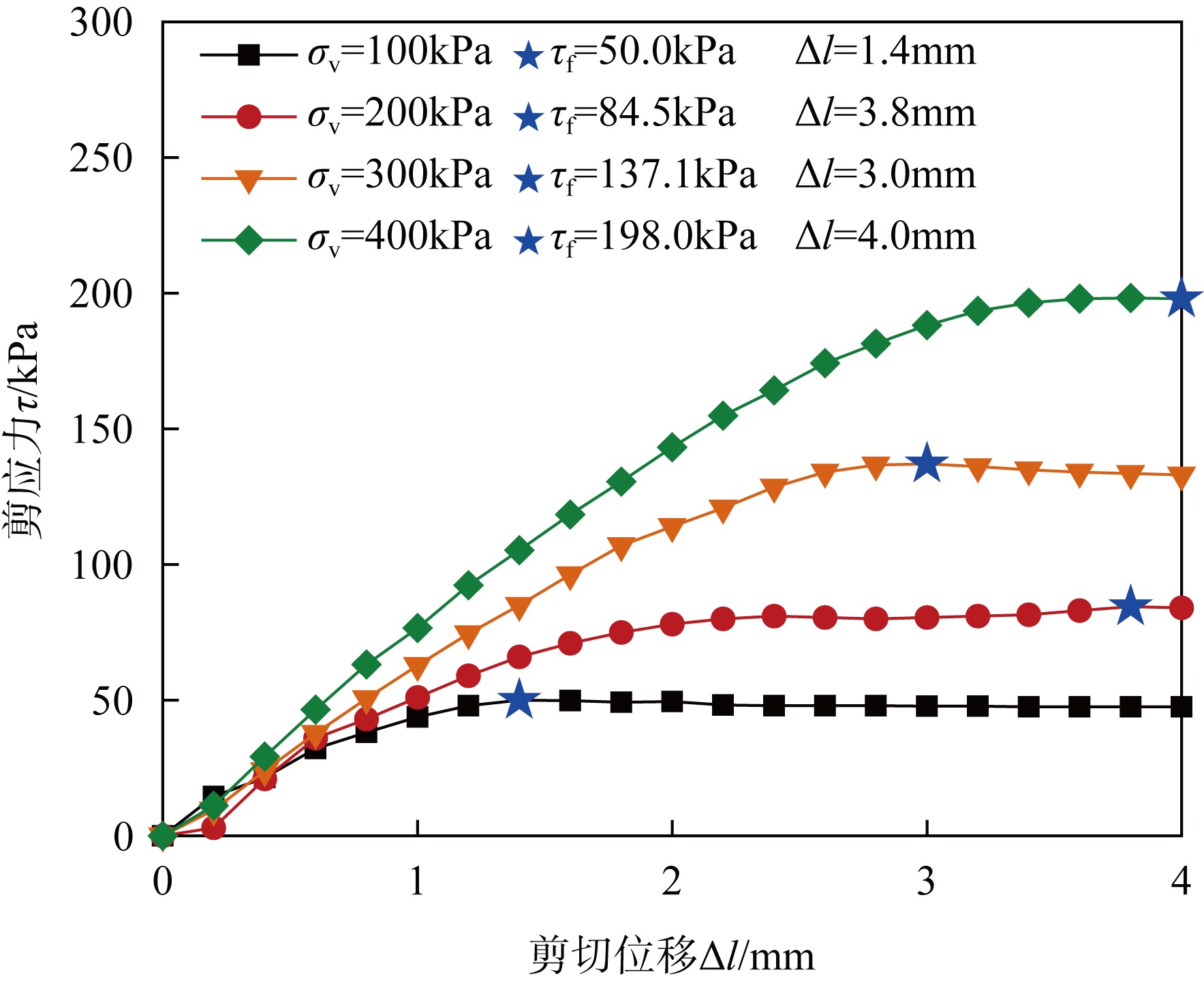
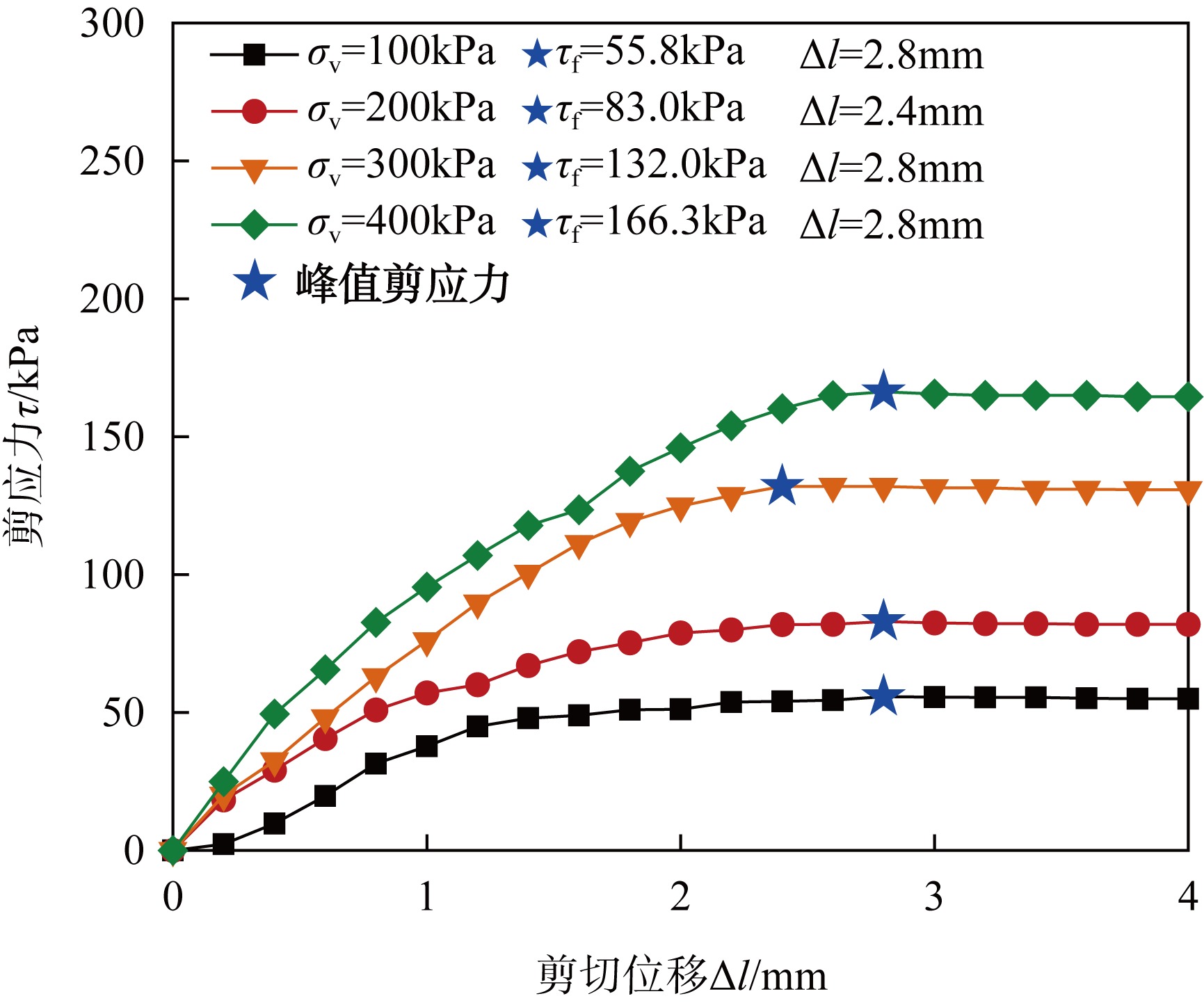
