热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 140-153.doi: 10.11978/2024218CSTR: 32234.14.2024218
南海典型岛礁浅海地形遥感监测及时序变化研究*
陈钰宸1( ), 付东洋1(
), 付东洋1( ), 陶邦一2, 李姬喆2, 祝依娴2, 刘贝1, 林烨1, 柴霞1
), 陶邦一2, 李姬喆2, 祝依娴2, 刘贝1, 林烨1, 柴霞1
- 1.广东海洋大学电子与信息工程学院, 广东 湛江 524088
2.自然资源部第二海洋研究所卫星海洋环境动力学国家重点实验室, 浙江 杭州 310012
-
收稿日期:2024-11-26修回日期:2025-01-25出版日期:2025-09-10发布日期:2025-10-14 -
通讯作者:付东洋 -
作者简介:陈钰宸(2000—), 女, 江苏省泰州市人, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋遥感应用研究。email: 295428711@qq.com
*感谢国家地理信息公共服务平台(
https://www.tianditu.gov.cn/ )、哥白尼数据中心(https://browser.dataspace.copernicus.eu/ )、NASA地球科学数据中心(https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/search )提供数据支撑。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2022YFC3103101); 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)重大专项团队项目(GML2021GD0809); 国家自然科学基金项目(42206187); 广东省教育厅重点科研项目(2023ZDZX4009)
Study on remote sensing monitoring and time series change of shallow sea topography of typical islands and reefs in the South China Sea*
