热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 153-164.doi: 10.11978/2023130CSTR: 32234.14.2023130
基于双浮标连续监测资料分析大亚湾西南部海域水体环境变化特征及其影响因素
奚琛1( ), 林宗轩2, 萨如拉3, 邓玺1, 刘强1, 倪亮1, 罗来才4, 马腾5, 谢智杰6, 陈思若2, 陈松泽3(
), 林宗轩2, 萨如拉3, 邓玺1, 刘强1, 倪亮1, 罗来才4, 马腾5, 谢智杰6, 陈思若2, 陈松泽3( )
)
- 1.中广核研究院有限公司, 广东 深圳 518000
2.海洋地球古菌组学重点实验室, 南方科技大学, 广东 深圳 518055
3.广东省深圳生态环境监测中心站, 广东 深圳 518049
4.深圳市朗诚科技股份有限公司, 广东 深圳 518000
5.哈尔滨工程大学, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
6.海洋科学与工程系, 南方科技大学, 广东 深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2023-08-29修回日期:2023-09-26出版日期:2024-07-10发布日期:2024-07-22 -
作者简介:奚琛(1994—), 男, 陕西省人, 主要从事核设备设计及研究工作。email: xichennice@qq.com
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(42141003); 广东省基础与应用基础研究基金深圳市联合基金项目(2021B1515120080); 南方科技大学深圳海洋地球古菌组学重点实验室项目(ZDSYS201802081843490); 广东大学生科技创新培育专项资金资助项目(pdjh2022c0029)
Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys
XI Chen1( ), LIN Zongxuan2, SA Rula3, DENG Xi1, LIU Qiang1, NI Liang1, LUO Laicai4, MA Teng5, XIE Zhijie6, CHEN Siruo2, CHEN Songze3(
), LIN Zongxuan2, SA Rula3, DENG Xi1, LIU Qiang1, NI Liang1, LUO Laicai4, MA Teng5, XIE Zhijie6, CHEN Siruo2, CHEN Songze3( )
)
- 1. China Nuclear Power Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd., Shenzhen 518000, China
2. Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Marine Archaea Geo-Omics, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
3. Shenzhen Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Center of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen 518049, China
4. Shenzhen Lightsun Industry Co. Ltd., Shenzhen 518000, China
5. Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
6. Department of Ocean Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518005, China
-
Received:2023-08-29Revised:2023-09-26Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-07-22 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42141003); Key Program of Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund (Guangdong-Shenzhen Joint Fund)(2021B1515120080); Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Marine Archaea Geo-Omics, Southern University of Science and Technology(ZDSYS201802081843490); Special Funds for the Cultivation of Guangdong College Students’ Scientific and Technological Innovation(pdjh2022c0029)
摘要:
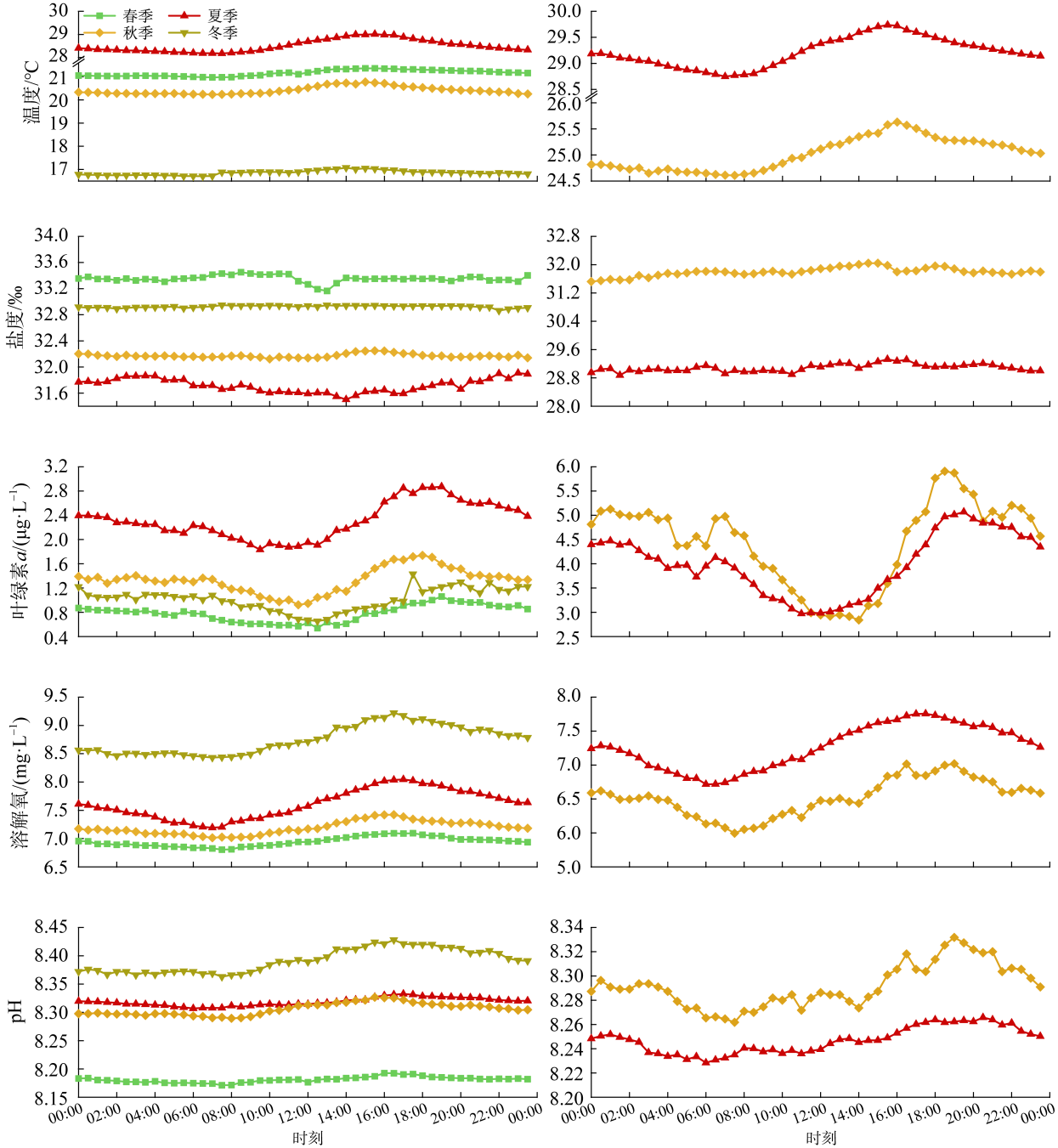
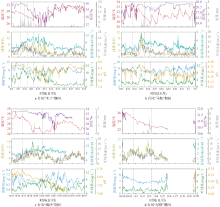
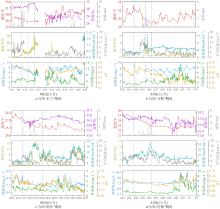
水质环境监测对了解海洋生态系统变化至关重要。本文利用2022—2023年期间位于大亚湾西南部海域的2个浮标的连续监测数据, 分析了水质环境的时间序列变化。结果表明, 大亚湾西南部海域的温度、盐度可能受太阳辐射与降水的影响, 具有明显的季节性差异, 即夏季温度高、盐度低, 冬季温度低、盐度较高; 而Chl a具有明显的昼夜节律, 溶解氧和pH存在相似的日变化模式。在夏、秋季, 大鹏澳较杨梅坑海域呈现出高温、低盐、低溶解氧、低pH和高Chl a的特点。Pearson相关性分析表明, 夏、秋季的温度、盐度、溶解氧、pH和Chl a之间存在显著的相关性, 且存在区域差异, 湾口附近, 海浪、上升流等水体运动可能是主要影响因素; 近岸, 径流输入可能是导致水质环境变化的主导因素。此外, 本文还记录了远距离台风引起的海浪及降水事件, 继而对大亚湾海域环境造成影响。解析沿海环境参数时间序列的变化特征, 对海洋生态系统的演变特征研究具有重要指示作用。
引用本文
奚琛, 林宗轩, 萨如拉, 邓玺, 刘强, 倪亮, 罗来才, 马腾, 谢智杰, 陈思若, 陈松泽. 基于双浮标连续监测资料分析大亚湾西南部海域水体环境变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 153-164.
XI Chen, LIN Zongxuan, SA Rula, DENG Xi, LIU Qiang, NI Liang, LUO Laicai, MA Teng, XIE Zhijie, CHEN Siruo, CHEN Songze. Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 153-164.