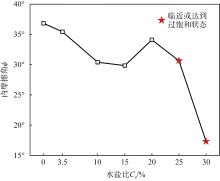
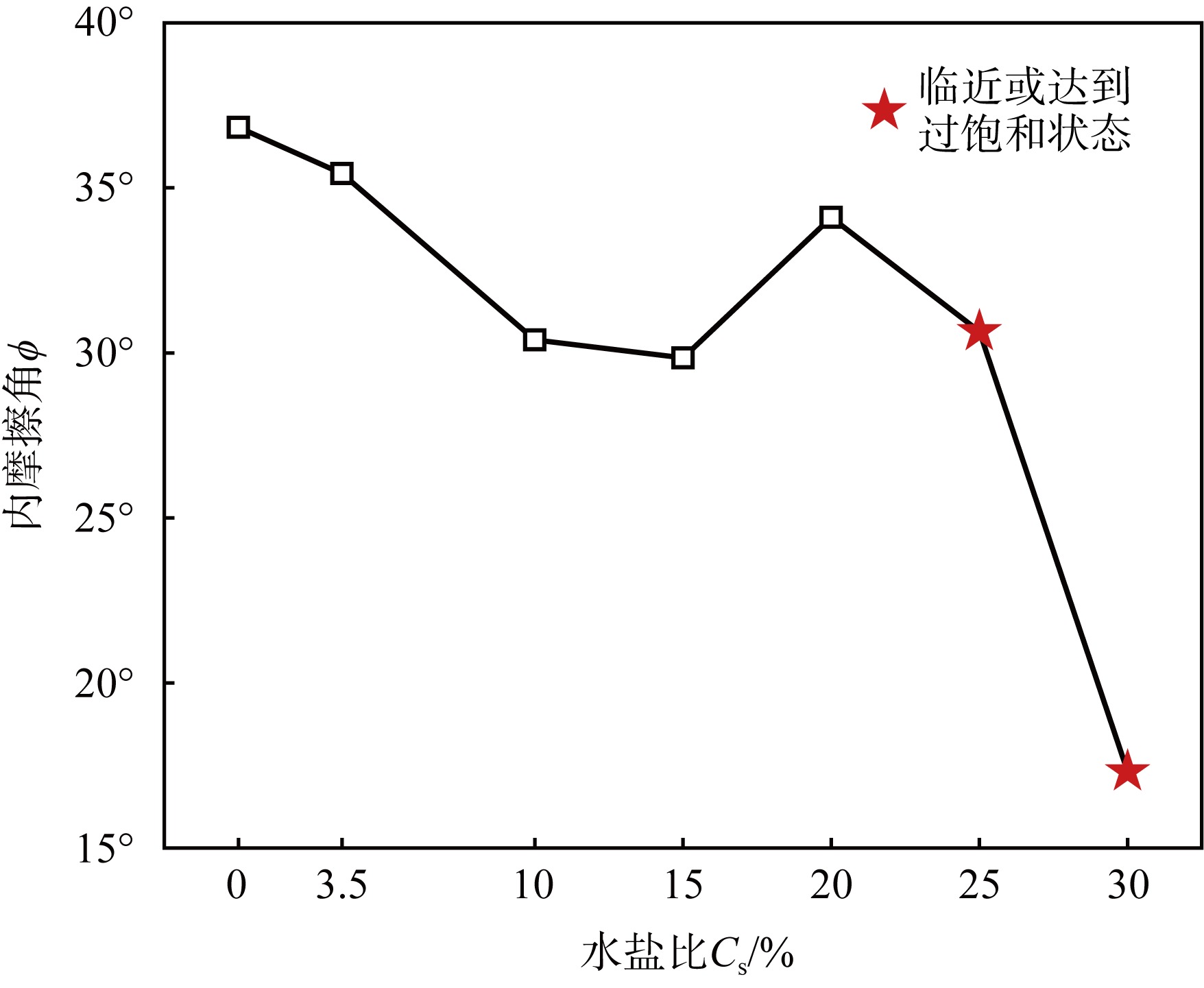
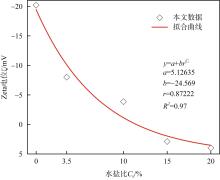