CHEN Yuchen1( ), FU Dongyang1(
), FU Dongyang1( ), TAO Bangyi2, LI Jizhe2, ZHU Yixian2, LIU Bei1, LIN Ye1, CHAI Xia1
), TAO Bangyi2, LI Jizhe2, ZHU Yixian2, LIU Bei1, LIN Ye1, CHAI Xia1
- 1. College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang 524088, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Satellite Ocean Environment Dynamics, Second Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, Hangzhou 310012, China
-
Received:2024-11-26Revised:2025-01-25Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-10-14 -
Contact:FU Dongyang -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFC3103101); Guangdong Provincial Laboratory of Southern Ocean Science and Engineering (Guangzhou) Major Project Team(GML2021GD0809); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42206187); Key Research Project of Guangdong Provincial Department of Education(2023ZDZX4009)
摘要:
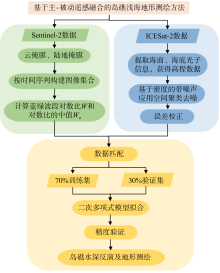
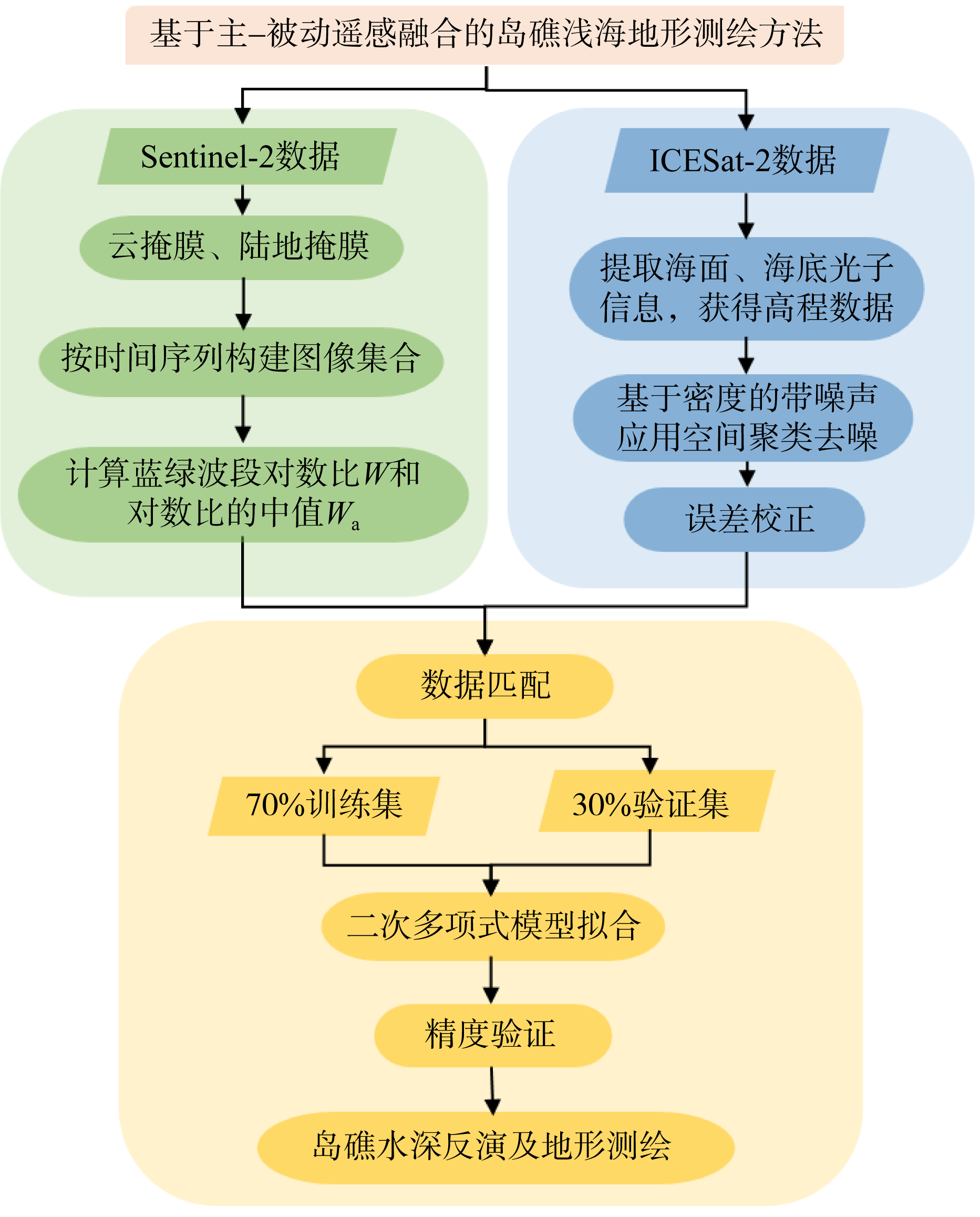
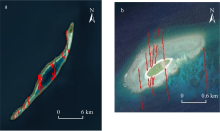
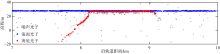
