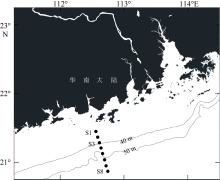
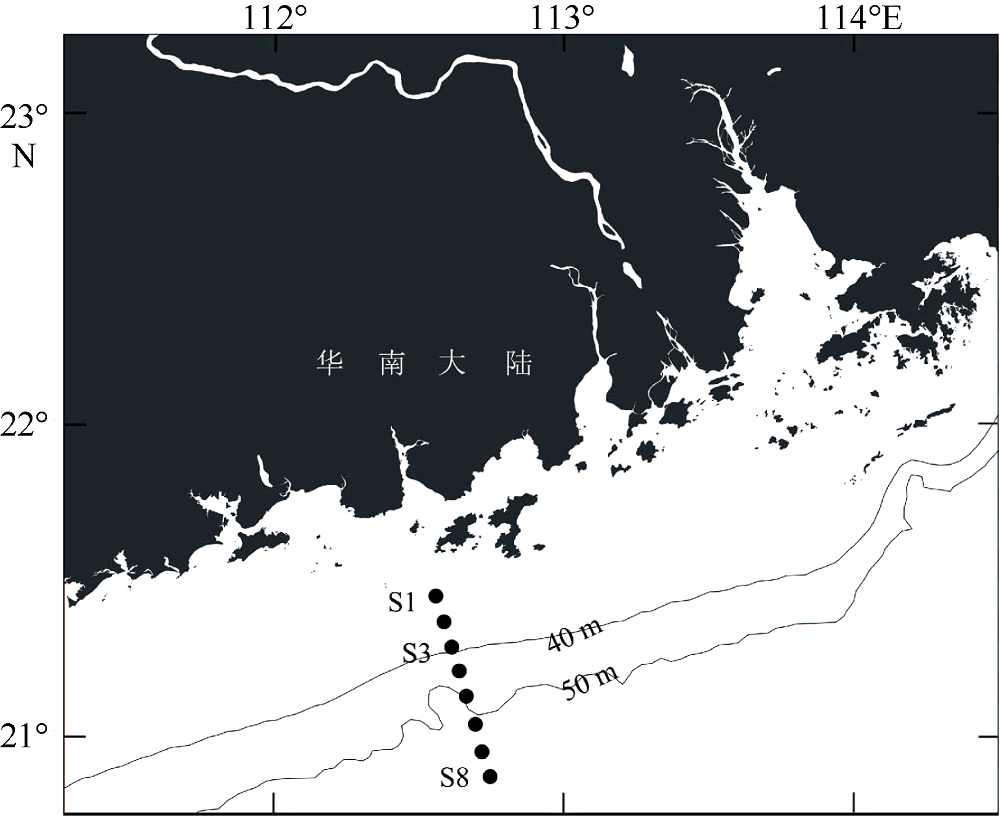
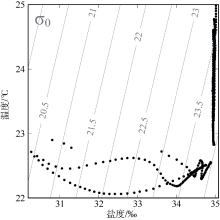
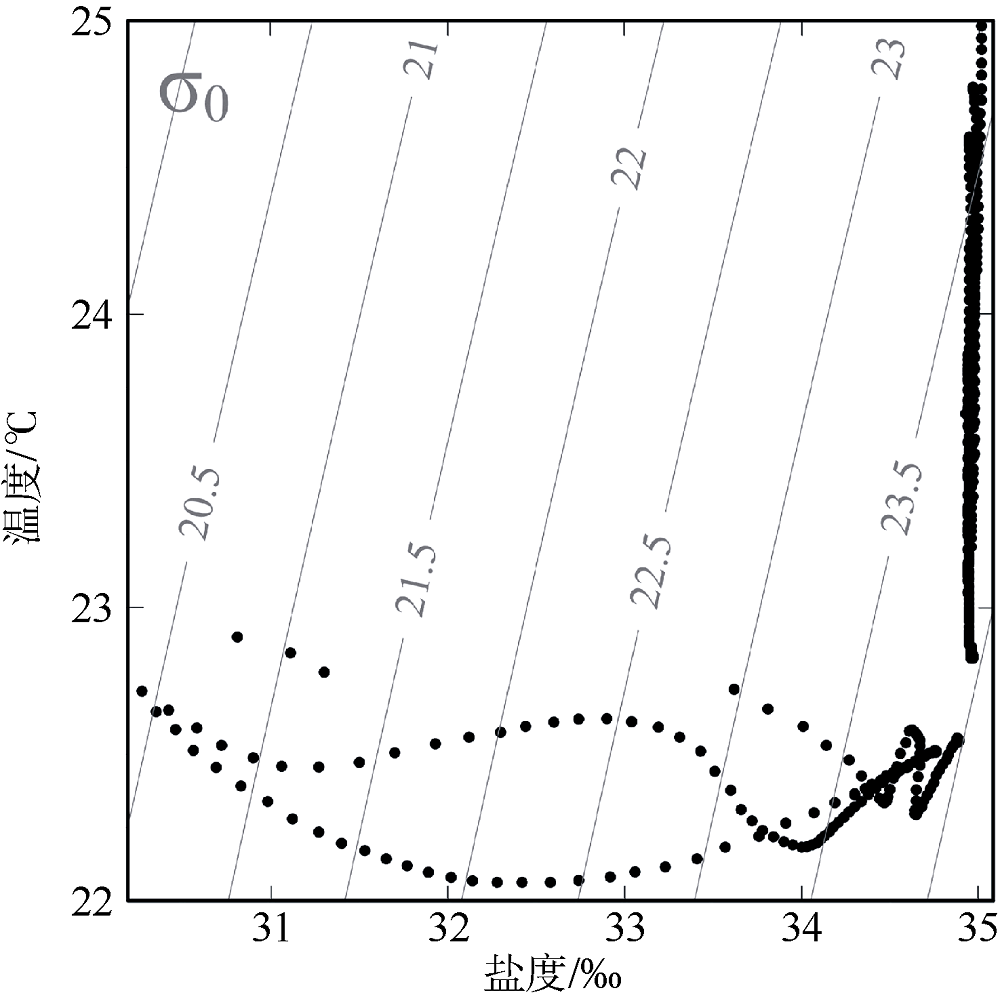
| [1] |
冯士筰, 李凤岐, 李少菁, 1999. 海洋科学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 1-524(in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
李洁, 经志友, 张偲, 2018. 季风环流影响下的南海海洋细菌多样性特征初探[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(6):1-15.
|
|
LI JIE, JING ZHIYOU, ZHANG SI, 2017. Preliminary investigation on the bacteria diversity coupled with the monsoon forced circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(6):1-15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
