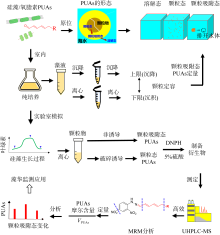
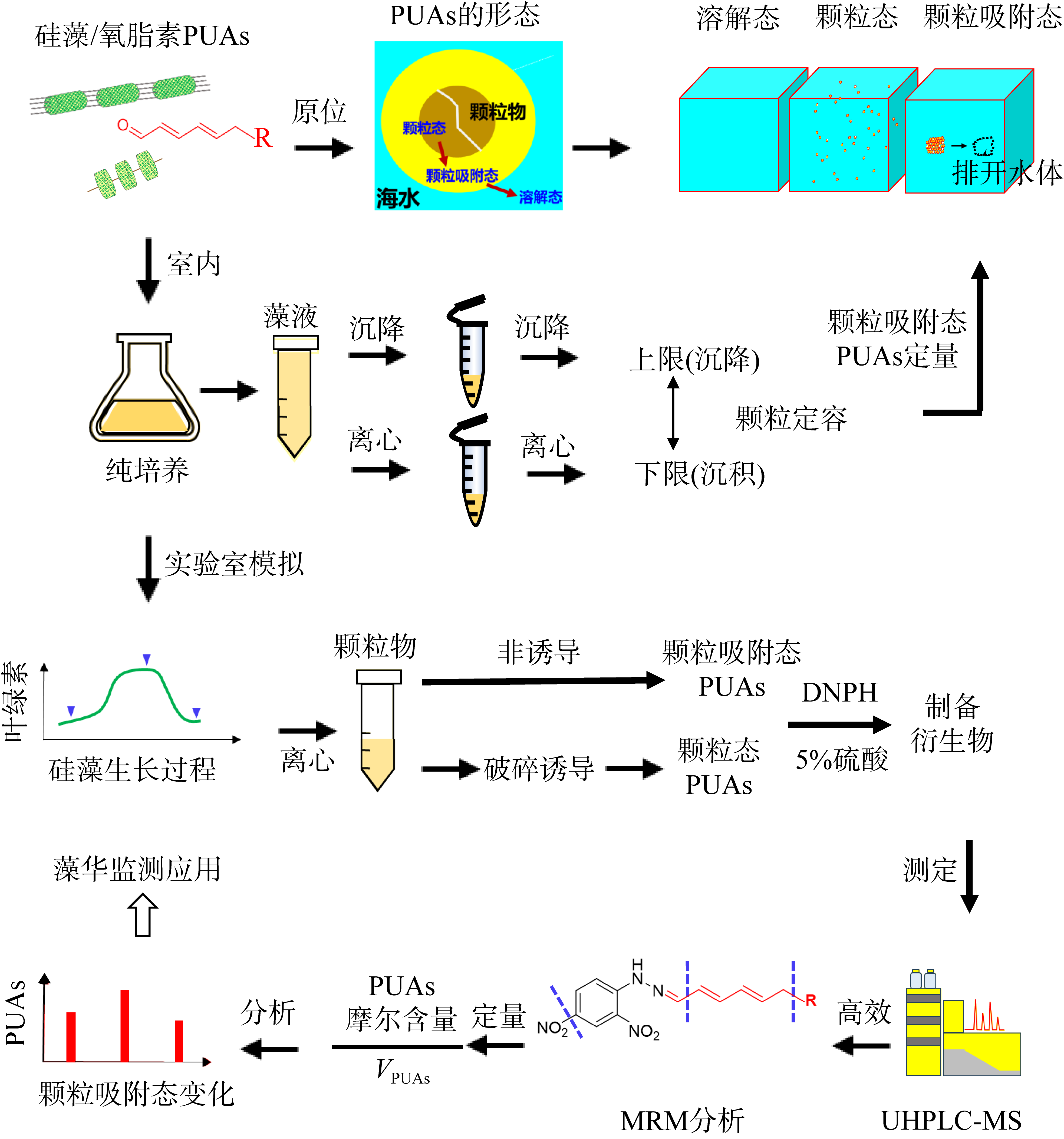
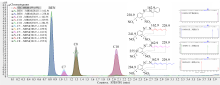
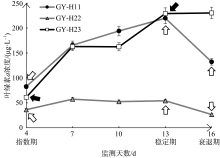
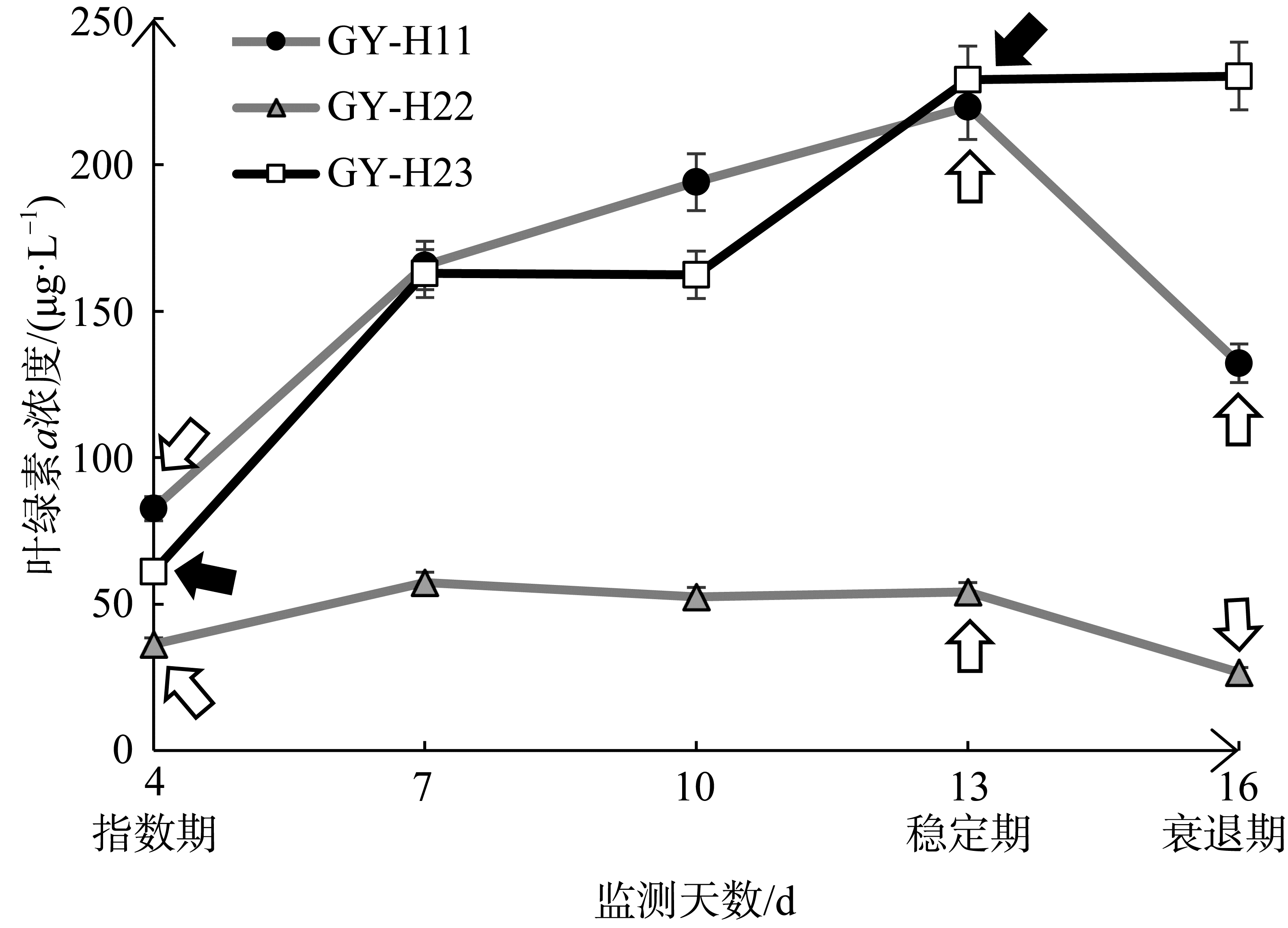
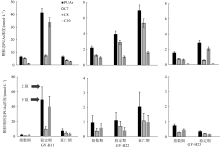
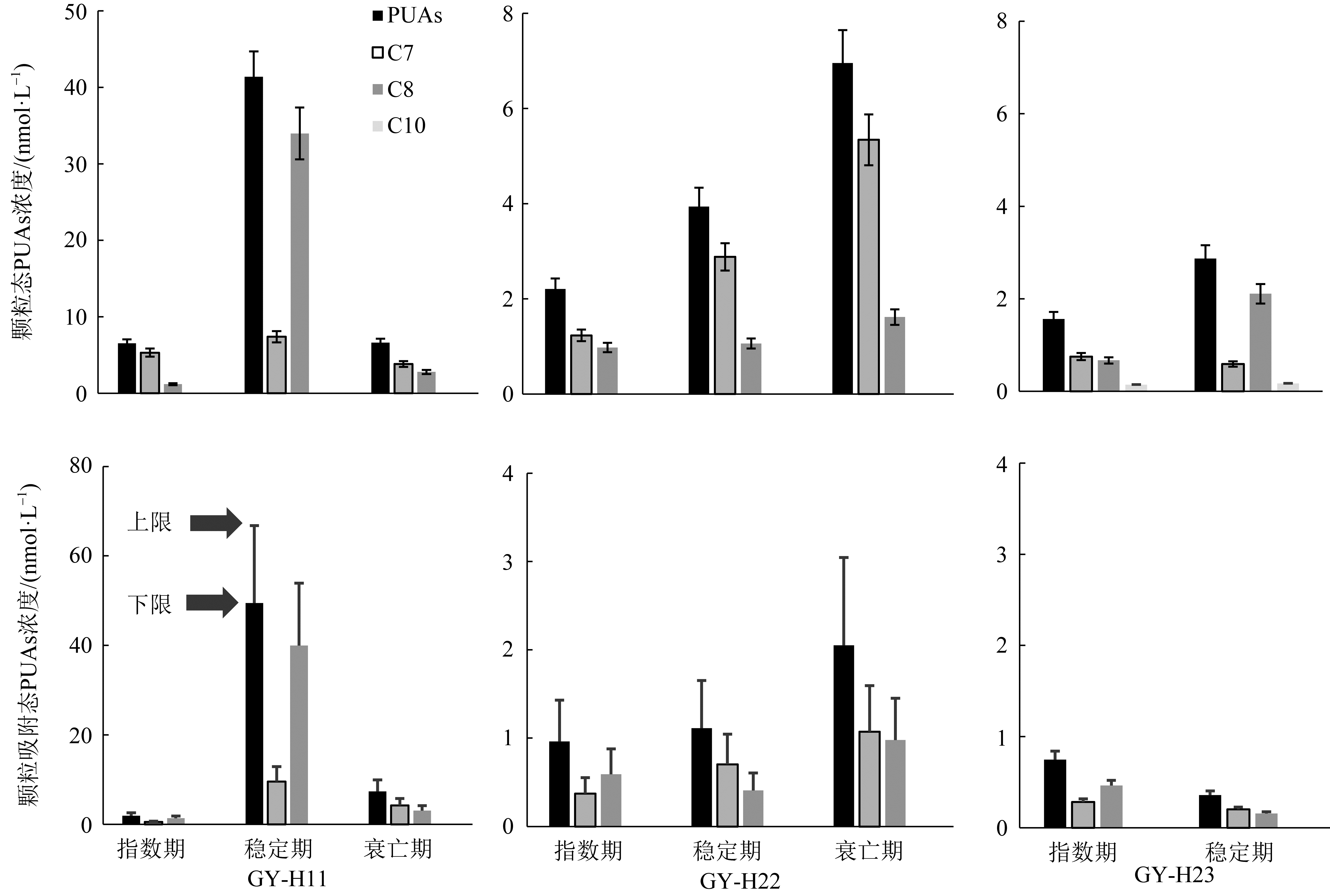
| [1] |
陈楠生, 张梦佳, 2021. 中国海洋浮游植物和赤潮物种的生物多样性研究进展(三): 南海[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 52(2): 385-435.
|
|
CHEN NANSHENG, ZHANG MENGJIA, 2021. Advances in the study of biodiversity of phytoplankton and red tide species in China (ⅲ): the South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 52(2): 385-435 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
葛在名, 吴正超, 刘子嘉, 等, 2020. 去吸附法测定珠江口颗粒附着细菌的丰度特征及其环境因子耦合研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 39(4): 505-510.
|
|
GE ZAIMING, WU ZHENGCHAO, LIU ZIJIA, et al, 2020. Using detaching method to determine the abundance of particle-attached bacteria from the Pearl River Estuary and its coupling relationship with environmental factors[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 39(4): 505-510 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
黄邦钦, 肖武鹏, 柳欣, 2021. 中国边缘海浮游植物群落时空格局与演变趋势[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 60(2): 390-397.