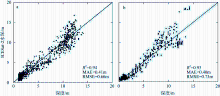
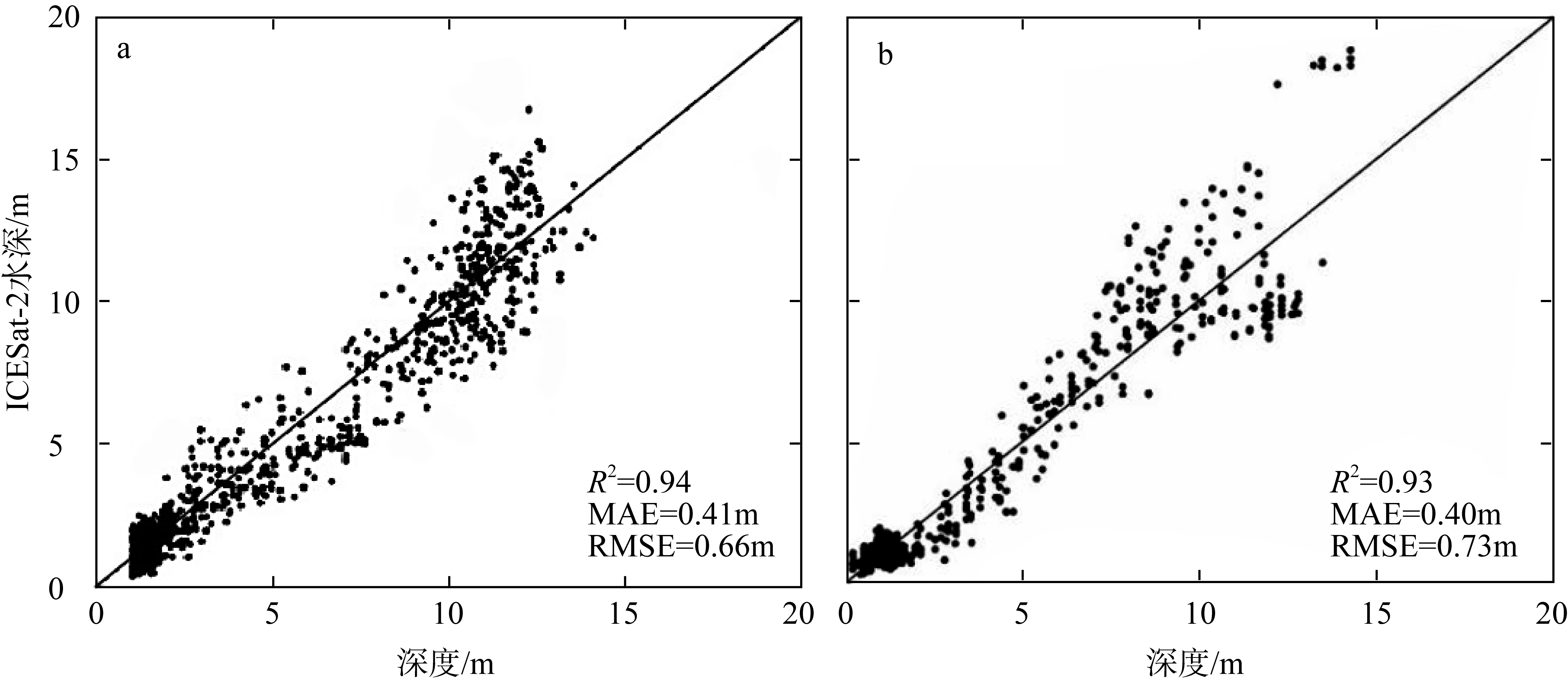
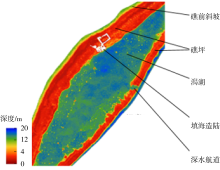
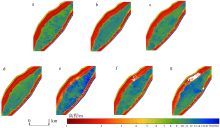
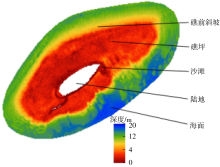
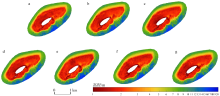
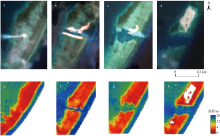
南沙群岛位于我国南海南部区域, 其地理位置对我国海洋权益、发展战略和国家安全都十分重要。开展南沙群岛岛礁水深及地形监测与变化研究, 对于国家战略具有重要意义。文章结合哨兵-2 (Sentinel-2)和冰、云和陆地高程卫星(ice, cloud, land elevation satellite-2, ICESat-2)数据, 采用主动-被动融合遥感测深算法, 对南海南沙群岛的柏礁和北子岛浅海区域的地形进行了反演研究及实验验证。这一方法能够利用时间序列分析, 揭示岛礁水深和地形的长期趋势和短期波动, 为理解人类活动和自然因素对岛礁地形变化的影响提供了新的视角。研究结果如下: 1) 验证了一个高精度的水深反演模型, 该模型在研究中表现出优异的性能, 相关系数R2 > 0.9, 平均绝对误差(mean absolute error, MAE) < 0.4m, 均方根误差(root-mean-square error, RMSE) < 0.7m。2) 2018—2024年间柏礁和北子岛地形及空间结构均发生了不同程度的变化。柏礁因填海造陆工程, 陆地面积增加; 北子岛则受自然因素影响, 出现动态变化。3) 柏礁的地形变化主要由人为因素驱动, 包括填海造陆、资源开采等。北子岛的变化则主要是自然因素的结果, 包括季风、台风、海水冲刷和沉积物淤积等。
中图分类号:
- P737.13
引用本文
陈钰宸, 付东洋, 陶邦一, 李姬喆, 祝依娴, 刘贝, 林烨, 柴霞. 南海典型岛礁浅海地形遥感监测及时序变化研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(5): 140-153.
