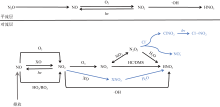
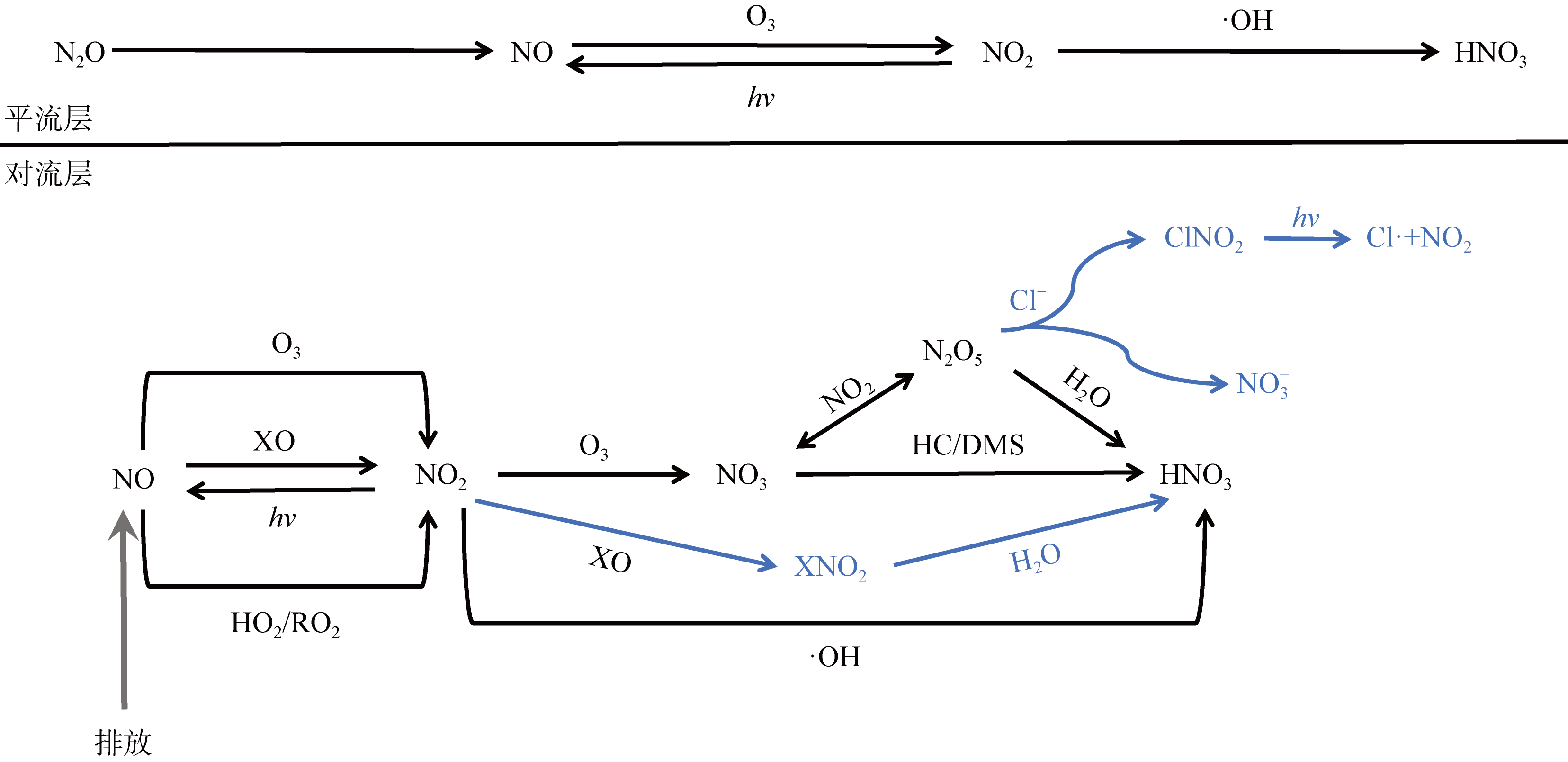
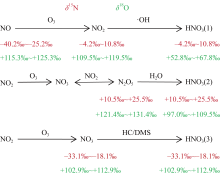
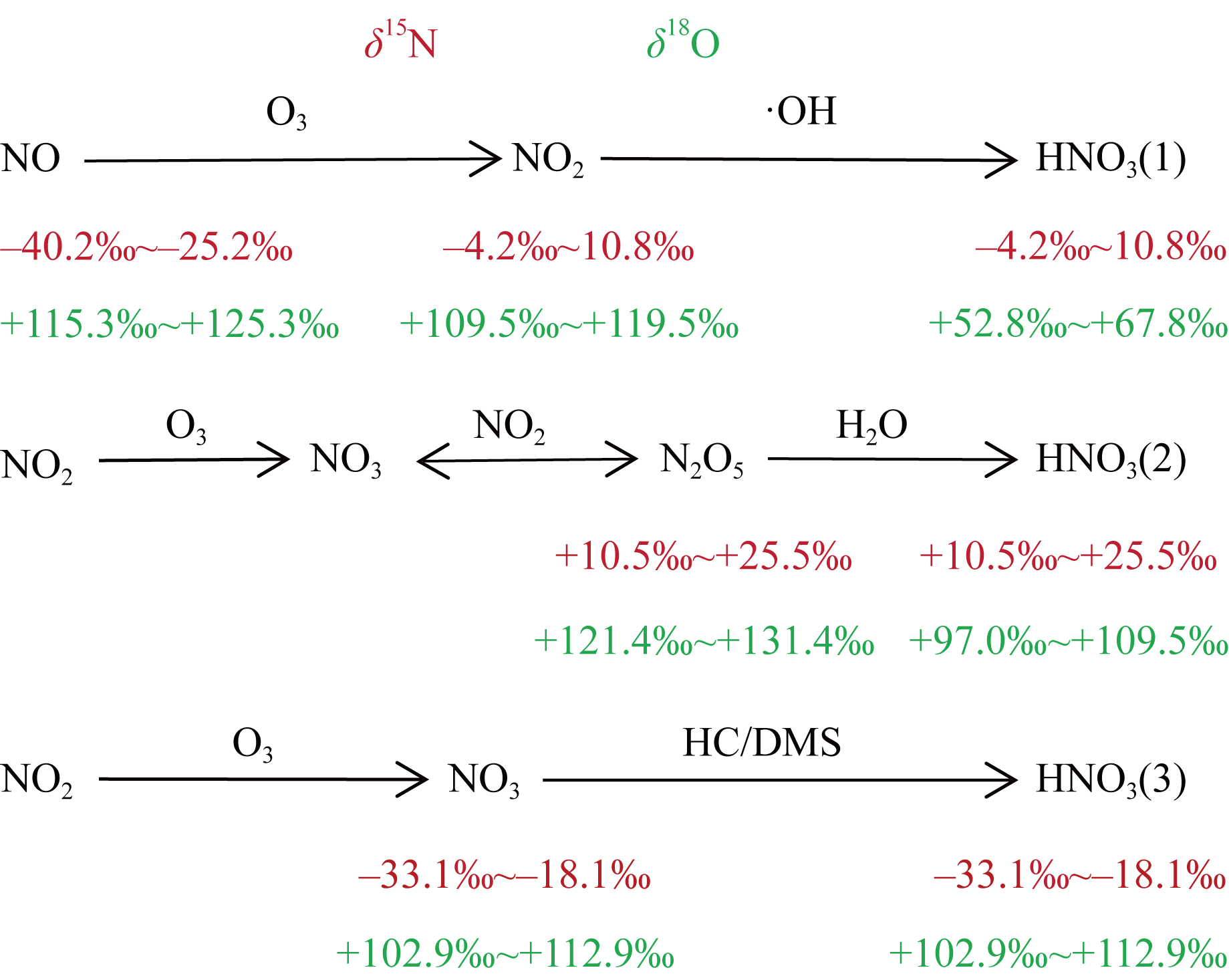
| [1] |
董鑫媛, 郭庆军, 魏荣菲, 等, 2020. 大气硝酸盐氧同位素异常及应用进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(3): 1022-1032.
|
|
DONG XINYUAN, GUO QINGJUN, WEI RONGFEI, et al, 2020. Research advances and applications on oxygen isotope anomaly in atmospheric nitrate[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(3): 1022-1032 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
李佩霖, 傅平青, 康世昌, 等, 2016. 大气气溶胶中的氮: 化学形态与同位素特征研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 35(1): 1-10.