|
|
HUANG BANGQIN, XIAO WUPENG, LIU XIN, 2021. Spatial-temporal distributions and successional patterns of phytoplankton communities in the Chinese marginal seas[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 60(2): 390-397 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
时免免, 赵艺, 常原恺, 等, 2023. 氧脂素信号调控气孔运动的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 59(11): 1987-1997.
|
|
SHI MIANMIAN, ZHAO YI, CHANG YUANKAI, et al, 2023. Advances in the understanding of stomatal regulation by oxylipin signals[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 59(11): 1987-1997 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
王慧, 蔡润林, 甘永亮, 等, 2022. 海洋浮游植物和藻际细菌的相互作用关系及其在海洋生态系统中的重要作用[J]. 汕头大学学报(自然科学版), 37(3): 3-21.
|
|
WANG HUI, CAI RUNLIN, GAN YONGLIANG, et al, 2022. The interactions between marine phytoplankton and bacterioplankton in phycosphere and their important roles in marine ecosystem[J]. Journal of Shantou University (Natural Science Edition), 37(3): 3-21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
张增虎, 唐丽丽, 张永雨, 2018. 海洋中藻菌相互关系及其生态功能[J]. 微生物学通报, 45(9): 2043-2053.
|
|
ZHANG ZENGHU, TANG LILI, ZHANG YONGYU, 2018. Algae-bacteria interactions and their ecological functions in the ocean[J]. Microbiology China, 45(9): 2043-2053 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
郑承志, 左丽明, 马旺, 等, 2021. 不同温度下抑食抑食金球藻、中肋骨条藻和海洋卡盾藻间的相互作用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40: 124-31.
doi: 10.11978/2020154
|
|
ZHENG CHENGZHI, ZUO LIMING, MA WANG, et al, 2021. Interactions among Aureococcus anophagefferens, Skeletonema costatum, and Chattonella marina under different temperatures[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 40: 124-31. (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
ARMBRUST E V, 2009. The life of diatoms in the world’s oceans[J]. Nature, 459(7244): 185-192.
|
| [9] |
BARTUAL A, ORTEGA M J, 2013. Temperature differentially affects the persistence of polyunsaturated aldehydes in seawater[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 10(5): 403.
|
| [10] |
CUTIGNANO A, LAMARI N, D’IPPOLITO G, et al, 2011. Lipoxygenase products in marine diatoms: a concise analytical method to explore the functional potential of oxylipins1[J]. Journal of Phycology, 47(2): 233-243.
|
| [11] |
D’IPPOLITO G, NUZZO G, SARDO A, et al, 2018. Lipoxygenases and lipoxygenase products in marine diatoms[M]// MOORE B S. Marine Enzymes and Specialized Metabolism - Part B. Amsterdam: Academic Press: 69-100.
|
| [12] |
DUNKER S, WILHELM C, 2018. Cell wall structure of coccoid green algae as an important trade-off between biotic interference mechanisms and multidimensional cell growth[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9: 719.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00719
pmid: 29706940
|
| [13] |
EDWARDS B R, BIDLE K D, VAN MOOY B A S, 2015. Dose-dependent regulation of microbial activity on sinking particles by polyunsaturated aldehydes: Implications for the carbon cycle[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(19): 5909-5914.
|
| [14] |
IANORA A, MIRALTO A, 2010. Toxigenic effects of diatoms on grazers, phytoplankton and other microbes: a review[J]. Ecotoxicology, 19(3): 493-511.
|
| [15] |
KUHLISCH C, DEICKE M, UEBERSCHAAR N, et al, 2017. A fast and direct liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method to detect and quantify polyunsaturated aldehydes and polar oxylipins in diatoms[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 15(1): 70-79.
|
| [16] |
MA XIAO, JOHNSON K B, GU BOWEI, et al, 2022. The in situ release of algal bloom populations and the role of prokaryotic communities in their establishment and growth[J]. Water Research, 219: 118565.
|
| [17] |
MALVIYA S, SCALCO E, AUDIC S, et al, 2016. Insights into global diatom distribution and diversity in the world’s ocean[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(11): E1516-E1525.