CHEN Yuchen, FU Dongyang, TAO Bangyi, LI Jizhe, ZHU Yixian, LIU Bei, LIN Ye, CHAI Xia. Study on remote sensing monitoring and time series change of shallow sea topography of typical islands and reefs in the South China Sea*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 140-153.
表4
北子岛水深反演结果分区域面积及面积变化率"
| 年份 | 沙滩区域面积/km2 | 沙滩区域面积变化率/% | 礁坪区域面积/km2 | 礁坪区域面积变化率/% | 礁前斜坡区域面积/km2 | 礁前斜坡区域面积变化率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 0.091 | 1.189 | 0.480 | |||
| 1.9 | -1.0 | -4.2 | ||||
| 2019 | 0.090 | 1.201 | 0.501 | |||
| -15.0 | 2.4 | 4.4 | ||||
| 2020 | 0.103 | 1.172 | 0.479 | |||
| -5.8 | 0.3 | 2.2 | ||||
| 2021 | 0.109 | 1.169 | 0.468 | |||
| 23.1 | -2.5 | 4.7 | ||||
| 2022 | 0.084 | 1.197 | 0.446 | |||
| -27.9 | 2.4 | -8.4 | ||||
| 2023 | 0.107 | 1.169 | 0.483 | |||
| -4.5 | 1.5 | -1.9 | ||||
| 2024 | 0.112 | 1.151 | 0.493 |
| [1] |
白宽宽, 李志威, 张鹏, 等, 2024. 基于多源遥感解译的洞庭湖区自然湖岸线演变过程研究[J]. 湖泊科学, 36(5): 1537-1549.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
曹彬才, 方勇, 江振治, 等, 2020. ICESat-2激光卫星与光学遥感影像融合水深测量[J]. 海洋测绘, 40(5): 21-25.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈安娜, 马毅, 张靖宇, 2018. 水深被动光学遥感反演模型适用性研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 37(6): 953-960.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈韶阳, 2011. 南沙群岛价值分类评价和开发策略研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
郭松涛, 邢帅, 张国平, 等, 2024. 异构卫星遥感数据融合的水深反演模型[J]. 测绘通报, 2024(5): 19-23.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
孔瑞瑶, 谢涛, 马明, 等, 2022. CatBoost模型在水深反演中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, (7): 33-37.
doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2022.0199 |
|
doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2022.0199 |
|
| [7] |
赖文典, 2022. 基于神经网络从大气层顶光学卫星数据反演光学浅水水深[D]. 福建: 厦门大学: 1-74.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李晨轩, 韦志刚, 2024. 1979—2021年中国南海海表风速和大风事件的变化特征[J]. 高原气象, 43(3): 696-710.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2023.00079 |
|
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2023.00079 |
|
| [9] |
李宁宁, 陈义兰, 唐秋华, 等, 2022. 岛礁周边水深光学遥感反演模型比较与分析[J]. 海洋测绘, 42(1): 50-54.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李全兴, 潘国富, 钱万民, 1996. 水深测量与海底面状况声探测技术的进展[J]. 海洋测绘, 16(1): 6-11.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
李文杰, 闫世强, 蒋莹, 等, 2019. 自适应确定DBSCAN算法参数的算法研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 55(5): 1-7, 148.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1809-0018 |
|
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1809-0018 |
|
| [12] |
李晓敏, 2021. 南海西沙群岛珊瑚岛礁高分遥感监测与动态研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
林丽茹, 赵辉, 2012. 南海海域浮游植物叶绿素与海表温度季节变化特征分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 30(4): 46-54.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
刘宝银, 2001. 南沙群岛遥感融合信息特征分析与计量[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
刘长达, 2022. ICESat-2与Sentinel-2浅海水深反演及海岸带分类研究[D]. 青岛: 自然资源部第一海洋研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
马毅, 张杰, 张靖宇, 等, 2018. 浅海水深光学遥感研究进展[J]. 海洋科学进展, 36(3): 331-351.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
孟文君, 李杰, 张凯, 等, 2021. 基于改进DBSCAN算法的ICESat-2海面点数据去噪处理及精度评估[J]. 海洋通报, 40(6): 675-682.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
潘春梅, 丁谦, 曹文玉, 2002. 南沙群岛岛礁地形地貌TM影像特征分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, 14(2): 34-37, 60.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
宋玮, 张杰, 姬光荣, 等, 2003. 基于SAR与TM图像的南沙双子群礁特征分析[C]// 海洋环境科学与数值模拟国家海洋局重点实验室, 中国海洋学会海洋遥感专业委员会, 中国遥感委员会, 等, 2003. 第十四届全国遥感技术学术交流会论文摘要集. 海洋科学进展, 22(suppl): 177-181 (in Chinese).