|
|
LI PEILIN, FU PINGQING, KANG SHICHANG, et al, 2016. Research progress on nitrogen in atmospheric aerosols: Chemical speciation and isotopic characteristics[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 35(1): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
李亲凯, 杨周, 黄俊, 等, 2016. 大气颗粒物稳定同位素组成的研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(4): 1063-1071.
|
|
LI QINKAI, YANG ZHOU, HUANG JUN, et al, 2016. A review of stable isotopic compositions of atmospheric particulate matter[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35(4): 1063-1071 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
毛绪美, 罗泽娇, 李永勇, 等, 2005. 地下水硝酸盐氮同位素分析最新方法——细菌反硝化法[J]. 地球学报, 2005, 26(z1):44-47.
|
|
MAO XUMEI, LUO ZEJIAO, LI YONGYONG, et al, 2005. Bacterial denitrification: A new method for nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in groundwater[J]. ACTA GEOSCIENTICA, 26(Sup.): 44-47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
宋韦, 刘学炎, 2024. 地-气系统活性氮来源与转化的同位素示踪研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 35(9): 2362-2371.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202409.031
|
|
SONG WEI, LIU XUEYAN, 2024. Research progress on isotope tracing on the sources and transformations of reactive nitrogen in the earth-atmosphere system[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 35(9): 2362-2371 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202409.031
|
| [6] |
孙文青, 陆光华, 薛晨旺, 等, 2019. 基于稳定同位素技术识别河流硝酸盐污染源研究进展[J]. 四川环境, 38(3): 193-198.
|
|
SUN WENQING, LU GUANGHUA, XUE CHENWANG, et al, 2019. Research progress on identification of nitrate pollution sources in rivers by using stable isotope technique[J]. Sichuan Environment, 38(3): 193-198 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
王海潮, 唐明金, 谭照峰, 等, 2020. 硝酰氯的大气化学[J]. 化学进展, 32(10): 1535-1546.
doi: 10.7536/PC200304
|
|
WANG HAICHAO, TANG MINGJIN, TAN ZHAOFENG, et al, 2020. Atmospheric chemistry of nitryl chloride[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 32(10): 1535-1546 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.7536/PC200304
|
| [8] |
肖红伟, 肖化云, 龙爱民, 等, 2012. 贵阳地区大气降水中δ15N-$\mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}$组成及来源分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 32(4): 940-945.
|
|
XIAO HONGWEI, XIAO HUAYUN, LONG AIMIN, et al, 2012. Nitrogen isotopic composition and source of nitrate in precipitation at Guiyang[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 32(4): 940-945 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
尹希杰, 杨海丽, 崔坤磊, 等, 2023. 细菌反硝化法与化学转化法测试硝酸盐氮氧同位素对比研究[J]. 同位素, 36(2): 176-185.
|
|
YIN XIJIE, YANG HAILI, CUI KUNLEI, et al, 2023. A comparative study of nitrogen and oxygen isotopes of nitrate by bacterial denitrifier and chemical conversion[J]. Journal of Isotopes, 36(2): 176-185 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
张雯淇, 章炎麟, 2019. 大气硝酸盐中氧同位素异常研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 64(7): 649-662.
|
|
ZHANG WENQI, ZHANG YANLIN, 2019. Oxygen isotope anomaly (Δ17O) in atmospheric nitrate: a review[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 64(7): 649-662 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
朱艳宸, 李丽, 王鹏, 等, 2020. 海洋氮循环中稳定氮同位素变化与地质记录研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 35(2): 167-179.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.012
|
|
ZHU YANCHEN, LI LI, WANG PENG, et al, 2020. Progress in the study of marine stable nitrogen isotopic changes and its geological records[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 35(2): 167-179 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.012
|
| [12] |
ALEXANDER B, SHERWEN T, HOLMES C D, et al, 2020. Global inorganic nitrate production mechanisms: comparison of a global model with nitrate isotope observations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 20(6): 3859-3877.
|
| [13] |
ALTIERI K E, HASTINGS M G, GOBEL A R, et al, 2013. Isotopic composition of rainwater nitrate at Bermuda: the influence of air mass source and chemistry in the marine boundary layer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 118(19): 11304-11316.
|
| [14] |
ALTIERI K E, FAWCETT S E, HASTINGS M G, 2021. Reactive nitrogen cycling in the atmosphere and ocean[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 49: 523-550.
|
| [15] |
ANDERSON L A, SARMIENTO J L, 1994. Redfield ratios of remineralization determined by nutrient data analysis[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 8(1): 65-80.