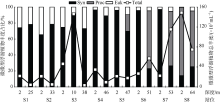
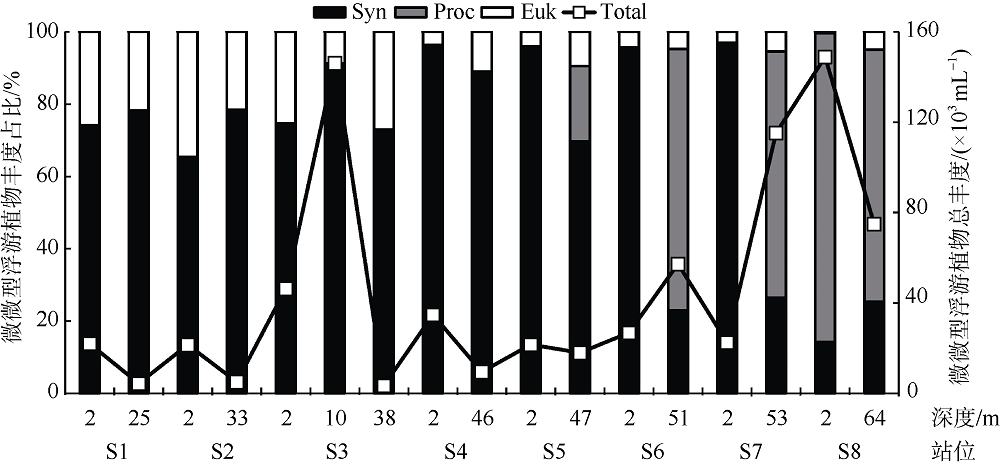
梁文钊, 唐丹玲, 2017. 南海西部夏季表层浮游植物粒径结构分布特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(4):93-101.
|
|
LIANG WENZHAO, TANG DANLING, 2017. Distribution characteristics of phytoplankton size structure in the western South China Sea in summer[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(4):93-101 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
刘华健, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 等, 2017. 珠江口浮游植物叶绿素a和初级生产力的季节变化及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(1):81-91.
