANG, FORÊT S, et al, 2014. The "Naked Coral" hypothesis revisited - evidence for and against scleractinian monophyly[J]. PLoS One, 9(4): e94774.
|
| [22] |
LIN MEIFANG, KITAHARA M V, LUO HAIWEI, et al, 2014. Mitochondrial genome rearrangements in the scleractinia/ corallimorpharia complex: implications for coral phylogeny[J]. Genome Biology & Evolution, 6(5): 1086-1095.
|
| [23] |
MIRANDA R J, TAGLIAFICO A, KELAHER B P, et al, 2018. Impact of invasive corals Tubastrea spp. on native coral recruitment[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 605: 125-133.
|
| [24] |
PAZ-GARCÍA D A, GALVÁN-TIRADO C, ALVARADO J J, et al, 2016. Variation in the whole mitogenome of reef-building Porites corals[J]. Conservation Genetics Resources, 8(2): 123-127.
|
| [25] |
ROMANO S L, CAIRNS S D, 2000. Molecular phylogenetic hypotheses for the evolution of scleractinian corals[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 67(3): 1043-1068.
|
| [26] |
VERON J E N, 2000. Corals of the world[M]. Townsville: Australian Institute of Marine Science: 1-1410.
|
| [27] |
YIU S K F, QIU JIANWEN, 2022. Three new species of the sun coral genus Tubastraea (Scleractinia: Dendrophylliidae) from Hong Kong, China[J]. Zoological Studies, 61: e45.
|
 ), 李颖心1,2,3,4, 宋严1,2,3,4, 朱晴1,2,3,4, 周伟华1,2,3(
), 李颖心1,2,3,4, 宋严1,2,3,4, 朱晴1,2,3,4, 周伟华1,2,3( ), 袁翔城1,2,3(
), 袁翔城1,2,3( ), 黄晖1,2,3, 刘胜1,2,3
), 黄晖1,2,3, 刘胜1,2,3
 ), LI Yingxin1,2,3,4, SONG Yan1,2,3,4, ZHU Qing1,2,3,4, ZHOU Weihua1,2,3(
), LI Yingxin1,2,3,4, SONG Yan1,2,3,4, ZHU Qing1,2,3,4, ZHOU Weihua1,2,3( ), YUAN Xiangcheng1,2,3(
), YUAN Xiangcheng1,2,3( ), HUANG Hui1,2,3, LIU Sheng1,2,3
), HUANG Hui1,2,3, LIU Sheng1,2,3