|
| [16] |
BANGE H W, 2008. Gaseous nitrogen compounds (NO, N2O, N2, NH3) in the ocean[M]// CAPONED G, BRONKD A, MULHOLLANDM R, Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. Amsterdam: Academic Press: 51-94.
|
| [17] |
BERHANU T A, SAVARINO J, BHATTACHARYA S K, et al, 2012. 170 excess transfer during the NO2 + O3 → NO3 + O2 reaction[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 136(4): 044311.
|
| [18] |
BEYN F, MATTHIAS V, DÄHNKE K, 2014. Changes in atmospheric nitrate deposition in Germany: an isotopic perspective[J]. Environmental Pollution, 194: 1-10.
|
| [19] |
BROOKS P D, STARK J M, MCINTEER B B, et al, 1989. Diffusion method to prepare soil extracts for automated nitrogen-15 analysis[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 53(6): 1707-1711.
|
| [20] |
BURGER J M, JOYCE E, HASTINGS M G, et al, 2023. A seasonal analysis of aerosol NO- 3 sources and NOx oxidation pathways in the Southern Ocean marine boundary layer[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 23(10): 5605-5622.
|
| [21] |
CHANG C C, LANGSTON J, RIGGS M, et al, 1999. A method for nitrate collection for δ15N and δ18O analysis from waters with low nitrate concentrations[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 56(10): 1856-1864.
|
| [22] |
CHEN TING-YU, CHEN CHIA-LI, CHEN YI-CHI, et al, 2022. Source apportionment and evolution of N-containing aerosols at a rural cloud forest in Taiwan by isotope analysis[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 22(19): 13001-13012.
|
| [23] |
CHUANG MING-TUNG, WU CHANG-FU, LIN CHUAN-YAO, et al, 2022. Simulating nitrate formation mechanisms during PM2. 5 events in Taiwan and their implications for the controlling direction[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 269: 118856.
|
| [24] |
COSTA A W, MICHALSKI G, SCHAUER A J, et al, 2011. Analysis of atmospheric inputs of nitrate to a temperate forest ecosystem from Δ17O isotope ratio measurements[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(15): L15805.
|
| [25] |
DAVIDSON E A, KINGERLEE W, 1997. A global inventory of nitric oxide emissions from soils[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 48(1/2): 37-50.
|
| [26] |
DE LEEUW G, SPOKES L, JICKELLS T, et al, 2003. Atmospheric nitrogen inputs into the North Sea: effect on productivity[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 23(17/18/19): 1743-1755.
|
| [27] |
DIACONU C, BRION N, ELSKENS M, et al, 2005. Validation of a dynamic ammonium extraction technique for the determination of 15N at enriched abundances[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 554(1/2): 113-122.
|
| [28] |
DONEY S C, MAHOWALD N, LIMA I, et al, 2007. Impact of anthropogenic atmospheric nitrogen and sulfur deposition on ocean acidification and the inorganic carbon system[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(37): 14580-14585.
pmid: 17804807
|
| [29] |
DUCE R A, LAROCHE J, ALTIERI K, et al, 2008. Impacts of atmospheric anthropogenic nitrogen on the open ocean[J]. Science, 320(5878): 893-897.
doi: 10.1126/science.1150369
pmid: 18487184
|
| [30] |
ELLIOTT E M, KENDALL C, WANKEL S D, et al, 2007. Nitrogen isotopes as indicators of NO(x) source contributions to atmospheric nitrate deposition across the midwestern and northeastern United States[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(22): 7661-7667.
|
| [31] |
ELLIOTT E M, KENDALL C, BOYER E W, et al, 2009. Dual nitrate isotopes in dry deposition: Utility for partitioning NOx source contributions to landscape nitrogen deposition[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 114(G4): 2008JG000889.
|
| [32] |
ELLIOTT E M, YU ZHONGJIE, COLE A S, et al, 2019. Isotopic advances in understanding reactive nitrogen deposition and atmospheric processing[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 662: 393-403.
doi: S0048-9697(18)35023-X
pmid: 30690373
|
| [33] |
FANG Y T, KOBA K, WANG X M, et al, 2011. Anthropogenic imprints on nitrogen and oxygen isotopic composition of precipitation nitrate in a nitrogen-polluted city in southern China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11(3): 1313-1325.