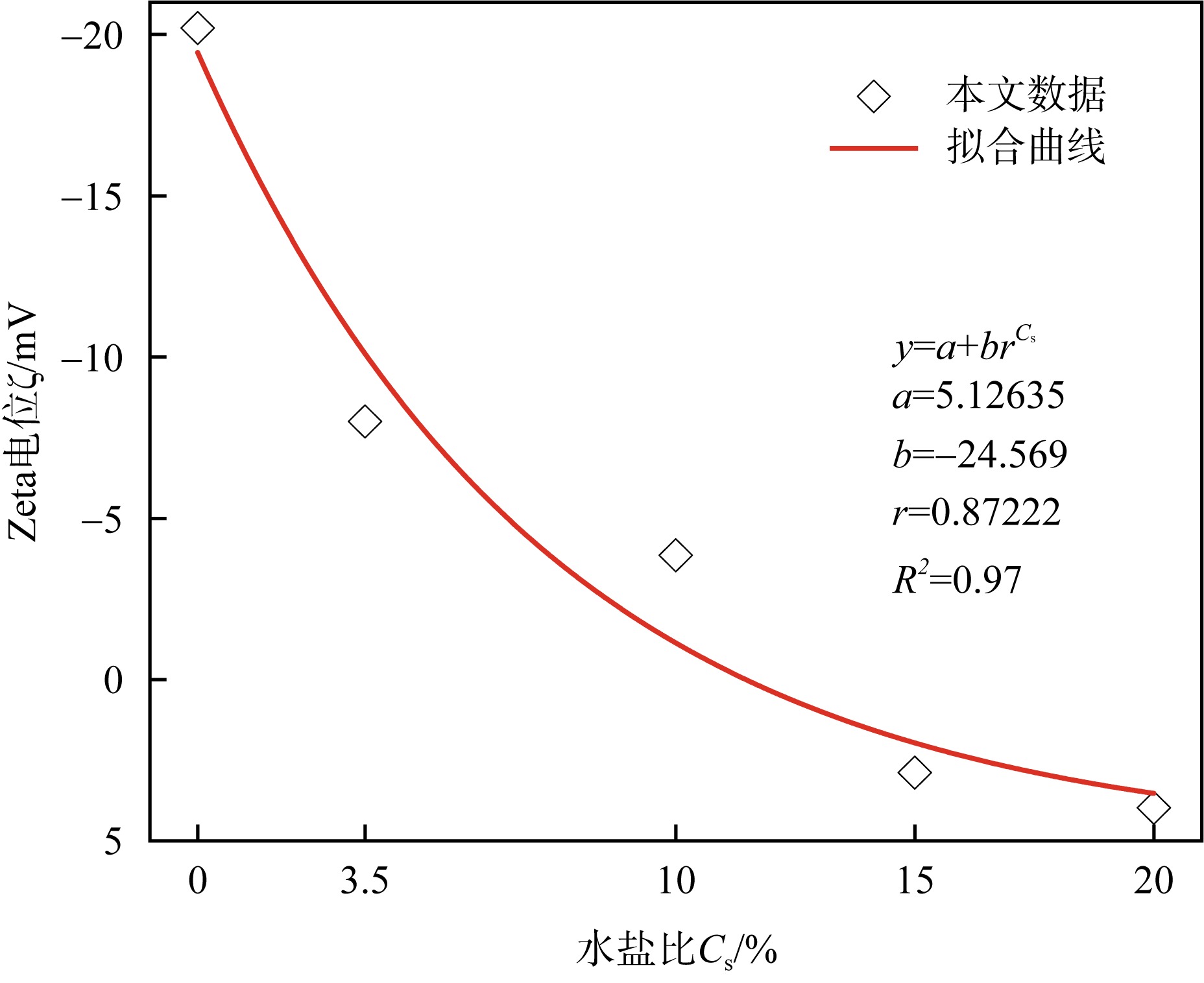
| [1] |
陈宾, 邓坚, 胡杰铭, 等, 2022, 钙质砂一维蠕变分形破碎特性宏微观试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 43(7): 1781-1790, 1853.
