| [1] |
丁旋, 方念乔, 万晓樵, 1999. 孟加拉湾晚第四纪冰期和间冰期古生产力演变研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 19(3): 49-58.
|
|
DING XUAN, FANG NIANQIAO, WAN XIAOQIAO, 1999. The study of the glacial-interglacial paleoproductivity evolution during late quaternary in the Bay of Bengal[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 19(3): 49-58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
方念乔, 陈学方, 胡超涌, 等, 2001. 东北印度洋深海记录基本特征及其对青藏高原隆升的响应[J]. 第四纪研究, 21(6): 490-499.
|
|
FANG NIANQIAO, CHEN XUEFANG, HU CHAOYONG, et al, 2001. Deep sea sedimentary records in the northeastern Indian ocean and their response to the uplift of the Qinghai-Xizang plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 21(6): 490-499 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
方念乔, 丁旋, 胡超涌, 等, 2004. 氧同位素第6期北印度洋的一次重大古海洋学事件[J]. 地球科学, 29(2): 127-134.
|
|
FANG NIANQIAO, DING XUAN, HU CHAOYONG, et al, 2004. A significant paleoceanographic event taking place in northeastern Indian Ocean during oxygen isotope stage 6[J]. Earth Science, 29(2): 127-134 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.1007/s11589-016-0144-5
|
| [4] |
官玉龙, 陈亮, 姜兆霞, 等, 2022. 东北印度洋源汇过程及古环境与古季风演化[J]. 地学前缘, 29(5): 102-118.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.9.18
|
|
GUAN YULONG, CHEN LIANG, JIANG ZHAOXIA, et al, 2022. Source-sink processes, paleoenvironment and paleomonsoon evolution in the Northeast Indian Ocean[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29(5): 102-118 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.9.18
|
| [5] |
胡昱洁, 李小艳, 宋召军, 等, 2023. 印度洋东经90°海岭表层沉积物浮游有孔虫分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 43(1): 105-117.
|
|
HU YUJIE, LI XIAOYAN, SONG ZHAOJUN, et al, 2023. Distribution and influencing factors of planktonic foraminifera in surface sediments of the Ninetyeast Ridge in Indian Ocean[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 43(1): 105-117 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
刘勇勤, 2002. 晚中新世以来东北印度洋赤道海岭的远洋沉积记录及其环境意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
|
|
LIU YONGQIN, 2003. Pelagic sedimentary records and its Palaeoenvironmental implication in Ninetyeast Ridge of the NE Indian Ocean since Middle Miocene[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
齐文菁, 李小艳, 范德江, 等, 2022. 印度洋东经90°海岭现代沉积物稀土元素组成及其物源示踪意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 42(2): 92-100.
|
|
QI WENJING, LI XIAOYAN, FAN DEJIANG, et al, 2022. Rare earth element composition of the surface sediments from the Ninetyeast Ridge and its implications for provenance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 42(2): 92-100 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
张兰兰, 陈木宏, 陈忠, 等, 2010. 南海表层沉积物中的碳酸钙含量分布及其影响因素[J]. 地球科学, 35(6): 891-898.
|
|
ZHANG LANLAN, CHEN MUHONG, CHEN ZHONG, et al, 2010. Distribution of calcium carbonate and its controlling factors in surface sediments of the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science, 35(6): 891-898 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
张振芳, 方念乔, 吴琳, 等, 2004. 孟加拉湾东经90°海岭中上新世以来沉积记录及亚洲季风[J]. 地球科学, 29(2): 157-161.
|
|
ZHANG ZHENFANG, FANG NIANQIAO, WU LIN, et al, 2004. Sedimentary records and Asian monsoon in Ninetyeast Ridge of bay of Bengal since Pliocene time[J]. Earth Science, 29(2): 157-161 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
张振国, 方念乔, 李文宝, 等, 2007. 东经90°海岭远洋沉积物非碳酸盐组分的粒度特征及环境指示意义[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 38(1): 85-87.
|
|
ZHANG ZHENGUO, FANG NIANQIAO, LI WENBAO, et al, 2007. The characteristics of the non-CaCO3 grain size of pelagic sediment from the Ninetyeast Ridge and its indicated significance of environment[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 38(1): 85-87 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
赵建青, 1996. 土壤中碳酸钙的测定[J]. 现代农业 (11): 20-21.