|
| [34] |
FELIX J D, ELLIOTT E M, 2014. Isotopic composition of passively collected nitrogen dioxide emissions: Vehicle, soil and livestock source signatures[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 92: 359-366.
|
| [35] |
FELIX J D, ELLIOTT E M, AVERY G B, et al, 2015. Isotopic composition of nitrate in sequential Hurricane Irene precipitation samples: Implications for changing NOx sources[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 106: 191-195.
|
| [36] |
FIBIGER D L, HASTINGS M G, 2016. First measurements of the nitrogen isotopic composition of NOx from biomass burning[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(21): 11569-11574.
|
| [37] |
GALLOWAY J N, TOWNSEND A R, ERISMAN J W, et al, 2008. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions[J]. Science, 320(5878): 889-892.
doi: 10.1126/science.1136674
pmid: 18487183
|
| [38] |
GOBEL A R, ALTIERI K E, PETERS A J, et al, 2013. Insights into anthropogenic nitrogen deposition to the North Atlantic investigated using the isotopic composition of aerosol and rainwater nitrate[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(22): 5977-5982.
|
| [39] |
GRUBER N, 2008. Chapter 1 - The marine nitrogen cycle: Overview and challenges[M]// CAPONED G, BRONKD A, MULHOLLANDM R, Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. San Diego: Academic Press: 1-50.
|
| [40] |
HASTINGS M G, SIGMAN D M, LIPSCHULTZ F, 2003. Isotopic evidence for source changes of nitrate in rain at Bermuda[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 108(D24): 4790.
|
| [41] |
HOERING T, 1957. The isotopic composition of the ammonia and the nitrate ion in rain[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 12(1/2): 97-102.
|
| [42] |
JICKELLS T D, BUITENHUIS E, ALTIERI K, et al, 2017. A reevaluation of the magnitude and impacts of anthropogenic atmospheric nitrogen inputs on the ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 31(2): 289-305.
|
| [43] |
JOHNSTON J C, THIEMENS M H, 1997. The isotopic composition of tropospheric ozone in three environments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 102(D21): 25395-25404.
|
| [44] |
JUNG F, 2015. Nitrogen isotopes in atmospheric deposition in northern Germany: consequences of emission changes[D]. Hamburg: University of Hamburg.
|
| [45] |
KATSURA H, 2012. Accounts of the effect of electrically charged clouds on the stable nitrogen isotope ratio and the anion concentration in cloud-based aerosols[J]. Scientific Research and Essays, 7(46): 3944-3952.
|
| [46] |
KAWASHIMA H, KURAHASHI T, 2011. Inorganic ion and nitrogen isotopic compositions of atmospheric aerosols at Yurihonjo, Japan: Implications for nitrogen sources[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 45(35): 6309-6316.
|
| [47] |
KIM I N, LEE K, GRUBER N, et al, 2014a. Increasing anthropogenic nitrogen in the North Pacific Ocean[J]. Science, 346(6213): 1102-1106.
|
| [48] |
KIM T W, LEE K, DUCE R, et al, 2014b. Impact of atmospheric nitrogen deposition on phytoplankton productivity in the South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(9): 3156-3162.
|
| [49] |
KIM T W, LEE K, NAJJAR R G, et al, 2011. Increasing N abundance in the northwestern Pacific Ocean due to atmospheric nitrogen deposition[J]. Science, 334(6055): 505-509.
|
| [50] |
KOJIMA K, MURAKAMI M, YOSHIMIZU C, et al, 2011. Evaluation of surface runoff and road dust as sources of nitrogen using nitrate isotopic composition[J]. Chemosphere, 84(11): 1716-1722.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.071
pmid: 21600627
|
| [51] |
KOSZELNIK P, GRUCA-ROKOSZ R, 2013. Determination of nitrate isotopic signature in waters of different sources by analysing the nitrogen and oxygen isotopic ratio[J]. Environmental Science Processes & Impacts, 15(4): 751-759.
|
| [52] |
KRANKOWSKY D, BARTECKI F, KLEES G G, et al, 1995. Measurement of heavy isotope enrichment in tropospheric ozone[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 22(13): 1713-1716.
|
| [53] |
LAO QIBIN, LI HONGLIANG, YAN JINPEI, et al, 2024. Hemispherical scale mechanisms of nitrate formation in global marine aerosols[J]. NPJ Climate and Atmospheric Science, 7: 139.