|
|
CHEN BIN, DENG JIAN, HU JIEMING, et al, 2022. Macroscopic and microscopic experimental study on fractal fragmentation characteristics of calcareous sand during one-dimensional compression creep[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 43(7): 1781-1790, 1853 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
陈炜韬, 王明年, 王鹰, 等, 2006. 含盐量及含水量对氯盐盐渍土抗剪强度参数的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学, 27(4): 1-5.
|
|
CHEN WEITAO, WANG MINGNIAN, WANG YING, et al, 2006. Influence of salt content and water content on the shearing strength parameters of chlorine saline soil[J]. China Railway Science, 27(4): 1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
谌民, 2019. 钙质粉土物理力学特性及其对钙质砂强度的弱化机理研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学.
|
|
CHEN MIN, 2019. Research on physical and mechanical properties of calcareous silt and its weakening mechanism of calcareous sand strength[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
雷学文, 丁豪, 王新志, 等, 2021. 钙质粉土的固结特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 42(4): 909-920.
|
|
LEI XUEWEN, DING HAO, WANG XINZHI, et al, 2021. Experimental study of consolidation properties of calcareous silt[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 42(4): 909-920 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
李洪良, 樊恒辉, 党进谦, 等, 2009. 介质环境中阳离子和酸碱度变化对粘土分散性的影响[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 20(6): 26-29.
|
|
LI HONGLIANG, FAN HENGHUI, DANG JINQIAN, et al, 2009. Effect of cation and pH value on dispersivity of clay in the medium environment[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 20(6): 26-29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
李育林, 2022. 海洋环境下硫酸盐-镁盐对砂浆中氯离子扩散影响研究[J]. 公路工程, 47(5): 150-155.
|
|
LI YULIN, 2022. Effects of sulfate-magnesium salt on the chloride ion diffusion in mortar under marine environment[J]. Highway Engineering, 47(5): 150-155 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
卢佩霞, 徐永福, 陈志明, 等, 2015. 滨海相盐渍土强度机理分析[J]. 公路交通科技, 32(8): 51-58.
|
|
LU PEIXIA, XU YONGFU, CHEN ZHIMING, et al, 2015. Analysis of strength mechanism of coastal saline soil[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 32(8): 51-58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
吕海敏, 2016. 盐分对遗址土体性质影响探究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学.
|
|
LÜ HAIMIN, 2016. Explore the impact of properties about soil sites on salts[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
马杰, 2022. 激光粒度分析仪在土工颗粒分析试验中的应用[J]. 土工基础, 36(3): 466-470, 496.
|
|
MA JIE, 2022. Application of laser particle size analyzer in the grain size distribution test for geotechnical purposes[J]. Soil Engineering and Foundation, 36(3): 466-470, 496 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
彭昌盛, 张倩, 徐兴永, 等, 2010. 团聚-分散行为对悬浮液Zeta电位的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 40(10): 121-126.
|
|
PENG CHANGSHENG, ZHANG QIAN, XU XINGYONG, et al, 2010. Effect of aggregation and dispersion on zeta potential of suspensions[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 40(10): 121-126 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
王文孟, 郭少春, 崔自治, 2014. 可溶盐对黄土触变性的作用效应研究[J]. 岩土力学, 35(12): 3385-3388, 3395.
|
|
WANG WENMENG, GUO SHAOCHUN, CUI ZIZHI, 2014. Study of effect of soluble salt on loess thixotropy[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 35(12): 3385-3388, 3395 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
王新志, 王星, 胡明鉴, 等, 2017. 吹填人工岛地基钙质粉土夹层的渗透特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 38(11): 3127-3135.
|
|
WANG XINZHI, WANG XING, HU MINGJIAN, et al, 2017. Study of permeability of calcareous silty layer of foundation at an artificial reclamation island[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 38(11): 3127-3135 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
杨德欢, 颜荣涛, 韦昌富, 等, 2016. 粉质黏土强度指标的水化学敏感性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 37(12): 3529-3536.
|
|
YANG DEHUAN, YAN RONGTAO, WEI CHANGFU, et al, 2016. A study of water chemical sensitivity of strength indices of silty clay[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 37(12): 3529-3536 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
张晨阳, 谌民, 胡明鉴, 等, 2019. 细颗粒组分含量对钙质砂抗剪强度的影响[J]. 岩土力学, 40(S1): 195-202.