表2
FB1环境参数季节平均值及秩(Z)和检验结果"
| 季节 | 环境参数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | DO/(mg·L−1) | pH | Chl a/(μg·L−1) | |
| 春季 | 21.16±2.18 | 33.35±1.28 | 6.95±0.74 | 8.18±0.20 | 0.79±0.36 |
| 夏季 | 28.51±2.48 | 31.72±2.82 | 7.61±0.86 | 8.32±0.16 | 2.31±1.52 |
| 秋季 | 20.41±2.63 | 32.17±0.81 | 7.19±0.67 | 8.31±0.10 | 1.33±1.15 |
| 冬季 | 16.82±0.59 | 32.93±0.06 | 8.75±1.14 | 8.39±0.10 | 1.03±0.45 |
| Z | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| P | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
表4
FB1和FB2环境参数夏、秋季平均值"
| 季节 | 环境参数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | DO/(mg·L−1) | pH | Chl a/(μg·L−1) | |
| FB1_夏季 | 28.51±2.48 | 31.72±2.82 | 7.61±0.86 | 8.32±0.16 | 2.31±1.52 |
| FB1_秋季 | 20.41±2.63 | 32.17±0.81 | 7.19±0.67 | 8.31±0.10 | 1.33±1.15 |
| FB2_夏季 | 29.21±2.87 | 29.08±3.21 | 7.26±0.97 | 8.24±0.12 | 4.00±2.85 |
| FB2_秋季 | 25.02±0.52 | 31.80±0.87 | 6.52±0.76 | 8.29±0.05 | 4.45±1.97 |
| [1] |
曹公平, 宋金宝, 樊伟, 2013. 2007年长江口邻近海域夏季上升流演变机制研究[J]. 海洋科学, 37(1): 102-112.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈飞羽, 2016. 大鹏澳海域微表层与次表层浮游植物光合色素时空分布特征研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈其焕, 庄亮钟, 陈兴群, 1990. 大亚湾叶绿素a与初级生产力[C]// 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 自然资源部第三海洋研究所:198-209.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈希荣, 2019. 2015年夏季珠江口区域水文特征的观测与分析[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
黄云峰, 江涛, 冯佳和, 等, 2012. 珠江口广州海域叶绿素a分布特征及环境调控因素[J]. 海洋环境科学, 31(3): 379-384, 404.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
孔祥鹏, 2014. 辽东湾顶自净能力季节变化与排污调控策略[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
李立, 曾刚, 许金殿, 1990a. 大亚湾1987年夏季冷水的入侵现象[C]// 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 自然资源部第三海洋研究所:95-99.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李立, 张炳凯, 曾刚, 1990b. 大亚湾的海流特征[C]// 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 自然资源部第三海洋研究所:87-94.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李禹辉, 邱云, 杨龙奇, 等, 2021. 大亚湾及其邻近海域夏季温度、盐度的分布特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 40(2): 284-292.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
林凯荣, 何艳虎, 雷旭, 等, 2013. 深圳市1960-2009年降雨时空变化分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 3(3): 18-23.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
林志兰, 2006. 海湾富营养化非点源污染的评估与控制研究——以福建罗源湾为例[D]. 厦门: 国家海洋局第三海洋研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
牟新悦, 陈敏, 张琨, 等, 2017. 夏季大亚湾悬浮颗粒有机物碳、氮同位素组成及其物源指示[J]. 海洋学报, 39(2): 39-52.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
宋国栋, 石晓勇, 祝陈坚, 2007. 春季黄海溶解氧的平面分布特征及主要影响因素初探[J]. 海洋环境科学, 26(6): 534-536.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
孙丽华, 陈浩如, 彭云辉, 等, 2003. 大亚湾大鹏澳周边河流中营养盐的分布及入海通量的估算[J]. 台湾海峡, 22(2): 211-217.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
田媛, 李涛, 胡思敏, 等, 2020. 广东省沿岸海域藻华发生的时空特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 39(1): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
王盼盼, 2015. 长江口及邻近海域沉积物再悬浮对水体营养盐的影响研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
王友绍, 王肇鼎, 黄良民, 2004. 近20年来大亚湾生态环境的变化及其发展趋势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 23(5): 85-95.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
吴仁豪, 蔡树群, 王盛安, 等, 2007. 大亚湾海域潮流和余流的三维数值模拟[J]. 热带海洋学报, 26(3): 18-23.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
谢福武, 刘华雪, 黄洪辉, 等, 2018. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构对温排水和营养盐输入的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(3): 55-64.