|
| [54] |
LI ZHENGJIE, WALTERS W W, HASTINGS M G, et al, 2022. Atmospheric nitrate formation pathways in urban and rural atmosphere of Northeast China: Implications for complicated anthropogenic effects[J]. Environmental Pollution, 296: 118752.
|
| [55] |
LIN GUAN-YU, CHEN HO-WEN, CHEN BIN-JIUN, et al, 2022. A machine learning model for predicting PM2.5 and nitrate concentrations based on long-term water-soluble inorganic salts datasets at a road site station[J]. Chemosphere, 289: 133123.
|
| [56] |
LIU WEIJIAN, XU YUNSONG, LIU WENXIN, et al, 2018. Oxidative potential of ambient PM2. 5 in the coastal cities of the Bohai Sea, northern China: Seasonal variation and source apportionment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 236: 514-528.
|
| [57] |
LUO L, YAO X H, GAO H W, et al, 2016. Nitrogen speciation in various types of aerosols in spring over the northwestern Pacific Ocean[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16(1): 325-341.
|
| [58] |
MAGNANI F, MENCUCCINI M, BORGHETTI M, et al, 2007. The human footprint in the carbon cycle of temperate and boreal forests[J]. Nature, 447(7146): 848-850.
|
| [59] |
MCDUFFIE E E, SMITH S J, O’ROURKE P, et al, 2020. A global anthropogenic emission inventory of atmospheric pollutants from sector- and fuel-specific sources (1970-2017): an application of the Community Emissions Data System (CEDS)[J]. Earth System Science Data, 12(4): 3413-3442.
|
| [60] |
MCILVIN M R, ALTABET M A, 2005. Chemical conversion of nitrate and nitrite to nitrous oxide for nitrogen and oxygen isotopic analysis in freshwater and seawater[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 77(17): 5589-5595.
doi: 10.1021/ac050528s
pmid: 16131070
|
| [61] |
MICHALSKI G, BHATTACHARYA S K, MASE D F, 2011. Oxygen isotope dynamics of atmospheric nitrate and its precursor molecules[M]//BASKARAN M. Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg: 613-635.
|
| [62] |
MICHALSKI G, SAVARINO J, BÖHLKE J K, et al, 2002. Determination of the total oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate and the calibration of a Δ17Ο nitrate reference material[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 74(19): 4989-4993.
|
| [63] |
MICHALSKI G, SCOTT Z, KABILING M, et al, 2003. First measurements and modeling of Δ17O in atmospheric nitrate[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(16): 1870.
|
| [64] |
MILLER D J, CHAI JIAJUE, GUO F, et al, 2018. Isotopic composition of in situ soil NOx emissions in manure-fertilized cropland[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(21): 12058-12066.
|
| [65] |
MILLER M F, 2002. Isotopic fractionation and the quantification of 17O anomalies in the oxygen three-isotope system an appraisal and geochemical significance[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66(11): 1881-1889.
|
| [66] |
MORIN S, ERBLAND J, SAVARINO J, et al, 2012. An isotopic view on the connection between photolytic emissions of NOx from the Arctic snowpack and its oxidation by reactive halogens[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 117(D14): D00R08.
|
| [67] |
MORIN S, SAVARINO J, FREY M M, et al, 2008. Tracing the origin and fate of NOx in the Arctic atmosphere using stable isotopes in nitrate[J]. Science, 322(5902): 730-732.
|
| [68] |
MORIN S, SAVARINO J, FREY M M, et al, 2009. Comprehensive isotopic composition of atmospheric nitrate in the Atlantic Ocean boundary layer from 65°S to 79°N[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 114(D5): D05303.
|
| [69] |
OCCHIPINTI C, ANEJA V P, SHOWERS W, et al, 2008. Back-trajectory analysis and source-receptor relationships: particulate matter and nitrogen isotopic composition in rainwater[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 58(9): 1215-1222.
|
| [70] |
PAHLOW M, RIEBESELL U, 2000. Temporal trends in deep ocean Redfield ratios[J]. Science, 287(5454): 831-833.
pmid: 10657291
|
| [71] |
PARK G H, LEE K, WANNINKHOF R, et al, 2008. Large, non-Redfieldian drawdown of nutrients and carbon in the extratropical North Atlantic Ocean (46°N): Evidence for dinitrogen fixation?[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 53(5): 1697-1704.