|
|
ZHANG CHENYANG, CHEN MIN, HU MINGJIAN, et al, 2019. Effect of fine particles content on shear strength of calcareous sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(S1): 195-202 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
张彤炜, 2018. 盐分对人工软黏土物理力学行为影响机制与本构模型[D]. 南京: 东南大学.
|
|
ZHANG TONGWEI, 2018. Pore water salinity effect on the physical mechanical behavior and constitutive model of artificial soft clay[D]. Nanjing: Dongnan University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
赵续月, 颜荣涛, 梁维云, 等, 2017. 渗透吸力对饱和黏土变形-强度特性的影响[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 37(3): 451-455.
|
|
ZHAO XUYUE, YAN RONGTAO, LIANG WEIYUN, et al, 2017. Effect of osmotic suction on strength characteristics of saturated clay[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 37(3): 451-455 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 2019. GB/T 50123-2019 土工试验方法标准[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社: 110-113.
|
|
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, 2019. GB/T 50123-2019 Standard for geotechnical testing method[S]. Beijing: Beijing China Planning Publishing House: 110-113 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
CHAPMAN D L, 1913. LI. A contribution to the theory of electrocapillarity[J]. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 25(148): 475-481.
|
| [19] |
CHEN BIN, CHAO DAIJIE, WU WENJUAN, et al, 2019. Study on creep mechanism of coral sand based on particle breakage evolution law[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 21(4): 1201-1214.
|
| [20] |
CHEN BIN, HU JIEMING, 2020. Fractal behavior of coral sand during creep[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 8: 134.
|
| [21] |
GOUY M, 1910. Sur la constitution de la charge électrique à la surface d'un electrolyte[J]. Journal de Physique Théorique et Appliquée, 9(1): 457-468.
|
| [22] |
JANG CHUNYONG, DING XUEMING, FANG HUAQIANG, et al, 2023. The undrained shear behavior of clean coral silt and coral silt-sand mixtures[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 51(5): 3596-3611.
|
| [23] |
MOHIUDDIN M A, HOSSAIN M S, KIM Y H, et al, 2022. Insight into the behavior of a caisson anchor under cyclic loading in calcareous silt[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 148(7): 04022047.
|
| [24] |
MOORE R, 1991. The chemical and mineralogical controls upon the residual strength of pure and natural clays[J]. Géotechnique, 41(1): 35-47.
|
| [25] |
SHEN JIANHUA, WANG XINZHI, WANG XING, et al, 2021. Effect and mechanism of fines content on the shear strength of calcareous sand[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 80(10): 7899-7919.
|
| [26] |
SHORTEN G G, 1995. Quasi-overconsolidation and creep phenomena in shallow marine and estuarine organo-calcareous silts, Fiji[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 32(1): 89-105.
|
| [27] |
WANG XING, CUI JIE, WU YANG, et al, 2021. Mechanical properties of calcareous silts in a hydraulic fill island-reef[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 39(1): 1-14.
|
| [28] |
WANG XINZHI, DING HAOZHEN, WEN DONGSHENG, et al, 2022. Vibroflotation method to improve silt interlayers of dredged coral sand ground-a case study[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 81: 472.
|
| [29] |
WANG XINZHI, JIAO YUYONG, WANG REN, et al, 2011. Engineering characteristics of the calcareous sand in Nansha Islands, South China Sea[J]. Engineering Geology, 120(1-4): 40-47.
|
| [30] |
WARKENTIN B P, YONG R N, 1960. Shear strength of montmorillonite and kaolinite related to interparticle forces[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 9(1): 210-218.
|
| [31] |
YUKSELEN Y, ERZIN Y, 2008. Artificial neural networks approach for zeta potential of Montmorillonite in the presence of different cations[J]. Environmental Geology, 54(5): 1059-1066.
|
 ), LI Yuancheng1, ZHANG Zhao2(
), LI Yuancheng1, ZHANG Zhao2( ), HU Jieming3
), HU Jieming3