|
|
LIU HUAJIAN, HUANG LIANGMIN, TAN YEHUI et al, 2017. Seasonal variations of chlorophyll a and primary production and their influencing factors in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(1):81-91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
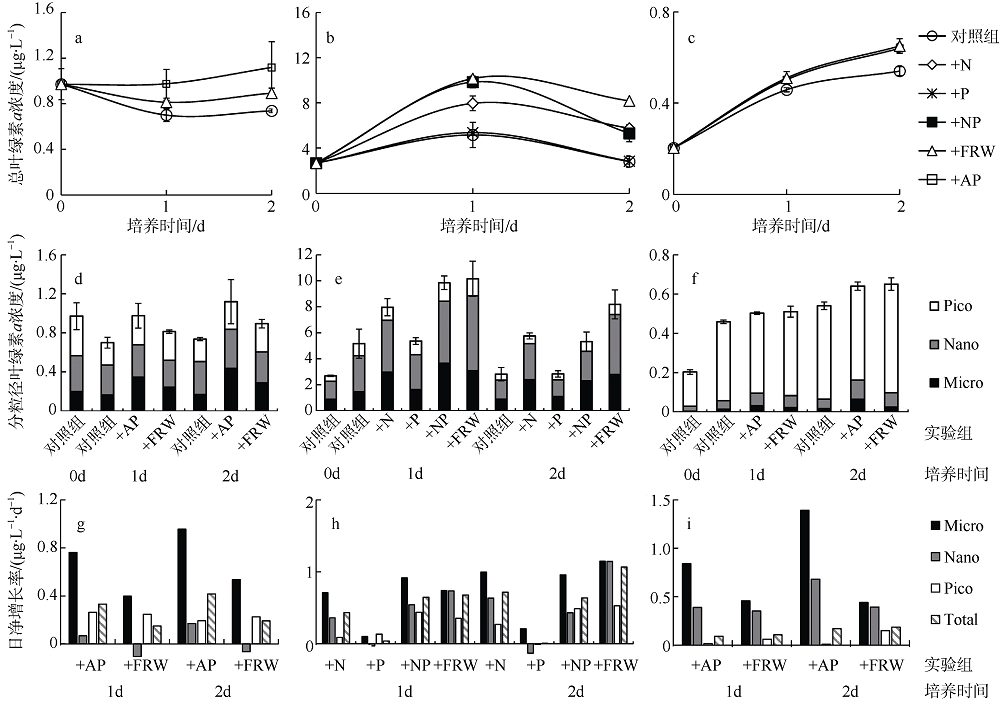
牟英春, 褚强, 张潮, 等, 2018. 南海浮游植物对沙尘和灰霾添加的响应[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(9):3512-3523.
|
|
MU YINGCHUN, CHU QIANG, ZHANG CHAO, et al, 2018. Responses of phytoplankton to dust and haze particle additions in the South China Sea[J]. China Environmental Science, 38(9):3512-3523 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
BOST C A, COTTÉ C, BAILLEUL F, et al, 2009. The importance of oceanographic fronts to marine birds and mammals of the southern oceans[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 78(3):363-376.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.11.022
|
| [7] |
BU-OLAYAN A H, AL-HASSAN R, THOMAS B V, 2001. Trace metal toxicity to phytoplankton of Kuwait coastal waters[J]. Ecotoxicology, 10(3):185-189.
doi: 10.1023/A:1016602329047
|
| [8] |
CHEN BINGZHANG, WANG LEI, SONG SHUQUN, et al, 2011. Comparisons of picophytoplankton abundance, size, and fluorescence between summer and winter in northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 31(14):1527-1540.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.06.018
|
| [9] |
CHEN Y L L, CHEN H Y, KARL D M, et al, 2004. Nitrogen modulates phytoplankton growth in spring in the South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(4-5):527-541.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2003.12.006
|
| [10] |
CHIEN C T, MACKEY K R M, DUTKIEWICZ S, et al, 2016. Effects of African dust deposition on phytoplankton in the western tropical Atlantic Ocean off Barbados[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 30(5):716-734.
doi: 10.1002/2015GB005334
|
| [11] |
CHISHOLM S W, 1992. Phytoplankton size[M]//FALKOWSKI P G, WOODHEAD A D, WOODHEAD A D, et al. Primary Productivity and Biogeochemical Cycles in the Sea. Boston, MA: Springer: 213-237.
|
| [12] |
CHU QIANG, LIU YING, SHI JIE, et al, 2018. Promotion effect of Asian dust on phytoplankton growth and potential dissolved organic phosphorus utilization in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 123(3):1101-1116.
doi: 10.1002/jgrg.v123.3
|
| [13] |
COALE K H, 1991. Effects of iron, manganese, copper, and zinc enrichments on productivity and biomass in the subarctic Pacific[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 36(8):1851-1864.