doi: 10.11978/2017083 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2017083 |
|
| [20] |
许金电, 黄奖, 邱云, 等, 2015. 浙闽沿岸水的空间结构特征及生消过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(1): 1-7.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.01.001 |
|
|
|
| [21] |
杨文超, 黄道建, 陈继鑫, 等, 2020. 大亚湾海域2009-2018年重金属时空分布及污染评价[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 52(5): 65-75.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
殷建平, 王友绍, 徐继荣, 等, 2006. 大亚湾温跃层形成及其对有关环境要素的影响[J]. 海洋通报, 25(4): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
曾流明, 1986. 粤东沿岸上升流迹象的初步分析[J]. 热带海洋, 5(1): 68-73.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
张炳楷, 曾刚, 李立, 1990. 大亚湾的水温和盐度[C]// 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 自然资源部第三海洋研究所: 67-74.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
郑利涛, 2019. 深圳大亚湾水质模拟与风险扩散预测研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
郑哲昊, 庄伟, 孙振宇, 等, 2020. 大亚湾及其邻近海域冬季温度、盐度的分布及日变化特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 39(1): 71-79.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
钟保粦, 1995. 用5天滑动平均气温作深圳市的四季划分[J]. 气象, 21(6): 22-23.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
朱明, 张学成, 茅云翔, 等, 2003. 温度、盐度及光照强度对海链藻(Thalassiosira sp. )生长的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 27(12): 58-61.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
pmid: 15361622 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [1] | 曾维特, 张东强, 刘兵, 杨永鹏, 张航飞, 吴多誉, 王晓林. 海南岛北部海湾表层海水重金属分布特征、主控因素及污染评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 156-167. |
| [2] | 孙翠慈, 岳维忠, 赵文杰, 王友绍. 大亚湾表层沉积物碳水化合物活性酶基因分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [3] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [4] | 姜迅, 武文, 宋德海. 大亚湾水质对人类活动响应的关键控制指标识别和量化解析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 182-191. |
| [5] | 陈靖夫, 钟瑜, 王磊, 郭雨沛, 邱大俊. 环境DNA分析大亚湾夜光藻藻华对真核浮游生物群落的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [6] | 张婉茹, 刘庆霞, 黄洪辉, 覃晓青, 李佳俊, 陈建华. 2020年冬季大亚湾西南海域主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [7] | 李傲, 冯洋, 王云涛, 薛惠洁. 基于OC-CCI数据的南海高叶绿素a浓度水域面积的时空变化研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 77-89. |
| [8] | 李尧, 向晨晖, 江志坚, 宋星宇. 大亚湾夏季浮游群落生产代谢特征及其影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 83-92. |
| [9] | 向晨晖, 刘甲星, 柯志新, 周林滨, 谭烨辉. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构和种类组成对淡澳河河口水加富的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(2): 49-60. |
| [10] | 张立明, 谭烨辉, 李佳俊, 黄小平, 刘甲星. 大亚湾夏季浮游植物群落结构及对淡澳河输入的响应特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [11] | 王卉,李恒翔,李路,严岩. 大亚湾大型海藻丛的大角玻璃钩虾种群分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(4): 52-58. |
| [12] | 谢福武, 宋星宇, 谭烨辉, 谭美婷, 黄亚东, 刘华雪. 模拟升温和营养盐加富对大亚湾浮游生物群落代谢的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(2): 48-57. |
| [13] | 徐东海, 王利杰, 姚永坚, 孙珍, 邱宁. 礼乐盆地碳酸盐岩时空分布特征及构造意义[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(6): 49-62. |
| [14] | 陈旭阳, 刘保良. 海洋在线监测浮标在赤潮监测中的应用研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(5): 20-24. |
| [15] | 庄晓珊, 桓清柳, 彭莹, 王节亮, 庞仁松, 周凯. 深圳东部近岸海域溶解氧的时空分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(5): 98-105. |
|
||