|
| [72] |
PROEMSE B C, MAYER B, CHOW J C, et al, 2012. Isotopic characterization of nitrate, ammonium and sulfate in stack PM2. 5 emissions in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region, Alberta, Canada[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 60: 555-563.
|
| [73] |
PROEMSE B C, MAYER B, FENN M E, et al, 2013. A multi-isotope approach for estimating industrial contributions to atmospheric nitrogen deposition in the Athabasca oil sands region in Alberta, Canada[J]. Environmental Pollution, 182: 80-91.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.07.004
pmid: 23896680
|
| [74] |
SAVARINO J, KAISER J, MORIN S, et al, 2007. Nitrogen and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of atmospheric nitrate in coastal Antarctica[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 7(8): 1925-1945.
|
| [75] |
SAVARINO J, MORIN S, ERBLAND J, et al, 2013. Isotopic composition of atmospheric nitrate in a tropical marine boundary layer[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(44): 17668-17673.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216639110
pmid: 23431201
|
| [76] |
SCANLAN D J, POST A F, 2008. Aspects of marine cyanobacterial nitrogen physiology and connection to the nitrogen cycle[M]// CAPONED G, BRONKD A, MULHOLLANDM R, Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. San Diego: Academic Press: 1073-1095.
|
| [77] |
SEINFELD J H, PANDIS S N, 2016. Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
|
| [78] |
SEOK M W, KIM D, PARK G H, et al, 2021. Atmospheric deposition of inorganic nutrients to the western north Pacific Ocean[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 793: 148401.
|
| [79] |
SHI GUITAO, MA HONGMEI, ZHU ZHUOYI, et al, 2021. Using stable isotopes to distinguish atmospheric nitrate production and its contribution to the surface ocean across hemispheres[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 564: 116914.
|
| [80] |
SHI JUN, OHTE N, TOKUCHI N, et al, 2014. Nitrate isotopic composition reveals nitrogen deposition and transformation dynamics along the canopy-soil continuum of a suburban forest in Japan[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 28(23): 2539-2549.
doi: 10.1002/rcm.7050
pmid: 25366401
|
| [81] |
SIGMAN D M, CASCIOTTI K L, ANDREANI M, et al, 2001. A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 73(17): 4145-4153.
pmid: 11569803
|
| [82] |
SILVA S R, KENDALL C, WILKISON D H, et al, 2000. A new method for collection of nitrate from fresh water and the analysis of nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 228(1/2): 22-36.
|
| [83] |
SMIRNOFF A, SAVARD M M, VET R, et al, 2012. Nitrogen and triple oxygen isotopes in near-road air samples using chemical conversion and thermal decomposition[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 26(23): 2791-2804.
doi: 10.1002/rcm.6406
pmid: 23124671
|
| [84] |
SONG WEI, LIU XUEYAN, WANG YANLI, et al, 2020. Nitrogen isotope differences between atmospheric nitrate and corresponding nitrogen oxides: a new constraint using oxygen isotopes[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 701: 134515.
|
| [85] |
SPOELSTRA J, 2004. Nitrate sources and cycling at the Turkey Lakes Watershed: A stable isotope approach[D. Waterloo: University of Waterloo.
|
| [86] |
STEINBERG D K, SABA G K, 2008. Nitrogen consumption and metabolism in marine zooplankton[M]// CAPONED G, BRONKD A, MULHOLLANDM R, Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. San Diego: Academic Press: 1073-1095. 1135-1196.
|
| [87] |
SUN WENWEN, HUO JUNTAO, FU QINGYAN, et al, 2022. Influence of meteorological factors and chemical processes on the explosive growth of PM2. 5 in Shanghai, China[J]. Atmosphere, 13(7): 1068.
|
| [88] |
VAN DER A R J, ESKES H J, BOERSMA K F, et al, 2008. Trends, seasonal variability and dominant NOx source derived from a ten year record of NO2 measured from space[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 113(D4): D04302.
|
| [89] |
VICARS W C, SAVARINO J, 2014. Quantitative constraints on the 17O-excess (Δ17O) signature of surface ozone: Ambient measurements from 50°N to 50°S using the nitrite-coated filter technique[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 135: 270-287.
|
| [90] |
WALTERS W W, MICHALSKI G, 2016. Theoretical calculation of oxygen equilibrium isotope fractionation factors involving various NOy molecules, ·OH, and H2O and its implications for isotope variations in atmospheric nitrate[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 191: 89-101.