doi: 10.4319/lo.1991.36.8.1851
|
| [14] |
CUI DONGYANG, WANG JIANGTAO, TAN LIJU, et al, 2016. Impact of atmospheric wet deposition on phytoplankton community structure in the South China Sea[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 173:1-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.02.011
|
| [15] |
DOWNING J A, OSENBERG C, SARNELLE O, 1999. Meta-analysis of marine nutrient-enrichment experiments: variation in the magnitude of nutrient limitation[J]. Ecology, 80(4):1157-1167.
doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[1157:MAOMNE]2.0.CO;2
|
| [16] |
DUCE R A, LAROCHE J, ALTIERI K, et al, 2008. Impacts of atmospheric anthropogenic nitrogen on the open ocean[J]. Science, 320(5878):893-897.
doi: 10.1126/science.1150369
pmid: 18487184
|
| [17] |
ECHEVESTE P, AGUSTÍ S, TOVAR-SÁNCHEZ A, 2012. Toxic thresholds of cadmium and lead to oceanic phytoplankton: Cell size and ocean basin-dependent effects[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 31(8):1887-1894.
doi: 10.1002/etc.1893
|
| [18] |
GAN JIANPING, CHEUNG A, GUO XIAOGANG, et al, 2009. Intensified upwelling over a widened shelf in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 114(C9):C09019.
|
| [19] |
GAO Y, ARIMOTO R, DUCE R A, et al, 1997. Temporal and spatial distributions of dust and its deposition to the China Sea[J]. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 49(2):172-189.
doi: 10.3402/tellusb.v49i2.15960
|
| [20] |
GUO CUI, YU J, HO T Y, et al, 2012. Dynamics of phytoplankton community structure in the South China Sea in response to the east Asian aerosol input[J]. Biogeosciences, 9(4):1519-1536.
doi: 10.5194/bg-9-1519-2012
|
| [21] |
HERUT B, ZOHARY T, KROM M D, et al, 2005. Response of east Mediterranean surface water to Saharan dust: on-board microcosm experiment and field observations[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 52(22-23):3024-3040.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2005.09.003
|
| [22] |
JICKELLS T D, AN Z S, ANDERSEN K K, et al, 2005. Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate[J]. Science, 308(5718):67-71.
pmid: 15802595
|
| [23] |
JORDI A, BASTERRETXEA G, TOVAR-SÁNCHEZ A, et al, 2012. Copper aerosols inhibit phytoplankton growth in the Mediterranean Sea[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(52):21246-21249.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207567110
pmid: 23236141
|
| [24] |
KIM Y, JEON J, KWAK M S, et al, 2018. Photosynthetic functions of Synechococcus in the ocean microbiomes of diverse salinity and seasons[J]. PLoS One, 13(1):e0190266.
pmid: 29293601
|
| [25] |
LI Q P, ZHOU WEIWEN, CHEN YINCHAO, et al, 2018. Phytoplankton response to a plume front in the northern South China Sea[J]. Biogeoscienses, 15(8):2551-2563.
|
| [26] |
LITCHMAN E, KLAUSMEIER C A, SCHOFIELD O M, et al, 2007. The role of functional traits and trade-offs in structuring phytoplankton communities: scaling from cellular to ecosystem level[J]. Ecology Letters, 10(12):1170-1181.
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01117.x
pmid: 17927770
|
| [27] |
LIU XIN, XIAO WUPENG, LANDRY M R, et al, 2016. Responses of Phytoplankton Communities to Environmental Variability in the East China Sea[J]. Ecosystems, 19(5):832-849.
doi: 10.1007/s10021-016-9970-5
|
| [28] |
LONG AIMIN, SUN LINGYAN, SHI RONGGUI, et al, 2013. Saltwater intrusion induced by a complete neap tide and its effect on nutrients variation in the estuary of Pearl river, China[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 290(5):1158-1168.
doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-12-00182.1
|
| [29] |
LU ZHONGMING, GAN JIANPING, DAI MINHAN, et al, 2010. The influence of coastal upwelling and a river plume on the subsurface chlorophyll maximum over the shelf of the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 82(1-2):35-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.03.002
|
| [30] |
MAHOWALD N M, HAMILTON D S, MACKEY K R M, et al, 2018. Aerosol trace metal leaching and impacts on marine microorganisms[J]. Nature Communication, 9:2614.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04970-7
|
| [31] |
MANN E L, AHLGREN N, MOFFETT J W, et al, 2002. Copper toxicity and cyanobacteria ecology in the Sargasso Sea[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 47(4):976-988.
doi: 10.4319/lo.2002.47.4.0976
|
| [32] |
MARAÑÉN E, FERNÁNDEZ A, MOURIÑO-CARBALLIDO B, et al, 2010. Degree of oligotrophy controls the response of microbial plankton to Saharan dust[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(6):2339-2352.