|
| [20] |
唐蕾, 2023. 1993—2019年南海海平面高度时空变化研究[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学: 1-54.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
王媞, 丛帅, 陈健斌, 等, 2024. 台风“杜苏芮”远端影响下黄河三角洲沉积特征变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 44(5): 50-57.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
汪万智, 邹欣庆, 李海宇, 2022. 南海珊瑚礁光学浅水海域多光谱遥感水深反演[J]. 高校地质学报, 28(5): 758-767.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
吴士存, 2022. 南沙争端的由来与发展: 南海纷争史国别研究[M]. 北京: 中华书局 (in Chinese).
|
| [24] |
肖海婷, 黄荣永, 刘羿, 等, 2024. 台风影响下西沙灰沙岛的时空变化特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 44(2): 157-177.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
谢丛霜, 陈鹏, 潘德炉, 2024. 主被动遥感融合辐射传输卷积神经网络水深反演方法[J]. 光子学报, 53(8): 46-58.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
熊媛, 黄荣永, 余克服, 2022. 基于多时相多光谱遥感影像的珊瑚礁面积估算方法研究: 以西沙群岛羚羊礁为例[J]. 海洋学报, 44(8): 151-168.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
杨鑫科, 2024. 海洋ICESat-2卫星激光雷达数据去噪处理及典型应用[D]. 杭州: 杭州电子科技大学.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
岳子琳, 朱卫东, 邱振戈, 等, 2022. 南海珊瑚岛礁地貌遥感识别研究[J]. 海洋科学, 46(4): 67-80.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
张更垒, 田振环, 杨娜娜, 等, 2023. 空天陆海一体化测绘技术在南海岛礁调查中的应用展望[J]. 海洋科学前沿, (4): 233-244.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
张清凌, 陈楚群, 施平, 2003. 南沙群岛海域水体漫衰减系数Kd(490)的特性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 22(1): 9-16.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
张晓冬, 张文静, 朱首贤, 等, 2016. 海口湾可见光遥感测深方法研究[J]. 海洋通报, 35(1): 54-63.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
张艳, 2024. 融合异源卫星数据结合BRT非线性方法的河流深度反演[J]. 水利科技与经济, 30(7): 148-151.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
赵辉, 齐义泉, 王东晓, 等, 2005. 南海叶绿素浓度季节变化及空间分布特征研究[J]. 海洋学报, 27(4): 45-52.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌, 2023. 全球变暖和厄尔尼诺事件[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 19(5): 663-666.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
朱串串, 2018. 长江口九段沙面积估算模型与演变分析[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
祝笑, 2024. 耦合IceSat-2和Sentinel-2卫星数据与BRT回归模型的河流水深反演[J]. 水利科技与经济, 30(10): 22-25.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
pmid: 18286131 |
| [46] |
pmid: 18319990 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
doi: 10.1364/AO.17.000379 pmid: 20174418 |
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [1] | 黄谕, 王琳, 麦志茂, 李洁, 张偲. 南海热带岛礁生物土壤结皮中细菌的分离及其固砂特性初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [2] | 李存, 崔林青, 杨红强, 龙丽娟, 田新朋. 三份南海岛礁珊瑚砂样品中可培养细菌多样性[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 149-158. |
| [3] | 陈本清, 杨燕明, 罗凯. 基于高分一号卫星多光谱数据的岛礁周边浅海水深遥感反演[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(2): 70-78. |
|
||