|
|
ZHAO JIANQING, 1996. Determination of calcium carbonate in soil[J]. Modern Agriculture, (11): 20-21.
|
| [12] |
BRETSCHNEIDER L, HATHORNE E C, HUANG HUANG, et al, 2021. Provenance and weathering of clays delivered to the Bay of Bengal during the Middle Miocene: linkages to tectonics and monsoonal climate[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 36(2): e2020PA003917.
|
| [13] |
CULLEN J L, PRELL W L, 1984. Planktonic foraminifera of the northern Indian Ocean: Distribution and preservation in surface sediments[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 9(1): 1-52.
doi: 10.1016/0377-8398(84)90022-7
|
| [14] |
DIVAKAR P, MALMGREN B A, 1999. Quaternary carbonate record from the equatorial Indian Ocean and its relationship with productivity changes[J]. Marine Geology, 161(1): 49-62.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00055-9
|
| [15] |
GUPTA S M, 2003. Orbital frequencies in radiolarian assemblages of the central Indian Ocean: implications on the Indian summer monsoon[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 197(1-2): 97-112.
doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00388-2
|
| [16] |
KLOOTWIJK C T, GEE J S, PEIRCE J W, et al, 1992. Neogene evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan region: constraints from ODP site 758, northern Ninety east Ridge; bearing on climatic change[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 95(1-2): 95-110.
doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(92)90167-4
|
| [17] |
MURGESE D S, DE DECKKER P, 2005. The distribution of deep-sea benthic foraminifera in core tops from the eastern Indian Ocean[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 56(1-2): 25-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2005.03.005
|
| [18] |
NAIK S S, DIVAKAR P D, 2016. Carbonate preservation during the ‘mystery interval’ in the northern Indian Ocean[J]. Geochemical Journal, 50(4): 357-362.
doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0420
|
| [19] |
QIU ZHUOYA, ZHANG LANLAN, XIANG RONG, et al, 2021. Biodiversity of radiolarians in surface sediments from the East Indian Ocean and their implication for water masses[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 177: 103625.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2021.103625
|
| [20] |
SHANKAR D, VINAYACHANDRAN P N, UNNIKRISHNAN A S, 2002. The monsoon currents in the north Indian Ocean[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 52(1): 63-120.
doi: 10.1016/S0079-6611(02)00024-1
|
| [21] |
SLOTNICK B S, LAURETANO V, BACKMAN J, et al, 2015. Early Paleogene variations in the calcite compensation depth: new constraints using old borehole sediments from across Ninetyeast Ridge, central Indian Ocean[J]. Climate of the Past, 11(3): 473-493.
doi: 10.5194/cp-11-473-2015
|
| [22] |
YE RUIJIE, ZHOU FENG, MA XIAO, et al, 2023. Energetic bottom current at the equatorial gap of the Ninety East Ridge in the Indian Ocean based on mooring data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 128(3): e2022JC018974.
|
| [23] |
ZHANG HANDAN, LUO YIMING, YU JIMIN, et al, 2022. Indian Ocean sedimentary calcium carbonate distribution and its implications for the glacial deep ocean circulation[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 284: 107490.
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2022.107490
|
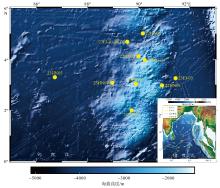
 ), 向荣1,2,3(
), 向荣1,2,3( ), 苏翔1,2,3(
), 苏翔1,2,3( ), 张兰兰1,2,3, 潘子锐1,3, 谢金沃4, 罗传秀1,2,3, 万随1,2,3
), 张兰兰1,2,3, 潘子锐1,3, 谢金沃4, 罗传秀1,2,3, 万随1,2,3
 ), XIANG Rong1,2,3(
), XIANG Rong1,2,3( ), SU Xiang1,2,3(
), SU Xiang1,2,3( ), ZHANG Lanlan1,2,3, PAN Zirui1,3, XIE Jinwo4, LUO Chuanxiu1,2,3, WAN Sui1,2,3
), ZHANG Lanlan1,2,3, PAN Zirui1,3, XIE Jinwo4, LUO Chuanxiu1,2,3, WAN Sui1,2,3