doi: 10.4319/lo.2010.55.6.2339
|
| [33] |
MOORE C M, MILLS M M, ARRIGO K R, et al, 2013. Processes and patterns of oceanic nutrient limitation[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(9):701-710.
doi: 10.1038/NGEO1765
|
| [34] |
MOORE C M, MILLS M M, MILNE A, et al, 2006. Iron limits primary productivity during spring bloom development in the central North Atlantic[J]. Global Change Biology, 12(4):626-634.
doi: 10.1111/gcb.2006.12.issue-4
|
| [35] |
MOORE L R, POST A F, ROCAP G, et al, 2002. Utilization of different nitrogen sources by the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus[J]. Limnology and Oceanography 47( 4):989-996.
|
| [36] |
MOUTIN T, THINGSTAD T F, VAN WAMBEKE F, et al, 2002. Does competition for nanomolar phosphate supply explain the predominance of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus?[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 47(5):1562-1567.
doi: 10.4319/lo.2002.47.5.1562
|
| [37] |
NICOLAÏ M, ROSIN C, TOUSSET N, et al, 1999. Trace metals analysis in estuarine and seawater by ICP-MS using on line preconcentration and matrix elimination with chelating resin[J]. Talanta, 50(2):433-444.
pmid: 18967734
|
| [38] |
OLSON R J, ZETTLER E R, DURAND M D, 1993. Phytoplankton analysis using flow cytometry[M]//KEMP P F, SHERR B F, SHERR E B, et al. Handbook of Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers: 175-186.
|
| [39] |
OU SUYING, ZHANG HONG, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2007. Horizontal characteristics of buoyant plume off the Pearl River Estuary during summer[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 50:652-657.
|
| [40] |
PARTENSKY F, BLANCHOT J, VAULOT D, 1999. Differential distribution and ecology of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus in oceanic waters: a review[J]. Bulletin de L’Institut Océanographique, 19:457-475.
|
| [41] |
PAYTAN A, MACKEY K, CHEN YING, et al, 2009. Toxicity of atmospheric aerosols on marine phytoplankton[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(12):4601-4605.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811486106
pmid: 19273845
|
| [42] |
TAN SHANGJIN, CHEUNG SHUNYAN, HO TUNGYUAN, et al, 2019. Metatranscriptomics of the bacterial community in response to atmospheric deposition in the Western North Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Genomics, 45:57-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2019.01.008
pmid: 30777732
|
| [43] |
WANG HUIJUN, CHEN HUOPO, 2016. Understanding the recent trend of haze pollution in eastern China: roles of climate change[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16(6):4205-4211.
doi: 10.5194/acp-16-4205-2016
|
| [44] |
WANG S S, HSU N C, TSAY S C, et al, 2012. Can Asian dust trigger phytoplankton blooms in the oligotrophic northern South China Sea?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(5):L05811.
|
| [45] |
YIN KEDONG, QIAN PEIYUAN, WU M C S, et al, 2001. Shift from P to N limitation of phytoplankton growth across the Pearl River estuarine plume during summer[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 221:17-28.
doi: 10.3354/meps221017
|
| [46] |
ZHANG CHAO, YAO XIAOHONG, CHEN YING, et al, 2019. Variations in the phytoplankton community due to dust additions in eutrophication, LNLC and HNLC oceanic zones[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 669:282-293.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.068
pmid: 30878935
|
| [47] |
ZHAO SANJUN, WEI JIANWEI, YUE HAIDONG, et al, 2010. Picophytoplankton abundance and community structure in the Philippine Sea, western Pacific[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 28(1):88-95.
|
| [48] |
ZUBKOV M V, SLEIGH M A, TARRAN G A, et al, 1998. Picoplanktonic community structure on an Atlantic transect from 50°N to 50°S[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 45(8):1339-1355.
|
| [49] |
ZWIRGLMAIER K, JARDILLIER L, OSTROWSKI M, et al, 2008. Global phylogeography of marine Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus reveals a distinct partitioning of lineages among oceanic biomes[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 10(1):147-161.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01440.x
pmid: 17900271
|
 ), 李芊1,2(
), 李芊1,2( ), 葛在名1,2, 刘子嘉1,2, 帅义萍1,2, 马梦真1,2
), 葛在名1,2, 刘子嘉1,2, 帅义萍1,2, 马梦真1,2
 ), Qian LI1,2(
), Qian LI1,2( ), Zaiming GE1,2, Zijia LIU1,2, Yiping SHUAI1,2, Mengzhen MA1,2
), Zaiming GE1,2, Zijia LIU1,2, Yiping SHUAI1,2, Mengzhen MA1,2