|
| [18] |
MIRALTO A, BARONE G, ROMANO G, et al, 1999. The insidious effect of diatoms on copepod reproduction[J]. Nature, 402: 173-176.
|
| [19] |
PARSONS T R, MAITA Y, LALLI C M, 1984. A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis[M]. Oxford:Oxfordshire; New York: Pergamon Press.
|
| [20] |
POHNERT G, 2000. Wound-activated chemical defense in unicellular planktonic algae[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 39(23): 4352-4354.
|
| [21] |
RIBALET F, WICHARD T, POHNERT G, et al, 2007. Age and nutrient limitation enhance polyunsaturated aldehyde production in marine diatoms[J]. Phytochemistry, 68(15): 2059-2067.
pmid: 17575990
|
| [22] |
RIBALET F, VIDOUDEZ C, CASSIN D, et al, 2009. High plasticity in the production of diatom-derived polyunsaturated aldehydes under nutrient limitation: physiological and ecological implications[J]. Protist, 160(3): 444-451.
doi: 10.1016/j.protis.2009.01.003
pmid: 19386544
|
| [23] |
RUSSO E, CAMPOS A M, D’IPPOLITO G, et al, 2021. Implementation in lipid extraction and analysis from phytoplankton: Skeletonema marinoi as case study[J]. Marine Chemistry, 232: 103964.
|
| [24] |
SEYMOUR J R, AMIN S A, RAINA J B, et al, 2017. Zooming in on the phycosphere: the ecological interface for phytoplankton-bacteria relationships[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2: 17065.
doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.65
pmid: 28555622
|
| [25] |
VIDOUDEZ C, CASOTTI R, BASTIANINI M, et al, 2011. Quantification of dissolved and particulate polyunsaturated aldehydes in the Adriatic sea[J]. Marine Drugs, 9(4): 500-513.
doi: 10.3390/md9040500
pmid: 21731545
|
| [26] |
WANG ZHAOHUI, WANG CHAOFAN, LI WEIGUO, et al, 2021. Interspecies competition between Scrippsiella acuminata and three marine diatoms: Growth inhibition and allelopathic effects[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 237: 105878.
|
| [27] |
WICHARD T, POULET S A, HALSBAND-LENK C, et al, 2005a. Survey of the chemical defence potential of diatoms: screening of fifty species for α, β, γ, δ-unsaturated aldehydes[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 31(4): 949-958.
|
| [28] |
WICHARD T, POULET S A, POHNERT G, 2005b. Determination and quantification of alpha, beta, gamma, delta-unsaturated aldehydes as pentafluorobenzyl-oxime derivates in diatom cultures and natural phytoplankton populations: application in marine field studies[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 814(1): 155-161.
|
| [29] |
WU ZHENGCHAO, LI Q P, 2016. Spatial distributions of polyunsaturated aldehydes and their biogeochemical implications in the Pearl River Estuary and the adjacent northern South China Sea[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 147: 1-9.
|
| [30] |
WU ZHENGCHAO, LI Q P, DONG YUAN, et al, 2021b. High-resolution surveys of phytoplankton-derived polyunsaturated aldehydes at frontal zones outside a eutrophic estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 126(3): e2020JG005808.
|
| [31] |
WU ZHENGCHAO, LI Q P, GE ZAIMING, et al, 2021a. Impacts of biogenic polyunsaturated aldehydes on metabolism and community composition of particle-attached bacteria in coastal hypoxia[J]. Biogeosciences, 18(3): 1049-1065.
|
| [32] |
WU ZHENGCHAO, LI Q P, RIVKIN R B, et al, 2023. Role of diatom-derived oxylipins in organic phosphorus recycling during coastal diatom blooms in the northern South China Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 903: 166518.
|
| [33] |
ZHANG SHUWEN, ZHENG TINGTING, LUNDHOLM N, et al, 2021. Chemical and morphological defenses of Pseudo-Nitzschia multiseries in response to zooplankton grazing[J]. Harmful Algae, 104: 102033.
|
 ), 吴正超1(
), 吴正超1( ), 程远月1, 吴梅林1, 李芊1,3(
), 程远月1, 吴梅林1, 李芊1,3( )
)
 ), WU Zhengchao1(
), WU Zhengchao1( ), CHENG Yuanyue1, WU Meilin1, LI Qian1,3(
), CHENG Yuanyue1, WU Meilin1, LI Qian1,3( )
)