|
| [91] |
WANKEL S D, CHEN YING, KENDALL C, et al, 2010. Sources of aerosol nitrate to the gulf of Aqaba: evidence from δ15N and δ18O of nitrate and trace metal chemistry[J]. Marine Chemistry, 120(1/2/3/4): 90-99.
|
| [92] |
WEI YUTING, ZHAO DONGHENG, ZHANG ZHANG, et al, 2024. The response of daytime nitrate formation to source emissions reduction based on chemical kinetic and thermodynamic model[J]. The Science of The Total Environment, 953: 176002.
|
| [93] |
XIAO HAO, DING SHIYUAN, JI CHUANWEN, et al, 2023. Strict control of biomass burning inhibited particulate matter nitrate pollution over Tianjin: Perspective from dual isotopes of nitrate[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 293: 119460.
|
| [94] |
XIAO HONGWEI, XIE LUHUA, LONG AIMIN, et al, 2015. Use of isotopic compositions of nitrate in TSP to identify sources and chemistry in South China Sea[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 109: 70-78.
|
| [95] |
YAN CHAO, THAM Y J, ZHA QIAOZHI, et al, 2019. Fast heterogeneous loss of N2O5 leads to significant nighttime NOx removal and nitrate aerosol formation at a coastal background environment of Southern China[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 677: 637-647.
|
| [96] |
YANG J T, HSU S C, DAI M H, et al, 2014. Isotopic composition of water-soluble nitrate in bulk atmospheric deposition at Dongsha Island: sources and implications of external N supply to the northern South China Sea[J]. Biogeosciences, 11(7): 1833-1846.
|
| [97] |
YANG J T, LEE K, ZHANG JIAZHONG, et al, 2020. Contrasting decadal trends of subsurface excess nitrate in the western and eastern North Atlantic Ocean[J]. Biogeosciences, 17(13): 3631-3642.
|
| [98] |
YANG XIN, COX R A, WARWICK N J, et al, 2005. Tropospheric bromine chemistry and its impacts on ozone: a model study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 110(D23): D23311.
|
| [99] |
YEATMAN S G, SPOKES L J, DENNIS P F, et al, 2001. Comparisons of aerosol nitrogen isotopic composition at two polluted coastal sites[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 35(7): 1307-1320.
|
| [100] |
ZHANG J, ZHANG G S, BI Y F, et al, 2011. Nitrogen species in rainwater and aerosols of the Yellow and East China Seas: Effects of the East Asian monsoon and anthropogenic emissions and relevance for the NW Pacific Ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 25(3): GB3020.
|
| [101] |
ZHANG WENHUI, BI XIAOHUI, ZHANG YUFEN, et al, 2022. Diesel vehicle emission accounts for the dominate NOx source to atmospheric particulate nitrate in a coastal city: Insights from nitrate dual isotopes of PM2. 5[J]. Atmospheric Research, 278: 106328.
|
| [102] |
ZHANG ZHENGEN, LI JUN, ZHANG RUIJIE, et al, 2024. Increase in agricultural-derived NHx and decrease in coal combustion-derived NOx result in atmospheric particulate N-$\text{NH}_{\text{4}}^{\text{+}}$ surpassing N-NO-3 in the South China Sea[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 58(15): 6682-6692.
|
| [103] |
ZHAO Y, ZHANG L, PAN Y, et al, 2015. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition to the northwestern Pacific: seasonal variation and source attribution[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(18): 10905-10924.
|
| [104] |
ZHAO ZHUYU, CAO FANG, FAN MEIYI, et al, 2021. Nitrate aerosol formation and source assessment in winter at different regions in NorthEast China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 267: 118767.
|
| [105] |
ZONG ZHENG, TIAN CHONGGUO, LI JUN, et al, 2020. Isotopic interpretation of particulate nitrate in the metropolitan city of Karachi, Pakistan: insight into the oceanic contribution to NOx[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(13): 7787-7797.
|
| [106] |
ZONG ZHENG, TIAN CHONGGUO, SUN ZEYU, et al, 2022. Long-term evolution of particulate nitrate pollution in North China: isotopic evidence from 10 offshore cruises in the Bohai Sea from 2014 to 2019[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 127(11): e2022JD036567.
|
 ), XIAO Hongwei1(
), XIAO Hongwei1( ), GUAN Wenkai2, XIAO Huayun1
), GUAN Wenkai2, XIAO Huayun1